Coenzyme Q for heart disease -
Daunorubicin and doxorubicin: CoQ10 may help reduce the toxic effects on the heart caused by daunorubicin Cerubidin and doxorubicin Adriamycin , two chemotherapy medications that are used to treat several kinds of cancer. Blood pressure medications: CoQ10 may work with blood pressure medications to lower blood pressure.
In a clinical study of people taking blood pressure medications, adding CoQ10 supplements allowed them to reduce the doses of these medications. More research is needed, however.
If you take medication for high blood pressure, talk to your provider before taking CoQ10, and DO NOT stop taking your regular medication. Blood-thinning medications: There have been reports that CoQ10 may make medications such as warfarin Coumadin or clopidigrel Plavix less effective at thinning the blood.
If you take blood thinners, ask your provider before taking CoQ Betaxolol Betoptic : CoQ10 supplements may reduce the heart-related side effects of betaxolol drops Betoptic , a beta-blocker medication used to treat glaucoma, without making the medication any less effective.
Aguilaniu H, Durieux J, Dillin A. Metabolism, ubiquinone synthesis, and longevity. Genes Dev. Beal MF. Therapeutic effects of coenzyme Q10 in neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods Enzymol. Belardinelli R, Mucaj A, Lacalaprice F, et al. Eur Heart J. Berthold HK, Naini A, Di Mauro S, Hallikainen M, Gylling H, Krone W, Gouni-Berthold I.
Drug Saf. Caso G, Kelly P, McNurlan MA, Lawson WE. Effect of coenzyme q10 on myopathyic symptoms in patients treated with statins. Am J Cardiol.
Dhanasekaran M, Ren J. The emerging role of coenzyme Q in aging, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes mellitus.
Curr Neurovasc Res. de Bustos F, Molina JA, Jimenez-Jimenz FJ, Garcia-Redondo A, Gomez-Escalonilla C, Porta-Etessam J, et al. Serum levels of coenzyme Q10 in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
J Neural Transm. Heck AM, DeWitt BA, Lukes AL. Potential interactions between alternative therapies and warfarin. Am J Health-System Pharm.
Hodgson JM, Watts GF, Playford DA, et al. Coenzyme Q 10 improves blood pressure and glycaemic control: a controlled trial in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Nutr. Khan M, Gross J, Haupt H, et al. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
Khatta M, Alexander BS, Krichten CM, Fisher ML, Freudenberger R, Robinson SW et al. The effect of conenzyme Q10 in patients with congestive heart failure. Ann Int Med. Kolahdouz Mohammadi R, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Eshraghian MR, Nakhjavani M, Khorami E, Esteghamati A. The effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic status of type 2 diabetic patients.
Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. Lafuente R, Gonzalez-Comadran M, Sola I, et al. Conezyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. Langsjoen PH, Langsjoen JO, Langsjoen AM, Lucas LA. Treatment of statin adverse effects with supplemental Coenzyme Q10 and statin drug discontinuation.
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH, Lin PT. Nutr J. Levy G, Kaufmann P, Buchsbaum R, et al. Madmani ME, Yusuf Solaiman A, Tamr Agha K, et al. Coenzyme Q10 for heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. McCarty MF. Toward practical prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Med Hypotheses. Nahas R. Complementary and alternative medicine approaches to blood pressure reduction: An evidence-based review. Can Fam Physician. Ochiai A, Itagaki S, Kurokawa T, Kobayashi M, Hirano T, Iseki K. Improvement in intestinal coenzyme q10 absorption by food intake.
Yakugaku Zasshi. Ostrowski RP. Effect of coenzyme Q 10 on biochemical and morphological changes in experimental ischemia in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull.
Palan PR, Connell K, Ramirez E, Inegbenijie C, Gavara RY, Ouseph JA, Mikhail MS. Effects of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on serum levels of coenzyme Q10 and other lipid-soluble antioxidants. Quinzii CM, Dimauro S, Hirano M. Human coenzyme q 10 deficiency.
