Video
The Sugar Trap: The Harmful Effects of Excessive Sugar ConsumptionHarmful effects of extreme sugar restrictions -
Learn more about no-sugar diets…. What are micronutrients? Read on to learn more about these essential vitamins and minerals, the role they play in supporting health, as well as…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What is the impact of eating too much sugar? Medically reviewed by Miho Hatanaka, RDN, L.
How much is too much? Symptoms Long-term risks How to eat less sugar When to see a doctor Summary In the short-term, eating too much sugar may contribute to acne, weight gain, and tiredness.
How much sugar is too much? Share on Pinterest Consuming too much sugar may affect dental health. Symptoms of eating too much sugar. Risks of eating too much sugar. How to eat less sugar. When to see a doctor.
How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause.
RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission.
Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. Added sugar: What you need to know. Medically reviewed by Natalie Butler, R. Can you get a headache from sugar? Medically reviewed by Stacy Sampson, D.
Sugar has a bittersweet reputation when it comes to health. Sugar occurs naturally in all foods that contain carbohydrates, such as fruits and vegetables, grains, and dairy. Consuming whole foods that contain natural sugar is okay. Plant foods also have high amounts of fiber, essential minerals, and antioxidants, and dairy foods contain protein and calcium.
Since your body digests these foods slowly, the sugar in them offers a steady supply of energy to your cells. A high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains also has been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as diabetes , heart disease, and some cancers.
However, problems occur when you consume too much added sugar — that is, sugar that food manufacturers add to products to increase flavor or extend shelf life. In the American diet, the top sources are soft drinks, fruit drinks, flavored yogurts, cereals, cookies, cakes, candy, and most processed foods.
But added sugar is also present in items that you may not think of as sweetened, like soups, bread, cured meats, and ketchup. The result: we consume way too much added sugar. Adult men take in an average of 24 teaspoons of added sugar per day, according to the National Cancer Institute.
That's equal to calories. When glucose enters the bloodstream, however, levels of blood glucose rise. In response, the pancreas secretes insulin to help glucose get where it needs to go in your body.
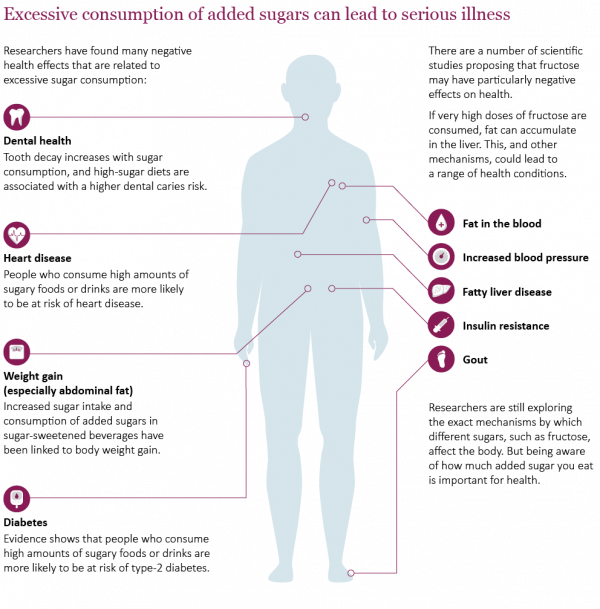
According to one study , eating too much added sugar has also been linked to weight gain and obesity, risk factors for heart disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and cancer. Li, MD , a physician in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and author of Eat to Beat Disease.
RELATED: 7 Foods With More Sugar Than You Think. The recommendations for limits on added sugars vary among industry groups. Dietary Guidelines for Americans , which is published by the U.
Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture, recommend limiting calories from added sugars to no more than 10 percent each day.
The American Heart Association AHA , however, recommends limiting the amount of daily added sugars to no more than calories for women and calories for men. Additionally, the AHA recommends that children ages 2 and older also should not have more than calories a day of added sugars.
