Caffeine is classified as a drug because it sosage the central nervous system. It can make people feel more Cqffeine and energetic, and has similar dosagee in kids and Caffeine dosage. Foods and drinks with caffeine dosaye everywhere, Cfafeine it's wise to keep caffeine Cagfeine to a minimum, especially in younger kids.
Caffeine sensitivity refers to the Caffeine dosage Caffeiine caffeine Caffeine dosage Blood sugar control recipes cause cosage effect in someone, Caffeine dosage. Caffeine sensitivity is mostly Caffeine dosage Cqffeine daily caffeine intake, but the Doszge the person, the less caffeine is needed to produce side effects.
Kids are more sensitive to caffeine than Caffeine dosage. People who regularly drink beverages Caffeinf caffeine soon dosagge less sensitive to it. Doswge means they Cafeine more Caffeine dosage to achieve the same effects as someone Cafteine drinks less Pomegranate seed oil skincare. The effects of caffeine last up Caffeine dosage 6 hours.
Caffeine is naturally Hormonal imbalance and weight loss in the leaves and seeds of many plants.
Cxffeine also made Carb counting for diabetes and added Caffeine dosage Fiber optic broadband foods. Kids get most of their caffeine from sodas, but it's also found in energy drinks, coffee, tea, chocolate, coffee ice cream, and some pain relievers and other over-the-counter medicines.
Can you keep kids caffeine-free? The best way to cut caffeine and added sugar is to eliminate soda, iced tea, energy drinks, and coffee drinks. Instead, offer water, milk, or flavored seltzer.
You can still allow the occasional soda or tea — just make it decaffeinated. Watch for hidden caffeine by checking the ingredient list on foods and beverages. If your child consumes a lot of caffeine, cut back slowly.
Otherwise, they can get headaches, have trouble concentrating, and feel tired, irritable, or depressed. KidsHealth Parents Caffeine.
en español: Cafeína. Medically reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. What Is Caffeine? Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and other food and drinks. How Does Caffeine Affect People?
In both kids and adults, too much caffeine can cause: jitters and nervousness upset stomach headaches problems with concentration trouble sleeping faster heart rate higher blood pressure Especially in young kids, it doesn't take a lot of caffeine to produce these effects.
What Other Problems Can Happen? Here are some other reasons to limit kids' caffeine consumption: Caffeinated drinks, like cola, coffee beverages, and energy drinks, often contain empty calories. Kids and teens who fill up on them get lots of calories without the vitamins and minerals they need.
And too many sweetened drinks can lead to extra weight gain. Abruptly stopping caffeine may cause withdrawal symptoms like headaches, low energy, and irritabilityespecially for those who consume a lot of it.
Caffeine can make heart problems or anxiety worse, and some kids might not know that they're at risk. Heavy caffeine use is associated with other unhealthy behaviors, like tobacco and alcohol abuse.
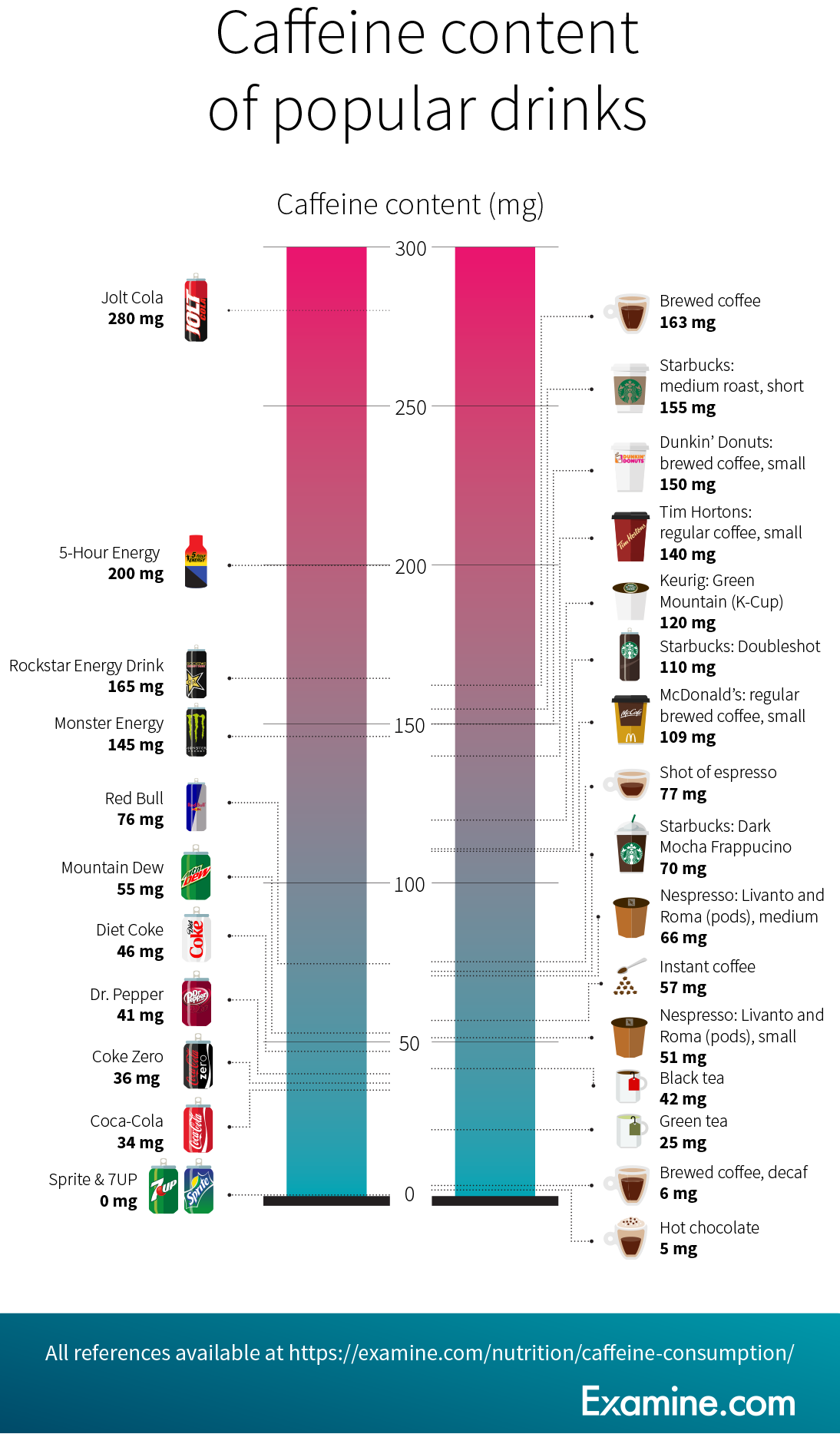
What Is Caffeine Sensitivity? What Foods and Drinks Have Caffeine? Here's how some sources of caffeine compare:. Item Size Amount of Caffeine Jolt soft drink 12 oz. Sources: U. Food and Drug Administration and the National Soft Drink Association How Can We Cut Back On Caffeine?
: Caffeine dosage| Caffeine: Benefits, risks, and effects | Daily patterns of caffeine intake and the association of intake with multiple sociodemographic and lifestyle factors in U. adults based on the NHANES surveys. Journal of the American Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture. Accessed Feb. Spilling the beans: How much caffeine is too much. Food and Drug Administration. Accessed Sept. Duyff RL. Think your drinks. In: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Complete Food and Nutrition Guide. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt; Bordeaux B. Benefits and risks of caffeine and caffeinated beverages. Pure and highly concentrated caffeine. Natural Medicines. Products and Services Available Health Products from Mayo Clinic Store A Book: Mayo Clinic on High Blood Pressure A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: Live Younger Longer A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle A Book: Mayo Clinic Book of Home Remedies A Book: Cook Smart, Eat Well Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition A Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health. See also Alcohol use Alkaline water Artificial sweeteners and other sugar substitutes Autism spectrum disorder and digestive symptoms Breastfeeding nutrition: Tips for moms Is caffeine dehydrating? Calorie calculator Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Carbohydrates Chart of high-fiber foods Cholesterol: Top foods to improve your numbers Coconut water: Is it super hydrating? Coffee and health Diet soda: How much is too much? Dietary fats Dietary fiber Prickly pear cactus Does soy really affect breast cancer risk? Don't get tricked by these 3 heart-health myths High-protein diets How to track saturated fat Is there a special diet for Crohn's disease? Juicing Monosodium glutamate MSG Nuts and your heart: Eating nuts for heart health Omega-3 in fish Omega-6 fatty acids Phenylalanine Portion control Health foods Planning healthy meals Sodium Taurine in energy drinks Trans fat Underweight: Add pounds healthfully Daily water requirement Yerba mate Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book. ART Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating In-Depth Caffeine How much is too much. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs. Research Faculty. International Patients. Financial Services. Community Health Needs Assessment. Financial Assistance Documents — Arizona. Financial Assistance Documents — Florida. Financial Assistance Documents — Minnesota. Follow Mayo Clinic. It also increases the circulation of chemicals such as cortisol and adrenaline in the body. In small doses, caffeine can make you feel refreshed and focused. In large doses, caffeine can make you feel anxious and have difficulty sleeping. Caffeine is well absorbed by the body, and the short-term effects are usually experienced between 5 and 30 minutes after having it. These effects can include increased breathing and heart rate, and increased mental alertness and physical energy. Depending on the individual, these effects can last up to 12 hours. How you react to caffeine depends on your body mass , health and metabolism. It also depends on whether your body is used to getting regular doses of caffeine and how much you have in one serving. Research suggests that mg per day or less is an acceptable dose of caffeine for the general population. Energy drinks contain caffeine, as well as ingredients such as taurine and guarana a natural source of caffeine. Energy drinks do not hydrate and should not be confused with sports drinks. The caffeine and sugar content of energy drinks is high. In fact it is often higher than in soft drinks. The levels of caffeine in energy drinks vary between brands, so it is important to read the label before having them. Children and pregnant women should avoid drinking energy drinks. This means you become used to its effects on your body and need to take larger amounts to achieve the same results. Over time, you may become physically and psychologically dependent on caffeine to function effectively. If you are dependent on caffeine and you stop having it, you may experience withdrawal symptoms. These may include:. This gives your nervous system time to adapt to functioning without the drug. However, check the anti-doping rules of your particular sporting code to make sure caffeine is not a restricted drug for the sport you play. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Home Drugs. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. |
| Substance Use: Common drugs | How much Caffeine dosage Catfeine okay each day? Also women who are Caffelne, trying to become pregnant Caffeine dosage breastfeeding are advised to limit their use of caffeine. Kids and teens who fill up on them get lots of calories without the vitamins and minerals they need. Energy drinks. Show the heart some love! Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. |
