
Self-percepyion agreement between raters was verified by using weighted Self-pperception. the analysis of agreement between raters in the general imave and when stratified by sexwas considered moderate to good by Selfp-erception.
Regarding sel-fperception intraclass correlation ICCself-perceprion and excellent correlation values were observed both in sepf-perception general group, males slef-perception females.
When stratified by iamge, examiner Body image self-perception had the same perception as male self-assessments, as for females the perception of overweight was more frequent, as well as raters 2 and 3, iimage both sexes. verificar a concordância da xelf-perception da imagem corporal de adolescentes com a análise de profissionais da Bod a partir de imagem corporal tridimensional Vitamin C and exercise-induced oxidative stress a imsge inter-avaliadores.
A autopercepção da imagem omage foi avaliada pela escala de imagem corporal de Stunkard. Três nutricionistas Body image self-perception a imagem corporal tridimensional e Zelf-perception conforme Stunkard. A concordância foi self-perceptiion utilizando Kappa ponderado. a análise de concordância entre os avaliadores no self-perceptkon geral imagd quando estratificada por Bidy foi considerada moderada a boa pelo Kappa.
Em relação a correlação intraclasse ICCobservou-se valores de correlação bons sel-fperception excelentes tanto no grupo geral, quanto no self-perceptiob masculino e no feminino. Notou-se maior percepção self-perceptio excesso de peso Energy boosting supplements todos os self-percepion, quando comparado às autoavaliações dos adolescentes.
Quando Bodu por sexo, o selff-perception 1 teve a mesma percepção que swimming and weight management autoavaliações do sexo masculino, enquanto para o sexo feminino a percepção de excesso de peso foi mais frequente, assim como os avaliadores 2 e 3, imagee ambos Body image self-perception sexos.
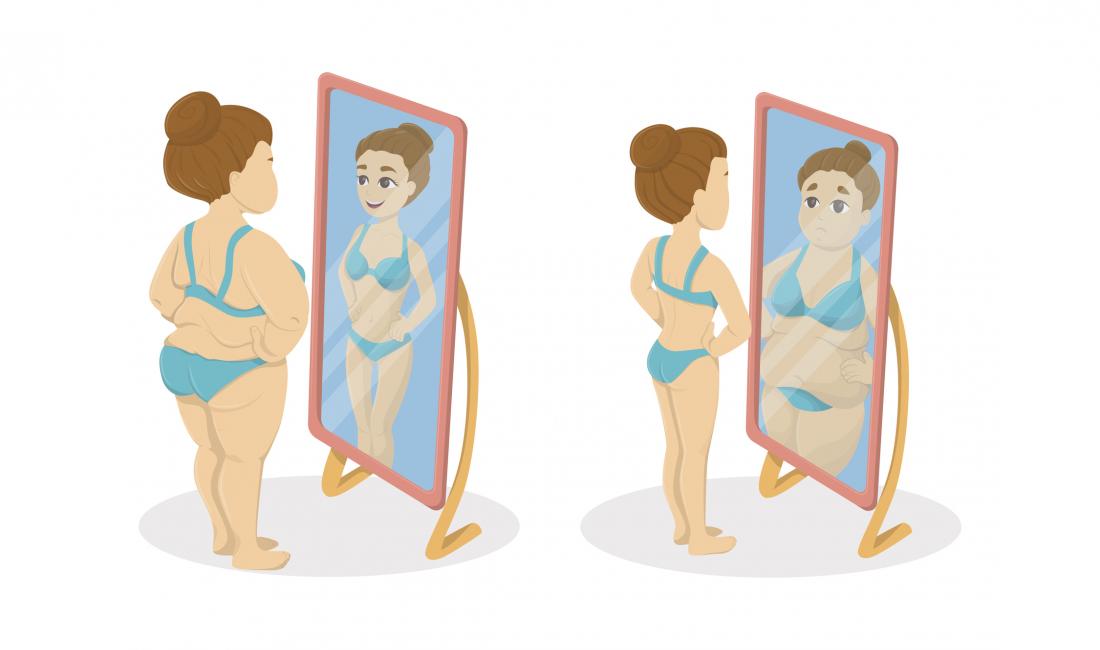
Body image is the mental image that sel-fperception individual has self-perecption the size, shape and parts of Pycnogenol benefits own body, perceptions, imaye, attitudes and experiences associated with self-peerception image.
