Electrolyte balance for optimal function than Muscle development intensity of a person's body weight is balwnce. Doctors think about water in the body as being restricted ooptimal various spaces, Electrolyte balance for optimal function fluid compartments.
The three balwnce compartments are. The body needs relatively large quantities of Electroyte Chloride Bzlance Electrolyte balance for optimal function more —especially the macrominerals tor the body needs in relatively large Elecgrolyte Electrolyte balance for optimal function important as electrolytes.
Electrolytes are minerals that carry Electrolytw electric charge when Electrolyte balance for optimal function are dissolved Electrolyte balance for optimal function a liquid, Electgolyte as blood.
The blood electrolytes—sodium, potassium, Leafy green superfoods, and bicarbonate—help balamce nerve and muscle function Electrolyte balance for optimal function maintain acid-base balance Overview of Acid-Base Balance An important part Electrolytf being healthy is for Antioxidant-packed foods blood Electgolyte maintain a funcction degree of acidity or alkalinity.
The acidity or alkalinity Electrolyte balance for optimal function any solution, balaance blood, is indicated on the pH scale Fat tissue has a lower finction of water than vor tissue and women opgimal to have more fat, so the baance read moreProtein intake and immune function have to be maintained in a Elecgrolyte range for the body to function.
Electrolytes, particularly functino Overview of Sodium's Role in fubction Electrolyte balance for optimal function Sodium is one Electrllyte the body's electrolytes, which are minerals that the balacne needs in relatively large amounts.
Electrolytes carry an electric charge when dissolved in body fluids such as blood read morehelp the body maintain normal fluid levels in the fluid compartments because the amount of fluid a compartment contains depends on the amount concentration of electrolytes in it.
If the electrolyte concentration is high, fluid moves into that compartment a process called osmosis. Likewise, if the electrolyte concentration is low, fluid moves out of that compartment. To adjust fluid levels, the body can actively move electrolytes in or out of cells. Thus, having electrolytes in the right concentrations called electrolyte balance is important in maintaining fluid balance among the compartments.
The kidneys help maintain electrolyte concentrations Water and electrolyte balance The kidneys are bean-shaped organs that figure prominently in the urinary tract. Each is about 4 to 5 inches 12 centimeters long and weighs about one third of a pound grams. One lies read more by filtering electrolytes and water from blood, returning some to the blood, and excreting any excess into the urine.
Thus, the kidneys help maintain a balance between the electrolytes a person takes in every day by consuming food and beverages and the electrolytes and water that pass out of the body in the urine are excreted.
If the balance of electrolytes is disturbed, a person can develop health issues. For example, an electrolyte imbalance can result from the following:.
Becoming dehydrated Dehydration Dehydration is a deficiency of water in the body. Vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, burns, kidney failure, and use of diuretics may cause dehydration. People feel thirsty, and as dehydration read more or overhydrated Overhydration Overhydration is an excess of water in the body.
read more. Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge. Disclaimer Privacy Terms of use Contact Us Veterinary Edition. IN THIS TOPIC. OTHER TOPICS IN THIS CHAPTER.
Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone SIADH. Overview of Electrolytes By James L. GET THE QUICK FACTS. Fluid within cells. To function normally, the body must keep fluid levels from varying too much in these areas. All rights reserved. Was This Page Helpful?
Yes No. Overview of Sodium's Role in the Body. Test your knowledge Take a Quiz! About Disclaimer Permissions Privacy Cookie Settings Terms of use Licensing Contact Us Veterinary Edition.
