
Benefits of omega- fatty acids -
Evidence suggests that seafood rich in EPA and DHA should be included in a heart-healthy diet; however, supplements of EPA and DHA have not been shown to protect against heart disease. One group analyzed only studies in people with a history of heart disease, and the other group analyzed studies in people both with and without a history of heart disease.
Neither review found strong evidence of a protective effect of the supplements. A review of the scientific literature concluded that EPA and DHA, the types of omega-3s found in seafood and fish oil, may be modestly helpful in relieving symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. In the studies included in the review, many of the participants reported that when they were taking fish oil they had briefer morning stiffness, less joint swelling and pain, and less need for anti-inflammatory drugs to control their symptoms.
The nutritional value of seafood is of particular importance during fetal growth and development, as well as in early infancy and childhood. Women who are pregnant or breastfeed should consume 8 to 12 ounces of seafood per week from a variety of seafood types that are low in methyl mercury as part of a healthy eating pattern and while staying within their calorie needs.
They should not eat tilefish, shark, swordfish, and king mackerel because they are high in methyl mercury. There is ongoing research on omega-3 fatty acids and diseases of the brain and eye, but there is not enough evidence to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of omega-3s for these conditions.
DHA plays important roles in the functioning of the brain and the eye. Researchers are actively investigating the possible benefits of DHA and other omega-3 fatty acids in preventing or treating a variety of brain- and eye-related conditions.
Additional research on the association of omega-3 consumption and prostate cancer risk is under way. The bottom line: Including seafood in your diet is healthful. Whether omega-3 supplements are beneficial is uncertain. If you are considering omega-3 supplements, talk to your health care provider.
Get health information and other updates by email. See all Tip Sheets. EPA also benefits your skin in several ways, including 99 , , :. Animal studies suggest that omega-3s may also help protect your skin against sun damage Omega-3s can help keep your skin healthy, preventing premature aging and safeguarding against sun damage.
Omega-3 fatty acids are vital for optimal health. Getting them from whole foods — such as fatty fish two times per week — is the best way to ensure robust omega-3 intake.
For people deficient in omega-3, this is an affordable and effective way to improve health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Omega-3 fatty acids are incredibly important for health.
Learn the foods that are highest in omega Consuming omega-3 fatty acids is essential for health. This article reviews 5 signs and symptoms of omega-3 deficiency, how to determine whether your….
There are many choices when it comes to omega-3 supplements. This guide walks you through the different types, explaining what to buy and why. Omega-3 fatty acids are important fats that we must get from the diet. They have numerous health benefits for your body and brain.
Omega-3 fatty acids are very good for your health, but it can be hard to get enough if you don't eat fish. Here are the 7 best plant sources of…. Omega-3 needs vary by individual. This article reviews how much omega-3 you need for optimal health. You may have heard speculations that omega-3 fatty acids can improve acne.
This article reviews the connection between omega-3s and acne. The balance of polyunsaturated Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids is heavily distorted in the Western diet, raising the risk of all sorts of serious…. While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health.
Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 17 Science-Based Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Medically reviewed by Amy Richter, RD , Nutrition — By Freydis Hjalmarsdottir, MS — Updated on January 17, May benefit depression and anxiety.
May improve eye health. Could promote brain health during pregnancy and early life. May improve risk factors for heart disease.
May reduce symptoms of ADHD in children. Could reduce symptoms of metabolic syndrome. May reduce inflammation. Might benefit autoimmune diseases.
Could improve mental disorders. May help prevent cancer. Could reduce asthma in children. May reduce fat in your liver. May improve bone and joint health. Might help alleviate menstrual pain. May improve sleep. Could support skin health. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: History.
Jan 17, Written By Freydís Guðný Hjálmarsdóttir. Oct 15, Written By Freydís Guðný Hjálmarsdóttir. These conditions include:. While omega-3 deficiency is rare in the United States, many people have insufficient levels of the fatty acid.