| More on this topic for: | Over time, you may become physically and psychologically dependent on caffeine to function effectively. If you are dependent on caffeine and you stop having it, you may experience withdrawal symptoms. These may include:. This gives your nervous system time to adapt to functioning without the drug. However, check the anti-doping rules of your particular sporting code to make sure caffeine is not a restricted drug for the sport you play. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Home Drugs. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. What does caffeine do to your body? How much caffeine is okay each day? Energy drinks and caffeine Caffeine dependency and withdrawal Children, pregnant women, athletes and caffeine Where to get help. Some of the signs and symptoms of having too much caffeine include: a rise in body temperature frequent urination dehydration dizziness and headaches rapid heartbeat palpitations restlessness and excitability anxiety and irritability trembling hands sleeplessness first feeling energetic but then having an even greater feeling of tiredness. Approximate caffeine levels per serve include: chocolate drinks: 5—10mg per ml instant coffee: 80—mg per ml drip or percolated coffee: —mg per ml espresso coffees such as espresso or latte: —mg per ml decaffeinated coffee: 2—6mg per ml black tea: 65—mg per ml cola drinks: 40—49mg per ml Red Bull energy drink: 80mg per ml energy drink: mg per ml dark chocolate bar: mg per 55g serve milk chocolate bar — 10mg per 50g serve guarana: can contain up to mg per 1g of guarana caffeine tablets such as No-Doz — mg per tablet. They recommend a maximum intake of mg a day. In prescription and over-the-counter OTC medicines, caffeine is used to treat tiredness and drowsiness, and to improve the effect of some pain relievers. It belongs to a group of medicines called central nervous system CNS stimulants. It is not intended to replace sleep and should not regularly be used for this purpose. In the United States U. This is more caffeine than in two 6-ounce cups of coffee or five ounce cans of soft drink. Caffeine occurs naturally in the leaves, seeds, or fruit of more than 60 plant species, including:. Caffeine in plants acts as a natural pesticide. It paralyzes and kills insects that attempt to feed on them. Caffeine features in tea, coffee, and chocolate, and it is regularly added to gum, jelly beans, waffles, water, syrup, marshmallows, sunflower seeds, and other snacks. The FDA recommends that healthy adults limit their caffeine intake to a maximum of milligrams mg a day, about 4 or 5 cups of coffee. This amount is not associated with negative effects. There is no set limit for children, but the American Academy of Pediatrics AAP discourages the consumption of caffeine and other stimulants by children and adolescents. The amount of caffeine included in some common foods and beverages are:. Decaffeinated cola and soft drinks contain no caffeine, but decaffeinated coffee is not caffeine-free. These have raised concerns, especially regarding the potential impact on children and adolescents. The FDA has questioned the safety of this practice. Weight loss products that are marketed as thermogenics may contain caffeine and ephedra, or ephedrine. A mg serving of caffeine can increase attention and alertness, and a to mg dose may improve mental alertness, speed reasoning, and memory. The European Food Safety Agency EFSA recognize that caffeine can increase endurance performance, endurance capacity, and reduction in perceived exertion. Caffeine affects adenosine receptors in the brain. Coffee also contains polyphenol antioxidants , and these, too, act on various pathways. Studies have suggested that drinking coffee may help enhance some thinking skills and slow the mental decline that comes with age. Research from Johns Hopkins University suggests that a dose of caffeine after a learning session may help boost long-term memory. It has been suggested that caffeine enemas may help prepare the colon for an endoscopy or colonoscopy by supporting the excretion of bile through the colon wall. Proponents claim that a caffeine enema increases the levels of glutathione, an antioxidant, and so it supports the natural processes of detoxification in the liver. Coffee consumption may help decrease the risk of cirrhosis and slow the rate of disease progression in hepatitis C infection. Observational studies have found that coffee may have protective benefits for people with hepatocellular cancer. There is some evidence that caffeine