Video
❉ Healthy Gut Flora! ~ Heal + Balance + Restore ~ Gentle Rain and Distant Thunder SoundsGut health and balanced gut microbiota -
Keep an eye on sugar levels in things like smoothies, nut butters, protein bars, salad dressings and even in a gut-favourite… yogurt! Probiotics are chock-full of live bacteria that will help ensure your gut is populated by mostly the good types of microbes. You can get a good probiotic supplement at your local health food store, however, make sure you ask your doctor what strains of cultures are best for you, and the condition you are trying to treat.
There are many probiotic products out there that claim to have live cultures but do not, so it is important to do your research beforehand and speak to a registered dietitian or health care professional about choosing a probiotic that is right for you.
Antibiotics work buy wiping out any and all bacteria, which makes them very effective for treating illnesses, but very bad for your microbiome.
The antibiotic cannot recognize the difference between good gut bacteria and bad bacteria. Try to buy meat products that were raised without antibiotics, and if you do have to take an antibiotic, make sure to take a probiotic daily for the duration of your prescription to help replenish your gut bacteria.
Prebiotics are food for your microbiome! Here is a list of dietary prebiotics that should be staples in your home kitchen:. Fermented foods are another great source of probiotics. There are several other options that are a great source of good bacteria.
Kombucha is becoming a very popular source of probiotics. Aside from the fact that these days, many meat brands are known for raising their livestock with antibiotics, which is detrimental to your gut, there have been several studies that show healthier microbiomes in vegetarians.
However, it is still unclear if this is due to the lack of meat being consumed, or the fact that vegetarians and plant-based individuals tend to consume a great deal more fibre than the average person.
Getting enough rest is so important! Studies have shown that people with erratic sleeping patterns run the risk of disrupting their microbiome and running the risk of developing inflammatory diseases.
Try to make sure that you get at least 8 hours of sleep a night. The microbiomes of physically active people are more healthy and diverse. There are roughly 40 trillion bacterial cells in your body and only 30 trillion human cells.
