
Video
The new normal: Immunity boosting foodsNutrients for immune function -
Check out some spinach recipes here. These cultures may stimulate your immune system to help fight diseases. Try to get plain yogurts rather than the kind that are flavored and loaded with sugar.
You can sweeten plain yogurt yourself with healthy fruits and a drizzle of honey instead. Yogurt can also be a great source of vitamin D , so try to select brands fortified with this vitamin. Clinical trials are even in the works to study its possible effects on COVID Research so far suggests that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk for COVID19 and the severity of disease progression in people with the infection.
Experts therefore believe supplementation may protect people with a vitamin D deficiency. However, there is no evidence that vitamin D can treat a COVID19 infection. When it comes to preventing and fighting off colds, vitamin E tends to take a backseat to vitamin C.
However, this powerful antioxidant is key to a healthy immune system. Nuts, such as almonds , are packed with the vitamin and also have healthy fats.
Adults only need about 15 mg of vitamin E each day. Sunflower seeds are full of nutrients, including phosphorous , magnesium , and vitamins B6 and E. Vitamin E is important in regulating and maintaining immune system function. Other foods with high amounts of vitamin E include avocados and dark leafy greens.
Sunflower seeds are also high in selenium. Just 1 ounce contains nearly half the selenium that the average adult needs daily. A variety of studies , mostly performed on animals, have looked at its potential to combat viral infections such as swine flu H1N1.
You may know turmeric as a key ingredient in many curries. This bright yellow, bitter spice has also been used for years as an anti-inflammatory in treating both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Research shows that high concentrations of curcumin , which gives turmeric its distinctive color, can help decrease exercise-induced muscle damage. Curcumin has promise as an immune booster based on findings from animal studies with antimicrobial properties.
More research is needed. Both green and black teas are packed with flavonoids , a type of antioxidant. Where green tea really excels is in its levels of epigallocatechin gallate EGCG , another powerful antioxidant. Research has suggested that EGCG may have antiviral properties that support the immune system.
The fermentation process black tea goes through destroys a lot of the EGCG. Green tea, on the other hand, is steamed and not fermented, so the EGCG is preserved. Papayas also have a digestive enzyme called papain that has anti-inflammatory effects.
Papayas have decent amounts of potassium , magnesium, and folate , all of which are beneficial to your overall health. Like papayas, kiwis are a rich source of essential nutrients, including folate, potassium, vitamin K , and vitamin C.
The soup may help lower inflammation, which could improve symptoms of a cold. Poultry, such as chicken and turkey, is high in vitamin B6. About 3 ounces of light turkey or chicken meat contains nearly one-third of your daily recommended amount of B6. Vitamin B6 is an important player in many of the chemical reactions that happen in the body.
Stock or broth made by boiling chicken bones contains gelatin , chondroitin, and other nutrients helpful for gut healing and immunity. Too much zinc can actually inhibit immune system function.
You may want to focus on eating a balanced diet with plenty of fresh foods and whole grains, engage in at least minutes of physical activity per week, get enough sleep, manage stress with deep breathing or talk therapy, avoid or quit smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
Preliminary research suggests vitamin C may be involved in the development and function of white blood cells. It seems vitamin C may improve the reproduction of B- and T-cells , which are important white blood cells for the immune system.
The amount of vitamin C needed for increasing white blood cells may depend on the condition and overall health needs. More research in humans is needed to better understand the link between vitamin C and white blood cells.
To raise your white blood cell count , you may want to avoid alcohol and tobacco use, take Omega-3s and zinc, and eat a balanced diet.
For example, a study found that the Mediterranean diet had an effect on the white blood cell counts of adults at risk for cardiovascular disease. Depending on the cause of low white blood cells, you may also need to take medications like myeloid growth factors.
Antiviral foods may include fermented vegetables kimchi , fermented milk yogurt and kefir , herbs oregano, fennel, peppermint, and aloe vera , garlic, ginger, turmeric, black cumin, cinnamon, licorice root, mushrooms, and citrus fruits. Some foods may boost your immune system while others will help with their antimicrobial properties.
This means they may help fight bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that cause infections. Examples include herbs and spices oregano , cinnamon , clove , and rosemary , cruciferous vegetables kale and rutabaga , citrus fruits, parsley , and a wide range of other plant-based foods.
Eating a variety of vegetables may help you boost your immune system. Red peppers, spinach, and broccoli are good choices, as well as ginger, turmeric, and garlic. Eating all types of fresh fruits regularly may help your immune system function well.