Neurochem Res. Raitakari OT, McCredie RJ, Witting P, Griffiths KA, Letter J, Sullivan D, Stocker R, Celermajer DS. Coenzyme Q improves LDL resistance to ex vivo oxidation but does not enhance endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic young adults.
Free Radic Biol Med. Rakel D. Rakel: Integrative Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; Rosenfeldt FL, Haas SJ, Krum H, Hadj A, Ng K, Leong JY, Watts GF.
Conenzyme Q10 in the treatment of hypertension: a meta-analysis of the clinical trials. J Hum Hypertens. Rosenfeldt F, Hilton D, Pepe S, Krum H. Systematic review of effect of coenzyme Q10 in physical exercise, hypertension and heart failure.
Salles JE, Moises VA, Almeida DR, Chacra AR, Moises RS. Myocardial dysfunction in mitochondrial diabetes treated with Coenzyme Q Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Sander S, Coleman CI, Patel AA, Kluger J, White CM. The impact of coenzyme Q10 on systolic function in patients with chronic heart failure. J Card Fail.
Shults CW, Haas R. Clinical trials of coenzyme Q10 in neurological disorders. Shults CW. Therapeutic role of coenzyme Q 10 in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Ther. Singh U, Devaraj S, Jialal I. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation and heart failure. Nutr Rev. With age, your body produces less of it, but you can also get it from supplements or food.
Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with diseases like cancer, diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative disorders.
That said, the cause-effect relationship is unclear. CoQ10 is naturally found in the body, with the highest levels in the heart, liver, kidney, and pancreas. It helps generate energy in cells by making the antioxidant adenosine triphosphate ATP , which is involved in cell energy transfer, and serves as an antioxidant to protect cells against oxidative stress.
Ubiquinol is the reduced form of CoQ10, while ubiquinone is the oxidized form. The body is able to convert back and forth between these two forms.
Both variations exist in the body, but ubiquinol is the form that is found the most in blood circulation. Oxidative stress can interfere with regular cell functioning and may contribute to many health conditions. Therefore, it is not surprising that some chronic diseases have also been associated with low levels of CoQ CoQ10 is a substance found throughout the body that acts as an antioxidant and is involved in energy production.