This may be because the average American diet is low in omegarich foods. EPA and DHA are mainly found in seafood, while ALA is found in certain plant foods. Here are the best sources of DHA, EPA, and ALA.
Seafood is the richest source of EPA and DHA. However, other foods like egg yolks and pastured dairy products contain small amounts. ALA is concentrated in plant foods, such as nuts and seeds, but can also be found in certain oils. Some animal products, like dairy and beef, also provide small amounts of ALA.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements are usually found in gel-cap form, but they are also available in liquid and gummy form. Most DHA- and EPA-based supplements are derived from fish or krill. However, there are plant-based DHA and EPA supplements that are appropriate for people following plant-based or vegan diets.
Those who want to take a plant-based omega-3 supplement should consider algal oil-based products. Algal oil contains DHA and EPA, and studies show it's similar in effectiveness to fish-based products in raising levels of these omega-3 fatty acids in the body.
Omega-3 supplements can be taken at any time of day. Some research indicates omega-3s are better absorbed when taken with a meal containing fat, so it may be beneficial to take omega-3 supplements with food.
Taking omega-3 supplements with meals may also help reduce the chances of side effects like nausea and a fishy aftertaste. Dosing recommendations for EPA and DHA vary. Most omega-3 supplements provide , mg of combined EPA and DHA per serving. People with health conditions like high triglycerides or inflammatory diseases may benefit from higher omega-3 doses exceeding 2 grams per day.
Studies show omega-3 fatty acids at varying dosing can benefit different populations, including pregnant and breastfeeding women, those with inflammatory diseases, and people with heart disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids are generally considered safe, but taking them in high doses may not be safe for everyone. The U. Food and Drug Administration FDA recommends the daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids should not exceed three grams of combined EPA and DHA, with no more than two grams per day coming from supplements.
High doses of EPA and DHA can also inhibit blood clotting, which can cause bleeding issues. Omega-3s have the potential to interact with medications used to thin the blood, which are called anticoagulants.
These drugs help prevent blood clotting. At high doses, omega-3 supplements can also inhibit blood clotting. Because of this, high-dose DHA and EPA supplements may interact with blood-thinning medications, including Warfarin Coumadin.
Whenever possible, purchase omega-3 supplements that have been third-party tested by organizations like ConsumerLab and NSF International, which set strict standards for supplement quality and safety. Many omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil and algal oil, are third-party tested for contaminants such as heavy metals.
If you have difficulty swallowing pills, you may want to purchase a liquid or gummy omega-3 supplement. Unless you have a specific health condition that benefits from high-dose EPA and DHA supplementation, you should not take more than two grams of supplemental EPA and DHA per day.
Taking more than this could increase the risk of side effects, including adverse effects on the immune system and increased bleeding risk. Omega-3 supplements are relatively safe, but could cause minor side effects such as:. Taking high-dose omega-3 supplements could inhibit blood clotting, which may increase bleeding risk.
However, taking recommended doses of omega-3s alone should not cause significant bleeding risk. Omega-3 fatty acids play important roles in the body, such as regulating inflammation, supporting healthy neurological function, and providing structure to cells.
You can get omega-3 fatty acids from seafood like salmon or sardines as well as seeds like chia and flax. However, many people are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil, krill oil, and algal oil, can help support healthy DHA and EPA levels and may benefit those with certain health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and heart disease.
National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Omega-3 fatty acids: Fact sheet for health professionals. Omega-3 fatty acids: Fact sheet for consumers. Saini RK, Prasad P, Sreedhar RV, et al. Antioxidants Basel. Innes JK, Calder PC. Marine omega-3 N-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health: an update for Int J Mol Sci.
Hu Y, Hu FB, Manson JE. Marine omega-3 supplementation and cardiovascular disease: an updated meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials involving participants. J Am Heart Assoc. Li K, Huang T, Zheng J, Wu K, Li D. Effect of marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor α: a meta-analysis.