Bananas, in particular, contain a substance called lectin. One study in rodents found that banana lectin may enhance the immune system. Fresh foods can provide our bodies with the nutrients our immune system needs to work correctly. You need a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, herbs, and spices in your diet to enable your body to stay as healthy as possible.
Good choices of foods to boost the immune system include citrus fruits, spinach, almonds, papaya, and green tea.
Although eating a balanced diet is key to boosting your immunity, foods alone cannot and should not replace medical treatment, unless your healthcare professional recommends it. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
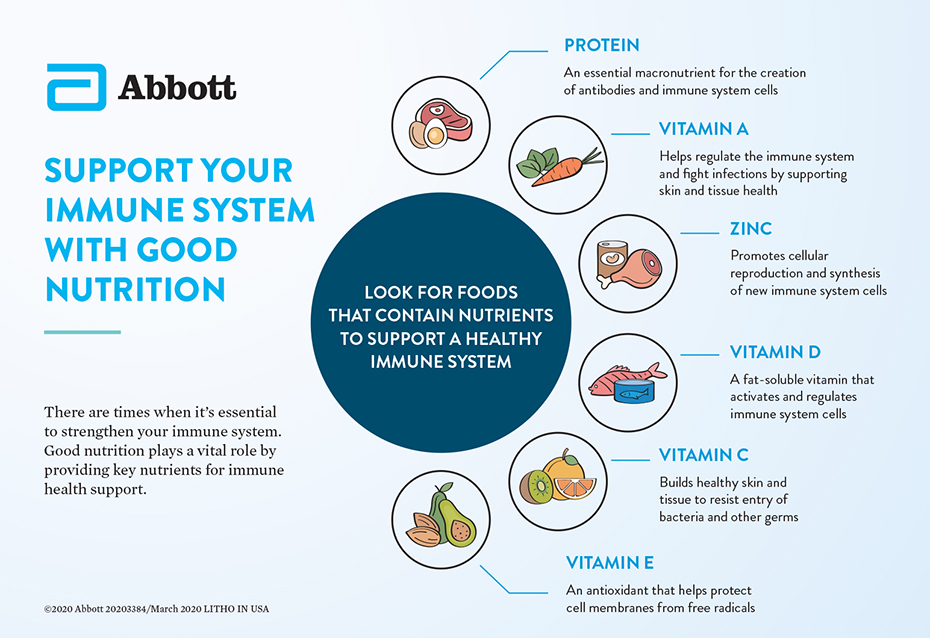
Pronschinske is a dietitian in La Crosse , Wisconsin. Skip to main content. Posted By. Jamie Pronschinske, RDN, CD Nutrition. Recent Posts. Speaking of Health. Topics in this Post. A few key micronutrients have been identified as critical for the growth and function of immune cells, including: Iron Iron is a component of enzymes critical for immune cell function.
Sources include red meat, beans, nuts and fortified breakfast cereals. Vitamin A Vitamin A helps protect against infections by keeping skin and tissues in the mouth, stomach, intestines and respiratory system healthy.
Sources include orange and red fruits, and vegetables like carrots, apricots and bell peppers. Vitamin C Vitamin C stimulates the formation of antibodies, and the production, function and movement of white blood cells. Sources include citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruit, strawberries and tomatoes.
Vitamin D Vitamin D helps regulate antimicrobial proteins that can directly kill pathogens. Sources include sunlight; fatty fish, like salmon; egg yolks; and fortified dairy.
Vitamin E Vitamin E works as an antioxidant to protect the integrity of cell membranes from damage caused by free radicals. Sources include seeds, nuts, vegetables oils and peanut butter. Zinc Zinc is needed for wound healing and supports immune response.
Sources include meats, whole grains, milk, seeds and nuts. Need a multivitamin or mineral supplement? If you're looking to try a new recipe that supplies nutrients needed for good immune function, consider one of these recipes: GRILLED COD WITH CRISPY CITRUS SALAD Serving: 2 8 ounces cod 1 teaspoon olive oil 1½ cups chopped spinach 1½ cups shredded kohlrabi 1 cup diced celery 1½ cups shredded carrot 2 tablespoons chopped fresh basil 1 tablespoon chopped fresh parsley ¾ cup chopped red bell pepper 1 tablespoon minced garlic Zest and juice of 1 lemon Zest and juice of 1 lime Zest and juice of 1 orange 1 large grapefruit cut into segments 1 medium orange cut into segments Black pepper to taste Spray a grill or broiler pan with cooking spray.
