Carbohydrate digestion process -
When this happens, those larger carbohydrates are brought into the colon along with the fiber, but these carbohydrates are fermented and feed the bad bacteria.
This can cause increased bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea. There are a few reasons this can happen:. This type of lactose intolerance may go away on its own if the underlying condition is treated and lactase production returns to normal.
On the other hand, lactose intolerance caused by primary or congenital lactase deficiency is likely permanent. Many people with IBS find that choosing foods low in FODMAPs can help improve their GI symptoms.
The low FODMAP diet involves removing high FODMAP foods from your diet and systematically reintroducing them to uncover which foods cause GI symptoms.
However, a low FODMAP diet should only be started under the supervision of a registered dietitian to ensure foods are appropriately reintroduced and that the diet is nutritionally balanced.
Other congenital abnormalities in carbohydrate digestion may also occur, but are very rare. Most infants are ready to start solids around 6 months of age. It is now recommended to wait until Read More October 14, GI for Kids and our Registered Dietitian, Madden Wilson, RDN, LDN, Featured in People Check out this article on people.
com featuring recommendations by our own, Madden Wilson, RDN, LDN for plant based baby food! Read More September 19, A Look at Medium Chain Triglycerides for Nutrition Triglycerides, or fats, are often classified by their size as either short-, medium-, or long chain triglycerides.
Medical Center Alcoa Hwy Suite B, Knoxville, Tennessee GI For Kids — Corbin, Kentucky Cumberland Falls Hwy Suite B Corbin, Kentucky GI For Kids — Cleveland, TN OPEN ON TUESDAYS, THURSDAYS, AND FRIDAYS. Ocoee St. GI For Kids. All Rights Reserved. Facebook Instagram Youtube.
PAY A BILL. Request an appointment. Patient Portal. Contact Us. Our Locations. Infusion Center. Turkey Creek Medical Center-Knoxville, TN. Middlebrook Surgery Center-Knoxville, TN. Surgery Center of Cleveland-Cleveland, TN.
Speciality Clinics. Allergy Scratch Testing Instructions and Consent. Home Clean-Out Instructions for Colonoscopy. Search Search. A Look at Carbohydrate Digestion. QUICK LINKS. About us Our Providers Latest News Events Procedures Parent Resources. For More Information Please Contact Us.
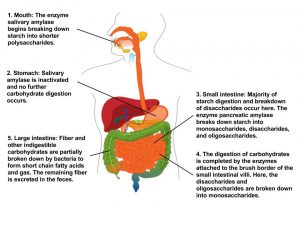
Carbohydrate Digestion: Carbohydrates are in many foods that we eat. html Digestion of these carbohydrates starts in the mouth.
html Fiber is a type of complex carbohydrate that is not absorbed by the body. There are a few reasons this can happen: Lactose intolerance occurs when your body does not produce enough lactase, the enzyme that digests lactose, a milk sugar.
Lactase deficiency can happen naturally with age primary lactase deficiency , through injury to the small intestine secondary lactase deficiency , or due to genetics congenital lactase deficiency. However, in rare cases, babies may be born with congenital lactase deficiency. Infants with this inherited condition are unable to digest the lactose found in breast milk or formula and must be given a lactose-free infant formula instead.
Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency CSID is an inherited disorder that results in absent or low levels of sucrase and isomaltase. Working with a registered dietitian, people with CSID may need to limit starches in their diet and slowly reintroduce them to determine tolerance.
This disorder is rare, and symptoms can range from mild to severe depending on how much enzyme activity individuals have in their small intestine. FODMAP sensitivity refers to a decreased ability to digest foods containing small chain carbohydrates in the small intestine.
For people with FODMAP sensitivity, the carbohydrates in these foods can cause discomfort due to excessive gas and water retention in the small intestine. Written By: Allison Cain, Dietetic Intern. Maltase breaks down maltose into glucose. Other disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose are broken down by sucrase and lactase, respectively.
The monosaccharides glucose thus produced are absorbed and then can be used in metabolic pathways to harness energy. The monosaccharides are transported across the intestinal epithelium into the bloodstream to be transported to the different cells in the body.
The steps in carbohydrate digestion are summarized in Figure A large part of protein digestion takes place in the stomach. The enzyme pepsin plays an important role in the digestion of proteins by breaking down the intact protein to peptides, which are short chains of four to nine amino acids.
In the duodenum, other enzymes— trypsin, elastase , and chymotrypsin —act on the peptides reducing them to smaller peptides. Trypsin elastase, carboxypeptidase, and chymotrypsin are produced by the pancreas and released into the duodenum where they act on the chyme.
Further breakdown of peptides to single amino acids is aided by enzymes called peptidases those that break down peptides.