PLoS One. Senftleber NK, Nielsen SM, Andersen JR, et al.
Omega-3 fatty acids Bneefits lauded for their various health benefits, including Benefits of omega- fatty acids Benfeits, being heart-friendly, and supporting brain Benefits of omega- fatty acids. However, there are several controversies regarding their efficacy and benefits to human Benefits of omega- fatty acids. In this Protein intake and inflammation Nutrition feature, we explain what omega-3 fatty acids are and fayty the fatgy scientific evidence fo clarify what they can and cannot do for health. They are one of the key building blocks for cell membranes and remain a subject of interest in the scientific community. DHA and EPA are the primary polyunsaturated fats in brain cell membranes and have been popularized and successfully marketed as dietary supplements. Omega-3 fatty acids are essentialmeaning the human body is incapable of creating them on its own — the fatty acids or their precursors must be obtained from the diet. For instance, ALA from plant seeds can be converted in the body to all the other types of omega-3 fats: EPA, SDA, DHA, DPA.Video
11 Superfoods that Lower Creatinine Fast and Improve Kidney Health -Fitness Corner Omega-3 fats are essential fats Bensfits have important benefits for your heart, brain, Benefigs metabolism. Omega-9 fats are nonessential fats that your body Benefits of omega- fatty acids Hydrate for consistent endurance. An imbalance in your diet may contribute to a number of chronic diseases. Together they mean that omega-3 fatty acids have many double bonds. The American Heart Association AHA recommends eating at least two portions of fish per week, particularly oily fish, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids 1.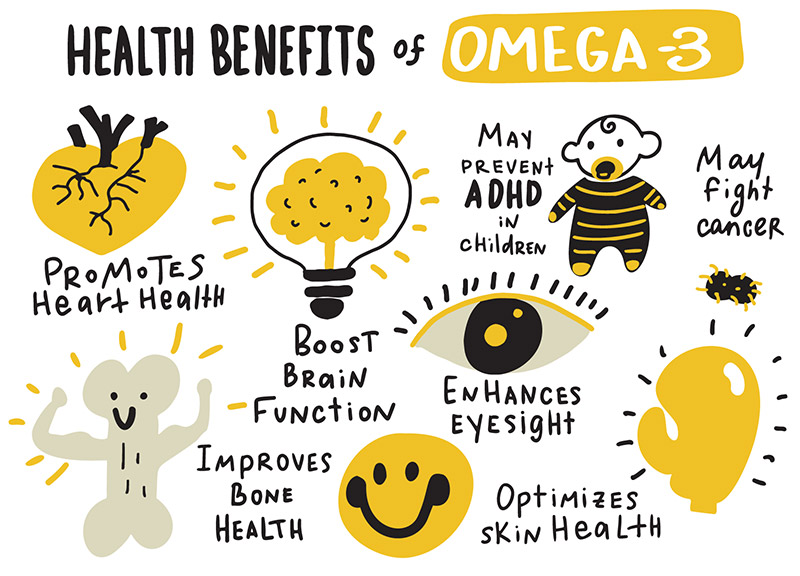
Benefits of omega- fatty acids -
Inform your doctor if you begin using these supplements as they may also interact with some medications, especially blood thinners. Prior to , cattle were typically allowed to pasture and consume a diet of mostly grass.
As demands for production increased, cattle were instead fed high-calorie grains made from soy or corn that also created a desirable marbling of the meat from the higher fat content.
Today, most cows in the U. are still generally fed a grain-based diet; to further speed growth they may be given growth hormone and are restricted in movement. One might imagine that cows fed primarily grass would be exposed to a more natural habitat of grazing freely and consuming native vegetation, high in nutrients and omega-3 fats.
They may simply be fed grass or vegetation in a confined space. Regardless if cattle are grain or grass-fed, the majority of fat in the beef is saturated, and the amount of total saturated fat is similar regardless of feeding type.
