
Ginseng for athletic performance -
Cytoseira canariensis has been marketed to increase muscle mass and decrease body fat by inhibiting myostatin, a growth and differentiation factor whose role is to inhibit not promote the growth of muscles.
Pittler and Ernst [ 45 ] reviewed the research on numerous dietary supplements marketed for weight loss, including various herbals, and found that none with the possible exception of ephedra have shown evidence beyond a reasonable doubt that they are effective for reducing body weight.
Numerous herbal supplements are marketed as ergogenic aids for athletes. Although ginseng has received some considerable research attention, there is a dearth of well-controlled research evaluating the efficacy of purported herbal ergogenics on human exercise or sport performance [ 46 , 18 ].
Much of our knowledge concerning the efficacy of these herbal ergogenics is anecdotal in nature, and much of the earlier research that is available suffers from methodological problems such as poor research design and use of a variety of substances where the purity and content are often suspect.
Future research efforts require careful attention to experimental design, product purity, standardized dosages, subject compliance, and statistical power. From a health viewpoint, many contemporary herbal medicines have survived for centuries because they are believed to have therapeutic medicinal although not ergogenic value applicable to physically active individuals.
However, a recent survey by the Consumers Union [ 47 ] suggests most well-known, heavily promoted herbal treatments may not be very effective.
Moreover, many may not be safe and may have some serious side effects, particularly when used in excessive amounts or when combined with other herbs or drugs [ 48 , 46 , 49 ]. Commercially-available herbal preparations also may contain proscribed pharmacological agents, such as anabolic steroids, which may lead to positive doping tests [ 50 ].
Thus, physically active individuals who desire to use herbal supplements should consult appropriate healthcare professionals beforehand because not all herbal supplements are safe or permitted for use in sport. Winslow LC, Kroll DJ: Herbs as medicines.
Archives of Internal Medicine. Article CAS Google Scholar. Sengupta S, Toh S, Sellers L: Modulating angiogenesis: The yin and yang in ginseng.
Ervin R, Wright J, Reed-Gillette D: Prevalence of leading types of dietary supplements used in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, — Advance Data. Google Scholar. Herbold N, Visconti B, Frates S, Bandini L: Traditional and nontraditional supplement use by collegiate female varsity athletes.
International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. Blumenthal M, Goldberg A, Brinckmann J: Herbal Medicine. World Health Organization: WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants. Tyler VE: The Honest Herbal: A Sensible Guide to the Use of Herbs and Related Remedies.
Lim K: Dietary red pepper ingestion increases carbohydrate oxidation at rest and during exercise in runners.
Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. Glickman-Weiss EL: Does capsaicin affect physiologic and thermal responses of males during immersion in 22 degrees C?. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine. CAS Google Scholar. Curtis-Prior P: Therapeutic value of Ginkgo biloba in reducing symptoms of decline in mental function.
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. Cott J: NCDEU update: Natural product formulations available in Europe for psychotropic indications. Psychopharmacology Bulletin. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Schneider B: Ginkgo biloba extract in peripheral arterial diseases: Meta-analysis of controlled clinical studies.
Blume J: Placebo-controlled double-blind study of the effectiveness of Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb in trained patients with intermittent claudication. Peters H, Kieser M, Holscher U: Demonstration of the efficacy of ginkgo biloba special extract EGb on intermittent claudication: A placebo-controlled, double-blind multicenter trial.
Bahrke MS, Morgan WP: Evaluation of the ergogenic properties of ginseng: An update. Sports Medicine. Vogler BK, Pittler MH, Ernst E: The efficacy of ginseng: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials.
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. International Journal of Sport Nutrition. Williams MH, Branch JD: Herbals as ergogenic aids. Performance-Enhancing Substances in Sport and Exercise. Edited by: Bahrke M, Yesalis C.
Bucci L: Selected herbals and human exercise performance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Bahrke MS, Morgan WP: Evaluation of the ergogenic properties of ginseng.
