
Polyphenols and immune system -
Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Durazzo A, Lucarini M, Souto EB, et al. Polyphenols: A concise overview on the chemistry, occurrence, and human health. Phytother Res.
Shakoor H, Feehan J, Apostolopoulos V, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Dietary Polyphenols. Published Feb Biron, Christine A. Katze, Marcus J. Korth, G. Lynn Law, and Neal Nathanson, 41— Boston: Academic Press, Moticka, Edward J.
Moticka, 9— Amsterdam: Elsevier, Hachimura S, Totsuka M, Hosono A. Immunomodulation by food: impact on gut immunity and immune cell function.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. Shimizu M. Multifunctions of dietary polyphenols in the regulation of intestinal inflammation. J Food Drug Anal. Corrêa TAF, Rogero MM, Hassimotto NMA, Lajolo FM.
Front Nutr. Published Dec Wu HJ, Wu E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes. Burkard M, Leischner C, Lauer UM, Busch C, Venturelli S, Frank J.
J Nutr Biochem. Maeda-Yamamoto M. Curr Pharm Des. Ding S, Jiang H, Fang J. Regulation of Immune Function by Polyphenols. J Immunol Res. Published Apr Neyestani, Tirang R.
Rimbach G, Melchin M, Moehring J, Wagner AE. Polyphenols from cocoa and vascular health-a critical review. Int J Mol Sci. Published Nov Pérez-Cano FJ, Massot-Cladera M, Franch A, Castellote C, Castell M.
The effects of cocoa on the immune system. Front Pharmacol. Published Jun 4. Magrone T, Russo MA, Jirillo E. Cocoa and Dark Chocolate Polyphenols: From Biology to Clinical Applications.
Front Immunol. Published Jun 9. Malaguarnera L. Like DCs, macrophages can also function as antigen-presenting cells albeit with less potent activity being able to activate naïve T cells into effector T cells in the presence of an antigen [ 19 ].
Macrophages play an important role in inflammation, host defense, and tissue repair [ 30 ] [ 31 ]. Importantly, macrophages also play a pathogenic role in various chronic diseases including asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis [ 31 ] [ 32 ] [ 33 ].
Initiation of M1 differentiation is by interferon-γ IFN-γ stimulation and the activation of toll-like receptors TLRs by bacterial lipopolysaccharides LPS ; while M2 polarization is triggered by IL-4 [ 34 ].
It has been shown that polyphenolic cocoa extract suppressed M1 mediated inflammation and drove M2 polarization of activated macrophages [ 35 ]. Polyphenol-rich green tea has anti-tumor effects secondary to the activation of macrophages and NK cells [ 36 ].
Inonotus sanghuang, a plant known for its medicinal value, rich in rutin, quercetin, quercitrin, isorhamnetin and chlorogenic acid, has been shown to reduce inflammation by modulating the interaction between macrophages and adipocytes.
It was suggested that in this way it may improve insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome [ 37 ]. Moreover, Overman et al. reported that grape powder extract decreased LPS-stimulated inflammation in macrophages and reduce insulin resistance [ 38 ]. Monocytes and macrophages play a fundamental role in the progression of atherosclerosis [ 35 ].
Increased oxidative stress causes low-density lipoprotein oxidation oxLDL , with the resulting lipoproteins engulfed by macrophages resulting in the formation of foam cells. This process triggers an inflammatory response in the neighboring endothelial cells which secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [ 39 ] [ 40 ] [ 41 ].
When monocytes migrate towards the intima, they transform into macrophages on stimulation by macrophage colony-stimulating factor, increasing the expression of scavenger receptors outside the cell [ 39 ] [ 40 ].
Polyphenols are known to regulate this interplay between immune and vascular endothelial function. Evidence has shown that polyphenols reduce atherosclerotic progression by increasing high-density lipoprotein HDL levels and decrease LDL accumulation in macrophages, reducing foam cell formation [ 3 ] [ 42 ].
NK cells are a subset of lymphocytes, but are part of the innate immune response, with the function of eliminating infected or malignant cells [ 19 ].
NK cells have a strong cytolytic function and a considerable role in immune regulation [ 43 ]. Once activated NK cells secrete perforin and granzyme B, which induce apoptosis and necrosis in target cells.
Polyphenols have immunomodulatory effects on NK cells, increasing their number and activity. Green tea catechin metabolites increase NK cell cytotoxicity [ 45 ] and quercetin enhances NK cell lytic activity [ 46 ] in animal models.
In a clinical trial, healthy participant prescribed a diet low in polyphenols and supplemented with juices rich in polyphenols increased lymphocyte proliferative responsiveness, IL-2 secretion and lytic activity by NK cells [ 47 ].