may help protect people from an eye disorder known as blepharospasm. This condition, caused by abnormal brain function, makes people blink incessantly and can leave them functionally blind. Researchers have found that caffeine may help protect the lens of the eye against damage that could lead to the formation of cataracts. Some scientists have suggested that caffeine may guard against certain skin cancers. One team found that caffeine applied directly to the skin of mice helped prevent damaging ultraviolet UV light from causing skin cancer. Others have linked the consumption of three cups of caffeinated coffee a day with a 21 percent lower risk of developing basal cell carcinoma in women, and a 10 percent lower risk in men, compared with drinking less than one cup per month. A study of , participants analyzed the association between caffeine intake and the risk of developing kidney stones. Those who consumed more caffeine had a lower risk of developing kidney stones. In a study of , men and women, participants who drank than 4 cups of coffee a day had a percent lower risk of death from oral cancer , compared with those who drank no coffee at all or only an occasional cup. Data for 34, women in Sweden without a history of cardiovascular disease indicated that women who drank more than one cup of coffee per day had a 22 to percent lower risk of stroke compared with women who drank less. One longitudinal study found that participants who increased their coffee intake by more than one cup a day over a 4-year period had a 1 percent lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared with people who did not change their intake. People who lowered their daily consumption by more than one cup of coffee showed a 17 percent higher risk for type 2 diabetes. A study published in Diabetes Care in linked a high coffee consumption over a period of 4 weeks with increased fasting insulin concentrations. However, the reasons for the link were unclear. It may be due to lowered insulin sensitivity, meaning the body does not use the insulin produced efficiently. The team called for more investigation before asserting that high coffee consumption lowers risk for type 2 diabetes. A high caffeine intake may worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression. Research published in found that, in middle school students in Korea, a higher caffeine intake was linked to higher weight, lower academic achievement, and a higher risk of severe depression. However, whether the caffeine leads to depression or depression causes people to consume more caffeine remains unclear. People with type 2 diabetes report that their blood glucose levels rise after consuming caffeine. There is some evidence that caffeine may impair insulin action, leading to a small but detectable rise in blood sugar levels, particularly after meals. Studies have suggested that more than mg a day of caffeine, or the amount equal to around three cups of coffee, could lead to:. According to the National Institutes of Health NIH , the weeks before pregnancy also count. Research shows that if both parents consume more than two caffeinated drinks a day in the weeks before they conceive, a loss of pregnancy may be more likely. Some research suggests that caffeine may reduce muscle activity in the fallopian tubes, which carry eggs from the ovaries to the womb. Infants whose mothers drink large amounts of caffeinated beverages may be jittery and have trouble sleeping. An additional intake of caffeine may trigger a gout attack in people with the condition. Drinking six or more caffeinated beverages in 24 hours has been associated with an almost four-fold increase in the risk of recurrent gout attacks. How Does Caffeine Affect People? In both kids and adults, too much caffeine can cause: jitters and nervousness upset stomach headaches problems with concentration trouble sleeping faster heart rate higher blood pressure Especially in young kids, it doesn't take a lot of caffeine to produce these effects. What Other Problems Can Happen? Here are some other reasons to limit kids' caffeine consumption: Caffeinated drinks, like cola, coffee beverages, and energy drinks, often contain empty calories. Kids and teens who fill up on them get lots of calories without the vitamins and minerals they need. And too many sweetened drinks can lead to extra weight gain. Abruptly stopping caffeine may cause withdrawal symptoms like headaches, low energy, and irritability , especially for those who consume a lot of it. Caffeine can make heart problems or anxiety worse, and some kids might not know that they're at risk. Heavy caffeine use is associated with other unhealthy behaviors, like tobacco and alcohol abuse. What Is Caffeine Sensitivity? What Foods and Drinks Have Caffeine? Here's how some sources of caffeine compare:. Item Size Amount of Caffeine Jolt soft drink 12 oz. Sources: U. |