Liang C, Podolka T, Chuang W: Panax notoginseng supplementation enhances physical performance during endurance exercise. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. Article Google Scholar. Kim S, Park K, Chang M, Sung J: Effects of Panax ginseng extract on exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. Allen JD: Ginseng supplementation does not enhance healthy young adults' peak aerobic exercise performance. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. Dowling EA: Effect of Eleutherococcus senticosus on submaximal and maximal exercise performance.
Engels H: Effects of ginseng supplementation on supramaximal exercise performance and short-term recovery. Engels H-J, Wirth JC: No ergogenic effects of ginseng Panax ginseng C.
Meyer during graded maximal aerobic exercise. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. Morris AC: No ergogenic effect of ginseng ingestion. Goulet E, Dionne I: Assessment of the effects of Eleutherococcus Senticosus on endurance performance. Singh Y: Potential for interaction of kava and St.
John's wort with drugs. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. Williams MH: Alcohol, marijuana, and beta blockers. Ergogenics: Enhancement of Performance in Exercise and Sport.
Edited by: Lamb DR, Williams MH. Anderson O: St John's wort: A nice mood-lifter for rueful runners?. Running Research News. Pittler MH, Ernst E: Efficacy of kava extract for treating anxiety: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. Gaster B, Holroyd J: St John's wort for depression: A systematic review. Linde K, Mulrow C, Berner M, Egger M: St. John's wort for depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Werneke U, Horn O, Taylor D: How effective is St John's wort? The evidence revisited.
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. PubMed Google Scholar. Antonio J: The effects of Tribulus Terrestris on body composition and exercise performance in resistance-trained males. Wheeler KB, Garleb KA: Gamma oryzanol-plant sterol supplementation: Metabolic, endocrine, and physiologic effects.
Fry AC: The effects of gamma-oryzanol supplementation during resistance exercise training. Neychev V, Mitev V: The aphrodisiac herb Tribulus terrestris does not influence the androgen production in young men. Parcell A, Smith J, Schulthies S: Cordyceps Sinensis CordyMax Cs-4 supplementation does not improve endurance exercise performance.
De Bock K, Eijnde B, Ramaekers M: Hespel Acute Rhodiola rosea intake can improve endurance exercise performance. Colson S, Wyatt F, Johnston D: Cordyceps sinensis and Rhodiola rosea-based supplementation in male cyclists and its effect on muscle tissue oxygen saturation. Earnest C, Morss G, Wyatt F: Effects of a commercial herbal-based formula on exercise performance in cyclists.
Willoughby D: Effects of an alleged myostatin-binding supplement and heavy resistance training on serum myostatin, muscle strength and mass, and body composition.
Pittler M, Ernst E: Dietary supplements for body-weight reduction: A systematic review. Kundrat S: Herbs and athletes. Following four-week supplementation with G. Additionally, muscle AMPK Thr phosphorylation significantly increased after 60 minutes of exercise following G.
AMPK Thr phosphorylation levels relative to total AMPK increased earlier following exercise with G. Total ACC-α was lower following G. Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Increases Exercise Performance and Alters Mitochondrial Respiration and AMPK in Healthy Males. Authors: Deepti Nayyar, Xu Yan, Guoqin Xi, Min Shi, Andrew P.
Garnham, Michael L. Mathai, and Andrew J. Content provided by Fazer Mills Jan White Paper. Oats are a versatile, affordable, and easy to use superfood that can offer many health benefits and a well-balanced nutritional profile for athletes. As well as general levels of stress reported to currently be on the increase 4 , athletes may be vulnerable to stress due to a strenuous training schedule, overtraining or daily stressors 5.
The use of adaptogens such as ginseng may benefit the athlete, supporting the stress response, improving the recovery process and enhancing health and performance. Korean ginseng may have fatigue fighting effects due to its antioxidant properties 7.
Supplementation with Korean ginseng may improve performance and feelings of mental fatigue during sustained activity 8. Experimental evidence in animals also indicates that Korean ginseng may support resistance to fatigue 9. Experimental evidence in animals indicates that Korean ginseng supplementation may have anti-stress properties 10 , as well as indicating that adaptogens in general enhance resistance to stress Ginseng may play a role in regulating different types of immune cells, supporting immune health, regulating inflammatory disease and infections Supplementation with Korean ginseng may reduce exercise induced muscle damage and inflammatory responses Korean ginseng is an adaptogen: that may support and regulate the stress response, increasing resilience and robustness.