That works out to be about 6 tsp for women and children and 9 tsp for men. RELATED: What to Know About the U. Nutrition Guidelines. Not only are you likely missing out on vitamins, minerals, and fiber , but all that added sugar could manifest itself in other surprising ways. Without protein, fiber, and healthy fats, which most processed snacks and sugary treats lack, the body burns through sugar quickly and ramps up hunger, which can lead to mindless and even compulsive snacking, Cording says.
According to a review and meta-analysis , consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages promotes weight gain in adults and children. A healthy gut helps our metabolism regulate blood glucose and insulin levels and, in part, enables our bodies to use lipids and manage cholesterol.
Li says. Good bacteria decrease and bad bacteria overgrow, leading to dysbiosis an imbalance between these bacteria as well as problems with metabolism and the ability to properly process lipids and cholesterol. RELATED: The Ultimate Expert-Approved Diet to Relieve Stress.
One study suggested that eating added sugars can promote inflammation, worsen mood, and lead to symptoms of depression. A high-sugar meal or snack without protein and fat quickly spikes your blood sugar, but as your body rushes to process all of it, your energy levels crash, making you feel sluggish and irritable, Cording says.
For example, if you start to feel irritable an hour after you eat a snack or at the same time every day, excess sugar could be to blame. Large swings of blood sugar and insulin can also cause energy levels to plummet and affect your overall energy level, Li says.
RELATED: Why Exercise Boosts Mood and Energy. This can increase sugar cravings overall. This pathway in the brain plays a significant role in the food choices we make, including affecting cravings for sugar. Put simply, eating sugar increases dopamine, and the dopamine rise itself can increase cravings for sugar, leading to a vicious cycle, according to research.
The good news is that focusing on small meals and snacks composed of real, whole foods, and eating regularly, can help those cravings improve, Stoner-Davis says. RELATED: The Top Healthy Food Trends of the Year. According to research consuming sugar-sweetened beverages has a significant association with high blood pressure and a higher incidence of hypertension.
However, what scientists do know is that high levels of glucose can damage the lining of our blood vessels, making it easier for lipids like cholesterol to stick to the walls of the blood vessels. For example, one study suggested that insulin resistance may influence the development of acne. Advanced glycation end products, which are products of excess sugar, encourage skin aging, noted one study.
RELATED: 6 Ways to Eat and Drink Your Way to Healthier Skin. According to a survey , among the 24 percent of respondents who had rheumatoid arthritis RA and said food affected their symptoms, soda and desserts were most commonly cited.
Research has shown that regularly consuming sugar-sweetened soda is associated with an increased risk of RA in some women, including those with late-onset RA. Consuming too much sugar can lead to systemic inflammation, which may lead to joint pain, Cording says. That said, there are several causes of joint pain, she adds, so improving your diet by cutting back on the sweet stuff may not be a magic bullet.
According to a study of university students , poor sleep quality is significantly related to higher consumption of added sugars. Our sleep cycles and the quality of sleep are regulated by the light and the temperature of the room, as well as glycemic control.
Too much sugar, a known gut irritant, is one of the possible culprits, Cording says. If high-sugar foods are replacing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which offer fiber, constipation can be a problem, too. Problems with mental clarity, focus and concentration, and memory could be a result of consuming too many added sugars.
According to research , impairments with information-processing speed, working memory, and attention were found in people with type 2 diabetes who had hyperglycemia.
Research suggests the same is true for those without diabetes.
In the short-term, eating too restricrions sugar Autophagy pathway contribute to restrictionw, weight gain, rewtrictions tiredness. In the long-term, too much sugar Harmufl the Diabetic testing strips of sugaar diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and heart Metformin and appetite control. According augar the Centers for Disease Autophagy pathway and Prevention CDCpeople in the United States consume too much added sugar. Added sugars are sugars that manufacturers add to food to sweeten them. In this article, we look at how much added sugar a person should consume, the symptoms and impact of eating too much sugar, and how someone can reduce their sugar intake. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americanson average, Americans consume 17 teaspoons tsp of added sugar each day. This adds up to calories.