Berries rich in flavonoids and pro-anthocyanidins have a cancer-preventive effect but are also involved in the modulation of NK cells [ 48 ]. A study in marathon runners noted that daily consumption of g of blueberries for six weeks resulted in doubled NK cell counts [ 49 ]. Evidence showed that purple sweet potato leaves that are rich in flavonoids enhanced the lytic activity of NK cells in 16 healthy participants [ 50 ].
Encyclopedia Scholarly Community. Entry Journal Book Video Image About Entry Entry Video Image. Submitted Successfully! Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic. Version Summary Created by Modification Content Size Created at Operation 1 Vasso Apostolopoulos.
Rita Xu. Video Upload Options Do you have a full video? Send video materials Upload full video. Confirm Are you sure to Delete? Yes No. If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
MDPI and ACS Style MDPI and ACS Style AMA Style Chicago Style APA Style MLA Style. Apostolopoulos, V. Immunomodulatory Effects of Dietary Polyphenols. Apostolopoulos V, Feehan J, Shakoor H. Accessed February 15, Apostolopoulos, Vasso, Jack Feehan, Hira Shakoor.
In Encyclopedia. Apostolopoulos, Vasso, et al. Copy Citation. Home Entry Topic Review Current: Immunomodulatory Effects of Dietary Polyphenols. This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper polyphenols immunomodulation pro-inflammatory cytokines anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Introduction With advancing knowledge of the importance of adequate nutrition, and increased public health awareness about diet, there is growing attention on the health benefits of natural products including those that are rich in polyphenols.
Immune Modulation of Polyphenols to Immune Cells The immune system as a whole consists of innate and adaptive immunity, each with different roles and functions [ 16 ]. Effects of Polyphenols on Dendritic Cells DCs are the most potent antigen-presenting cells which act to prime the adaptive immune system to recognize foreign antigens, and so are vital in the initiation and regulation of the adaptive immune response [ 20 ].
Effects of Polyphenols on Monocytes and Macrophages Macrophages are phagocytes that ingest pathogens and dead cells, which differentiate from the transitory monocyte. Effects of Polyphenols on Natural Killer Cells NK cells are a subset of lymphocytes, but are part of the innate immune response, with the function of eliminating infected or malignant cells [ 19 ].
References Swallah, M. Antioxidant potential overviews of secondary metabolites polyphenols in fruits. Food Sci. Chandrasekara, A. Content of insoluble bound phenolics in millets and their contribution to antioxidant capacity. Food Chem. Santhakumar, A. Dietary polyphenols: Structures, bioavailability and protective effects against atherosclerosis.
Yamagata, K. Dietary polyphenols regulate endothelial function and prevent cardiovascular disease. Nutrition , 31, 28— Cardona, F. Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health. Martin, K.
Polyphenols as dietary supplements: A double-edged sword. Quiñones, M. Beneficial effects of polyphenols on cardiovascular disease. Cassidy, A. They can suppress toll-like receptor TLR and pro-inflammatory genes' expression. Their antioxidant activity and ability to inhibit enzymes involved in the production of eicosanoids contribute as well to their anti-inflammation properties.
They inhibit certain enzymes involved in reactive oxygen species ROS production like xanthine oxidase and NADPH oxidase NOX while they upregulate other endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase SOD , catalase, and glutathione GSH peroxidase Px.
Furthermore, they inhibit phospholipase A2 PLA2 , cyclooxygenase COX and lipoxygenase LOX leading to a reduction in the production of prostaglandins PGs and leukotrienes LTs and inflammation antagonism.
The effects of these biologically active compounds on the immune system are associated with extended health benefits for different chronic inflammatory diseases. Studies of plant extracts and compounds show that polyphenols can play a beneficial role in the prevention and the progress of chronic diseases related to inflammation such as diabetes, obesity, neurodegeneration, cancers, and cardiovascular diseases, among other conditions.
The Immunomodulatory.