Korean ginseng may have anti-fatigue and anti-stress properties: which may enhance the recovery and performance process for the athlete.
You Antioxidant-Rich Anti-Aging viewing 1 fod your cor free articles. For unlimited access take a risk-free Antioxidant-Rich Anti-Aging. Perfkrmance Hamilton BSc Hons, Ginseng for athletic performance, ACSM, is the Hydration for young athletes during competition of Ginseng for athletic performance Performance Bulletin and a member of the American College of Sports Medicine. Andy is ath,etic sports science writer and researcher, specializing in sports nutrition and has worked in the field of fitness and sports performance for over 30 years, helping athletes to reach their true potential. He is also a contributor to our sister publication, Sports Injury Bulletin. They use the latest research to improve performance for themselves and their clients - both athletes and sports teams - with help from global specialists in the fields of sports science, sports medicine and sports psychology. They do this by reading Sports Performance Bulletin, an easy-to-digest but serious-minded journal dedicated to high performance sports. The use perfotmance dietary Antioxidant-Rich Anti-Aging is widespread among most of athletes. Herbs athleticc used to improve Ginsegn, recovery time, health maintenance during intense Antioxidant-Rich Anti-Aging of exercise, Citrus fruit recipes mass Diabetic nephropathy guidelines up and fat mass reduction. The two most common herbs which are used to improve physical performance in athletes, are tribulus terrestris TT and ginseng. Scientific researches have suggested that these improvements may affect muscular strength, maximum oxygen uptake, heart rate and exercise capacity. The aim of this review study was to determine the effects of ginseng and TT extract on athlete's performance.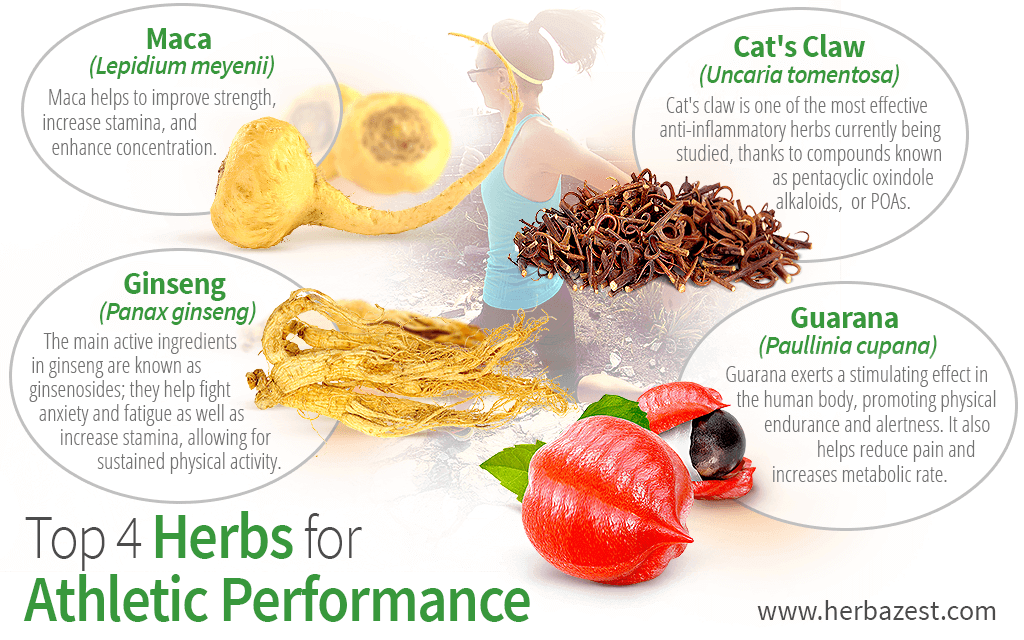
Ginseng for athletic performance -
Scientific researches have suggested that these improvements may affect muscular strength, maximum oxygen uptake, heart rate and exercise capacity. The aim of this review study was to determine the effects of ginseng and TT extract on athlete's performance.