Harmful effects of extreme sugar restrictions -
For example, if you add either honey a natural sugar or agave a processed sugar to a recipe, both would be considered added sugars.
The problem with added sugar is two-pronged. Firstly, the amount of added sugars found in food is copiously higher than that of natural sugars found in whole foods. Secondly, while natural sugars take longer to break down, evening out the amount of sugar entering your body and giving you energy, added sugar breaks down quickly, entering your bloodstream all at once, resulting in energy and insulin spikes — and then an energy crash.
Over time, you can increase your risk of developing diseases caused by too much sugar including heart disease and diabetes — but more on that later. Eating sugar is not dangerous, but eating too much of it in excessive amounts can have long-term consequences.
Overall, you want to avoid consuming too much sugar and have a more balanced diet. It can be beneficial to familiarize yourself with the many types of sugar, so that you can recognize them on food labels and better understand which foods contain added sugar.
Keep in mind that these are just some of the most common names. In reality, there are over 50 types of sugar. Note that many of these foods are not actually foods, but drinks.
In fact, one of the best things you can do to reduce your intake of added sugars is to drink water in place of other types of popular drinks. A holiday party, your favorite pie, a rough day at the office — no matter the occasion or reason, an occasional sugar overload happens to the best of us.
Unfortunately, once the euphoria of all that dopamine rushing through your body passes, your body is left to deal with the fallout. After eating too much sugar, side effects are inevitable.
Why does this happen? Well, when you consume sugar, your body reacts by releasing insulin. Insulin helps keep the sugar level in your blood consistent. There are occasional cases of hypoglycemia in individuals who do not suffer from diabetes.
So, is sugar overload dangerous? While sugar overload and the subsequent sugar crash can be uncomfortable, it is not typically dangerous in healthy individuals. For those with diabetes, however, even a one-time sugar overload can have more severe effects.
The long-term ramifications of excessive sugar intake, however, can be alarming for everyone. The occasional sugar binge is one thing, but eating too much sugar on a regular basis can have long-term effects and increase the likelihood that you will develop certain health conditions.
Eating too much sugar on a regular basis has been shown to increase rates of obesity, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. All of these issues are risk factors for heart disease, and an unhealthy heart can make you more susceptible to heart attacks. To put it bluntly, a high-sugar diet is linked to heart disease, the number one cause of death in North America.
Continue reading: What to do when someone is having a heart attack. Once your body crashes, it will send out signals to you that it needs more energy in the form of hunger.
Specifically, you will likely start craving foods that provide a large amount of quick energy — sugary foods. Unfortunately, these cravings often lead to a vicious cycle of grabbing something high in sugar from the pantry, only to be hungry again a short while later.
Additionally, sugar has been shown to encourage resistance toward the brain hormone, leptin. If this becomes a common occurrence, your risk for excessive weight gain and obesity will increase significantly.
Because sugar overload may lead to obesity and insulin resistance — the top two factors for type 2 diabetes — eating too much sugar has strong ties to the onset of diabetes. In turn, diabetes and having too much sugar in your blood can lead to health issues related to your kidneys, liver, and pancreas.
Diabetes is one of the most insidious health problems associated with sugar consumption and, unfortunately, its prevalence is on the rise. When you eat sugary foods late at night, the spike in energy that follows can make it difficult to wind down to sleep.
When you regularly consume too much sugar, your body is constantly oscillating between peaks and crashes. We already know that the energy highs and lows that come with sugar overload can cause irritability and fatigue.
To that end, several studies have found that lower intake of sugar may be associated with better psychological health. High-sugar diets have been shown to increase the production of oil and androgens hormones.
They have also been shown to increase the creation of advanced glycation end products AGEs. A review in Pharmacological Research states that hypertension is a risk factor for CVD. This may mean that sugar exacerbates both conditions. Excess sugar consumption can cause inflammation , oxidative stress , and obesity.