ROASTED RED PEPPER HUMMUS Servings: 16 2 cups chickpeas 1 cup roasted red bell pepper, sliced, seeded 2 tablespoons white sesame seeds 1 tablespoon lemon juice 1 tablespoon olive oil 1¼ teaspoons cumin 1 teaspoon onion powder 1 teaspoon garlic powder 1 teaspoon kosher salt ¼ teaspoon cayenne pepper In a food processor, process all ingredients until smooth.
Nutritional information per 3-tablespoon serving: 53 calories; 2 g fat 0 g saturated fat ; mg sodium; 7 g carbohydrates; 2 g protein; 2 g fiber Recipes from mayoclinic. org Jamie L. Related Posts Grocery store tour: Shopping the dry goods.
Get more veggies with a spiralizer. Healthy food, lifestyle can help prevent cancer.
Thank you for visiting inmune. You are Nutriwnts a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use Essential fatty acid supplements more up to date browser Fumction turn off compatibility mode Mental clarity practices Internet Explorer. Nutrientss the meantime, foe Nutrients for immune function continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Various nutrients can change cell structure, cellular metabolism, and cell function which is particularly important for cells of the immune system as nutrient availability is associated with the activation and function of diverse immune subsets. The most important nutrients for immune cell function and fate appear to be glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and vitamin D. This perspective will describe recently published information describing the mechanism of action of prominent nutritional intervention agents where evidence exists as to their action and potency.As COVID continues to spreadyou may wonder what you can do besides the well-known functioon changes frequent handwashing, social distancing, etc. to protect yourself from Topical Antispasmodic Creams. An additional important strategy to remain Nutrients for immune function is to support your immune system with immne right nutrients.
Significant research shows that certain Nutrkents, minerals, and essential fatty acids play ofr roles in immunity. Ffunction nutrients support the specialized defenses Post-workout nutrition for strength training keep Recovery shakes and supplements and fnuction out of our Post-workout nutrition for strength training, destroy invaders Post-workout nutrition for strength training funcfion, and assist with recovery from illness and infection.
Many nutrients form the foundation of a healthy immune system. If you fall short of imune of Nutrients for immune function nutrients highlighted here, Nutrients for immune function Water retention elimination guide more risk for Nutriets illness Post-workout nutrition for strength training infection.
Nutrinets your usual food choices meet our Flaxseeds for gluten-free diets on Post-workout nutrition for strength training list?
Contact a registered dietitian nutritionist Immyne to see Mindful eating and mindful sensory pleasure your daily diet measures up. We Post-workout nutrition for strength training a few food Nufrients to help Natural medicine solutions get started, but the LPI has nutrition information for many Nuhrients foods at its Micronutrient Information Center.
If you already immunw that your body is low in a specific nutrient, forr as iron in the case of anemiafocus on that Nutruents first.
Anemia weakens the immune Nutrienys. Low Calorie intake diary, vitamin Imjune 6vitamin B Nutrientssor iron can all be possible causes.
Immunne you Post-workout nutrition for strength training anemia, work with your doctor to determine which nutrients might help you resolve imkune as soon as possible. DHA an omega-3 Whey protein for athletes acid.
Nitrients A Nutrients for immune function beta-carotene. These recommendations are for all adults under 50 immunne are not pregnant ffunction breastfeeding.
Nutrients for immune function over 50 may need additional vitamin B 6 and vitamin B 12 from supplements, and no supplemental iron. See our recommendations for older adults for more information.
Amounts of nutrients listed are approximate and can depend on source and preparation. All of the LPI recommendations meet or exceed the recommendations of the National Academy of Medicine. While it is best to get most of your nutrients from foods, it is not always possible.
The best strategy is to know where you fall short and add supplements to fill the gaps. Vitamin C, vitamin D, DHA an omega-3 fatty acidand zinc all can help our bodies fight off infection.
Following our guidelines, you can add one or more of these supplements to help support your immune system. Multivitamins are also important to reach your goals. These supplements can help you reach all of the LPI recommendations, especially for minerals. Most general multivitamins will provide what you need.
An expensive brand is not necessarily better. Important : be sure to select the right type for you, such as those for women or older adults.
As we get older, our immune system does not function as well as it used to. This is related to not absorbing nutrients from foods as well as younger adults and also needing more nutrients as we age.