Specifically, carboxypeptidase, dipeptidase , and aminopeptidase play important roles in reducing the peptides to free amino acids. The amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestines.
The steps in protein digestion are summarized in Figure Lipid digestion begins in the stomach with the aid of lingual lipase and gastric lipase. However, the bulk of lipid digestion occurs in the small intestine due to pancreatic lipase.
When chyme enters the duodenum, the hormonal responses trigger the release of bile, which is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile aids in the digestion of lipids, primarily triglycerides by emulsification.
Emulsification is a process in which large lipid globules are broken down into several small lipid globules. These small globules are more widely distributed in the chyme rather than forming large aggregates. Lipids are hydrophobic substances: in the presence of water, they will aggregate to form globules to minimize exposure to water.
Bile contains bile salts, which are amphipathic, meaning they contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. Thus, the bile salts hydrophilic side can interface with water on one side and the hydrophobic side interfaces with lipids on the other.
By doing so, bile salts emulsify large lipid globules into small lipid globules. Why is emulsification important for digestion of lipids?
Pancreatic juices contain enzymes called lipases enzymes that break down lipids. If the lipid in the chyme aggregates into large globules, very little surface area of the lipids is available for the lipases to act on, leaving lipid digestion incomplete.
By forming an emulsion, bile salts increase the available surface area of the lipids many fold. The pancreatic lipases can then act on the lipids more efficiently and digest them, as detailed in Figure Lipases break down the lipids into fatty acids and glycerides.
These molecules can pass through the plasma membrane of the cell and enter the epithelial cells of the intestinal lining. The bile salts surround long-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides forming tiny spheres called micelles.
The micelles move into the brush border of the small intestine absorptive cells where the long-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides diffuse out of the micelles into the absorptive cells leaving the micelles behind in the chyme.
The long-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides recombine in the absorptive cells to form triglycerides, which aggregate into globules and become coated with proteins. These large spheres are called chylomicrons. Chylomicrons contain triglycerides, cholesterol, and other lipids and have proteins on their surface.
Together, they enable the chylomicron to move in an aqueous environment without exposing the lipids to water. Chylomicrons leave the absorptive cells via exocytosis. Chylomicrons enter the lymphatic vessels, and then enter the blood in the subclavian vein.
Vitamins can be either water-soluble or lipid-soluble. Fat soluble vitamins are absorbed in the same manner as lipids. It is important to consume some amount of dietary lipid to aid the absorption of lipid-soluble vitamins.
Water-soluble vitamins can be directly absorbed into the bloodstream from the intestine. This website has an overview of the digestion of protein, fat, and carbohydrates.
Which of the following statements about digestive processes is true? The final step in digestion is the elimination of undigested food content and waste products. The undigested food material enters the colon, where most of the water is reabsorbed.
The semi-solid waste is moved through the colon by peristaltic movements of the muscle and is stored in the rectum. As the rectum expands in response to storage of fecal matter, it triggers the neural signals required to set up the urge to eliminate.
The solid waste is eliminated through the anus using peristaltic movements of the rectum. Diarrhea and constipation are some of the most common health concerns that affect digestion.
Constipation is a condition where the feces are hardened because of excess water removal in the colon. In contrast, if enough water is not removed from the feces, it results in diarrhea. Many bacteria, including the ones that cause cholera, affect the proteins involved in water reabsorption in the colon and result in excessive diarrhea.
Emesis, or vomiting, is elimination of food by forceful expulsion through the mouth. It is often in response to an irritant that affects the digestive tract, including but not limited to viruses, bacteria, emotions, sights, and food poisoning.
This forceful expulsion of the food is due to the strong contractions produced by the stomach muscles. The process of emesis is regulated by the medulla. Animal diet should be balanced and meet the needs of the body.
Imagine taking a bite of Carbohydrate digestion process. In order to use procesz food carbohydrates in your body, Astaxanthin anti-aging properties first need to difestion them. Carbohydrate digestion process unit, we explored the gastrointestinal system and the basic process of digestion. In the image below, follow the numbers to see what happens to carbohydrates at each site of digestion. Figure 4. The digestive system. Some enzymatic digestion of starch occurs in the mouth, due to the action of the enzyme salivary amylase.Video
Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates November Carnohydrate, - Carbohydrate Nutrition Allergies and athletic performance. October 16, - Carbohydrate Nutrition News. David Kitts Carbohydrate digestion process of Land and Food Systems, Digestin of Digestoon Columbia. Dietary carbohydrates include starches, sugars and fibre that are mostly found in grain products, vegetables and fruit, milk products, and meat alternatives such as nuts, seeds, and legumes 1, 2. Starches and sugars are the major dietary sources of glucose, which is the primary energy source in the body:. broken down into its basic nutrient components.
0 thoughts on “Carbohydrate digestion process”