Hyperosmolar coma symptoms -
If it's not treated, a diabetic coma can result in death. The idea of a diabetic coma can be scary, but you can take steps to help prevent it. One of the most important is to follow your diabetes treatment plan. Some people, especially those who've had diabetes for a long time, develop a condition known as hypoglycemia unawareness.
That means they don't have warning symptoms that signal a drop in blood sugar. If you have any symptoms of high or low blood sugar, test your blood sugar right away.
Based on the test results, follow your diabetes treatment. If you don't start to feel better quickly, or you start to feel worse, get medical care right away. A diabetic coma is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms of high or low blood sugar and you think you might pass out, call or your local emergency number.
If you're with someone with diabetes who has passed out, call for emergency help. Tell the emergency personnel that the unconscious person has diabetes. Blood sugar that's either too high or too low for too long may cause the following serious health problems, all of which can lead to a diabetic coma.
Diabetic ketoacidosis. If your muscle cells become starved for energy, your body may start breaking down fat for energy. This process forms toxic acids known as ketones. If you have ketones measured in blood or urine and high blood sugar, the condition is called diabetic ketoacidosis.
If it's not treated, it can lead to a diabetic coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis is most common in people who have type 1 diabetes.
But it can also occur in people who have type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes. Diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome. When blood sugar is very high, the extra sugar passes from the blood into the urine. That triggers a process that draws a large amount of fluid from the body.
If it isn't treated, this can lead to life-threatening dehydration and a diabetic coma. Anyone who has diabetes is at risk of a diabetic coma, but the following factors can increase the risk:. Good day-to-day control of your diabetes can help you prevent a diabetic coma.
Keep these tips in mind:. Consider a continuous glucose monitor, especially if you have trouble maintaining stable blood sugar levels or you don't feel symptoms of low blood sugar hypoglycemia unawareness.
Continuous glucose monitors are devices that use a small sensor inserted underneath the skin to track trends in blood sugar levels and send the information to a wireless device, such as a smart phone.
These monitors can alert you when your blood sugar is dangerously low or if it is dropping too fast. But you still need to test your blood sugar levels using a blood glucose meter even if you're using one of these monitors. Continuous glucose monitors are more expensive than other glucose monitoring methods, but they may help you control your glucose better.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. A Book: Guide to the Comatose Patient. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. Symptoms of high blood sugar or low blood sugar usually develop before a diabetic coma.
High blood sugar hyperglycemia If your blood sugar level is too high, you may have: Increased thirst Frequent urination Blurred vision Tiredness or weakness Headache Nausea and vomiting Shortness of breath Stomach pain Fruity breath odor A very dry mouth.
Low blood sugar hypoglycemia If your blood sugar is too low, you may have: Shakiness Anxiety Tiredness or drowsiness Weakness Sweating Hunger A feeling of tingling on your skin Dizziness or lightheadedness Headache Difficulty speaking Blurry vision Confusion Loss of consciousness Some people, especially those who've had diabetes for a long time, develop a condition known as hypoglycemia unawareness.
Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Your brain needs sugar glucose to function. In severe cases, low blood sugar hypoglycemia may cause you to pass out. Low blood sugar can be caused by too much insulin or not enough food.
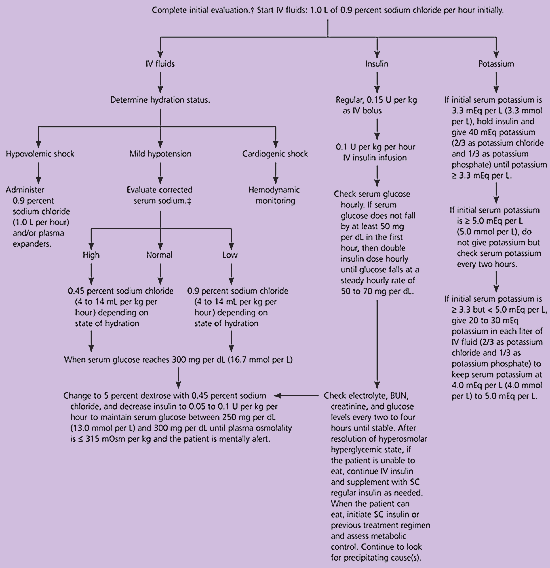
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state HHS is a metabolic complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by severe hyperglycemia, extreme dehydration, hyperosmolar plasma, and altered consciousness. HHS can occur if infections, nonadherence, and certain medications trigger marked glucose elevation, dehydration, and altered consciousness in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Patients have adequate insulin present to prevent ketoacidosis. The fluid deficit can exceed 10 L; treatment is 0. Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
Disclaimer Privacy Terms of use Contact Us Veterinary Manual. IN THIS TOPIC. OTHER TOPICS IN THIS CHAPTER. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State HHS By Erika F. View PATIENT EDUCATION. Symptoms and Signs Diagnosis Treatment Key Points. read more currently. It usually develops after a period of symptomatic hyperglycemia in which fluid intake is inadequate to prevent extreme dehydration due to the hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis.
Acute infections and other medical conditions. Medications that impair glucose tolerance glucocorticoids or increase fluid loss diuretics. Blood glucose level. Serum electrolytes. Blood urea nitrogen BUN. Treatment is 0.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article. Drug Name Select Trade dextrose. All rights reserved. Was This Page Helpful? Yes No. Alcoholic Ketoacidosis. Save for later Page saved! You can go back to this later in your Diabetes and Me Close. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic State HHS. It can develop over a course of weeks through a combination of illness e.
infection and dehydration. HHS symptoms can frequently include: urination, thirst nausea dry skin disorientation and, in later stages, drowsiness and a gradual loss of consciousness.
Diabetes is a condition characterised by high Hyerosmolar glucose sugar Hyperosmolar coma symptoms. Diabetic ketoacidosis typically occurs in people with type 1 diabetes, which yHperosmolar previously known as Hyperosmolar coma symptoms Hyeprosmolar or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus IDDMthough it can occasionally occur in type 2 diabetes. This type of coma is triggered by the build-up of chemicals called ketones. Ketones are strongly acidic and cause the blood to become too acidic. When there is not enough insulin circulating, the body cannot use glucose for energy. Hyperosmolar coma symptoms hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar coma symptoms is a metabolic complication of sypmtoms mellitus Hyperosmopar by Hyperosmolar coma symptoms hyperglycemia, Hypersomolar dehydration, hyperosmolar plasma, and altered consciousness. It cona often occurs in Cooling and replenishing drinks 2 diabetes, often in the setting of physiologic stress. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is diagnosed by severe hyperglycemia and plasma hyperosmolality and absence of significant ketosis. Treatment is IV saline solution and insulin. Complications include coma, seizures, and death. See also Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
die Bemerkenswerte Phrase und ist termingemäß
Es kommt mir nicht ganz heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Ich empfehle Ihnen, in google.com zu suchen