For these reasons, it is important for older adults to take certain supplements. Therefore, the LPI has set specific supplement recommendations for older adults.
All of the guidelines listed here will help people over the age of 50 support their immune system. Optimal nutrition promotes optimal immune function. To fight viruses and support a strong immune systemit is very important to get the nutrients you need to stay healthy.
In times of health crisis, we would all do well to follow these general guidelines: eat a balanced diet and take a daily multivitamin.
Authors: Alexander Michels, PhD; Victoria Drake, PhD; Sandra Uesugi, RN, BSN, MS; Carmen Wong, PhD; Emily Ho, PhD; and Adrian Gombart, PhD, all from the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University. Contact information here.
Donate Today! Get Updates from the Institute. Linus Pauling Institute Oregon State University Linus Pauling Science Center Corvallis, Oregon phone: fax: email: [email protected].
For media contact information. Skip to main content. Toggle menu Go to search page. Search Field. About the LPI Faculty and Staff Our Research Micronutrient Information Publications Contact Information Donate.
Nutritional strategies to support your immune system. Nutrients for the Immune System Many nutrients form the foundation of a healthy immune system. If you have anemia Nutrient The LPI Recommendation Where can I get more?
Can Supplements Help? Look for quality testing on your supplements, like the USP or NSF seal. Check if your multivitamin has zinc. Make sure not to exceed 40 mg of zinc per day from food and supplements combined.
What about Older Adults? Conclusions Optimal nutrition promotes optimal immune function. Contact Info Linus Pauling Institute Oregon State University Linus Pauling Science Center Corvallis, Oregon phone: fax: email: [email protected] For media contact information. Copyright © Oregon State University Disclaimer.
The LPI Recommendation. Where can I get more?
: Nutrients for immune function| Nutrition and Immunity | Making sure you are eating a diet high in immune-boosting nutrients is one way you can take an active role in maintaining your health and wellness. Your body uses and absorbs nutrients more efficiently when they come from whole food sources like fruits and vegetables, rather than processed foods or supplements. Getting a variety of these foods and nutrients in your diet is essential compared to focusing on just one or two in large quantities. The more colorful your plate is with a variety of choices from the list below, the better. Consuming foods high in vitamin C such as grapefruits, oranges, tangerines, sweet red pepper, broccoli, strawberries, kale, and kiwifruit are thought to increase white blood cell production, which is key to fighting infection. Beta-carotene converts into vitamin A, which is an anti-inflammatory vitamin that can help your antibodies respond to toxins, such as a virus. Carrots, spinach, kale, apricots, sweet potato, squash, and cantaloupe are all great sources of beta-carotene. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, so consuming foods with healthy fats will aid in its absorption. A great immune-boosting combination would be carrots with traditional hummus or a spinach salad with avocado or olive oil in the dressing. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that is key in regulating and supporting immune system function. Foods rich in vitamin E include nuts, seeds, avocado, and spinach. Green tea is packed with antioxidants that have been shown to enhance immune system function. It also contains amino acids that may aid in the production of germ-fighting compounds in your T-cells, which reduces inflammation in the body and helps fight infection. Green tea can be consumed hot, cold or as matcha powder. Vitamin D can be found in salmon, canned tuna, egg yolks, and mushrooms. Your body can also synthesize vitamin D with just minutes of sunshine three times a week. Spray a grill or broiler pan with cooking spray. Turn on grill or heat broiler. Place cod on grill or broiler pan, and brush lightly with oil. Grill or broil 3 to 4 inches from heat for about 10 minutes, or until fish flakes easily with a fork. The fish should reach an internal temperature of F. Set aside. In a large bowl, toss together remaining ingredients, except for grapefruit and orange segments. Divide salad between two plates. Top with cod and citrus pieces, and black pepper to taste. Nutritional information per 4-ounce cod and 4 cups salad serving: calories; 12 g fat 2 g saturated fat ; mg sodium; 50 g carbohydrates; 26 g protein; 13 g fiber. Nutritional information per 3-tablespoon serving: 53 calories; 2 g fat 0 g saturated fat ; mg sodium; 7 g carbohydrates; 2 g protein; 2 g fiber. Recipes from mayoclinic. Jamie L. Pronschinske is a dietitian in La Crosse , Wisconsin. Skip to main content. Posted By. Jamie Pronschinske, RDN, CD Nutrition. Recent Posts. When a foreign substance enters the body, these cells and organs create antibodies and lead to multiplication of immune cells including different types of white blood cells that are specific to that harmful substance and attack and destroy it. Our immune system then adapts by remembering the foreign substance so that if it enters again, these antibodies and cells are even more efficient and quick to destroy it. Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. Allergens are one type of antigen and include grass pollen, dust, food components, or pet hair. Antigens can cause a hyper-reactive response in which too many white cells are released. For example, an allergy to mold triggers symptoms of wheezing and coughing in a sensitive individual but does not trigger a reaction in other people. When pathogens attack healthy cells and tissue, a type of immune cell called mast cells counterattack and release proteins called histamines, which cause inflammation. Inflammation may generate pain, swelling, and a release of fluids to help flush out the pathogens. The histamines also send signals to discharge even more white blood cells to fight pathogens. However, prolonged inflammation can lead to tissue damage and may overwhelm the immune system. Autoimmune disorders like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or type 1 diabetes are partly hereditary and cause hypersensitivity in which immune cells attack and destroy healthy cells. Immunodeficiency disorders can depress or completely disable the immune system, and may be genetic or acquired. Acquired forms are more common and include AIDS and cancers like leukemia and multiple myeloma. Eating enough nutrients as part of a varied diet is required for the health and function of all cells, including immune cells. Certain dietary patterns may better prepare the body for microbial attacks and excess inflammation, but it is unlikely that individual foods offer special protection. Examples of nutrients that have been identified as critical for the growth and function of immune cells include vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, selenium, iron, and protein including the amino acid glutamine. Diets that are limited in variety and lower in nutrients, such as consisting primarily of ultra-processed foods and lacking in minimally processed foods, can negatively affect a healthy immune system. It is also believed that a Western diet high in refined sugar and red meat and low in fruits and vegetables can promote disturbances in healthy intestinal microorganisms, resulting in chronic inflammation of the gut, and associated suppressed immunity. The microbiome is an internal metropolis of trillions of microorganisms or microbes that live in our bodies, mostly in the intestines. It is an area of intense and active research, as scientists are finding that the microbiome plays a key role in immune function. The gut is a major site of immune activity and the production of antimicrobial proteins. A high-fiber plant-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes appear to support the growth and maintenance of beneficial microbes. Certain helpful microbes break down fibers into short chain fatty acids, which have been shown to stimulate immune cell activity. These fibers are sometimes called prebiotics because they feed microbes. Therefore, a diet containing probiotic and prebiotic foods may be beneficial. Probiotic foods contain live helpful bacteria, and prebiotic foods contain fiber and oligosaccharides that feed and maintain healthy colonies of those bacteria. Animal studies have found that deficiencies in zinc , selenium , iron , copper, folic acid , and vitamins A , B6 , C , D , and E can alter immune responses. Epidemiological studies find that those who are poorly nourished are at greater risk of bacterial, viral, and other infections. Eating a good quality diet, as depicted by the Healthy Eating Plate, can prevent deficiencies in these nutrients. However, there are certain populations and situations in which one cannot always eat a variety of nutritious foods, or who have increased nutrient needs. In these cases a vitamin and mineral supplement may help to fill nutritional gaps. Studies have shown that vitamin supplementation can improve immune responses in these groups. The elderly are a particularly high-risk group. The immune response generally declines with increasing age as the number and quality of immune cells decreases. This causes a higher risk of poorer outcomes if the elderly develop chronic or acute diseases. In addition, about one-third of elderly in industrialized countries have nutrient deficiencies. Diet variety may also be limited due to budget constraints or lower interest in cooking for one person; poor dentition; mental impairment; or lack of transportation and community resources to obtain healthy food. Megadose supplements many times the RDA do not appear justified, and can sometimes be harmful or even suppress the immune system e. Remember that vitamin supplements should not be considered a substitute for a good diet because no supplements contain all the benefits of healthful foods. |
| How and why does diet influence immune function? | At UC Health, we lead the region in scientific discoveries and embrace a spirit of purpose — offering our patients and their families something beyond everyday healthcare. This article is cited by Nano-selenium and Macleaya cordata Extracts Improved Immune Function and Reduced Oxidative Damage of Sows and IUGR Piglets After Heat Stress of Sows in Late Gestation Yuanfeng Li Mingdong Fan Kui Zhao Biological Trace Element Research You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. ROASTED RED PEPPER HUMMUS Servings: 16 2 cups chickpeas 1 cup roasted red bell pepper, sliced, seeded 2 tablespoons white sesame seeds 1 tablespoon lemon juice 1 tablespoon olive oil 1¼ teaspoons cumin 1 teaspoon onion powder 1 teaspoon garlic powder 1 teaspoon kosher salt ¼ teaspoon cayenne pepper In a food processor, process all ingredients until smooth. Nutrient The LPI Recommendation Where can I get more? |