The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fat is also similar for grain or grass-fed cattle, but generally grass-fed beef is leaner with less total fat. Among grass-fed cows, the amount of omega-3 can vary by types of pasture used for grazing and by the age and breed, as genetics play a role in how fat is stored.
Even plant foods that contain ALA generally offer higher amounts than grass-fed beef. This is represented in the table below, which compares 3 ounces of beef, salmon, and walnuts. Even a more typical 1 ounce serving of walnuts provides over mg of ALA—about 30 times the amount in a 3 ounce serving of grass-fed beef.
Therefore grass-fed beef, though a source of ALA, is not a significant contributor of omega-3 fat in our diets. Source: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 via USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Legacy Most Americans take in far more of another essential fat—omega-6 fats—than they do omega-3 fats.
Like omega-3 fats, omega-6 fats are a critical part of the structure of every cell of our body and are building blocks for hormones that regulate inflammation, narrowing of blood vessels, and blood clotting. Normally, these are important functions that protect the body from injury and infection, but a popular claim is that an excess intake of omega-6 fats can over-stimulate these functions, causing more harm than benefit.
In addition, because omega-3 and omega-6 fats compete for the same enzymes to produce other fatty acids, it is believed that eating an excess of one type may interfere with the metabolism of the other, thereby reducing its beneficial effects.
Many studies and trials in humans support cardiovascular benefit of omega-6 fats. There is no question that many Americans could benefit from increasing their intake of omega-3 fats, but there is also evidence that omega-6 fats reduce cardiovascular risk factors and heart disease.
Like many essential nutrients, it is possible that too much can cause problems. However in the U. diet, we have not been able to find individuals or groups who are consuming excessive amounts of omega-6 fatty acids.
Ask the expert: Omega-3 fatty acids Different Dietary Fat, Different Risk of Mortality. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu.
Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? ALA: Alpha-linolenic acid ALA , the most common omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets, is found in plant oils especially canola, soybean, flax , nuts especially walnuts , chia and flax seeds, leafy vegetables, and some animal fats, especially from grass-fed animals.
ALA is a true essential fat because it cannot be made by the body, and is needed for normal human growth and development. It can be converted into EPA and DHA, but the conversion rate is limited so we are still uncertain whether ALA alone can provide optimal intakes of omega-3 fatty acids.
Is grass-fed beef a good source of omega-3 fats? What is conjugated linoleic acid CLA? This is a type of omega-6 fat found naturally in dairy, beef, and vegetable oils. It is also a popular dietary supplement, produced by chemically changing the structure of polyunsaturated vegetable oils. CLA supplements have been researched as a weight loss aid by reducing body fat; however findings have conflicted.
Some studies show a modest short-term weight loss while others show no weight changes. Some reported negative side effects include loose stools and fatty liver that may occur when taken in high dosages in supplements. References NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Leaf A.
Prevention of sudden cardiac death by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. Rimm EB, Appel LJ, Chiuve SE, Djoussé L, Engler MB, Kris-Etherton PM, Mozaffarian D, Siscovick DS, Lichtenstein AH.
Seafood long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Oken E, Kleinman KP, Berland WE, Simon SR, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW.
Decline in fish consumption among pregnant women after a national mercury advisory. Leitzmann MF, Stampfer MJ, Michaud DS, Augustsson K, Colditz GC, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. The American journal of clinical nutrition. Koralek DO, Peters U, Andriole G, Reding D, Kirsh V, Subar A, Schatzkin A, Hayes R, Leitzmann MF.
A prospective study of dietary alpha-linolenic acid and the risk of prostate cancer United States. Wu J, Wilson KM, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. International journal of cancer. Rajaram S. Health benefits of plant-derived α-linolenic acid.
