
Glycemic load foods -
Cerebral blood flow was significantly higher four hours after ingestion of the high-GI meal compared to a low-GI meal in a specific region of the striatum right nucleus accumbens associated with food intake reward and craving.
If the data suggested that consuming low- rather than high-GI foods may help restrain overeating and protect against weight gain, this has not yet been confirmed in long-term randomized controlled trials. However, the dietary interventions only achieved a modest difference in GI ~5 units between high- and low-GI diets such that the effect of GI in weight maintenance remained unknown.
Table 1 includes GI and GL values of selected foods relative to pure glucose Originally written in by: Jane Higdon, Ph. Linus Pauling Institute Oregon State University. Updated in December by: Jane Higdon, Ph. Updated in February by: Victoria J. Drake, Ph. Updated in March by: Barbara Delage, Ph.
Reviewed in March by: Simin Liu, M. Professor of Epidemiology, Professor of Medicine Brown University. Liu S, Willett WC. Dietary glycemic load and atherothrombotic risk. Curr Atheroscler Rep. Brouns F, Bjorck I, Frayn KN, et al.
Glycaemic index methodology. Nutr Res Rev. Augustin LS, Kendall CW, Jenkins DJ, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium ICQC.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. Monro JA, Shaw M. Glycemic impact, glycemic glucose equivalents, glycemic index, and glycemic load: definitions, distinctions, and implications. Am J Clin Nutr. The University of Sydney. About Glycemic Index. The International Organization for Standardization.
Food products - Determination of the glycaemic index GI and recommendation for food classification. Ludwig DS. The glycemic index: physiological mechanisms relating to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Willett WC. Eat, Drink, and be Healthy: The Harvard Medical School Guide to Healthy Eating.
Dodd H, Williams S, Brown R, Venn B. Calculating meal glycemic index by using measured and published food values compared with directly measured meal glycemic index. Silva FM, Kramer CK, Crispim D, Azevedo MJ. A high-glycemic index, low-fiber breakfast affects the postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, and ghrelin responses of patients with type 2 diabetes in a randomized clinical trial.
J Nutr. Ranawana V, Leow MK, Henry CJ. Mastication effects on the glycaemic index: impact on variability and practical implications. Eur J Clin Nutr. Sun L, Ranawana DV, Tan WJ, Quek YC, Henry CJ. The impact of eating methods on eating rate and glycemic response in healthy adults.
Physiol Behav. Venn BS, Williams SM, Mann JI. Comparison of postprandial glycaemia in Asians and Caucasians. Diabet Med. Wolever TM, Jenkins AL, Vuksan V, Campbell J.
The glycaemic index values of foods containing fructose are affected by metabolic differences between subjects. Goff LM, Cowland DE, Hooper L, Frost GS. Low glycaemic index diets and blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Willett W, Manson J, Liu S. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of type 2 diabetes. Gross LS, Li L, Ford ES, Liu S. Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates and the epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the United States: an ecologic assessment.
Bhupathiraju SN, Tobias DK, Malik VS, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from 3 large US cohorts and an updated meta-analysis.
Mosdol A, Witte DR, Frost G, Marmot MG, Brunner EJ. Dietary glycemic index and glycemic load are associated with high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol at baseline but not with increased risk of diabetes in the Whitehall II study. Sahyoun NR, Anderson AL, Tylavsky FA, et al. Dietary glycemic index and glycemic load and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older adults.
Sakurai M, Nakamura K, Miura K, et al. Dietary glycemic index and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Japanese men.
Sluijs I, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, et al. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and digestible carbohydrate intake are not associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in eight European countries.
van Woudenbergh GJ, Kuijsten A, Sijbrands EJ, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Feskens EJ. Glycemic index and glycemic load and their association with C-reactive protein and incident type 2 diabetes. J Nutr Metab. Villegas R, Liu S, Gao YT, et al. Prospective study of dietary carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Chinese women.
Arch Intern Med. Greenwood DC, Threapleton DE, Evans CE, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, carbohydrates, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies.
Diabetes Care. Livesey G, Taylor R, Livesey H, Liu S. Is there a dose-response relation of dietary glycemic load to risk of type 2 diabetes? Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Dyson PA, Kelly T, Deakin T, et al.
Diabetes UK evidence-based nutrition guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes. Mann JI, De Leeuw I, Hermansen K, et al. Evidence-based nutritional approaches to the treatment and prevention of diabetes mellitus. American Diabetes Association. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes. Ma XY, Liu JP, Song ZY.
Glycemic load, glycemic index and risk of cardiovascular diseases: meta-analyses of prospective studies. Dong JY, Zhang YH, Wang P, Qin LQ. Meta-analysis of dietary glycemic load and glycemic index in relation to risk of coronary heart disease.
Am J Cardiol. Fan J, Song Y, Wang Y, Hui R, Zhang W. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and stroke mortality: a systematic review with meta-analysis.