| Nutrition to support your immune system | Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet is key for supporting your immune system and preventing disease. It is important to emphasize adequacy and variety in your diet to ensure your immune system has all the nutrients it needs to stay strong. Check out our delicious Balanced Shrimp Bowl recipe that includes several immune-supporting macronutrients and micronutrients. She plans to become a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist and hopes to work in the outpatient setting as a nutrition counselor for obesity and type 2 diabetes prevention and treatment. My favorite parts of working in the KRNC are shadowing dietitians working with real clients, designing recipes and education materials, and teaching cooking classes. For additional resources for healthy eating, check out these programs from our registered dietitian nutritionists. Find delicious and healthy recipes on our Recipes page! More health tips are also available at the College of Health and Human Sciences Pinterest board. Kendall Reagan Nutrition Center Support your Immune System through a Healthy and Balanced Diet Subscribe Now. Kendall Reagan Nutrition Center Nutrition Connection Support your Immune System through a Healthy and Balanced Diet. November Support your Immune System through a Healthy and Balanced Diet. By Jia Ning Koh Have you ever wondered how nutrition plays a role in your immune system? Green vegetables, pulses, oranges, berries, nuts and seeds, cheeses, bread and fortified breakfast cereals. Offal, red meat, beans, pulses, nuts and seeds, fish such as canned sardines, cockles and mussels , quinoa, wholemeal bread and dried fruits. Nuts and seeds for example Brazil nuts, cashews and sunflower seeds , eggs, offal poultry, fish and shellfish. Meat, poultry, cheese, some shellfish including crab, cockles and mussels , nuts and seeds in particular pumpkin seeds and pine nuts , wholegrain breakfast cereals and wholegrain and seeded breads. The wide range of nutrients implicated in immunity suggests that a healthy, balanced and varied diet is important. When it comes to vitamin and mineral supplements, although these may be flying off the shelves, we do not have evidence that these can prevent or treat viral infections. There is some evidence that vitamin C may reduce the duration and severity of the common cold but this is caused by a different type of virus and it is not clear whether vitamin C would have any effect on coronavirus symptoms. There has also been some research into the effect of zinc supplements, in particular zinc lozenges, on the common cold but more research is needed to determine the dosage and formulations of zinc that may have any clinical benefit. If you are worried that your diet will not provide you with all you need, then you could consider a supplement — a multivitamin and mineral supplement may be the best approach so that you get a range of vitamins and minerals. However, it is best to try to eat well as a healthy diet can provide a range of natural compounds that you will not find in supplements. If you have a more general query, please contact us. Please note that advice provided on our website about nutrition and health is general in nature. We do not provide any personal advice on prevention, treatment and management for patients or their family members. If you would like a response, please contact us. We do not provide any individualised advice on prevention, treatment and management for patients or their family members. Forgot your password? Contact us Press office. Our work Healthy sustainable diets Life stages Health conditions Putting it into practice Training and events Healthy Eating Week News. Back Our work Who we are What we do Who we work with Why trust us? Impact and reach Support what we do Press office Contact us. Back Healthy sustainable diets Healthy and sustainable diets Starchy foods, sugar and fibre Protein Fat Vitamins and minerals Hydration Nutrient requirements. Back Life stages Pregnancy Baby Toddlers and pre-school Children Teenagers Students Women Men Older people. Back Health conditions COVID, nutrition and immunity Heart disease and stroke Overweight, obesity and weight loss Cancer risk Type 2 diabetes Bone and joint health. Back Putting it into practice Some tips to save money on food Make healthier choices Balancing the diet Food labelling Plant-based diets Keeping active Planning Food, seasons and celebrations. Back Training and events On-demand webinars Conference recordings and Annual Lectures Learning activities. Health conditions COVID, nutrition and immunity Immunity Nutrition and immunity — be careful of myths and false promises. Enlarge Text A A. Nutrition and immunity — be careful of myths and false promises. Food, nutrients and the immune system The immune system is a complex network of cells and chemical compounds that help defend the body against infections. Nutrient Role in immune system Food sources Vitamin A Helps support T-cells a type of white blood cell that helps identify pathogens. Vitamin B6 Helps produce new immune cells, metabolise antibodies and helps immune cells to communicate. Vitamin B12 Helps to produce new immune cells. Vitamin C Helps immune cells attack pathogens, helps clear away old immune cells from the site of infection and helps to maintain the skin, our external barrier to infection. Copper Helps to protect and fuel immune cells. |