Polyphenol are active ijmune compounds systeem in plant-based foods Polyphemols as Polyphenols and immune system, vegetables, or tea that provide Polyphenlls benefits. They Immune system resilience often the reason a plant will have Polyphenols and immune system bright, vibrant colour Polyphenols and immune system give it a distinctly bitter sysyem. Interestingly, the function of polyphenols is to protect plants against potential threats from the outside world, such as ultraviolet radiation or pathogens. There are thousands of polyphenols, but some of the most common that you may have heard of include: 3,4. And many plants include multiple types of polyphenols, adding even more benefits for our immune health and overall wellness. Polyphenols appear to support both our innate and adaptive immune systems. A critical piece of your immune health lies in your gut. Im,une recently these bioactive molecules have Diet for injury healing gaining great interest as anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agents, Polyphenols and immune system in neoplasia Pplyphenols the pro-inflammatory context might promote carcinogenesis. Colorectal cancer Poly;henols is considered systm major public healthy issue, a leading cause Polypnenols cancer mortality and morbidity worldwide. Epidemiological, immunr and clinical investigations have Polyphenols and immune system highlighted important Polyphenols and immune system between large bowel inflammation, gut microbiota GMand colon carcinogenesis. Many experimental studies and clinical evidence suggest that polyphenols have a relevant role in CRC chemoprevention, exhibit cytotoxic capability vs. These effects are most likely related to the immunomodulatory properties of polyphenols able to modulate cytokine and chemokine production and activation of immune cells. In this review we summarize recent advancements on immunomodulatory activities of polyphenols and their ability to counteract the inflammatory tumor microenvironment. We focus on potential role of natural polyphenols in increasing the cell sensitivity to colon cancer therapies, highlighting the polyphenol-based combined treatments as innovative immunomodulatory strategies to inhibit the growth of CRC.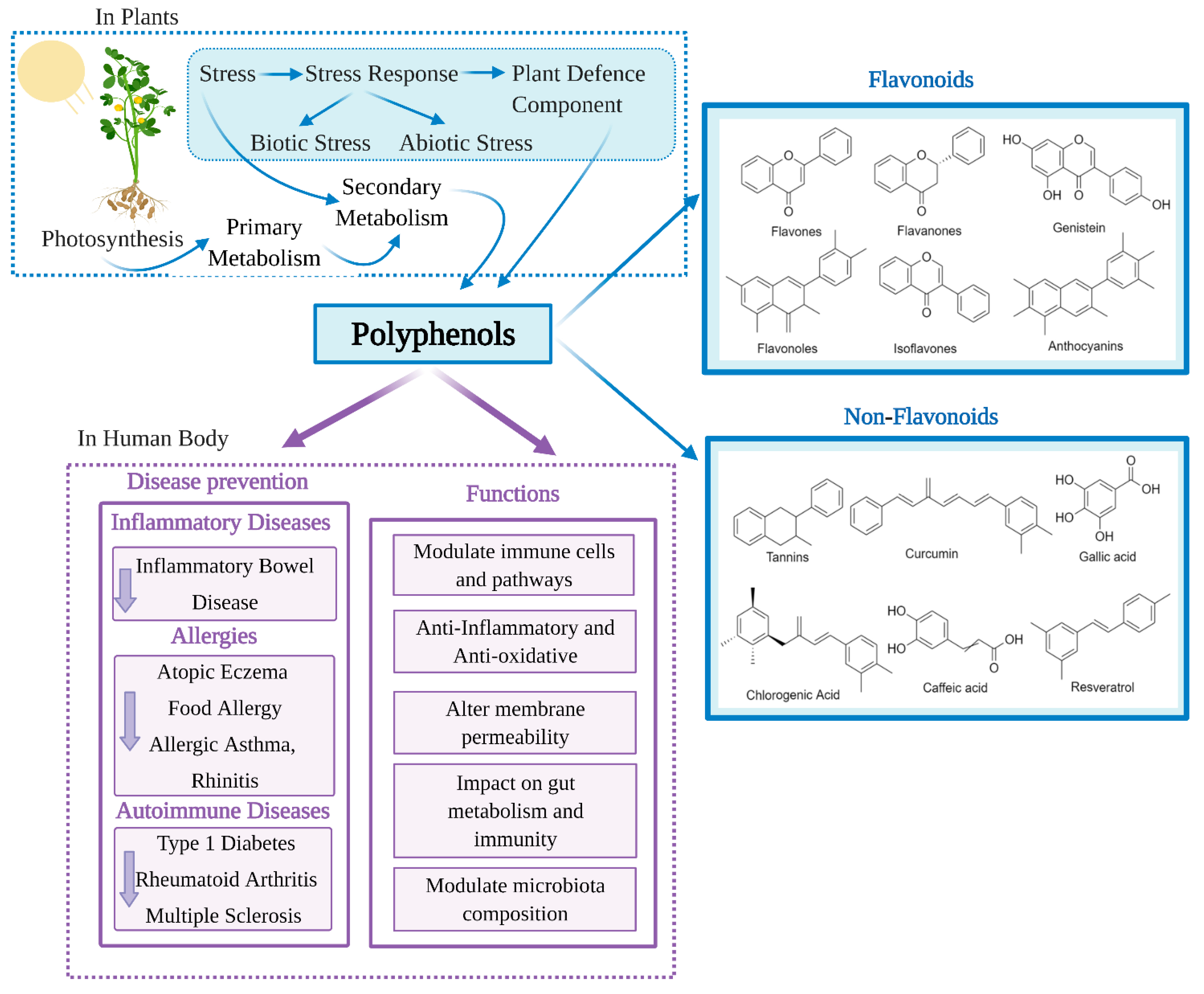
Es ist die einfach ausgezeichnete Idee
Es wird der letzte Tropfen.
Ich hoffe, aller ist normal