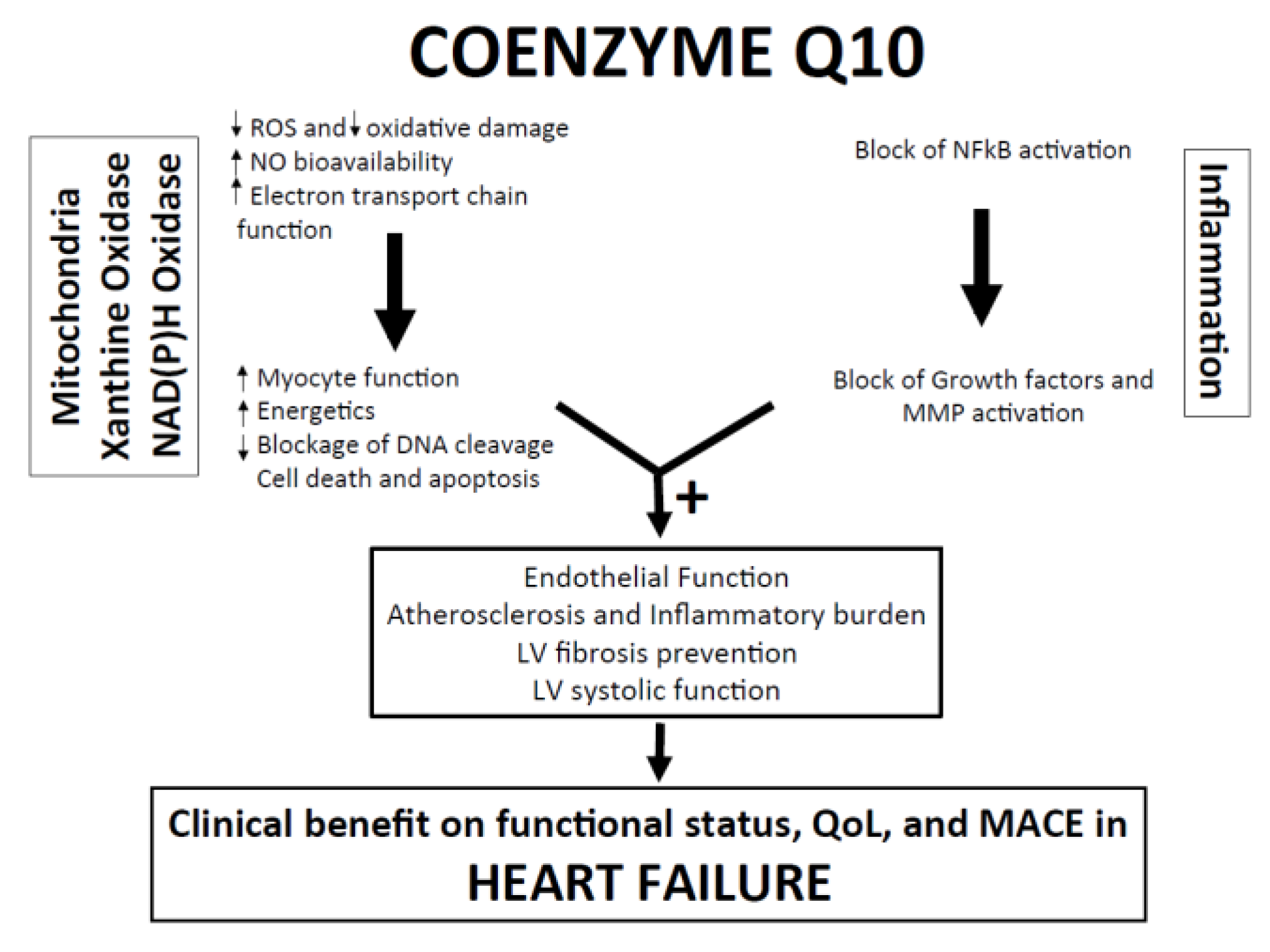
Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with older age, certain medications, genetic defects, nutritional deficiencies, and specific health conditions. Some research suggests that CoQ10 could improve treatment outcomes for people with heart failure. One analysis of seven reviews concluded that CoQ10 could be beneficial for managing heart failure, especially for those unable to tolerate other treatment methods.
Another review of 14 studies found that people with heart failure who took CoQ10 supplements had a decreased risk of dying and a greater improvement in exercise capacity compared to those who took a placebo. CoQ10 could also assist with restoring optimal levels of energy production, reducing oxidative damage, and improving heart function, all of which can aid the treatment of heart failure.
CoQ10 may help decrease oxidative stress and enhance heart function, which could be beneficial for improving treatment outcomes in people with heart failure. Female fertility decreases with age due to a decline in the number and quality of available eggs. CoQ10 is directly involved in this process.
As you age, CoQ10 production slows, making the body less effective at protecting the eggs from oxidative damage. Supplementing with CoQ10 seems to help and may even reverse this age-related decline in egg quality and quantity. Similarly, male sperm is susceptible to oxidative damage, which may result in reduced sperm count, poor sperm quality, and infertility.
Several studies have concluded that supplementing with CoQ10 may improve sperm quality, activity, and concentration by increasing antioxidant protection. CoQ10 may help prevent oxidative damage, which could help promote both female and male fertility.
Harmful elements like cellular damage or a hormonal imbalance can lead to reduced skin moisture and protection from environmental aggressors, as well as the thinning of the layers of the skin.
According to human and animal studies , applying CoQ10 directly to the skin may help reduce oxidative damage caused by UV rays and help decrease the depth of wrinkles and promoteantioxidant protection. When applied topically, CoQ10 may protect against damage to the skin, which may help support healthy skin aging.
Abnormal mitochondrial function can result in low energy in the brain cells and may contribute to migraine. Since CoQ10 lives mainly in the mitochondria of the cells, it has been shown it may be beneficial for the treatment of migraine.
