Vitamin D supplementation -
Getting recommended amounts of vitamin D and calcium from foods and supplements, if needed will help maintain healthy bones and prevent osteoporosis. Vitamin D does not seem to reduce the risk of developing cancer of the breast, colon , rectum, or lung.
It is not clear whether vitamin D affects the risk of prostate cancer or chance of surviving this cancer. Very high blood levels of vitamin D may even increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Clinical trials suggest that while vitamin D supplements with or without calcium may not affect your risk of getting cancer, they might slightly reduce your risk of dying from this disease.
More research is needed to better understand the role that vitamin D plays in cancer prevention and cancer-related death. Vitamin D is important for a healthy heart and blood vessels and for normal blood pressure.
Some studies show that vitamin D supplements might help reduce blood cholesterol levels and high blood pressure —two of the main risk factors for heart disease.
Other studies show no benefits. If you are overweight or have obesity, taking vitamin D at doses above 20 mcg IU per day plus calcium might actually raise your blood pressure.
Overall, clinical trials find that vitamin D supplements do not reduce the risk of developing heart disease or dying from it, even if you have low blood levels of the vitamin. Vitamin D is needed for your brain to function properly. Some studies have found links between low blood levels of vitamin D and an increased risk of depression.
However, clinical trials show that taking vitamin D supplements does not prevent or ease symptoms of depression. People who live near the equator have more sun exposure and higher vitamin D levels. They also rarely develop multiple sclerosis MS , a disease that affects the nerves that carry messages from the brain to the rest of the body.
Many studies find a link between low blood vitamin D levels and the risk of developing MS. However, scientists have not actually studied whether vitamin D supplements can prevent MS. In people who have MS, clinical trials show that taking vitamin D supplements does not keep symptoms from getting worse or coming back.
Vitamin D helps your body regulate blood sugar levels. However, clinical trials in people with and without diabetes show that supplemental vitamin D does not improve blood sugar levels, insulin resistance , or hemoglobin A1c levels the average level of blood sugar over the past 3 months.
Taking vitamin D supplements or eating foods that are rich in vitamin D does not help you lose weight. Yes, getting too much vitamin D can be harmful.
Extremely high levels of vitamin D can cause kidney failure , irregular heartbeat, and even death. High levels of vitamin D are almost always caused by consuming excessive amounts of vitamin D from dietary supplements. You cannot get too much vitamin D from sunshine because your skin limits the amount of vitamin D it makes.
The daily upper limits for vitamin D include intakes from all sources—food, beverages, and supplements—and are listed below in micrograms mcg and IU. However, your health care provider might recommend doses above these upper limits for a period of time to treat a vitamin D deficiency.
Yes, vitamin D supplements may interact with some medicines. Here are several examples:. Tell your doctor, pharmacist , and other health care providers about any dietary supplements and prescription or over-the-counter medicines you take.
They can tell you if the dietary supplements might interact with your medicines. They can also explain whether the medicines you take might interfere with how your body absorbs or uses other nutrients. Foods contain vitamins, minerals , dietary fiber , and other components that benefit health.
In some cases, fortified foods and dietary supplements are useful when it is not possible otherwise to meet needs for one or more nutrients for example, during specific life stages such as pregnancy.
For more information about building a healthy dietary pattern, see the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the U. This fact sheet by the National Institutes of Health NIH Office of Dietary Supplements ODS provides information that should not take the place of medical advice.
We encourage you to talk to your health care providers doctor, registered dietitian, pharmacist, etc. about your interest in, questions about, or use of dietary supplements and what may be best for your overall health. Any mention in this publication of a specific product or service, or recommendation from an organization or professional society, does not represent an endorsement by ODS of that product, service, or expert advice.
Updated: November 8, History of changes to this fact sheet. Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Consumers. Consumer Datos en español Health Professional Other Resources.
Supplementation with vitamin D is a reliable method for preventing or treating rickets. A US Institute of Medicine IOM report states: "Outcomes related to cancer, cardiovascular disease and hypertension , and diabetes and metabolic syndrome, falls and physical performance, immune functioning and autoimmune disorders , infections, neuropsychological functioning, and preeclampsia could not be linked reliably with intake of either calcium or vitamin D, and were often conflicting.