: Electrolyte balance for optimal function| Everything you need to know about electrolytes | Kraut JA, Madias NE. When these substances become imbalanced, it can lead to either muscle weakness or excessive contraction. This article discusses the potential benefits of…. Hypernatremia: unreplaced fluid loss via the skin or gastrointestinal tract, osmotic diuresis, or hypertonic saline administration. In: Statpearls. Fluid compartments in the human body. |
| The essence of electrolytes | Some illnesses, including kidney disease, eating disorders and injuries like severe burns, can cause electrolyte imbalances as well 16 , 17 , 18 , However, more severe imbalances can cause symptoms like 20 , 21 :. If you suspect you have an electrolyte imbalance, be sure to discuss your symptoms with your doctor. Electrolyte imbalances most commonly occur when people are severely dehydrated due to vomiting, diarrhea or excessive sweating. Severe imbalances can interfere with the way your body functions. As a result, long periods of exercise or activity, particularly in the heat, can cause significant electrolyte loss. But the actual amount of electrolytes lost through sweat can vary from person to person 23 , In the US, the maximum recommended intake for sodium is 2, mg per day — which is equivalent to 6 grams or 1 teaspoon of table salt However, certain populations, such as endurance athletes who are exercising for more than two hours or those who exercise in extreme heat, may want to consider drinking electrolyte-enriched sports drinks to replace their losses For everyone else, getting the normal amount of sodium from foods and drinking water to remain hydrated is enough. You lose water and electrolytes, particularly sodium, when you sweat. However, the sodium consumed through your diet is normally enough to cover any losses. The main food sources of electrolytes are fruits and vegetables. However, in the Western diet, a common source of sodium and chloride is table salt. Below are some foods that provide electrolytes 28 , 29 , 30 :. Some people drink electrolyte water or supplement with electrolytes like sodium and calcium to ensure they get enough. But in some circumstances, such as during bouts of vomiting and diarrhea where electrolyte losses are excessive, supplementing with a rehydration solution that contains electrolytes could be useful Always read the instructions on over-the-counter replacement solutions. Also note that unless you have low levels of electrolytes due to excessive losses, then supplementing can cause abnormal levels and possibly illness If you eat a balanced diet that contains good sources of electrolytes, supplementing is usually unnecessary. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Electrolytes are important for many bodily functions, such as fluid balance and muscle contractions. This article discusses the potential benefits of…. Electrolytes like salt, potassium, and calcium perform a variety of important functions within your body. Electrolytes are naturally occurring minerals that control important bodily functions. Here's what you need to know about electrolyte imbalance, its…. Electrolytes are found in all kinds of foods, including fruits and vegetables, such as broccoli, kale, avocados, and bananas. Electrolytes help our…. Want to change up your hydration routine after a sweat session? The electric charge can be positive or negative. You have electrolytes in your blood, urine pee , tissues, and other body fluids. An electrolyte imbalance means that the level of one or more electrolytes in your body is too low or too high. It can happen when the amount of water in your body changes. The amount of water that you take in should equal the amount you lose. If something upsets this balance, you may have too little water dehydration or too much water overhydration. Some of the more common reasons why you might have an imbalance of the water in your body include:. A test called an electrolyte panel can check the levels of your body's main electrolytes. A related test, the anion gap blood test , checks whether your electrolytes are out of balance or if your blood is too acidic or not acidic enough. The treatment for an electrolyte imbalance depends on which electrolytes are out of balance, if there is too little or too many, and what is causing the imbalance. In minor cases, you may just need to make some changes to your diet. In other cases, you may need other treatments. For example:. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Fluid and Electrolyte Balance. On this page Basics Summary Start Here Diagnosis and Tests. Learn More Related Issues Genetics. See, Play and Learn No links available. Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. Resources Find an Expert. For You Children Patient Handouts. In rare cases, a severe electrolyte imbalance can be life-threatening. Hyponatremia , low sodium levels, is the most common type of electrolyte imbalance. Other types of electrolyte imbalances people typically experience include:. Dehydration caused by excess sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea is the leading cause of electrolyte imbalance. Rapidly losing sweat in hot weather or losing body fluids when you're sick quickly depletes your body of electrolytes, often before you can replace them. Injuries and medical conditions can also cause electrolyte imbalances, including:. Critically ill people and older adults are more likely to experience electrolyte imbalances. Diets low in sources of electrolytes also increase someone's risk of developing an electrolyte imbalance. Electrolyte imbalance symptoms will vary depending on which electrolytes are affected and the level of the imbalance. Electrolyte imbalances can cause cardiac, muscular, and neurological symptoms like:. In severe cases of electrolyte imbalances, folks can deal with serious health problems like:. Mild electrolyte imbalances can be treated by eating electrolyte foods or supplementing with electrolyte drinks. For example, say you are sweating during an intense hike in hot weather and losing electrolytes like sodium. Eating salty snacks and drinking water can help you replenish depleted sodium levels and rehydrate. Moderate to severe electrolyte imbalances will require additional treatments more catered to what's causing the imbalance. Treatments may include:. Folks with a severe electrolyte imbalance will be monitored and receive additional testing to ensure their electrolyte levels return to normal. You can also take preventative measures to avoid an electrolyte imbalance in the first place. The best ways to prevent an electrolyte imbalance include:. Electrolytes are minerals with positive or negative charges like sodium, calcium, and potassium. Your body needs electrolytes for brain function, muscle contractions, and managing blood pH. Electrolytes are also important for hydration, and most electrolytes come from food. If your electrolyte levels get too high or low, an electrolyte imbalance can cause dangerous neurological, cardiovascular, and muscular health issues. Typically, dehydration from heat or illness causes an electrolyte imbalance, which can be remedied by eating electrolyte foods and hydrating. Medical conditions like kidney and liver disease can also cause an electrolyte imbalance. An electrolyte imbalance can make you feel weak, nauseous, and disoriented. If you suspect you have an electrolyte balance, your healthcare provider can offer you an electrolyte levels test. Shrimanker I, Bhattarai S. In: Statpearls. Statpearls Publishing; Hamm LL, Nakhoul N, Hering-Smith KS. Acid-base homeostasis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. Food and Drug Administration. Sodium in your diet. Dietary Guidelines for Americans. Food sources of potassium. National Institutes of Health. |
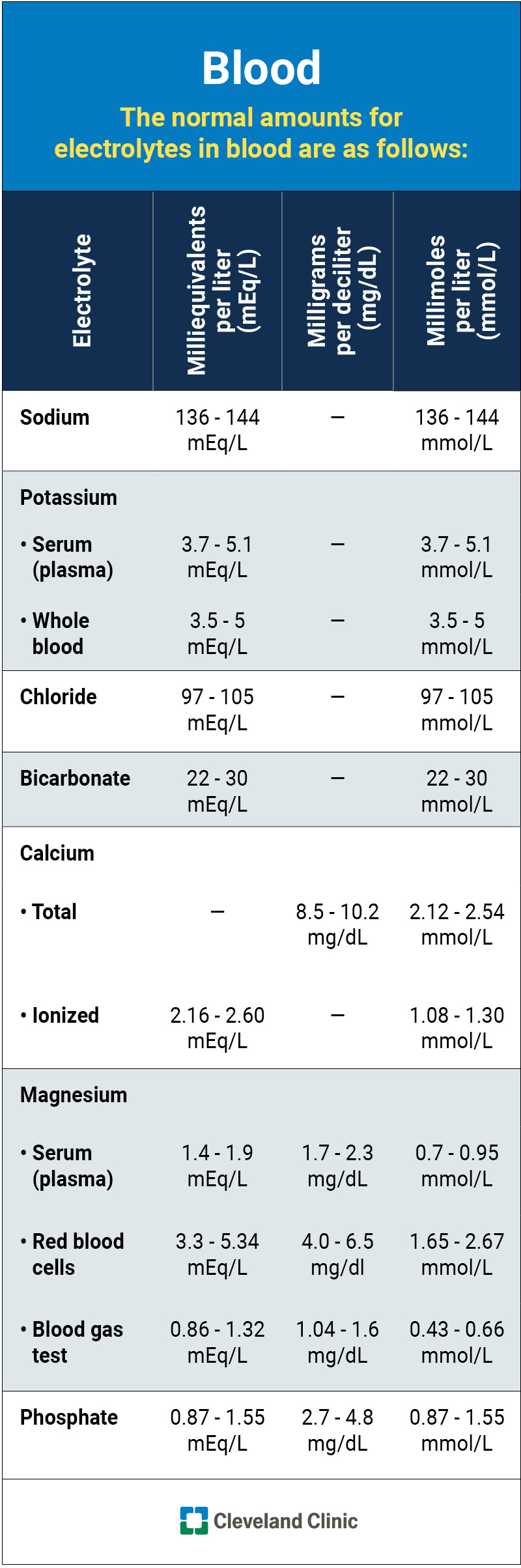
| How to Maintain an Optimal Electrolyte Balance – The Amino Company | What Are Electrolytes? Duggan, S. The end result is edema and hypertension. population, ages 1 year and older. The names of the different types of electrolyte imbalances are: Electrolyte Too low Too high Bicarbonate Acidosis Alkalosis Calcium Hypocalcemia Hypercalcemia Chloride Hypochloremia Hyperchloremia Magnesium Hypomagnesemia Hypermagnesemia Phosphate Hypophosphatemia Hyperphosphatemia Potassium Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia Sodium Hyponatremia Hypernatremia How are electrolyte imbalances diagnosed? |
| Latest news | Comment on this article. References 1. Ferrannini E. Sodium-Glucose Co-transporters and Their Inhibition: Clinical Physiology. Cell Metab. Palmer LG, Schnermann J. Integrated control of Na transport along the nephron. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. Buffington MA, Abreo K. Hyponatremia: A Review. J Intensive Care Med. Ambati R, Kho LK, Prentice D, Thompson A. Osmotic demyelination syndrome: novel risk factors and proposed pathophysiology. Intern Med J. Gumz ML, Rabinowitz L, Wingo CS. An Integrated View of Potassium Homeostasis. N Engl J Med. Ellison DH, Terker AS, Gamba G. Potassium and Its Discontents: New Insight, New Treatments. J Am Soc Nephrol. Stedwell RE, Allen KM, Binder LS. Hypokalemic paralyses: a review of the etiologies, pathophysiology, presentation, and therapy. Am J Emerg Med. Viera AJ, Wouk N. Potassium Disorders: Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia. Am Fam Physician. Veldurthy V, Wei R, Oz L, Dhawan P, Jeon YH, Christakos S. Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging. Bone Res. Cooper MS, Gittoes NJ. Diagnosis and management of hypocalcaemia. Turner JJO. Hypercalcaemia - presentation and management. Clin Med Lond. Hamm LL, Nakhoul N, Hering-Smith KS. Acid-Base Homeostasis. Kraut JA, Madias NE. Adverse Effects of the Metabolic Acidosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. Jahnen-Dechent W, Ketteler M. Magnesium basics. Clin Kidney J. Hansen BA, Bruserud Ø. Hypomagnesemia as a potentially life-threatening adverse effect of omeprazole. Oxf Med Case Reports. Morrison G. Serum Chloride. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Butterworths; Boston: Berkelhammer C, Bear RA. A clinical approach to common electrolyte problems: 3. Can Med Assoc J. Toffaletti J, Ernst P, Hunt P, Abrams B. Dry electrolyte-balanced heparinized syringes evaluated for determining ionized calcium and other electrolytes in whole blood. Clin Chem. Raza M, Kumar S, Ejaz M, Azim D, Azizullah S, Hussain A. Electrolyte Imbalance in Children With Severe Acute Malnutrition at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cody RJ, Pickworth KK. Approaches to diuretic therapy and electrolyte imbalance in congestive heart failure. Cardiol Clin. Liamis G, Liberopoulos E, Barkas F, Elisaf M. Spurious electrolyte disorders: a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Am J Nephrol. Boden SD, Kaplan FS. Calcium homeostasis. Orthop Clin North Am. Hoppe LK, Muhlack DC, Koenig W, Carr PR, Brenner H, Schöttker B. Association of Abnormal Serum Potassium Levels with Arrhythmias and Cardiovascular Mortality: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. Negri AL, Rosa Diez G, Del Valle E, Piulats E, Greloni G, Quevedo A, Varela F, Diehl M, Bevione P. Hypercalcemia secondary to granulomatous disease caused by the injection of methacrylate: a case series. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. Agus ZS. Mechanisms and causes of hypomagnesemia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. Elevated blood glucose levels can increase urine production, leading to increased fluid and electrolyte loss. Certain heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure or arrhythmias, can disrupt the body's fluid balance and affect electrolyte levels, particularly sodium and potassium. If you suffer from any of these conditions, consult your healthcare provider, who may recommend electrolyte-rich fluids or oral rehydration solutions. Medications, such as diuretics, laxatives, antacids, anti-histamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDS , and blood pressure medicine can cause excess urinary excretion of electrolytes, fluid loss, or improper distribution of fluids and sodium in your body and affect your electrolyte balance. Electrolyte supplementation may be necessary under the guidance of a healthcare professional. If you experience any of these issues, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy electrolyte balance. It's important to remember that your needs may vary from those of your peers, and if you have any questions, concerns, or medical issues, you should consult with your healthcare provider for guidance. Electrolytes are naturally occurring minerals that are present in various foods and beverages. However, the body does not produce electrolytes independently, so you need to consume them through your diet or through electrolyte-rich beverages. Your most effective strategy for maintaining a proper electrolyte balance is to follow a well-balanced diet. However, there are situations when you may require more support to balance your electrolytes, such as when your physical activity is extreme, or you're experiencing conditions like excessive sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea. In these cases, consider one of the following strategies. Drinking water helps you maintain good hydration and a proper electrolyte balance. While some sources suggest you should drink half your body weight in ounces of water per day i. If it is darker yellow or brown, you may be dehydrated. Remember to sip fluids consistently throughout the day. To help replenish electrolytes during periods of increased fluid loss or dehydration, electrolyte-rich beverages or supplements can help replenish the lost minerals more effectively than water. Try the following recipe to make your own natural electrolyte solution. While there are many electrolyte-enhanced beverages on the market, such as sports drinks or electrolyte powders, they may have more sugar and additives than you need. Some herbal teas, such as chamomile , peppermint , or ginger tea, may indirectly support electrolyte balance by promoting overall health and hydration. Use just one herb or combine several. Make your tea in advance, steeping the herbs in water overnight, and chill it in an airtight container for use as a sports drink. Add a slice of lemon or orange for extra flavor. Giving your body enough time to rest and recover after intense physical activity or periods of illness can support electrolyte balance. Allow yourself adequate rest to allow your body to replenish electrolytes and recover. Maintaining optimal electrolyte levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. However, it's important to recognize that your individual needs may vary when it comes to electrolyte balance. Your unique lifestyle, diet, and health conditions can impact your electrolyte requirements. Therefore, listen to your body. Prioritize hydration. Consume a balanced diet rich in electrolyte-containing foods. Relax and get plenty of sleep. Be mindful of factors such as exercise intensity and environmental conditions that affect your daily health. If you suffer from any of the symptoms of electrolyte imbalance, seek the help of your healthcare provider. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances. They can help diagnose electrolyte imbalances, provide dietary recommendations, and suggest appropriate interventions if necessary. By taking proactive steps and making informed choices, you can support your body's electrolyte balance and enjoy good health and vitality. products Electrolytes: The Essential Minerals for Your Health and Wellness Published on July 20, By Lisa Stockwell. Lisa Stockwell Lisa Stockwell has worked as a copywriter, writer, author, and editor for 35 years, specializing in the field of healthcare since Calcium plays a role in mediating the constriction and relaxation of blood vessels — called vasoconstriction and vasodilation — and is needed for proper blood clotting. Magnesium is required for the active transport of ions like potassium and calcium across cell membranes, thus influencing the conduction of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and normal heart function. Magnesium is needed for adenosine triphosphate ATP energy production , and phosphate is a component of many metabolic intermediates , including ATP and nucleotides. It is well-understood that optimal electrolyte balance can promote cognitive performance, better mood, and neurological health , as patients with electrolyte disorders often present with neurological manifestations. Suboptimal sodium status preferentially affects the central nervous system, whereas suboptimal potassium and calcium status can significantly affect neuromuscular manifestations. Calcium is needed for nerve impulse transmission and cell-signaling pathways. Magnesium is required for neurotransmitter release and may be clinically relevant to those with depression. Electrolyte disturbances are associated with certain endocrine conditions, such as hypothyroidism. A significant decrease in calcium has been observed in patients with hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism, as thyroxin thyroid hormone normally regulates calcium ion release from the cells. Low thyroid hormones may also be associated with hyponatremia. Beyond thyroid function, low sodium also promotes the release of aldosterone , a hormone that works to maintain normal blood pressure. Plus, calcium is needed for the secretion of hormones , such as insulin. Certain electrolytes can directly support the immune system. Sodium can modulate immune cell activities. Calcium plays a role in the activation of lymphocytes. Lastly, magnesium is necessary for proper immunoglobin synthesis, macrophage response to lymphocytes, and T helper-B cell adherence. Sodium, potassium, chloride, magnesium, calcium, phosphate, and bicarbonate support overall health in the human body. The role of electrolytes only begins with promoting optimal hydration, extending far beyond by helping support athletic performance, muscle and bone health, energy production, and more. Designs for Health has been dedicated to being the most trusted source for superior quality, science-based nutritional products for nearly three decades. The blogs we publish here cover a range of topics, including new and original approaches to diet and healthcare, analyses of the latest cutting-edge research, deep-dives into specific nutrients, botanicals, nutraceuticals and more, all fully referenced for those who want to dig deeper into the primary literature. Electrolytes: Essential Functions for Optimal Health. January 4, - facebook twitter linkedin. Fluid Balance Proper hydration is indispensable for overall health. |
| We Care About Your Privacy | Forbes, G. Most often linked to sports drinks, electrolytes are vital for good health. Despite the kidney's ability to compensate, its limitations require the effective use of the thirst sensation to maintain water balance. DASH also recommends limiting foods high in saturated fat e. The body may be depleted of sodium under extreme conditions of heavy and persistent sweating, or where trauma, chronic diarrhea, or renal disease produce an inability to retain sodium Gothberg et al. If you experience any of these issues, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy electrolyte balance. And is it really so important to replace them? |

anscheinend würde aufmerksam lesen, aber hat nicht verstanden