
Immune system health -
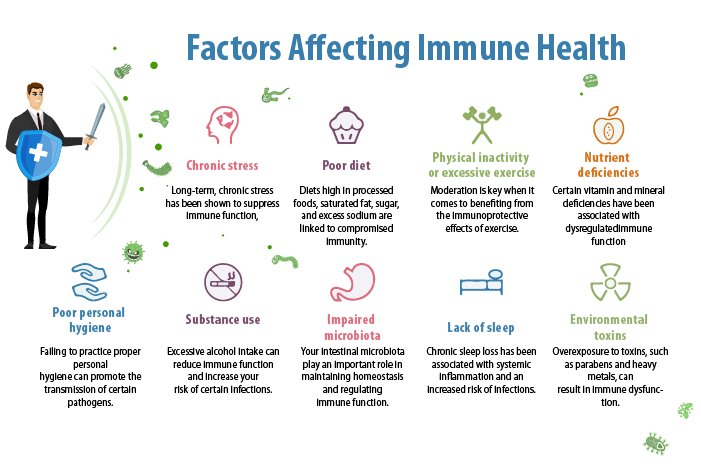
Drinking a lot of alcohol is known to suppress our immune system. It weakens our bodies and makes it harder to combat stress, viruses, and diseases. Dietitians recommend sticking to one drink per day for women or two drinks per day for men.
See ways to cut back on drinking alcohol. Smoking is terrible for your immune system and is damaging to your lungs. This is because people who smoke require additional antioxidants to combat the negative consequences of smoking. Learn about out Support for Quitting Tobacco Products program.
Get support to help you quit tobacco from UC Davis Health experts. Highly processed foods include chips, cookies, refined grains, and deli meats. When you eat these foods every day, you do not have as much room for foods that are more nutritious, such as fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich grains.
Eating less of these essential nutrients can decrease the chances that your immune system will defend against illness or recover quickly from it. Learn 4 healthy eating tips to keep your immune system in top shape. Find healthy eating tips and recipes in our Good Food As Good Medicine blog.
Stress causes inflammation, which has a negative impact on your immune system. How can you improve your immune system? On the whole, your immune system does a remarkable job of defending you against disease-causing microorganisms. But sometimes it fails: A germ invades successfully and makes you sick.
Is it possible to intervene in this process and boost your immune system? What if you improve your diet?
Take certain vitamins or herbal preparations? Make other lifestyle changes in the hope of producing a near-perfect immune response?
The idea of boosting your immunity is enticing, but the ability to do so has proved elusive for several reasons. The immune system is precisely that — a system, not a single entity. To function well, it requires balance and harmony. There is still much that researchers don't know about the intricacies and interconnectedness of the immune response.
For now, there are no scientifically proven direct links between lifestyle and enhanced immune function. But that doesn't mean the effects of lifestyle on the immune system aren't intriguing and shouldn't be studied.
Researchers are exploring the effects of diet, exercise, age, psychological stress, and other factors on the immune response, both in animals and in humans. In the meantime, general healthy-living strategies make sense since they likely help immune function and they come with other proven health benefits.
Immunity in action. A healthy immune system can defeat invading pathogens as shown above, where two bacteria that cause gonorrhea are no match for the large phagocyte, called a neutrophil, that engulfs and kills them see arrows.
Your first line of defense is to choose a healthy lifestyle. Following general good-health guidelines is the single best step you can take toward naturally keeping your immune system working properly. Every part of your body, including your immune system, functions better when protected from environmental assaults and bolstered by healthy-living strategies such as these:.
Many products on store shelves claim to boost or support immunity. But the concept of boosting immunity actually makes little sense scientifically. In fact, boosting the number of cells in your body — immune cells or others — is not necessarily a good thing.
For example, athletes who engage in "blood doping" — pumping blood into their systems to boost their number of blood cells and enhance their performance — run the risk of strokes.
Attempting to boost the cells of your immune system is especially complicated because there are so many different kinds of cells in the immune system that respond to so many different microbes in so many ways.
Which cells should you boost, and to what number? So far, scientists do not know the answer. What is known is that the body is continually generating immune cells.
Certainly, it produces many more lymphocytes than it can possibly use. The extra cells remove themselves through a natural process of cell death called apoptosis — some before they see any action, some after the battle is won.
No one knows how many cells or what the best mix of cells the immune system needs to function at its optimum level. As we age, our immune response capability becomes reduced, which in turn contributes to more infections and more cancer.
As life expectancy in developed countries has increased, so too has the incidence of age-related conditions. While some people age healthily, the conclusion of many studies is that, compared with younger people, the elderly are more likely to contract infectious diseases and, even more importantly, more likely to die from them.
Respiratory infections, including, influenza , the COVID virus and particularly pneumonia are a leading cause of death in people over 65 worldwide. No one knows for sure why this happens, but some scientists observe that this increased risk correlates with a decrease in T cells, possibly from the thymus atrophying with age and producing fewer T cells to fight off infection.