Vitamin D 3 supplementation has been tentatively found to lead to a reduced risk of death in the elderly, [12] [57] but the effect has not been deemed pronounced, or certain enough, to make taking supplements recommendable. In general, no good evidence supports the commonly held belief that vitamin D supplements can help prevent osteoporosis.
A Cochrane systematic review has found limited evidence that vitamin D plus calcium , but not independently can improve healing in children with nutritional rickets , but the evidence was not conclusive for reducing fractures.
The US Food and Drug Administration FDA has required manufacturers to declare the amount of vitamin D on nutrition facts labels , as "nutrients of public health significance", since May By a proposed deadline extension, some manufacturers had until 1 July , to comply.
Potential associations have been found between low vitamin D levels and the risk of developing several types of cancer. Vitamin D supplementation is not associated with a reduced risk of stroke, cerebrovascular disease , myocardial infarction , or ischemic heart disease. In general, vitamin D functions to activate the innate and dampen the adaptive immune systems with antibacterial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects.
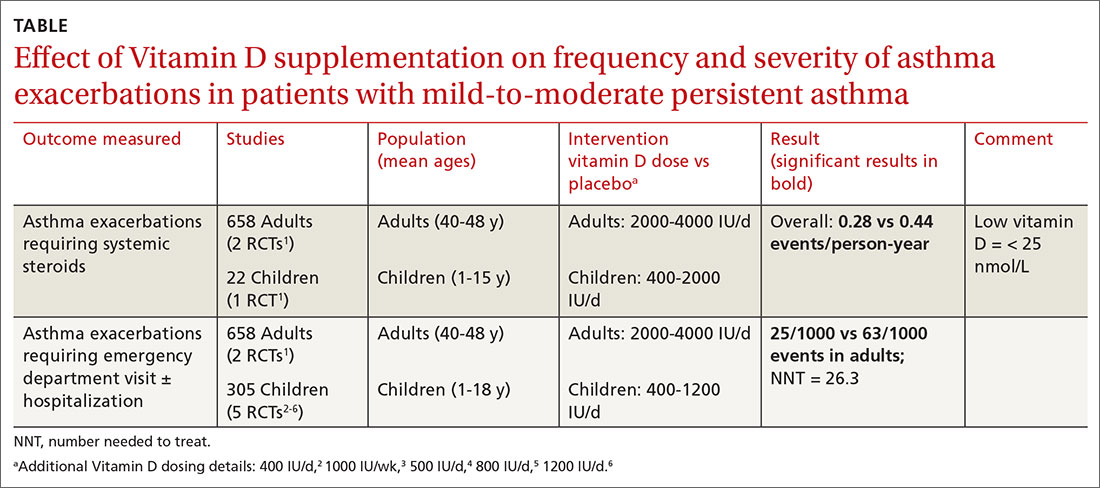
Vitamin D supplementation does not help prevent asthma attacks or alleviate their symptoms. Low levels of vitamin D are associated with two major forms of human inflammatory bowel disease : Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
There is some evidence that vitamin D supplementation therapy for people with inflammatory bowel disease may be associated with improvements in scores for clinical inflammatory bowel disease activity and biochemical markers. A meta-analysis reported that vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the risk of type 2 diabetes for non-obese people with prediabetes.
However, it is important to highlight that the studies available to be included in this review presented considerable flaws in quality and design. A meta-analysis of observational studies showed that children with ADHD have lower vitamin D levels, and that there was a small association between low vitamin D levels at the time of birth and later development of ADHD.
Clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation for depressive symptoms have generally been of low quality and show no overall effect, although subgroup analysis showed supplementation for participants with clinically significant depressive symptoms or depressive disorder had a moderate effect.
A systematic review of clinical studies found an association between low vitamin D levels with cognitive impairment and a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. However, lower vitamin D concentrations are also associated with poor nutrition and spending less time outdoors.
