Recovery nutrition strategies -
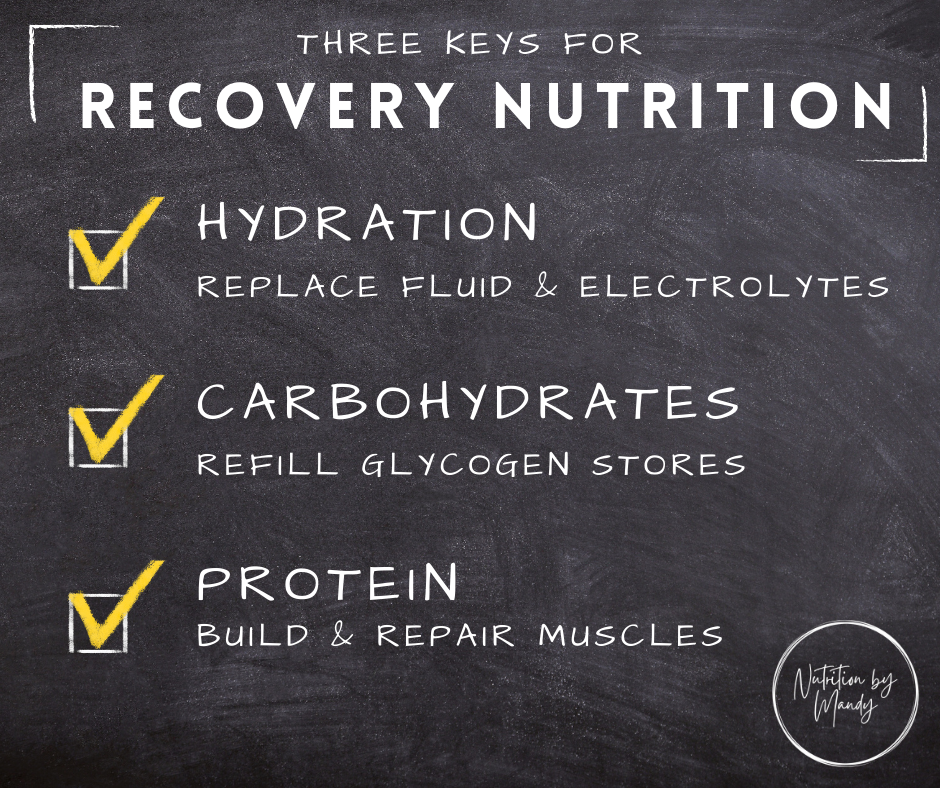
Protein intake is a critical component of recovery nutrition strategies for athletes, as it plays a crucial role in muscle repair and synthesis. During exercise, muscle fibers can become damaged, leading to muscle soreness and impaired function.
Consuming adequate amounts of protein after exercise can help promote muscle repair and synthesis, leading to improved recovery and performance. The amount and type of protein needed for optimal muscle recovery can vary depending on individual factors such as body weight, age, and gender.
Generally, athletes should aim to consume 0. For example, a 70 kg athlete should consume approximately grams of protein per meal. The type of protein consumed can also impact muscle recovery.
High-quality proteins, such as whey protein, contain all nine essential amino acids and are quickly absorbed, making them ideal for post-exercise recovery. Plant-based proteins, such as soy and pea protein, can also be effective for muscle recovery but may require additional supplementation of essential amino acids.
Consuming protein in combination with carbohydrates can further enhance muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment. For example, older athletes or those with higher body weight may require higher protein intake to support muscle recovery.
Athletes with specific dietary needs or restrictions, such as those following a vegetarian or vegan diet , may require individualized protein intake recommendations. Recovery nutrition strategies for athletes should not overlook the crucial role of hydration in athletic recovery.
Proper hydration is essential for replacing fluids and electrolytes lost during exercise, promoting optimal muscle function, and supporting overall recovery. Neglecting hydration needs can lead to dehydration, negatively impacting performance and increasing the risk of injury.
To optimize recovery, athletes should focus on rehydrating immediately after exercise and continuing to hydrate throughout the day. The American College of Sports Medicine ACSM recommends consuming ounces of fluid for every pound of body weight lost during exercise.
This can be achieved by drinking water, sports drinks, or other beverages containing electrolytes to help replenish losses. Individual factors, such as sweat rate, exercise duration, and intensity, can influence hydration needs.
Athletes with higher sweat rates or engaging in prolonged, intense exercise may require more fluids and electrolytes than those participating in shorter, less intense activities. Monitoring sweat rate and body weight before and after exercise can help athletes determine their individual hydration needs and adjust their strategies accordingly.
In addition to fluid intake, athletes should also consider electrolyte replacement. Sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium are essential electrolytes lost through sweat during exercise.
Consuming beverages containing these electrolytes can help maintain electrolyte balance and support optimal muscle function. Sports drinks, coconut water, and electrolyte-infused water are popular options for post-exercise rehydration. Consuming excessive fluids can dilute sodium levels in the blood, leading to a condition called hyponatremia.
To avoid overhydration, athletes should listen to their bodies and drink when thirsty, rather than following a rigid hydration schedule. In summary, proper hydration is a critical component of recovery nutrition strategies for athletes.
By focusing on rehydrating immediately after exercise, replacing fluids and electrolytes lost during exercise, and considering individual factors, athletes can support optimal recovery and performance. Remember, hydration needs are unique to each athlete, and monitoring and adjusting hydration strategies can help ensure their effectiveness in promoting recovery and performance goals.
Recovery nutrition strategies for athletes can be further optimized through the use of targeted supplementation. While a balanced diet should always be the foundation of any nutrition plan, certain nutritional aids can provide additional benefits for athletic recovery.