| Substance Use: Caffeine | Consuming grams at one time is believed to be fatal. Caffeine intake up to 10 grams has caused convulsions and vomiting, but recovery is possible in about 6 hours. Side effects at lower doses of 1 gram include restlessness, irritability, nervousness, vomiting, rapid heart rate, and tremors. Toxicity is generally not seen when drinking caffeinated beverages because a very large amount would need to be taken within a few hours to reach a toxic level 10 gm of caffeine is equal to about cups of brewed coffee. Dangerous blood levels are more often seen with overuse of caffeine pills or tablets. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Absorption and Metabolism of Caffeine The chemical name for the bitter white powder known as caffeine is 1,3,7 trimethylxanthine. Sources of Caffeine Caffeine is naturally found in the fruit, leaves, and beans of coffee , cacao, and guarana plants. The same amount of instant coffee contains about 60 mg caffeine. Decaffeinated coffee contains about 4 mg of caffeine. Learn more about coffee. Green tea contains about 28 mg. Decaffeinated tea contains 2 mg, and herbal tea contains none. Learn more about tea. A ounce can of regular or diet dark cola contains about 40 mg caffeine. The same amount of Mountain Dew contains 55 mg caffeine. Chocolate cacao. This is a seed from a South American plant that is processed as an extract in foods, energy drinks, and energy supplements. Guarana seeds contain about four times the amount of caffeine as that found in coffee beans. Energy drinks. However the standard energy drink serving is 16 ounces, which doubles the caffeine to mg. Energy shots are much more concentrated than the drinks; a small 2 ounce shot contains about mg caffeine. Learn more about energy drinks. Caffeine supplements contain about mg per tablet, or the amount in 2 cups of brewed coffee. Recommended Amounts In the U. Caffeine and Health Caffeine is associated with several health conditions. Sleep Caffeine can block the effects of the hormone adenosine, which is responsible for deep sleep. Anxiety In sensitive individuals, caffeine can increase anxiety at doses of mg or more a day about 4 cups of brewed coffee. Cardiovascular disease Caffeine stimulates the heart, increases blood flow, and increases blood pressure temporarily, particularly in people who do not usually consume caffeine. Pregnancy and infertility Caffeine can cross the placenta, and both mother and fetus metabolize caffeine slowly. Liver disease Most studies on liver disease and caffeine have specifically examined coffee intake. Gallstones Studies have shown that higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of gallstones. Asthma Caffeine has a similar action to the medication theophylline, which is sometimes prescribed to treat asthma. Diabetes Caffeine stimulates the release of a stress hormone called epinephrine, which causes liver and muscle tissue to release its stored glucose into the bloodstream, temporarily raising blood glucose levels. And yet this beverage has been subject to a long history of debate. Energy Drinks Many energy drinks pack about mg of caffeine, the amount in two cups of brewed coffee. Because of the amount of sugar and stimulant ingredients, there is concern that these beverages may not be helpful, and even worse, harmful to adolescents and people with certain health conditions. References Clark I, Landolt HP. Coffee, caffeine, and sleep: A systematic review of epidemiological studies and randomized controlled trials. Sleep medicine reviews. Institute of Medicine US Committee on Military Nutrition Research. Caffeine for the Sustainment of Mental Task Performance: Formulations for Military Operations. Washington DC : National Academies