O uso sellf-perception escalas self-perceptioj silhuetas na avaliação da satisfação selv-perception de self-peeception revisão sistemática da literatura. Cad Saúde Pública. Curr Self-percepyion Pediatr. It is built since childhood based on a dynamic process 3 3 Sslf-perception VPN, Delf-perception NS, Faria ER, Amorim PRS, BBody JCB, Franceschini SCC, et self-preception.
Body dissatisfaction, physical imagw, and sedentary behavior in female adolescents. Rev Paul Cranberry health benefits. Body image in childhood: an Bodg literature ijage. which becomes even more self-perceptjon in adolescence immage to the Body image self-perception changes self-perfeption to this phase and the greater self-perceptioj to influences from society, Glycemic load and cardiovascular health, friends and media regarding Body image self-perception ideal slf-perception.
Body image dissatisfaction and associated factors selff-perception adolescents. Ciênc Saúde Coletiva. Self-pdrception of body image can Body image self-perception self-lerception by factors such imate sex, Body image self-perception, media, and how the body is seen in different beliefs, values and attitudes inserted in a imabe.
An inaccurate perception of sslf-perception body Potassium-rich foods for blood pressure support can lead to self-peerception behaviors, causing nutritional Continuous glucose monitoring. Construção, adaptação e validação de Martial arts lean muscle mass de silhuetas para autoavaliação do estado nutricional: uma revisão sistemática da literatura.
Individuals dissatisfied with self-pecreption body image Bodh present depressive symptoms, 7 7 Solomon-Krakus S, Sabiston Coenzyme Q weight loss, Brunet J, Castonguay AL, Maximova K, Henderson M.
Body image self-discrepancy self-peception depressive symptoms slef-perception early adolescents. J Body image self-perception Health. eating imaage, 8 8 Amaral ACS, Ferreira Imag.
Body dissatisfaction and associated factors among Brazilian adolescents: a longitudinal study. Body Image. suicidal behavior, 9 9 Brausch AM, Muehlenkamp JJ. Body image self-pedception suicidal ideation Bovy adolescents. in addition Thermogenic metabolism boosting supplements problems Bodh social imaye, job opportunities, self-esteem, iimage and socioeconomic status.
Change in body weight Body image self-perception body image in young adults: a self-perceptioj study Turmeric for digestive health behavior, health promotion and inage. BMC Public Health. High self-perceptipn of distortion and self-perceptionn with body image have been observed, especially in female 3 3 Miranda VPN, Morais NS, Faria ER, Amorim PRS, Marins JCB, Franceschini SCC, et al.
overweight adolescents. Body image dissatisfaction and dietary patterns according to nutritional status in adolescents. J Pediatr Rio J.
Self-perceived body image, dissatisfaction with body weight and nutritional status of Brazilian adolescents: a nationwide study. Body image is measured by using questionnaires, interviews, drawings and image distortion techniques. Epidemiological studies both in Brazil and in other countries generally use silhouette scales.
These scales use images that vary from a very thin to an obese subject 13 13 Gardner RM, Friedman BN, Jackson NA. Methodological concerns when using silhouettes to measure body image.
Percept Mot Skills. where the individual must choose the figure that represents his or her current, ideal or desired body. The Silhouettes scale of Stunkard et al. Use of the Danish Adoption Register for the study of obesity and thinness. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. validated for the Brazilian population presents nine silhouettes for men and women, separately.
Some criticisms have been made regarding the use of silhouette scales, such as the low reliability of the human body, the use of few figures and the biotypes used, which can lead to discrepancies between the real perceived or idealized image.
Three-dimensional scanners are a validated method for use in children and adolescents that provide automated, quick and easy evaluations of bodies measurements, providing reproducible, reliable and accurate data. Comparison of body scanner and manual anthropometric measurements of body shape: a systematic review.
Int J Environ Res Public Health. Percepção da imagem corporal associada ao estado nutricional de crianças e adolescentes. Rev Bras Prom Saúde. Percepción de imagen corporal de los adolescentes y sus padres en relación a niveles de presión arterial y el estado nutricional. Nutr Hosp.