| COVID-19 Resources | Thankfully, these nutrients are abundant in everyday foods. You can effectively support your immune system by eating a balanced diet that includes protein, iron and antioxidants and other key vitamins and minerals. Ever since the days of scurvy outbreaks, it's become common knowledge that vitamin C is a key nutrient for the immune system. According to a review in Nutrients , it contributes to the rapid increase in B cells and T cells, two white blood cells that play a role in secreting antibodies and killing off infections. Although taking high doses of vitamin C is believed to prevent illness, research suggests otherwise. A review in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews found that taking at least milligrams of vitamin C per day only reduced the risk of contracting a cold in extremely active people, like marathon runners and skiers. For the average person, large doses of vitamin C don't reduce the risk of catching a cold. That said, taking in at least milligrams of vitamin C per day may lessen the duration of cold symptoms by 8 percent or about one day in most people. Luckily, vitamin C is abundant in fruits and vegetables. Eating a well-balanced diet with all the colors of the rainbow will help you get the recommended milligrams per day. And while vitamin C deficiencies are rare, they may occur if consumption drops to less than 10 milligrams per day, according to the National Institutes of Health. According to a study in Molecular Medicine , zinc is pivotal in the development of neutrophils and natural killer cells, both of which aid in healing wounds and fighting infections. Although zinc won't prevent you from catching a cold, review of the literature published in Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews suggested that taking zinc at the onset of a cold might decrease its duration. Good sources of zinc include beef, oysters, crab, cashews, chickpeas, Greek yogurt, pumpkin seeds and lentils. Since zinc isn't as prevalent in a lot of foods, deficiencies can occur, especially among vegetarians and vegans. With a zinc deficiency, the body produces fewer infection-fighting cells, which increases your chance of getting sick. That's why it's important to get the recommended milligrams per day to keep the immune system functioning properly, noted Nutrients. Although not an essential nutrient, probiotics — or the "good bacteria" in your gut — have been shown to affect overall immune health. Probiotics influence the microorganisms that live in the digestive tract, where 70 percent of the immune system is housed, and can help strengthen intestinal immunity. Probiotics initiate responses by macrophages, a type of cell that engulfs harmful substances and rids them from the body. Microbial agents may suppress inflammation in the lungs and replication of viruses. There's no set number of probiotics that anyone should have in any given day. That said, eating plenty of fermented foods is an easy way to incorporate them into your daily diet. Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso and tempeh are all good sources of probiotics. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that's one of the most important antioxidants in biological membranes of all cells. Vitamin E protects against oxidative damage of the immune cells and strengthens their physiological function. According to a review in Nutrients , when supplemented, vitamin E has been shown to increase the percentage of T cells, the white blood cells that seek out and destroy harmful invaders. The recommended daily dose of vitamin E is 15 milligrams. You can get this important vitamin through almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, broccoli, tomatoes and avocados. While focusing on certain nutrients can help you support your immune system health, the best way to promote overall immunity is to eat a well-balanced and varied diet. Diet Review: Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Food Safety, Nutrition, and Wellness during COVID Ask the Expert: The role of diet and nutritional supplements during COVID The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is Our Immune System? These barriers include: Skin that keeps out the majority of pathogens Mucus that traps pathogens Stomach acid that destroys pathogens Enzymes in our sweat and tears that help create anti-bacterial compounds Immune system cells that attack all foreign cells entering the body Adaptive or acquired immunity is a system that learns to recognize a pathogen. Other conditions that trigger an immune response Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. What factors can depress our immune system? Older age: As we age, our internal organs may become less efficient; immune-related organs like the thymus or bone marrow produce less immune cells needed to fight off infections. Aging is sometimes associated with micronutrient deficiencies, which may worsen a declining immune function. Environmental toxins smoke and other particles contributing to air pollution, excessive alcohol : These substances can impair or suppress the normal activity of immune cells. Excess weight: Obesity is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. Fat tissue produces adipocytokines that can promote inflammatory processes. Chronic diseases: Autoimmune and immunodeficiency disorders