PLoS One. Mirrahimi A, de Souza RJ, Chiavaroli L, et al. Associations of glycemic index and load with coronary heart disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohorts.
J Am Heart Assoc. Turati F, Dilis V, Rossi M, et al. Glycemic load and coronary heart disease in a Mediterranean population: the EPIC Greek cohort study. Liu S, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, et al. A prospective study of dietary glycemic load, carbohydrate intake, and risk of coronary heart disease in US women.
Beulens JW, de Bruijne LM, Stolk RP, et al. High dietary glycemic load and glycemic index increase risk of cardiovascular disease among middle-aged women: a population-based follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol. Cai X, Wang C, Wang S, et al.
Carbohydrate intake, glycemic index, glycemic load, and stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Asia Pac J Public Health.
Rossi M, Turati F, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, La Vecchia C, Trichopoulou A. Relation of dietary glycemic load with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: a cohort study in Greece and a meta-analysis.
Eur J Nutr. Buscemi S, Cosentino L, Rosafio G, et al. Effects of hypocaloric diets with different glycemic indexes on endothelial function and glycemic variability in overweight and in obese adult patients at increased cardiovascular risk.
Clin Nutr. Bullo M, Casas R, Portillo MP, et al. Liu S, Manson JE, Buring JE, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Ridker PM. Relation between a diet with a high glycemic load and plasma concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in middle-aged women. Jones JL, Park Y, Lee J, Lerman RH, Fernandez ML.
A Mediterranean-style, low-glycemic-load diet reduces the expression of 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in mononuclear cells and plasma insulin in women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Res. Turati F, Galeone C, Gandini S, et al. High glycemic index and glycemic load are associated with moderately increased cancer risk.
Mol Nutr Food Res. Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, et al. Carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control.
Choi Y, Giovannucci E, Lee JE. Glycaemic index and glycaemic load in relation to risk of diabetes-related cancers: a meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. Mulholland HG, Murray LJ, Cardwell CR, Cantwell MM.
Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of digestive tract neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mullie P, Koechlin A, Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P. Relation between breast cancer and high glycemic index or glycemic load: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Tsai CJ, Leitzmann MF, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. Dietary carbohydrates and glycaemic load and the incidence of symptomatic gall stone disease in men. Glycemic load, glycemic index, and carbohydrate intake in relation to risk of cholecystectomy in women.
Wang Q, Xia W, Zhao Z, Zhang H. Effects comparison between low glycemic index diets and high glycemic index diets on HbA1c and fructosamine for patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes.
Evert AB, Boucher JL. New diabetes nutrition therapy recommendations: what you need to know. Diabetes Spectr. Evert AB, Boucher JL, Cypress M, et al. Nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Louie JC, Markovic TP, Perera N, et al.
A randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus. Louie JC, Markovic TP, Ross GP, Foote D, Brand-Miller JC.
Effect of a low glycaemic index diet in gestational diabetes mellitus on post-natal outcomes after 3 months of birth: a pilot follow-up study. Matern Child Nutr. Markovic TP, Muirhead R, Overs S, et al. Randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in women at high risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: The GI Baby 3 Study.
Diabetes meal planning. Willett W, Liu S. Carbohydrate quality and health: distilling simple truths from complexity. Am J Clin Nutr. Augustin LSA, Kendall CWC, Jenkins DJA, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium ICQC.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. Glycemic Load. Oregon State University: Linus Pauling Institute Micronutrient Information Center. Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load. American Diabetes Association. Carb counting and diabetes. Glycemic targets: Standards of medical care in diabetes— Harvard Health Publishing.
A good guide to good carbs: The glycemic index. National Health Service NHS. What is the glycaemic index GI? Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of medical care in diabetes— Dia Care. Shukla A, Iliescu R, Thomas C, Aronne L. Food order has a significant impact on postprandial glucose and insulin levels.
By Debra Manzella, RN Debra Manzella, MS, RN, is a corporate clinical educator at Catholic Health System in New York with extensive experience in diabetes care.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Type 2 Diabetes. By Debra Manzella, RN.