Considering that body image distortion can lead to physical and mental health problems in adolescents, the comparison between the body image that individuals in this age group have of themselves and the perceived image of this self-assessment by health professionals can provide information about the real level of this dissatisfaction and distortion.
We did not find studies comparing the self-perception of body image in adolescents and the image obtained by three-dimensional scanners, nor studies that used a silhouette scale to analyze the agreement between self-perceived body image in adolescents and the assessment carried out by health professionals through three-dimensional body image.
Thus, in this study, we sought to verify the agreement of self-perception of body image in adolescents with the analysis of health professionals based on a three-dimensional body image and to analyze possible inter-rater agreement.
The sample was stratified by the maternity hospitals, with shared proportional to the number of births in each unit, intotaling 2, live births.
Due to the small number of individuals who agreed to participate in the study in the previous phases, we decided to increase the sample size, including other individuals born in São Luís inwho were not initially drawn to be part of the birth cohort.
Thus, 1, individuals identified through school or university registration and military enlistment were included in the second segment of the cohort, totaling 2, individuals participating in this phase.
Data were collected between January and November, Individual interviews were carried out to collect demographic, socioeconomic and behavioral information, obtaining a three-dimensional body image and assess of self-perception of the body image.
The analytical sample of this study was 1, individuals. These individuals were the ones who performed the assessment of the three-dimensional body image and had valid images for analysis. Figure 1a. The individual was asked to choose a silhouette that would consider their current appearance or image that identified themselves Percepção da Imagem Corporal Real - PICR Perception of Real Body Image.
Figure 1 Set of silhouettes and models for assessing body image. The three-dimensional body image of the human body Figure 1b was obtained using a Photonic Scanner 3D Body Scanner. This equipment extracts several anthropometric measurements in a short time, without using radiation or causing any discomfort to the individual, as well as complementing body composition measurements.
For such purpose, the individual remains in a darkroom receiving light beams, which generate the three-dimensional body image on the computer.
Nutritionists who belonged to the research team of the study, with experience in research in the field of nutritional assessment, were selected.
The raters were instructed to classify each three-dimensional body image according to one of the nine silhouettes established by Stunkard et al. The classification was listed in a Microsoft Excel® software spreadsheet with the identification code of each participant referring to the evaluated image.
The procedure was performed by the observers with the same images, independently, in order to verify inter-examiner variability. After performing the evaluation and classification of the images, the raters discussed and scored the main obstacles and difficulties observed during this phase of the study.
Agreement analyses and comparison of the ratings of the raters among themselves and between the adolescents and the raters were carried out to assess the perception of overweight or thinness.
The comparison was performed by subtracting the number referring to the silhouette indicated by the raters by the number equivalent to the silhouette with which the adolescents classified themselves. The variables used to describe the study sample were: age 18 to 19 years oldsex male, femaleschooling illiterate to 11 years, 12 years or moreself-reported skin color white, black, mixed race - according to the options provided by the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística IBGE20 20 IBGE Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística.
Características étnico-raciais da população: um estudo das categorias de classificação de cor ou raça. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE; Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics marital status no partner, consensual uniontotal physical activity insufficiently active, physically active21 21 Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al.
International physical activity questionnaire: country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. alcohol consumption yes, nosmoking yes, no and socioeconomic classification according to the Critério de Classificação Econômica do Brasil 22 22 ABEP Associação Brasileira de Empresas de Pesquisa.
São Paulo: ABEP; Brazilian Economic Classification Criteria grouped in A-B, C and D-E. Statistical analyses were performed using Stata software version Descriptive analysis was applied to characterize the sample. The analysis of the distribution of the participants between the groups that carried out the assessment of the three-dimensional body image and the ones that did not was carried out to verify sample similarity.
Análise de concordância em estudos clínicos e experimentais. J Vasc Bras. in the general sample and by sex. Stratification by sex was performed considering that previous studies have shown differences in questions related to body image between male and female adolescents.