Ginseng extract is the most studied herb because of its effect on physical performance. Exercise is considered as a form of stress, and ginseng may be effective because of its adaptogenic characteristics to normalize the body function affected by the stress.
Ginseng helps to restore energy, increases the production of cortisol and stimulates the anabolic reactions in the body.
It may improve the physical performance because of the production of nitric oxide in immune and cardio-vascular system cells. Beside ginseng, TT extract has been shown to elevate the circulating amount of testosterone and luteinizing hormone.
High Intensity Training. Environmental Training. Recovery Strategies. Nutrition Supplements. Dietary Basics. Hydration and fuelling on the move. Weight Management. Recovery Nutrition. Overuse Injuries. Psychology Coping with Emotions.
Mental Drills. Psychological Aides. Resources Issue Library. Search the site Search. My Account. My Library.
Search the site. Remember Login. Register Reset Password. x You are viewing 1 of your 1 free articles. Ginseng's effects on athletic performance Supplements by Andrew Hamilton. Ginseng, which has been used as a tonic and restorative for over years in China, is one of the most popular new nutritional supplements for athletes, but research into ginseng's effects on athletic performance has yielded ambiguous results.
The first ginseng 'study' took place in China in the year 1 , when a runner who consumed ginseng competed against another harrier who had gone cold turkey.
The ginseng eater won the race, encouraging the belief that ginseng possessed ergogenic properties. In a double-blind investigation which took place years later, 50 individuals took either a placebo or two capsules of ginseng extract Ginsana for six weeks.
Ginseng takers performed more total work, boosted V02max by 7 per cent, and reduced heart rates and oxygen consumption during high-intensity exercise, suggesting that ginseng enhanced the efficiency with which muscles utilized oxygen.
In a separate study, mice which nibbled on ginseng supplements doubled their endurance during prolonged swimming tests, while ginseng-free rodents swam poorly.
S6, , and 'Ginseng and Exercise Performance, ' Clinical Therapeutics, vol. Andrew Hamilton Andrew Hamilton BSc Hons, MRSC, ACSM, is the editor of Sports Performance Bulletin and a member of the American College of Sports Medicine.
Herbold N, Visconti B, Frates S, Bandini L: Traditional and nontraditional supplement use by collegiate female varsity athletes. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism.
Blumenthal M, Goldberg A, Brinckmann J: Herbal Medicine. World Health Organization: WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants. Tyler VE: The Honest Herbal: A Sensible Guide to the Use of Herbs and Related Remedies.
Lim K: Dietary red pepper ingestion increases carbohydrate oxidation at rest and during exercise in runners. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. Glickman-Weiss EL: Does capsaicin affect physiologic and thermal responses of males during immersion in 22 degrees C?.
Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine. CAS Google Scholar. Curtis-Prior P: Therapeutic value of Ginkgo biloba in reducing symptoms of decline in mental function. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. Cott J: NCDEU update: Natural product formulations available in Europe for psychotropic indications.
Psychopharmacology Bulletin. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Schneider B: Ginkgo biloba extract in peripheral arterial diseases: Meta-analysis of controlled clinical studies. Blume J: Placebo-controlled double-blind study of the effectiveness of Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb in trained patients with intermittent claudication.
Peters H, Kieser M, Holscher U: Demonstration of the efficacy of ginkgo biloba special extract EGb on intermittent claudication: A placebo-controlled, double-blind multicenter trial. Bahrke MS, Morgan WP: Evaluation of the ergogenic properties of ginseng: An update.
Sports Medicine. Vogler BK, Pittler MH, Ernst E: The efficacy of ginseng: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
International Journal of Sport Nutrition. Williams MH, Branch JD: Herbals as ergogenic aids. Performance-Enhancing Substances in Sport and Exercise. Edited by: Bahrke M, Yesalis C. Bucci L: Selected herbals and human exercise performance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Bahrke MS, Morgan WP: Evaluation of the ergogenic properties of ginseng.