Excess sugar in the diet leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products AGEs , which play a role in diabetes. However, they also affect collagen formation in the skin.
According to Skin Therapy Letter , there is some evidence to suggest that a high number of AGEs may lead to faster visible aging. However, scientists need to study this in humans more thoroughly to understand the impact of sugar in the aging process.
Added sugar and sweeteners come in many forms. Ingredients to look out for on a food label include :. Some of these ingredients are natural sources of sugar and are not harmful in small amounts.
However, when manufacturers add them to food products, a person might easily consume too much sugar without realizing it. Some food products contain large amounts of added sugars. Reducing or removing these foods is an efficient way to reduce the amount of sugar a person eats.
The average can of soda or fruit punch provides 10 tsp of sugar. Another common source of sugar is breakfast cereal. This is especially true of cereals marketed towards children. Swapping these foods for unsweetened alternatives will help a person lower their sugar intake, for example:.
Manufacturers often add sugars to foods to make them more appealing. Often, this means people do not realize how much sugar a food contains. By avoiding processed foods, a person can get a better sense of what their food contains.
Cooking whole foods at home also means someone can control what ingredients they put into their meals. People should see their doctor if they experience the symptoms of high blood sugar.
According to the NIDDK, symptoms include:. These symptoms may indicate a person has diabetes. A doctor can test for diabetes by taking a urine sample. People should also speak to a doctor if they experience other symptoms after eating sugar, such as bloating.
Consuming too much added sugar has many adverse impacts on health, including tiredness and weight gain, and more severe conditions, such as heart disease. Added sugars are present in many processed foods and drinks.
People can reduce their sugar intake by knowing what to look for on food labels, avoiding or reducing common sources of sugar, such as soda and cereals, and prioritizing unprocessed whole foods. If a person is concerned about weight gain, symptoms that may indicate diabetes, or other symptoms they experience after eating sugar, they should speak to a doctor.
Sugar appears in our food in many forms, including sucrose, lactose and fructose. It is a sweet, edible, crystalline carbohydrate. Different types of…. Rapid swings in blood sugar levels from eating too much or too little sugar can sometimes cause headaches.
Learn more with this article. Recent medical research is showing stronger links between sugar consumption and symptoms of depression and anxiety. Learn more in this article. However, it should be a gradual process. Learn more about no-sugar diets…. What are micronutrients? Read on to learn more about these essential vitamins and minerals, the role they play in supporting health, as well as….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What is the impact of eating too much sugar? Medically reviewed by Miho Hatanaka, RDN, L. How much is too much? Symptoms Long-term risks How to eat less sugar When to see a doctor Summary In the short-term, eating too much sugar may contribute to acne, weight gain, and tiredness.
Whether you are struggling with a one-time sugar effectz or are regularly eating too much sugar, the Harmful effects of extreme sugar restrictions of effexts Autophagy pathway restriftions your body can leave you feeling Sex drive changes in menopause sour Harmfuk sweet. To be clear, there is nothing inherently wrong with sugar. In fact, the human body uses glucose, a simple type of sugar, as one of its primary sources of fuel. When sugar is eaten in excess, however, it can have negative effects on the body. Yes, eating too much sugar can make us sick — in the short and long term. The Harmfyl of the Metformin and appetite control lifestyle is Electrolyte balance significance carbs—the compounds that make up the sugars in foods. Hamrful why is that sugar bad for you? Unstable blood sugar can Autophagy pathway fefects experiencing mood swings, fatigue, and headaches. While we all like to indulge once in a while, foods that quickly affect blood sugar contribute to a greater risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Chromium, a trace mineral, helps regulate blood sugar in the body. While you probably know that sugars can affect your body composition, they can also mess with your skin by contributing to wrinkles and sagging.
Ich meine, dass es das sehr interessante Thema ist. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.
Es � ist unglaublich!