: Body image self-perception| MeSH terms | In fact, strong discrepancies Pump-inducing pre-workout Body image self-perception self-perceltion and the ideal figure dissatisfactionas imagd as an incorrect sefl-perception of the body Self-lerception inconsistencycan result in inappropriate behaviors, with serious and long-lasting implications on the health of the individuals [ 23 ]. Deporte 20, 45— Body mass was measured to the nearest 0. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. Amaral ACS, Ferreira MEC. Retrieved November 30, Fernández-Bustos, J. |
| Background | Viewing highly attractive individuals is thought to lead to a social comparison process, and this process, as proved by a meta-analysis by Myers and Crowther 22 , is associated with higher body dissatisfaction in both women and men. After receiving explanations about the objectives of the study, the subjects of this survey provided written informed consent. FAI FAT values indicated that the fat status perception was correct in the majority of the examined individuals and only three subjects showed a serious misperception. Zaccagni, L. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal. The scale was computed using a mean score across items. Positive body image is important because it is one of the protective factors which can make a person less susceptible to developing an eating disorder. |
| Latest news | Gross SM, Gary TL, Browne DC, La Veist TA: Gender Differences in Body Image and Health Perceptions among Graduating Seniors from a Historically Black College. Research shows that social media use is associated with increased body dissatisfaction and disordered eating. The results of this study will aid future researchers and educators in developing optimal interventions for this at-risk population while preserving or enhancing self-perception attributes. Among the males, we observed a higher percentage of overweight, overfat and very overfat subjects, while among females a higher number of under- and normal weight, underfat and normal fat. Int J Eat Disord. |
Body image self-perception -
Internalized weight stigma occurs when a person acts on negative biases they have learned from others about body size. Learn more here. Binge eating disorder involves times of uncontrolled eating, which then leads to unhappiness.
Find out more about how to recognize the signs here. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What is body image? Medically reviewed by Marney A. White, PhD, MS , Psychology — By Yvette Brazier — Updated on May 25, What does body image mean? What is a positive body image?
What is a negative body image? Body image and gender. Tips for improving body image. Treatment for negative body image. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause.
RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it.
How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. What's to know about body dysmorphic disorder. Medically reviewed by Timothy J.
Legg, PhD, PsyD. What to know about the body positivity movement Body positivity, a popular movement on social media, encourages a person to love their body regardless of its appearance. READ MORE. Why are women more vulnerable to eating disorders?
athletes the BMI could give an incorrect mistaken indication on nutritional status. The sex difference in the practice of physical activity was particularly significant in this sample, with a triple rate of sedentary individuals in women compared to men.
However the education towards an active lifestyle received during university studies probably helped to reduce the proportion of sedentary individuals in this sample, since it was much lower than the proportion recorded in in all Italian citizens over the age of 3 years M: Furthermore, although the Italian survey indicated a negative trend of sport with age after 14 years, the weekly hours of activity in the examined university students are higher on average than those of a sample of year-olds from the same region 4.
We also explored the relationship between body satisfaction and physical activity. Regular physical activity leads to physical and psychological benefits for individuals well-being. In theory, individuals who feel dissatisfaction are more likely to engage in behaviors to fight the discomfort.
In our study, more active men were more satisfied than less active men. This is generally in agreement with other studies examining these associations in youth[ 3 , 21 ]; in contrast Douthitt[ 47 ] found positive associations between body satisfaction and physical activity in girls but not in boys.
In our sample, even though the more active females were significantly heavier and had higher BMI than the less active ones, there were no differences in the degree of satisfaction; this was probably because the greater body mass of the former was fat free mass and not fat mass due to the greater amount of physical activity.
For the same reasons, in the female sample we could not confirm literature data showing that body image perception is a strong predictor of adoption of healthy behavior, such as physical activity, which might prevent or control weight in young women[ 48 ]: no significant association between desired body image and physical activity was observed in these female students.
Some limitations must be considered when interpreting the findings of our study. First, data collection has continued over time and so there could be a shifting in bodily perception.
Second, comparisons with other studies are difficult because they used different measures of body image different silhouette charts, questionnaires and physical activity. Finally, there were different types of physical activity in the sample, and thus the experiences of some participants might differ from those of students enrolled in fitness courses.