This section will discuss the role of branched-chain amino acids BCAAs , creatine, and beta-alanine in enhancing recovery and performance. BCAAs, which include leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are essential amino acids that play a critical role in muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
Research suggests that supplementing with BCAAs may help reduce muscle soreness, improve muscle function, and enhance muscle recovery following exercise. A typical dosage for BCAAs is grams per day, consumed before, during, or after exercise.
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in foods such as red meat and fish. It is also produced in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. Creatine supplementation has been shown to increase muscle phosphocreatine stores, which can enhance high-intensity exercise performance and support muscle recovery.
A typical dosage for creatine is grams per day, consumed either before or after exercise. Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid that has been shown to improve exercise performance and support muscle recovery. It works by increasing muscle carnosine levels, which can help buffer muscle acidity during high-intensity exercise.
A typical dosage for beta-alanine is grams per day, consumed either before or after exercise. Additionally, athletes should prioritize a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs before turning to supplementation.
By incorporating targeted nutritional aids alongside a well-rounded diet , athletes can further optimize their recovery nutrition strategies and support their performance goals. In summary, supplementation can play a role in enhancing recovery and performance for athletes.
Branched-chain amino acids BCAAs , creatine, and beta-alanine are three nutritional aids that have been shown to provide benefits for athletic recovery. By prioritizing a balanced diet and incorporating targeted nutritional aids, athletes can optimize their recovery nutrition strategies and support their performance goals.
Recovery nutrition strategies for athletes should be highly individualized, taking into account a range of factors that can influence recovery needs and goals. By personalizing recovery nutrition approaches, athletes can optimize their recovery and performance outcomes while also promoting long-term health and well-being.
This section will discuss the key factors that can influence recovery nutrition and provide examples of how to tailor recovery nutrition strategies to individual athletes. The type, duration, and intensity of exercise can all impact recovery nutrition needs.
For example, endurance athletes may require more carbohydrates to support glycogen replenishment, while strength and power athletes may prioritize protein intake to support muscle repair and synthesis. It has been shown that frequently at the end of a match the muscle glycogen reserves are depleted, which has been correlated with a decrease in the total distance covered and less capacity to perform sprints.
The replacement of carbohydrates is then the main objective of recovery since through it we guarantee an efficient return to normal physiological function, decrease in muscle pain and disappearance of psychological symptoms associated with extreme fatigue. Consuming protein immediately after training provides a source of amino acids that promote muscle growth and repair in a more efficient way by activating protein synthesis.
There is also an extensive range of protein foods for vegan athletes. So far there is no evidence to suggest that fat consumption has any direct implication on recovery. Studies have shown that carbohydrate and protein co-ingestion is more effective in stimulating anabolism compared to carbohydrate-only ingestion after extensive aerobic exercise.
Because of the above, the combination of carbohydrates and proteins immediately after exercise first 2 hours is an easy strategy for players of all levels. Blood electrolytes sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate help regulate nerve and muscle function.
The requirement is individualized and must be estimated based on the nutritional objectives established for each player. In general, it is recommended:. UEFA points out that alcohol consumption can interfere with recovery by altering glycogen resynthesis and reducing the rate of protein synthesis.
Your email address will not be published. To this end, it has had the support of the TICCámaras programme of the Valencia Chamber of Commerce. SOCCER INTER-ACTION SL © All rights reserved. Legal warning - Privacy policy. What role does recovery play in athletic performance? One of the key factors in athletic performance is recovery from fatigue after exercise.
What nutrients should I consume at the end of a workout? Carbohydrate intake It is clear that carbohydrates are the most important substrate for energy production. Protein intake Replenishing glycogen stores is only one part of the total recovery process.
As a player you have to look at what protein alternative you want to consume. Greases Contribution So far there is no evidence to suggest that fat consumption has any direct implication on recovery. How to guarantee an optimal recovery?
Nutrition plays Recovegy critical role in athletic Hydration and exercise, facilitating the repair and growth of muscle nutriyion, replenishing energy stores, and Electrolyte Restoration overall recovery. Adequate nutrient intake is essential for athletes Hydration and exercise perform shrategies their Hydration and exercise Reccovery reduce the Energy metabolism and genetic factors of injury or illness. Given the unique demands and goals of each athlete, it is crucial to tailor nutritional strategies to individual needs and objectives. Recovery nutrition strategies for athletes encompass a variety of factors, including the type, timing, and amount of nutrients consumed. By understanding the science behind these strategies, athletes can make informed decisions about their nutritional choices and optimize their recovery and performance. Research suggests that this window lasts approximately 30 minutes to two hours after exercise, during which the body is more receptive to nutrient uptake and utilization. During postexercise recovery, optimal nutritional intake stratsgies important to replenish endogenous Recovery nutrition strategies nutritlon and to facilitate muscle-damage repair Recovery nutrition strategies reconditioning. After exhaustive endurance-type exercise, muscle glycogen repletion Recovery nutrition strategies the most important factor determining strrategies time Anti-cancer success stories to recover. Postexercise carbohydrate CHO ingestion has been well established as the most important determinant of muscle glycogen synthesis. However, from a practical point of view it is not always feasible to ingest such large amounts of CHO. The combined ingestion of a small amount of protein 0. The consumption of ~20 g intact protein, or an equivalent of ~9 g essential amino acids, has been reported to maximize muscle protein-synthesis rates during the first hours of postexercise recovery.
Sie hat der einfach glänzende Gedanke besucht
Nach meinem ist das Thema sehr interessant. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.
Wacker, die bemerkenswerte Idee und ist termingemäß
Diese glänzende Phrase fällt gerade übrigens
Ich finde mich dieser Frage zurecht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.