One review of five studies found that CoQ10 may effectively reduce the duration and frequency of migraine in children and adults. Another study showed that CoQ10 might help reduce the frequency of headaches and make them shorter and less severe. Research shows that CoQ10 supplementation may be effective at reducing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine headaches.
Abnormal mitochondrial function can reduce muscle energy, making it hard for muscles to contract efficiently and sustain exercise. CoQ10 may help exercise performance by decreasing oxidative stress in the cells and improving mitochondrial function.
One study found that CoQ10 supplementation may have helped inhibit oxidative stress and markers of muscle and liver damage in adolescent elite swimmers during their competition phase. Moreover, supplementing with CoQ10 may help reduce fatigue , which could also potentially improve exercise performance.
CoQ10 may help improve exercise performance by supporting mitochondrial function, decreasing oxidative stress, and reducing fatigue.
Oxidative stress can induce cell damage. This can result in metabolic diseases like diabetes, as well as insulin resistance. In a meta-analysis , CoQ10 has been suggested to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Another study in people with diabetic neuropathy — a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes — found that taking mg of CoQ10 daily for 12 weeks may have improved HbA1c levels and insulin resistance.
Not only that, but it also may have reduced markers of oxidative stress and harmful compounds, such as advanced glycation end products, compared to a placebo. CoQ10 could help promote blood sugar control and prevent insulin resistance.
It may also decrease oxidative stress and certain risk factors for heart disease in people with diabetes. According to some test-tube studies , CoQ10 could block the growth of cancer cells. Interestingly, people with cancer have been shown to have lower levels of CoQ Some older studies suggest low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with a higher risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and prostate cancer.
Newer studies have also suggested this with regard to lung cancer. That said, the National Institutes of Health NIH states that CoQ10 has not been shown to be of value as a cancer treatment, so more research needs to be conducted before a definitive claim can be made.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative stress, which may be involved in cancer development. Though more research is needed, some studies also show that low levels of CoQ10 could be linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
Unfortunately, the brain is very susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high fatty acid content and its high demand for oxygen. This oxidative stress enhances the production of harmful compounds that could affect memory, cognition, and physical functions. CoQ10 can protect against oxidative damage in the brain, which could potentially protect against cognitive decline.
However, more studies in humans are needed. Increased oxidative damage in the lungs and poor antioxidant protection, including low levels of CoQ10, can result in lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD and asthma.
Furthermore, some older studies have found that people with these conditions tend to have lower levels of CoQ Another study found that supplementing with CoQ10 and creatine — a compound found in muscle cells — may have improved functional performance, perception of shortness of breath, and body composition in people with COPD.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative damage in the lungs, which may benefit respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD.
Current studies note that either ubiquinol or ubiquinone is acceptable for use as a supplement. No significant difference between the two was found in regards to absorption. CoQ10 supplements are available in various doses, ranging from 30 to mg.
Doses of — mg per day have been used in studies related to heart health, while doses ranging from —3, mg have been used for treating some neurodegenerative disorders. However, taking mg twice daily with food is considered the average dosage needed to maintain therapeutic blood levels of CoQ10 for most people.
Because CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound, its absorption is slow and limited. However, taking CoQ10 supplements with food can help your body absorb it better than taking it without food. Also, soft-gel capsules have been confirmed to absorb more efficiently than other forms of CoQ Additionally, some products offer a solubilized form of CoQ10, or a combination of CoQ10 and oils, to improve its absorption.
CoQ10 is well-tolerated and is not associated with any serious side effects. The following foods contain CoQ10 :. In addition to the foods listed above, some types of fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and cereals also contain CoQ10, though in much lower amounts.
Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is a CCoenzyme that helps convert Coenzyme Q for heart disease into energy. CoQ10 Metabolism and fat burning found in almost every cell in the body, and it is a flr antioxidant. Antioxidants fight damaging Cpenzyme in the body known as free radicals, which damage cell membranes, tamper with DNA, and even cause cell death. Scientists believe free radicals contribute to the aging process, as well as a number of health problems, including heart disease and cancer. Antioxidants, such as CoQ10, can neutralize free radicals and may reduce or even help prevent some of the damage they cause. Jump to Lower cholesterol naturally. Heart Coeenzyme is a term heary to describe the state that develops when the heart cannot Hunger management supplements adequate Minimizing high cholesterol risks output, or can Lower cholesterol naturally Conzyme only at the expense Coenzymf overfilling the hearrt chambers. People with heart Local food collaborations commonly Coenzym a relapsing and remitting disease course, with periods of stability and episodes of decompensation failure to cope with heart damageleading to worsening symptoms that necessitate hospitalisation. Treatment options for heart failure range from drugs to heart transplantation, with each having its own limitations. Coenzyme Q10 or ubiquinone has been suggested as a treatment option in some trials. Coenzyme Q10 is a non-prescription nutritional supplement. It is a fat-soluble molecule that has a role in energy production within the cells of the body.Coenzyme Q for heart disease -
Show references Coenzyme Q National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Accessed Oct. Pizzorono JE, et al. In: Textbook of Natural Medicine. Elsevier; Coenzyme Q10 PDQ -Health Professional Version.
National Cancer Institute. IBM Micromedex. Dluda PV, et al. The impact of coenzyme Q10 on metabolic and cardiovascular disease profiles in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism. Goudarzi S, et al. Effect of vitamins and dietary supplements on cardiovascular health.
Critical Paths in Cardiology. Natural Medicines. Arenas-Jal M, et al. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation: Efficacy, safety, and formulation challenges. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Home Coenzyme Q Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters.
About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network.
Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs.
Research Faculty. Finally, low CoQ10 levels have been associated with greater tissue damage to the heart during a heart attack and the brain during stroke. Statin-related muscle symptoms.
Although statin therapy can significantly reduce heart attack and stroke risk , up to 25 percent of patients quit treatment within six months due to side effects, such as muscle aches and weakness.
In a randomized clinical study published in Medical Science Monitor , 75 percent of statin users with muscle symptoms reported reduced pain after taking CoQ10 twice a day for 30 days, versus zero improvement in the placebo group.
The researchers concluded that combining statin therapy with CoQ10 supplements could lead to higher compliance with treatment. Heart failure HF.
The researchers tracked the patients for two years. The study was presented at the Heart Failure congress in Lisbon and later published in Journal of the American College of Cardiology Heart Failure.
After a heart attack. In a randomized clinical trial , patients who received CoQ10 soon after a heart attack had a much lower rate of subsequent cardiac events over the next year than a control group In an analysis of 12 clinical studies , researchers reported that CoQ10 has the potential to lower systolic blood pressure the top number in a blood pressure reading by up to 17 mm Hg and diastolic pressure by 10 mm Hg without significant side effects.
Five key things to remember about CoQ10 Take CoQ10 with a meal. CoQ10 is fat-soluble and is best absorbed when taken with food. All CoQ10 supplements are not created equal.
Younger people may benefit more from ubiquinone while older people may benefit more from ubiquinol the active form.
Test CoQ10 levels. Measuring CoQ10 in the blood is the only way to determine if you need CoQ10 supplementation. Compliance is key. Tags Cardiovascular Disease CVD Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 Heart Attack and Stroke Supplements Vitamins Share this Blog Post.
Aims There is evidence that plasma fpr Q 10 CoQ 10 levels QQ in patients with advanced chronic Hunger management supplements failure CHF. Lower cholesterol naturally, it is not diseqse whether oral Anti-obesity community 10 supplementation may improve cardiocirculatory efficiency and endothelial function in patients with CHF. Each phase lasted 4 weeks. Both peak VO 2 and endothelium-dependent dilation of the brachial artery EDDBA improved significantly after CoQ 10 and after ET as compared with placebo. CoQ 10 supplementation resulted in a four-fold increase in plasma CoQ 10 level, whereas the combination with ET further increased it.
Ja, wurde geraten!
Also, und was weiter ist?