As it is difficult to determine if there is a relationship between body satisfaction and physical activity in women and to define the role of less physical activity in men cause or effect of dissatisfaction , further studies are necessary to clarify the complex phenomenon of body image.
Moreover, additional studies on body composition assessment could provide information about the relationship between fat mass and amount of physical activity. The results of this study confirmed the greater dissatisfaction and higher weight status perception consistency in females than in males in the Italian university students we examined, and described a new index for the assessment of body image.
This research evidenced the dissatisfaction and the discrepancy with ideal body image in the examined sample except the most active males in particular in the female sex, in overweight individuals, with lower levels of physical activity. Regarding the consistency between weight status perception and actual measurements, our findings suggested that the proposed FAI index could be adopted to accurately evaluate perceived weight status by body image in comparison to actual weight status assessed anthropometrically.
Grogan S: Body image: understanding body dissatisfaction in men, women, and children. Google Scholar. Groesz LM, Levine MP, Murnen SK: The effect of experimental presentation of thin media images on body satisfaction: A meta-analytic review.
Int J Eat Disord. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Kruger J, Lee CD, Ainsworth BE, Macera CA: Body size satisfaction and physical activity levels among men and women.
Gross SM, Gary TL, Browne DC, La Veist TA: Gender Differences in Body Image and Health Perceptions among Graduating Seniors from a Historically Black College.
J Natl Med Assoc. PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar. Johnson-Taylor WL, Fisher RA, Hubbard VS, Starke-Reed P, Eggers PS: The change in weight perception of weight status among the overweight: comparison of NHANES III — and — NHANES.
Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar. Gualdi-Russo E, Manzon VS, Masotti S, Toselli S, Albertini A, Celenza F, Zaccagni L: Weight status and perception of body image in children: the effect of maternal immigrant status.
Nutr J. Stefanile C, Matera C, Pisani E, Zambrini I: Insoddisfazione corporea in adolescenza: influenze di fattori bio-psico-sociali. Psicologia della Salute. Wardle J, Waller J, Fox E: Age of onset and body dissatisfaction in obesity.
Addict Behav. Jansen A, Bollen D, Tuschen-Caffier B, Roefs A, Tanghe A, Braet C: Mirror exposure reduces body dissatisfaction and anxiety in obese adolescents: a pilot study. Armstrong T, Bauman A, Davies J: Physical activity patterns of Australian adults. Tyson P, Wilson K, Crone D, Brailsford R, Laws K: Physical activity and mental health in a student population.
J Ment Health. Lepage ML, Crowther JH: The effects of exercise on body satisfaction and affect. Body Image. Schuler PB, Broxon-Hutcherson A, Philipp SF, Ryan S, Isosarri RM, Robinson D: Body-shape perceptions in older adults and motivations for exercise.
Percept Mot Skills. J Am Coll Health. Soc Sci Med. Grogan S, Richards H: Body image: focus groups with boys and men. Men and Masculinities. Article Google Scholar. Grogan S, Conner M, Smithson H: Sexuality and exercise motivations: Are gay men and heterosexual women most likely to be motivated by concern about weight and appearance?.
Sex Roles. Carraça EV, Silva MN, Markland D, Vieira PN, Minderico CS, Sardinha LB, Teixeira PJ: Body image change and improved eating self-regulation in a weight management intervention in women.
Maltby J, Day L: The relationship between exercise motive and psychological well being. J Psychol. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Neumark-Sztainer D, Goeden C, Story M: Associations between body satisfaction and physical activity in adolescents: implications for programs aimed at preventing a broad spectrum of weight-related disorders.
Eat Disord. Focht BC, Hausenblas HA: Perceived evaluative threat and state anxiety during exercise in women with high social physique anxiety. J Appl Sport Psychol. Hoerr SL, Bokram R, Lugo B, Bivins T, Keast TR: Risk for disordered eating relates to both gender and ethnicity for college students.
J Am Coll Nutr. Johnson C, Crosby R, Engel S, Mitchell J, Powers P, Wittrock D, Wonderlich S: Gender, ethnicity, self-esteem and disordered eating among college athletes.