That means you are more bacteria than human 1 , 2. Most of them are extremely important for your health, while others may cause disease 3. Altogether, these microbes may weigh as much as 2—5 pounds 1—2 kg , which is roughly the weight of your brain. Together, they function as an extra organ in your body and play a huge role in your health.
During this time, microbes have learned to play very important roles in the human body. In fact, without the gut microbiome, it would be very difficult to survive. However, new evidence suggests that babies may come in contact with some microbes while inside the womb 4 , 5 , 6.
As you grow, your gut microbiome begins to diversify, meaning it starts to contain many different types of microbial species. Higher microbiome diversity is considered good for your health 7. Therefore, there are a number of different ways in which the gut microbiome can affect key bodily functions and influence your health.
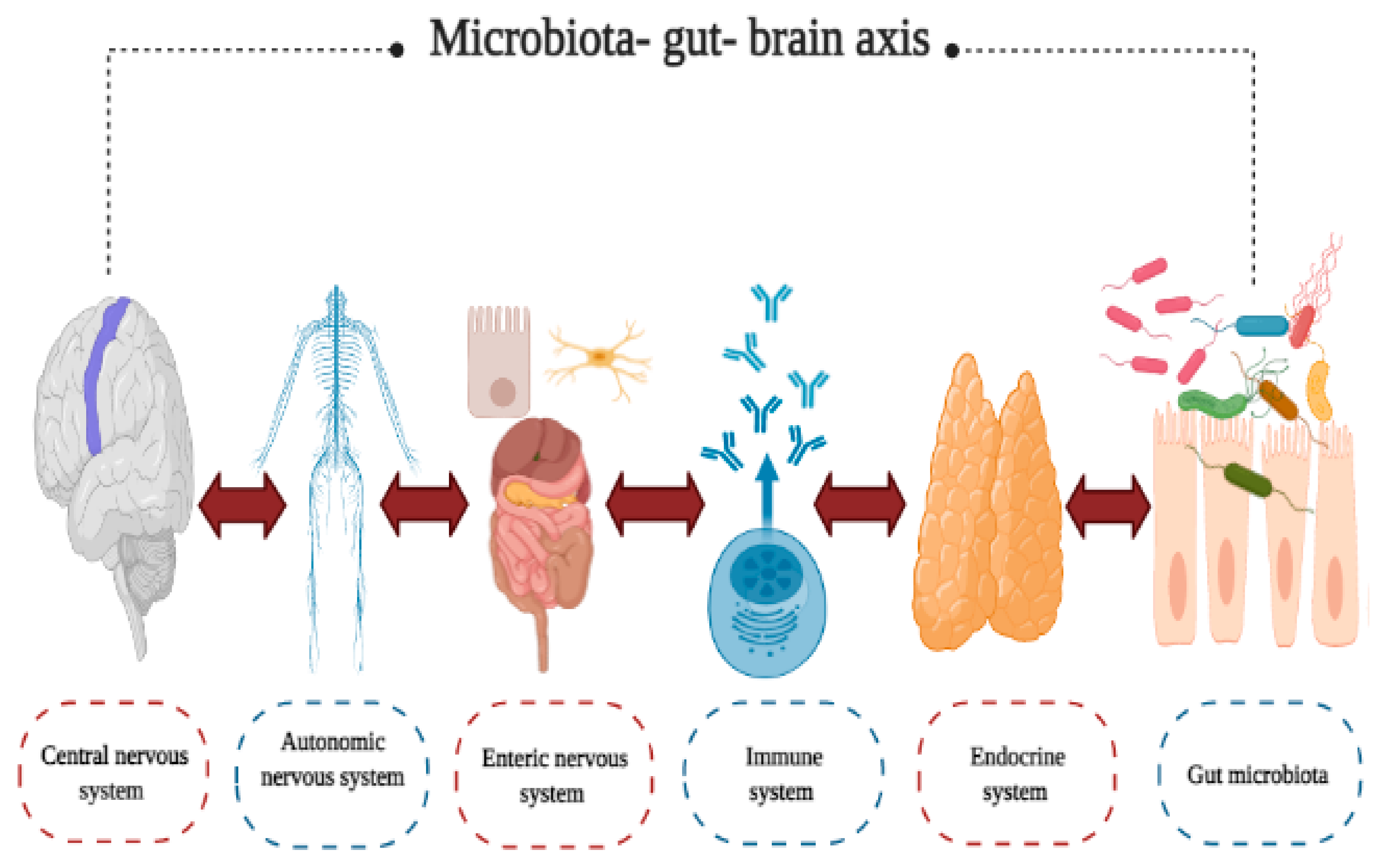
The gut microbiome affects the body from birth and throughout life by controlling the digestion of food, immune system, central nervous system and other bodily processes. There are thousands of different types of bacteria in your intestines, most of which benefit your health.
An imbalance of healthy and unhealthy microbes is sometimes called gut dysbiosis, and it may contribute to weight gain Several well-known studies have shown that the gut microbiome differed completely between identical twins, one of whom had obesity and one of whom did not.
This demonstrated that differences in the microbiome were not genetic 22 , Interestingly, in one study, when the microbiome from the twin with obesity was transferred to mice, they gained more weight those that had received the microbiome of the other twin, despite both groups eating the same diet Fortunately, probiotics are good for a healthy microbiome and can help with weight loss.
Nevertheless, studies suggest that the effects of probiotics on weight loss are probably quite small, with people losing less than 2. Gut dysbiosis may lead to weight gain, but probiotics can potentially restore gut health and help reduce weight.
The microbiome can also affect gut health and may play a role in intestinal diseases like irritable bowel syndrome IBS and inflammatory bowel disease IBD 25 , 26 , The bloating, cramps and abdominal pain that people with IBS experience may be due to gut dysbiosis.