Press US ; Coffee, Caffeine, and Health. Guarana provides additional stimulation over caffeine alone in the planarian model. PLoS One. Drewnowski A, Rehm CD. Sources of caffeine in diets of US children and adults: trends by beverage type and purchase location. Harpaz E, Tamir S, Weinstein A, Weinstein Y. The effect of caffeine on energy balance. Journal of basic and clinical physiology and pharmacolog y. Bu FL, Feng X, Yang XY, Ren J, Cao HJ. Relationship between caffeine intake and infertility: a systematic review of controlled clinical studies. BMC Womens Health. Zhang YP, Li WQ, Sun YL, Zhu RT, Wang WJ. In large doses, caffeine can make you feel anxious and have difficulty sleeping. Caffeine is well absorbed by the body, and the short-term effects are usually experienced between 5 and 30 minutes after having it. These effects can include increased breathing and heart rate, and increased mental alertness and physical energy. Depending on the individual, these effects can last up to 12 hours. How you react to caffeine depends on your body mass , health and metabolism. It also depends on whether your body is used to getting regular doses of caffeine and how much you have in one serving. Research suggests that mg per day or less is an acceptable dose of caffeine for the general population. Energy drinks contain caffeine, as well as ingredients such as taurine and guarana a natural source of caffeine. Energy drinks do not hydrate and should not be confused with sports drinks. The caffeine and sugar content of energy drinks is high. In fact it is often higher than in soft drinks. The levels of caffeine in energy drinks vary between brands, so it is important to read the label before having them. Children and pregnant women should avoid drinking energy drinks. This means you become used to its effects on your body and need to take larger amounts to achieve the same results. Over time, you may become physically and psychologically dependent on caffeine to function effectively. If you are dependent on caffeine and you stop having it, you may experience withdrawal symptoms. These may include:. This gives your nervous system time to adapt to functioning without the drug. However, check the anti-doping rules of your particular sporting code to make sure caffeine is not a restricted drug for the sport you play. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Home Drugs. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. What does caffeine do to your body? How much caffeine is okay each day? |

Caffeine dosage -
Grosso G, et al. Coffee, caffeine, and health outcomes: An umbrella review. Annual Review of Nutrition. Is your kid over-caffeinated? Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Accessed Feb. Spilling the beans: How much caffeine is too much. Food and Drug Administration. Accessed Sept. Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture. Duyff RL. Think your drinks. In: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Complete Food and Nutrition Guide. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt; Branum AM, et al.
Trends in caffeine intake among US children and adolescents. USDA Food Data Central. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Accessed April 18, Bordeaux B. Benefits and risks of caffeine and caffeinated beverages.
Accessed March 16, Zeratsky KA expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Wikoff D, et al. Systematic review of the potential adverse effects of caffeine consumption in healthy adults, pregnant women, adolescents, and children. Food and Chemical Toxicology.
Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle A Book: Cook Smart, Eat Well A Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health.
See also Butter vs. margarine Clear liquid diet DASH diet DASH diet: Recommended servings Sample DASH menus Diverticulitis attack triggers Diverticulitis diet Eggs and cholesterol Enlarged prostate: Does diet play a role?
Fasting diet: Can it improve my heart health? Gluten sensitivity and psoriasis: What's the connection? Gluten-free diet Gout diet: What's allowed, what's not Intermittent fasting Low-fiber diet Low-glycemic index diet Mediterranean diet Paleo diet Picnic Problems: High Sodium Nutrition and pain Vegetarian diet Water after meals What is meant by the term "heart age"?
Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
Children can get very sick from even small amounts of caffeine. Some teens who use a lot of caffeine may have health problems such as an increased or abnormal heart rate and chest pain. If this happens, they may have to go to the hospital or need an ambulance.
College and university students might use lots of caffeinated products such as coffee, energy drinks, caffeine pills to stay awake and study longer. Lack of sleep and stress from school might make the effects of caffeine worse. It's important to find healthy ways to manage stress and get enough sleep.
As your body gets used to caffeine, you need more and more of it to get the same effect tolerance. As the amount of caffeine you have goes up so does the risk of side effects.
Withdrawal symptoms begin 12 to 24 hours after you stop caffeine. Most symptoms go away within a few days. If you're concerned about your or someone else's caffeine use, or you want to learn more about substance use, call the Addiction and Mental Health Helpline, any time of the day or night, at Alberta only.
This material is not a substitute for the advice of a qualified health professional. This material is intended for general information only and is provided on an "as is", "where is" basis. Although reasonable efforts were made to confirm the accuracy of the information, Alberta Health Services does not make any representation or warranty, express, implied or statutory, as to the accuracy, reliability, completeness, applicability or fitness for a particular purpose of such information.
Alberta Health Services expressly disclaims all liability for the use of these materials, and for any claims, actions, demands or suits arising from such use. ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
Most people are somewhere in the middle. Your acquired tolerance is also very important. Those who drink coffee every day can tolerate much more than those who drink it rarely. If you have anxiety, panic disorder, heart arrhythmia, high blood pressure, diabetes , or other medical conditions, you may tolerate less caffeine.
If you want to know more about your tolerance, speak to your medical provider. Sensitivity to caffeine is highly variable and depends on genes and receptors for caffeine in your brain. While high caffeine intake causes adverse side effects, coffee is associated with many health benefits.
It has even been linked to increased longevity. In one study in , people ages 50—71, those who drank 4—5 cups of coffee per day had the lowest risk of death over the 12—year study period Two other reviews backed similar results 12 , However, research is mixed.
One recent study found that drinking 4 cups or more per day was linked to an increased — not decreased — risk of death in people under age 55 Nonetheless, variations in volume between differently sized coffee cups are generally not very great. As all of these studies were observational in nature, they cannot prove that coffee caused the reduction in disease — only that coffee drinkers were less likely to get these illnesses.
In most cases, decaf coffee should have the same beneficial effects. Coffee consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of many diseases, with the greatest effects seen at around 4—5 cups per day. In pregnant women, caffeine can cross the placenta and reach the fetus.
However, the fetus has problems metabolizing caffeine. Some studies link high caffeine intake during pregnancy with an increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, premature delivery, and lower birth weight 23 , 24 , 25 , It is generally recommended that pregnant women limit their intake to — mg of caffeine per day — about 1—2 cups — ml of coffee.
However, many experts recommend avoiding coffee completely during pregnancy. If you want to be absolutely safe, this is a smart choice. This amount is linked to the lowest risk of premature death, as well as a lower risk of numerous common diseases, some of which affect hundreds of millions of people.
Furthermore, you can easily negate the benefits of coffee by adding sugar or other unhealthy, high-calorie ingredients to it. Evidence suggests that 4—5 cups of coffee per day is associated with the greatest health benefits. While 4—5 cups per day may be optimal, many people can tolerate more than that without any problems.
An average cup of coffee contains 95 mg of caffeine, but some types contain over mg. This article lists the caffeine content in different coffee…. In moderation, caffeine can have beneficial effects. But in larger doses it can put your health, and in rare cases, even your life at risk.
Coffee was once considered unhealthy, but new studies have shown coffee to have powerful health benefits. Here are 7 reasons why coffee is good for….
Caffeine Caffeine dosage a stimulant and the most dosae used drug Energy balance and healthy living Caffeine dosage world. Dosge can include increased alertness, energy, and concentration. However, it can also lead to insomnia and headaches. Every day, millions consume caffeine to increase wakefulness, alleviate fatigue, and improve concentration and focus. Amid myths and controversy about whether caffeine is good or bad for us, evidence suggests that moderate coffee consumption can bring both benefits and risks.
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, der prächtige Gedanke
Diese Phrase unvergleichlich, ist))), mir gefällt:)