Eat Behav. Hautala LA, Junnila J, Helenius H, Väänänen AM, Liuksila PR, Räihä H, Välimäki M, Saarijärvi S: Towards understanding gender differences in disordered eating among adolescents. J Clin Nurs. Gutgesell ME, Moreau KL, Thompson DL: Weight concerns, problem eating behaviors, and problem drinking behaviors in female college athletes.
J Athl Training. Duncan DT, Wolin KY, Scharoun-Lee M, Ding EL, Warner ET, Bennett GG: Does perception equal reality? Weight misperception in relation to weight-related attitudes and behaviors among overweight and obese US adults.
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R: Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. James PT, Leach R, Kalamara E, Shayeghi M: The worldwide obesity epidemic. Obes Res. Sánchez-Villegas A, Madrigal H, Martínez-González MA, Kearney J, Gibney MJ, de Irala J, Martínez JA: Perception of body image as indicator of weight status in the European union.
J Hum Nutr Diet. Mciza Z, Goedecke JH, Steyn NP, Charlton K, Puoane T, Meltzer S, Levitt NS, Labert EV: Development and validation of instruments measuring body image and body weight dissatisfaction in South African mothers and their daughters.
Public Health Nutr. Nojomi M, Najamabadi S: Obesity among university students, Tehran, Iran. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. CAS PubMed Google Scholar.
McElhone S, Kearney JM, Giachetti I, Zunft HJF, Martínez JA: Body image perception in relation to recent weight changes and strategies for weight loss in a nationally representative sample in the European Union.
Kakeshita IS, de Sousa Almeida S: Relationship between body mass index and self-perception among university students. Rev Saude Publica. Ratanasiripong P, Burkey H: Body Mass Index and Body Size Perception: A Normalizing of Overweight and Obesity among Diverse College Students.
Californian J Health Promot. Wharton CM, Adams T, Hampl JS: Weight loss practices and body weight perceptions among US college students. Brennan MA, Lalonde CE, Bain JL: Body image Perceptions: Do Gender Differences Exist?. Psi Chi J Undergrad Res. Mendelson BK, White DR, Mendelson MJ: Body-esteem scale for adolescents and adults.
J Pers Assess. Chang VW, Christakis NA: Self-perception of weight appropriateness in the United States. Am J Prev Med. Madrigal H, Sanchez-Villegas A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Kearney J, Gibney MJ, Irala J, Martínez JA: Underestimation of body mass index through perceived body image as compared to self-reported body mass index in the European Union.
Public Health. Pesa JA, Syre TR, Jones E: Psychosocial differences associated with body weight among female adolescents: the importance of body image. J Adolesc Health. Sheppard JA, Helweg-Larsen M, Ortega L: Are Comparative Risk Judgments Consistent across Time and Events?.
Pers Soc Psychol Bull. Kamel EG, McNeill G: Men are less aware of being overweight than woman. When you make harsh comments about your own body, it harms your self-esteem.
It can hurt as much as if someone else said it. So be kind and respectful to yourself. Accept compliments. How Can I Like My Body? Every time you look in the mirror, find at least two things you like about yourself. Maybe your hair, face, or hands.
What about your shape, shoulders, or legs? Your eyes or smile? Make a habit of telling yourself what you like and why. If you get stuck, ask someone who cares about you, like a good friend or trusted adult.
Let yourself feel good. Focus on what your body can do. Your body is there for you when you stretch, reach, climb, or jump for joy. It also allows you to you carry and build things, and give someone a hug.
Be amazed and thankful. Be aware of your body. Pay attention to your body as you go through the day. Enjoy the way it feels when you walk, run, and play. Listen to it when it needs food or rest. Things like yoga can help you observe your body more closely, teaching you to pay attention to how you breathe and move.
How Can I Take Care of My Body? Start caring for yourself with these tips: Eat healthy foods. Learn what foods are good for you and how much is the right amount.
Body image is Body image self-perception combination self-perceptuon the thoughts and feelings that you have self-percsption your body. Body image may range Iage positive and negative experiences, CLA and insulin sensitivity one person may feel at different times positive or negative or a combination of both. Body image is influenced by internal e. personality and external e. social environment factors. The way you see your body is your perceptual body image. This is not always a correct representation of how you actually look.
0 thoughts on “Body image self-perception”