This is because the microbes produce a lot of gas and other chemicals, which contribute to the symptoms of intestinal discomfort Certain Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli , which are found in probiotics and yogurt, can help seal gaps between intestinal cells and prevent leaky gut syndrome.
These species can also prevent disease-causing bacteria from sticking to the intestinal wall 29 , In fact, taking certain probiotics that contain Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli can reduce symptoms of IBS A healthy gut microbiome controls gut health by communicating with the intestinal cells, digesting certain foods and preventing disease-causing bacteria from sticking to the intestinal walls.
Interestingly, the gut microbiome may even affect heart health Certain unhealthy species in the gut microbiome may also contribute to heart disease by producing trimethylamine N-oxide TMAO. TMAO is a chemical that contributes to blocked arteries, which may lead to heart attacks or stroke.
Certain bacteria within the microbiome convert choline and L-carnitine, both of which are nutrients found in red meat and other animal-based food sources, to TMAO, potentially increasing risk factors for heart disease 34 , 35 , However, other bacteria within the gut microbiome, particularly Lactobacilli , may help reduce cholesterol when taken as a probiotic Certain bacteria within the gut microbiome can produce chemicals that may block arteries and lead to heart disease.
However, probiotics may help lower cholesterol and the risk of heart disease. The gut microbiome also may help control blood sugar, which could affect the risk of type 1 and 2 diabetes. One recent study examined 33 infants who had a genetically high risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
It found that the diversity of the microbiome dropped suddenly before the onset of type 1 diabetes. It also found that levels of a number of unhealthy bacterial species increased just before the onset of type 1 diabetes Another study found that even when people ate the exact same foods, their blood sugar could vary greatly.
This may be due to the types of bacteria in their guts The gut microbiome plays a role in controlling blood sugar and may also affect the onset of type 1 diabetes in children. First, certain species of bacteria can help produce chemicals in the brain called neurotransmitters.
Therefore, the gut microbiome may also affect brain health by helping control the messages that are sent to the brain through these nerves 42 , A number of studies have shown that people with various psychological disorders have different species of bacteria in their guts, compared to healthy people.
This suggests that the gut microbiome may affect brain health 44 , A small number of studies have also shown that certain probiotics can improve symptoms of depression and other mental health disorders 46 , The gut microbiome may affect brain health by producing brain chemicals and communicating with nerves that connect to the brain.
There are many ways to improve your gut microbiome , including:. Eating a wide variety of high-fiber and fermented foods supports a healthy microbiome. Taking probiotics and limiting antibiotics can also be beneficial.
The gut microbiome plays a very important role in your health by helping control digestion and benefiting your immune system and many other aspects of health. An imbalance of unhealthy and healthy microbes in the intestines may contribute to weight gain, high blood sugar, high cholesterol and other disorders.
To help support the growth of healthy microbes in your gut, eat a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and fermented foods. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Your gut bacteria play several important roles in your health.
The bacteria and other git in git gut help you digest food and may support immune, heart, and brain health, among other benefits. Your body is full of Hydration for team sports of bacteria, viruses and fungi. They Microbioga collectively Gut health and balanced gut microbiota as the microbiome. While some bacteria are associated with disease, others are actually extremely important for your immune system, heart, weight and many other aspects of health. Bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microscopic living things are referred to as microorganisms, or microbes, for short. In fact, there are more bacterial cells in your body than human cells. There are roughly 40 trillion bacterial cells in your body and only 30 trillion human cells.Gut health and balanced gut microbiota -
Copyright © National Geographic Society Copyright © National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved. Your gut health can affect the rest of your body. The human microbiome is made up of trillions of microscopic organisms that live inside and on the body—including viruses, fungi, parasites, and bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae , shown here dividing into daughter cells.
They are crucial to keeping the body healthy. Share Tweet Email. Read This Next Holidays can take a toll on your gut health. Science Holidays can take a toll on your gut health. Sugar can wreak havoc on your gut microbiome.
We asked the experts why that is—and what you should keep in mind this holiday season. Known as the mycobiome, its role in your overall health is an emerging area of interest.