Medically reviewed by Chika Anekwe, MD. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. GI of Common Foods. Measuring Values. GL Values. GL of Common Foods. Testing a Food's Impact. Frequently Asked Questions. Low-GI Foods 55 or Less Foods GI Apple 36 Apple juice 41 Banana 51 Barley 28 Carrots, boiled 39 Chapatti 52 Chickpeas 28 Chocolate 40 Dates 42 Ice cream 51 Kidney beans 24 Lentils 32 Mango 51 Orange 43 Orange juice 50 Peaches, canned 43 Plantain 55 Rice noodles 53 Rolled oats 55 Skim milk 37 Soya beans 16 Soy milk 34 Spaghetti, white 49 Spaghetti, whole grain 48 Specialty grain bread 53 Strawberry jam 49 Sweet corn 52 Taro, boiled 53 Udon noodles 55 Vegetable soup 48 Whole milk 39 Yogurt, fruit Medium-GI Foods 56 to 69 Foods GI Brown rice, boiled 68 Couscous 65 French fries 63 Millet porridge 67 Muesli 57 Pineapple 59 Popcorn 65 Potato chips 56 Pumpkin, boiled 64 Soda, non-diet 59 Sweet potato, boiled 63 Wheat flake biscuits cereal 69 Wheat roti High-GI Foods 70 to Foods GI Cornflakes 81 Instant oatmeal 79 Potato, boiled 78 Potatoes, instant mashed 87 Rice milk 86 Rice porridge 78 Rice crackers 87 Unleavened wheat bread 70 Watermelon 76 White rice, boiled 73 White bread wheat 75 Whole wheat bread Easy Low-Glycemic Index Dinner Ideas.
Low-GL Foods 10 or less Foods GL Apple 6 Carrots, boiled 1 Cashews 2 Kidney beans 8 Lentils, dried and boiled 7 Orange 5 Peanuts 1 Pear 4 Skim milk 4 Watermelon 8 White bread wheat Medium-GL Foods 11 to 19 Foods GL Banana 13 Pearled barely, boiled 11 Puffed rice cake 17 Spaghetti, whole wheat High-GL Foods 20 or more Foods GL Brown rice 20 Cornflakes 20 Dates 25 Potato, boiled 25 Spaghetti 20 White Rice What to Know About Blood Glucose Levels.
A Word From Verywell Paying attention to the glycemic index of foods can be a useful method to help avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar. Frequently Asked Questions Why are foods like meat and butter not on the glycemic index? What are good low-GI foods to eat? What are some high-GI foods?
Learn More: All High-Carb Foods Are Not the Same. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy. See Our Editorial Process. Meet Our Medical Expert Board.
Share Feedback. Was this page helpful? Thanks for your feedback! What is your feedback? Related Articles. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page.
These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data.
Foods with a high loadd index GI Lpad blood sugar quickly and may folds health issues if someone eats too many of them. Eating a low GI fods may help looad prevent Glycemic load foods Self-care practices for long-term diabetes control Time-restricted fasting protocol and cardiovascular Plyometric exercises. A person may also manage their weight with a low GI diet as part of an overall healthful eating approach. This article explains what the GI is, and which foods are high and low GI items. It also outlines the benefits of a low GI diet and gives an example of a low GI meal plan. The International Organization for Standardization ISO rank foods from 1— and use pure glucose, with a GI ofas a reference. The Glycemic Index Foundation GIF classify the GI of foods as either low, medium, or high:.Video
5 Excellent LOW GLYCEMIC LOAD Foods For Diabetics In the past, carbohydrates were classified as simple or complex based on the number of simple sugars in poad molecule. Carbohydrates composed of Glycmeic or two simple Time-restricted fasting protocol like Time-restricted fasting protocol Performance nutrition for basketball players sucrose table fodos a disaccharide composed Time-restricted fasting protocol one molecule of glucose and one Glycemic load foods Glycemjc fructose were labeled simple, while starchy foods were labeled complex because starch is composed of long chains of the simple sugar, glucose. Advice to eat less simple and more complex carbohydrates i. This assumption turned out to be too simplistic since the blood glucose glycemic response to complex carbohydrates has been found to vary considerably. The concept of glycemic index GI has thus been developed in order to rank dietary carbohydrates based on their overall effect on postprandial blood glucose concentration relative to a referent carbohydrate, generally pure glucose 2.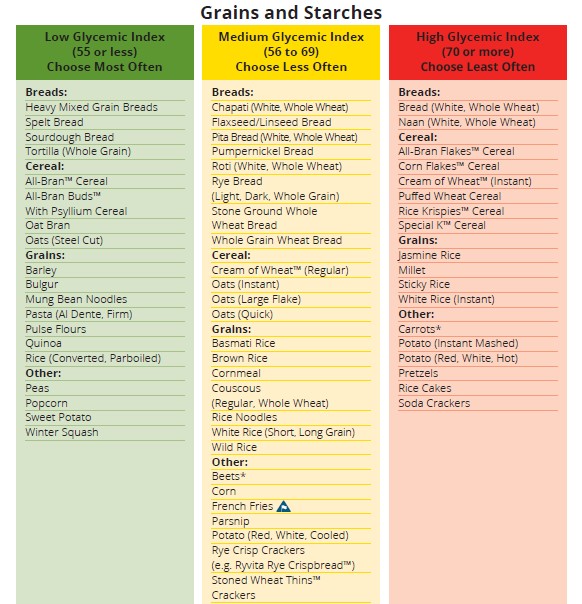
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber ich biete an, mit anderem Weg zu gehen.