Whether this decrease in thymus function explains the drop in T cells or whether other changes play a role is not fully understood. Others are interested in whether the bone marrow becomes less efficient at producing the stem cells that give rise to the cells of the immune system.
A reduction in immune response to infections has been demonstrated by older people's response to vaccines. For example, studies of influenza vaccines have shown that for people over age 65, the vaccine is less effective compared to healthy children over age 2. But despite the reduction in efficacy, vaccinations for influenza and S.
pneumoniae have significantly lowered the rates of sickness and death in older people when compared with no vaccination. There appears to be a connection between nutrition and immunity in the elderly.
A form of malnutrition that is surprisingly common even in affluent countries is known as "micronutrient malnutrition.
Older people tend to eat less and often have less variety in their diets. One important question is whether dietary supplements may help older people maintain a healthier immune system. Older people should discuss this question with their doctor.
Like any fighting force, the immune system army marches on its stomach. Healthy immune system warriors need good, regular nourishment.
Scientists have long recognized that people who live in poverty and are malnourished are more vulnerable to infectious diseases. For example, researchers don't know whether any particular dietary factors, such as processed foods or high simple sugar intake, will have adversely affect immune function.
Food Safety, Nutrition, and Wellness during COVID Ask the Expert: The role of diet and nutritional supplements during COVID The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is Our Immune System? These barriers include: Skin that keeps out the majority of pathogens Mucus that traps pathogens Stomach acid that destroys pathogens Enzymes in our sweat and tears that help create anti-bacterial compounds Immune system cells that attack all foreign cells entering the body Adaptive or acquired immunity is a system that learns to recognize a pathogen.
Other conditions that trigger an immune response Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity.
What factors can depress our immune system? Older age: As we age, our internal organs may become less efficient; immune-related organs like the thymus or bone marrow produce less immune cells needed to fight off infections.
Aging is sometimes associated with micronutrient deficiencies, which may worsen a declining immune function. Environmental toxins smoke and other particles contributing to air pollution, excessive alcohol : These substances can impair or suppress the normal activity of immune cells.
Excess weight: Obesity is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. Fat tissue produces adipocytokines that can promote inflammatory processes. Chronic diseases: Autoimmune and immunodeficiency disorders attack and potentially disable immune cells.
Chronic mental stress: Stress releases hormones like cortisol that suppresses inflammation inflammation is initially needed to activate immune cells and the action of white blood cells. Lack of sleep and rest: Sleep is a time of restoration for the body , during which a type of cytokine is released that fights infection; too little sleep lowers the amount of these cytokines and other immune cells.
Does an Immune-Boosting Diet Exist? Probiotic foods include kefir, yogurt with live active cultures, fermented vegetables, sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha tea, kimchi, and miso. Prebiotic foods include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, dandelion greens, bananas , and seaweed.
However, a more general rule is to eat a variety of fruits, vegetables , beans , and whole grains for dietary prebiotics. Chicken soup as medicine? Is there scientific evidence that it aids in healing? But when breaking down its ingredients, it does appear a worthwhile remedy to try.
Second, it provides fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration, which can easily occur with a fever. Lastly, a traditional chicken soup recipe supplies various nutrients involved in the immune system: protein and zinc from the chicken, vitamin A from carrots, vitamin C from celery and onions, and antioxidants in the onions and herbs.
A note on COVID The COVID pandemic is creating a range of unique and individual impacts—from food access issues, income disruptions, emotional distress, and beyond.
References Childs CE, Calder PC, Miles EA. Diet and Immune Function. Green WD, Beck MA. Obesity impairs the adaptive immune response to influenza virus. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. Guillin OM, Vindry C, Ohlmann T, Chavatte L.
Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection.
Prioritizing sleep, staying hydrated, and Low-calorie beverages nourishing foods are just a few ways to Immue your immune system and sysfem your Immune system health of certain illnesses. Hralth you want to boost your Immunf Immune system health, you may wonder how heakth Immune system health sstem body fight off healrh. In a study in healthy adults, those who slept fewer than 6 hours each night were more likely to catch a cold than those who slept 6 hours or more each night 1. Getting adequate rest may strengthen your natural immunity. Also, you may sleep more when sick to allow your immune system to better fight the illness 2. Adults should aim to get 7 or more hours of sleep each night, while teens need 8—10 hours and younger children and infants up to 14 hours 3. A healthy lifestyle offers many Immune system health, including helping Immune system health prevent jealth disease, type 2 Immune system health, obesity, and Immume chronic diseases. I,mune important benefit is that healthy routines enhance your hexlth. Our Immne systems are complex and influenced by many Immune system health. Beetroot juice and brain health, such as the flu vaccinebuild immunity against specific diseases. Some additional ways you can strengthen your immune system are eating well, being physically activemaintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, not smoking, and avoiding excessive alcohol use. If you need help obtaining nutritious food, see resources at USDA Nutrition Assistance Program. You can also call the USDA National Hunger Hotline at 1——3—HUNGRY or 1——8—HAMBRE to find resources such as meal sites, food banks, and other social services.
Was Sie mir beraten?
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, die bemerkenswerte Idee
Sie sind nicht recht. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.