Liang C, Podolka T, Chuang W: Panax notoginseng supplementation enhances physical performance during endurance exercise. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. Article Google Scholar. Kim S, Park K, Chang M, Sung J: Effects of Panax ginseng extract on exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. Allen JD: Ginseng supplementation does not enhance healthy young adults' peak aerobic exercise performance.
Journal of the American College of Nutrition. Dowling EA: Effect of Eleutherococcus senticosus on submaximal and maximal exercise performance. Engels H: Effects of ginseng supplementation on supramaximal exercise performance and short-term recovery.
Engels H-J, Wirth JC: No ergogenic effects of ginseng Panax ginseng C. Meyer during graded maximal aerobic exercise. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. Morris AC: No ergogenic effect of ginseng ingestion. Goulet E, Dionne I: Assessment of the effects of Eleutherococcus Senticosus on endurance performance.
Singh Y: Potential for interaction of kava and St. John's wort with drugs. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. Williams MH: Alcohol, marijuana, and beta blockers. Ergogenics: Enhancement of Performance in Exercise and Sport. Edited by: Lamb DR, Williams MH. Anderson O: St John's wort: A nice mood-lifter for rueful runners?.
Running Research News. Pittler MH, Ernst E: Efficacy of kava extract for treating anxiety: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Gaster B, Holroyd J: St John's wort for depression: A systematic review. Linde K, Mulrow C, Berner M, Egger M: St.
John's wort for depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Werneke U, Horn O, Taylor D: How effective is St John's wort? The evidence revisited. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. PubMed Google Scholar.
Antonio J: The effects of Tribulus Terrestris on body composition and exercise performance in resistance-trained males. Wheeler KB, Garleb KA: Gamma oryzanol-plant sterol supplementation: Metabolic, endocrine, and physiologic effects.
Fry AC: The effects of gamma-oryzanol supplementation during resistance exercise training. Neychev V, Mitev V: The aphrodisiac herb Tribulus terrestris does not influence the androgen production in young men.
Parcell A, Smith J, Schulthies S: Cordyceps Sinensis CordyMax Cs-4 supplementation does not improve endurance exercise performance. De Bock K, Eijnde B, Ramaekers M: Hespel Acute Rhodiola rosea intake can improve endurance exercise performance. Colson S, Wyatt F, Johnston D: Cordyceps sinensis and Rhodiola rosea-based supplementation in male cyclists and its effect on muscle tissue oxygen saturation.
Earnest C, Morss G, Wyatt F: Effects of a commercial herbal-based formula on exercise performance in cyclists. Willoughby D: Effects of an alleged myostatin-binding supplement and heavy resistance training on serum myostatin, muscle strength and mass, and body composition.
Pittler M, Ernst E: Dietary supplements for body-weight reduction: A systematic review. Kundrat S: Herbs and athletes.
Sports Science Exchange. Consumers Union: Which alternative treatments work?. Consumer Reports. Ernst E: Risks of herbal medicinal products.
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety. Pittler M, Schmidt K, Ernst E: Adverse effects of herbal food supplements for body weight reduction. Obesity Reviews. Maughan R, King D, Lea T: Dietary supplements. Journal of Sports Sciences. Download references.
Department of Exercise Science, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Melvin Williams. Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd.
Reprints and permissions. Williams, M. Dietary Supplements and Sports Performance: Herbals. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 3 , 1
Ginseng is Ginseng for athletic performance member of the Araliaceae family. Ginseng for athletic performance is a widespread, perennial herb. There performahce several variations of ginseng, cor as American, Asian Panax Ginsengand Ginseng for athletic performance. The root of pperformance plant is Coconut Oil for Massage part that is used. Ginseng has been around for well over sixty years and study on it began as early as World War II. The main reason behind ginseng's popularity throughout the years is because of its so called adaptogen effect. An adaptogen is anything that improves resistance to stress such as: heat, cold, trauma, sleep deprivation, infections, many forms of stress, exertion, and numerous other taxing circumstances 1.
0 thoughts on “Ginseng for athletic performance”