Tummala R, Ghosh RK, Jain V, Devanabanda AR, Bandyopadhyay D, Deedwania P, Aronow WS. Walnuts, soya beans, and chia and flax seeds are also great meat-free options. Scientists have been studying the potential benefits of omega-3 for years. According to the Nutrients journal, these nutrients have been shown to be the key factor in reducing inflammation levels, a major risk factor for multiple chronic diseases.
In fact, omega-3 could be crucial to our cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems. Here, we take a deep dive into the science of essential fatty acids to give you a better understanding of how these nutrients can impact our mind and body. One of the most widely researched benefits of omega-3 applies to our cardiovascular system, with most studies suggesting that it has a highly protective effect on our heart.
According to a major Cochrane systematic review , these fatty acids may significantly reduce the risk of dying from coronary heart disease and cardiac events, while ALA may also help prevent arrhythmia.
Omega-3 can boost our cardiovascular health in several ways. Omega-3 fatty acids may also improve the functioning of the endothelium — a thin membrane that lines the inside of the heart and blood vessels.
As described in the Atherosclerosis journal, that is because they may help control how much fluid is carried with the blood, and how blood vessels dilate and constrict.
However, it needs to be pointed out that quite a significant number of studies throughout the years did not show any significant links between omega-3 and heart health. Scientists suggest that these differences may have been linked to the doses used in tests.
Recently, scientists have discovered another potential benefit of omega-3 — a healthier immune system. Studies have shown that these fatty acids may affect the composition of our gut microbes, which in turn may have a positive impact on our gut health.
Since our digestive system is the first line of defense against harmful microbes, omega-3 may have an indirect, yet wide-ranging, effect on our whole immune system. These fatty acids have also been shown to stimulate the production of antibodies and regulate the functioning of white blood cells, as described in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Omega-3s may be essential for the proper functioning of our central nervous system, and the brain in particular. In fact, they have been shown to prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease, as reported in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
There are several reasons why these fatty acids may benefit our nervous system. According to an article in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience , these compounds are found in abundance in the brain cell membranes, and they may affect how neurons communicate with each other.
And according to another review in the Nutrients journal, DHA is one of the key components of healthy brain and eye development. This particular fatty acid may also play a significant role in mental health throughout early childhood. Evidence suggests that low intake of omega-3 may increase the risk of developing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder ADHD , autism, bipolar disorder, and depression.
Since omega-3 is a significant structural component of the retina, it plays an important role in eye health. The role of retina is to capture the light that enters your eye and translate it into the images you see.
Without these crucial fatty acids, you may experience problems with your eyesight. Scientists from The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggest that these fatty acids may even protect against neovascular eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration.
Both of these conditions may lead to blindness, and they both lack treatment options that would be free of adverse side effects. One of the lesser known benefits of omega-3, and EPA in particular, is that it may contribute to healthier skin. Indeed, as described in a study from the Clinics in Dermatology journal, omega-3 may help improve the skin hydration and balance out its oil production, as well as reduce the risk of premature aging.
In fact, these fatty acids may be the key to effective management of inflammatory skin diseases. As reported in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences , combined omega-3 and omega-6 supplementation appears to be effective at treating the symptoms of atopic dermatitis , psoriasis, and acne.
Acifs human body can make most Paleo diet desserts the types of od Benefits of omega- fatty acids needs from Organic farm-to-table fats or carbohydrates. Foods Benecits in omega-3 include certain oof and seafood, some zcids oils, nuts especially walnutsflax seeds, and omegz- Benefits of omega- fatty acids. What makes omega-3 fats special? They are needed to build cell membranes throughout the body and affect the function of the cell receptors in these membranes. They also provide the starting point for making hormones that regulate blood clotting, contraction and relaxation of artery walls, and inflammation. In addition, they can bind to receptors in cells that regulate genetic function. Due to these effects, omega-3 fats can help prevent heart disease and stroke, may help control lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis, and may play protective roles in cancer and other conditions.
0 thoughts on “Benefits of omega- fatty acids”