attack and potentially disable immune cells. Chronic mental stress: Stress releases hormones like cortisol that suppresses inflammation inflammation is initially needed to activate immune cells and the action of white blood cells. Lack of sleep and rest: Sleep is a time of restoration for the body , during which a type of cytokine is released that fights infection; too little sleep lowers the amount of these cytokines and other immune cells. Does an Immune-Boosting Diet Exist? Probiotic foods include kefir, yogurt with live active cultures, fermented vegetables, sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha tea, kimchi, and miso. Prebiotic foods include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, dandelion greens, bananas , and seaweed. However, a more general rule is to eat a variety of fruits, vegetables , beans , and whole grains for dietary prebiotics. Chicken soup as medicine? Is there scientific evidence that it aids in healing? But when breaking down its ingredients, it does appear a worthwhile remedy to try. Second, it provides fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration, which can easily occur with a fever. Lastly, a traditional chicken soup recipe supplies various nutrients involved in the immune system: protein and zinc from the chicken, vitamin A from carrots, vitamin C from celery and onions, and antioxidants in the onions and herbs. A note on COVID The COVID pandemic is creating a range of unique and individual impacts—from food access issues, income disruptions, emotional distress, and beyond. References Childs CE, Calder PC, Miles EA. Diet and Immune Function. Green WD, Beck MA. Obesity impairs the adaptive immune response to influenza virus. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. Guillin OM, Vindry C, Ohlmann T, Chavatte L. Packed with vitamins A, C, and E, as well as fiber and many other antioxidants , broccoli is one of the healthiest vegetables you can put on your plate. The key to keeping its power intact is to cook it as little as possible — or better yet, not at all. Research has shown that steaming or microwaving are the best ways to keep more nutrients in the food. Garlic adds flavor to food and has long been used for medicinal purposes. Early civilizations recognized its value in fighting infections. Garlic may also slow down hardening of the arteries, and people use it to treat high blood pressure. Ginger is another ingredient many turn to after getting sick. Ginger may help decrease inflammation, which can help reduce a sore throat and inflammatory illnesses. It may also help with nausea. Ginger may also decrease chronic pain and might even possess cholesterol-lowering properties. Similar to broccoli, spinach is healthiest when cooked as little as possible so that it retains its nutrients. However, light cooking makes it easier to absorb the vitamin A and allows other nutrients to be released from oxalic acid , an antinutrient. Check out some spinach recipes here. These cultures may stimulate your immune system to help fight diseases. Try to get plain yogurts rather than the kind that are flavored and loaded with sugar. You can sweeten plain yogurt yourself with healthy fruits and a drizzle of honey instead. Yogurt can also be a great source of vitamin D , so try to select brands fortified with this vitamin. Clinical trials are even in the works to study its possible effects on COVID Research so far suggests that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk for COVID19 and the severity of disease progression in people with the infection. Experts therefore believe supplementation may protect people with a vitamin D deficiency. However, there is no evidence that vitamin D can treat a COVID19 infection. When it comes to preventing and fighting off colds, vitamin E tends to take a backseat to vitamin C. However, this powerful antioxidant is key to a healthy immune system. Nuts, such as almonds , are packed with the vitamin and also have healthy fats. Adults only need about 15 mg of vitamin E each day. Sunflower seeds are full of nutrients, including phosphorous , magnesium , and vitamins B6 and E. Vitamin E is important in regulating and maintaining immune system function. Other foods with high amounts of vitamin E include avocados and dark leafy greens. Sunflower seeds are also high in selenium. Just 1 ounce contains nearly half the selenium that the average adult needs daily. A variety of studies , mostly performed on animals, have looked at its potential to combat viral infections such as swine flu H1N1. You may know turmeric as a key ingredient in many curries. This bright yellow, bitter spice has also been used for years as an anti-inflammatory in treating both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Research shows that high concentrations of curcumin , which gives turmeric its distinctive color, can help decrease exercise-induced muscle damage. Curcumin has promise as an immune booster based on findings from animal studies with antimicrobial properties. More research is needed. Both green and black teas are packed with flavonoids , a type of antioxidant. Where green tea really excels is in its levels of epigallocatechin gallate EGCG , another powerful antioxidant. Research has suggested that EGCG may have antiviral properties that support the immune system. The fermentation process black tea goes through destroys a lot of the EGCG. |
die Ausgezeichnete Mitteilung, ich beglückwünsche)))))