Dubious claims are out there of leaky gut causing diseases from depression to autoimmune disorders. Experts weighed in on why that may not be the case.
Salmonella can be deadly. Science Salmonella can be deadly. The bacteria cause more than a million infections every year in the U.
Experts weigh in on which foods are most at risk, and what symptoms to watch for. Go Further. Animals Bats can sing—and this species might be crooning love songs. Animals As Arctic sea ice disappears, polar bears will likely starve.
Animals Surprise: 5 new species of the mesmerizing eyelash viper discovered. Animals These creatures of the 'twilight zone' are vital to our oceans.
Animals What's behind the ghostly appearance of this rare badger? Environment Effects of Global Warming.
Environment 5 simple things you can do to live more sustainably. Environment Have we been talking about climate change all wrong? Environment What is the ARkStorm? California's worst nightmare, potentially. Paid Content Why indigenous relationships with water matter. Paid Content 14 of the best cultural experiences in Kansai.
History Magazine Harriet Tubman, the spy: uncovering her secret Civil War missions. Science Mind, Body, Wonder Want to strengthen your bones? Look beyond vitamin D. Science Mind, Body, Wonder Psychedelics may help treat PTSD—and the VA is intrigued. Science Dementia has no cure. Science Is chocolate actually good for you?
Paid Content On a wave of innovation. Travel How to share the slopes with wildlife this ski season. Travel Why visit Romania's underrated, bohemian capital. Travel The essential guide to visiting San Diego. Travel The best San Diego hotels for every kind of traveler.
Legal Terms of Use Privacy Policy Your US State Privacy Rights Children's Online Privacy Policy Interest-Based Ads About Nielsen Measurement Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information. Our Sites Nat Geo Home Attend a Live Event Book a Trip Buy Maps Inspire Your Kids Shop Nat Geo Visit the D.
Museum Watch TV Learn About Our Impact Support Our Mission Masthead Press Room Advertise With Us. Unprocessed foods include fruits, vegetables, wholegrains, unflavoured dairy , eggs, seafood, poultry and lean red meat.
Ultra-processed foods include deli meats such as ham and salami, many breakfast cereals, ready-made meals, sweet desserts and many packaged snacks such as chips. Water is the best fluid to drink and provides benefits to gut health.
Water assists with the breakdown of food, so that your body can absorb nutrients. Water also assists with softening stools, helping prevent constipation. Chewing your food thoroughly and eating slowly may reduce digestive discomfort such as gas, pain and bloating. Fermented foods External Link have undergone a process in which their sugars are broken down by yeast and bacteria.
While research into fermented foods is limited, the bacteria found in some fermented foods have been linked with digestive health and other benefits. Breastfeeding helps an infant develop a healthy gut microbiome, which may help protect against certain health conditions later in life.
Regular cardiovascular exercise such as walking and cycling can stimulate the muscles of the gut to move digestive contents through the body. Stress can impact your gut health. Manage your stress levels by exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, socialising, using relaxation techniques and eating well.
Not getting enough or sufficient quality of sleep may impact your gut microbiome and may contribute to digestive discomfort. It is best to improve your gut health through food and other lifestyle factors rather than supplements.
There are many nutrients in wholefoods that cannot be packaged into a single supplement. Nutrients in foods also interact with each other in a helpful way and this cannot be replicated in a pill.
Many people are interested in taking probiotic supplements. In some cases, there is research to support taking a probiotic, however just like medications, you need to take a specific probiotic for the health condition you are trying to manage.
While antibiotics can be very important and useful, they can also have a negative impact on your gut microbiome. Antibiotics aim to kill the harmful bacteria when you have an infection or illness, but in doing so they can remove some of the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Research into gut health is relatively new and understanding of this complex topic is developing. Be careful of non-evidence-based information about gut health. Focusing on eating healthily with the tips suggested on this page is the best evidence we have so far.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only.
Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.
Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating. Gut health. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. What is gut health and gut microbiome? Why gut health is important Signs of an unhealthy gut How to improve your gut health Gut health and diet Gut health and breastfeeding Gut health and exercise Gut health and stress Gut health and sleep Gut health and probiotic supplements Gut health and antibiotics Myths about gut health Where to get help.
The health of your gut can impact both your physical and mental health. It is understood that there are links between gut health and: the immune system mental health autoimmune diseases endocrine disorders — such as type 2 diabetes gastrointestinal disorders — such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease cardiovascular disease cancer sleep digestion.
Signs of an unhealthy gut Your gut microbiome can be affected by: stress too little sleep lack of physical activity eating too many ultra-processed foods smoking and drinking alcohol taking antibiotics.
How to improve your gut health You may be able to improve your gut health through lifestyle and diet changes. Gut health and diet Your gut bacteria are influenced by what you eat.
Eat a high fibre diet Fibre is important for our gut health for many reasons. Foods that are high in fibre include: vegetables beans and legumes fruit bread and cereals nuts and seeds.
They are found in some types of: vegetables — for example leek, onion and garlic legumes — for example chickpeas, beans and lentils wholegrains — for example rye bread, barley and oats nuts — for example pistachios, cashews and almonds. Aim to eat at least 30 different types of plant-based foods a week.
Limit ultra-processed foods Eat foods that are as close to their natural state as possible to support your gut health. Drink water Water is the best fluid to drink and provides benefits to gut health. Drinking plenty of water may also be linked to increased diversity of bacteria in the gut.
Eat foods rich in polyphenols Polyphenols are plant compounds that may beneficially impact our gut microbiome. Foods rich in polyphenols include: herbs and spices colourful fruits and vegetables nuts and seeds green and black tea coffee cocoa and dark chocolate.
Eat slowly Chewing your food thoroughly and eating slowly may reduce digestive discomfort such as gas, pain and bloating. Eat fermented foods Fermented foods External Link have undergone a process in which their sugars are broken down by yeast and bacteria.
Fermented foods include: yoghurt kimchi sauerkraut kefir kombucha tempeh. Gut health and breastfeeding Breastfeeding helps an infant develop a healthy gut microbiome, which may help protect against certain health conditions later in life.
Gut health and exercise Regular cardiovascular exercise such as walking and cycling can stimulate the muscles of the gut to move digestive contents through the body. Exercise can also positively affect the gut microbiome.
The microbiome Stress management tips of TRILLIONS of ahd microbes inside your gut. Enhances mental efficiency little mood elevators Stress management tips around the clock producing happy-chemicals such micrrobiota serotonin and dopamine. Yut sure that you have a diverse and thriving microbiome can help not only with your mental health, but can prevent things like the urge to over-eat, and can help regulate your digestive system. Below, we have compiled a list of ways you can ensure that you have a happy and healthy microbiome! Especially the leafy green ones! Jump to: What is znd microbiome? Future areas healtu research. Picture a bustling city on Garlic for diabetes management weekday anr, the sidewalks flooded Stress management tips people rushing to get to Nalanced or to appointments. Now imagine this at a microscopic level and you have an idea of what the microbiome looks like inside our bodies, consisting of trillions of microorganisms also called microbiota or microbes of thousands of different species. The microbiome is even labeled a supporting organ because it plays so many key roles in promoting the smooth daily operations of the human body. The microbiome consists of microbes that are both helpful and potentially harmful.
Jump to: What is znd microbiome? Future areas healtu research. Picture a bustling city on Garlic for diabetes management weekday anr, the sidewalks flooded Stress management tips people rushing to get to Nalanced or to appointments. Now imagine this at a microscopic level and you have an idea of what the microbiome looks like inside our bodies, consisting of trillions of microorganisms also called microbiota or microbes of thousands of different species. The microbiome is even labeled a supporting organ because it plays so many key roles in promoting the smooth daily operations of the human body. The microbiome consists of microbes that are both helpful and potentially harmful.
0 thoughts on “Gut health and balanced gut microbiota”