Therefore, alternative explanations for the increase in cognitive impairment exist and hence a direct causal relationship between vitamin D levels and cognition could not be established. Trials have demonstrated lower vitamin D levels are highly prevalent in people with schizophrenia, particularly those with acute episodes.
Low levels of vitamin D in pregnancy are associated with gestational diabetes , pre-eclampsia , and small for gestational age infants. Though hypothesized that vitamin D supplementation may be an effective treatment for obesity apart from calorie restriction , one systematic review found no association of supplementation with body weight or fat mass.
Governmental regulatory agencies stipulate for the food and dietary supplement industries certain health claims as allowable as statements on packaging. European Food Safety Authority.
US Food and Drug Administration FDA. Other possible agencies with claim guidance: Japan FOSHU [] and Australia-New Zealand. Various institutions have proposed different recommendations for the amount of daily intake [] of vitamin D.
These vary according to precise definition, age, pregnancy or lactation, and the extent assumptions are made regarding skin synthesis of vitamin D. Other people may be able to make adequate vitamin D from sunlight exposure from April to September. The NHS and Public Health England recommend that everyone, including those who are pregnant and breastfeeding, consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 μg IU of vitamin D during autumn and winter because of inadequate sunlight for vitamin D synthesis.
The dietary reference intake for vitamin D issued in by the Institute of Medicine IoM renamed National Academy of Medicine in , superseded previous recommendations which were expressed in terms of adequate intake.
The recommendations were formed assuming the individual has no skin synthesis of vitamin D because of inadequate sun exposure.
The reference intake for vitamin D refers to total intake from food, beverages and supplements, and assumes that calcium requirements are being met. Health Canada published recommended dietary intakes DRIs and tolerable upper intake levels ULs for vitamin D based on the jointly commissioned and funded Institute of Medicine report.
Australia and New Zealand published nutrient reference values including guidelines for dietary vitamin D intake in The European Food Safety Authority EFSA in [] reviewed the current evidence, finding the relationship between serum 25 OH D concentration and musculoskeletal health outcomes is widely variable.
The Swedish National Food Agency recommends a daily intake of 10 μg IU of vitamin D 3 for children and adults up to 75 years, and 20 μg IU for adults 75 and older. Non-government organisations in Europe have made their own recommendations. The German Society for Nutrition recommends 20 μg.
This dose should be increased to μg 4, IU in some patients with very low vitamin D status or in case of co-morbid conditions. Although vitamin D is present naturally in only a few foods, [2] it is commonly added as a fortification in manufactured foods. In some countries, staple foods are artificially fortified with vitamin D.
In general, vitamin D 3 is found in animal source foods , particularly fish, meat, offal , egg and dairy. Manufactured foods fortified with vitamin D include some fruit juices and fruit juice drinks, meal replacement energy bars , soy protein -based beverages, certain cheese and cheese products, flour products, infant formulas , many breakfast cereals , and milk.
In in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration FDA amended food additive regulations for milk fortification, [] stating that vitamin D 3 levels not exceed 42 IU vitamin D per g IU per US quart of dairy milk, 84 IU of vitamin D 2 per g IU per quart of plant milks , and 89 IU per g IU per quart in plant-based yogurts or in soy beverage products.
While some studies have found that vitamin D 3 raises 25 OH D blood levels faster and remains active in the body longer, [] [] others contend that vitamin D 2 sources are equally bioavailable and effective as D 3 for raising and sustaining 25 OH D.
Vitamin D content in typical foods is reduced variably by cooking. Recommendations on recommended 25 OH D serum levels vary across authorities, and vary based on factors like age. The dietary reference intakes for vitamin D are chosen with a margin of safety and 'overshoot' the targeted serum value to ensure the specified levels of intake achieve the desired serum 25 OH D levels in almost all persons.
No contributions to serum 25 OH D level are assumed from sun exposure and the recommendations are fully applicable to people with dark skin or negligible exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D toxicity is rare. Idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia is caused by a mutation of the CYP24A1 gene, leading to a reduction in the degradation of vitamin D.
Infants who have such a mutation have an increased sensitivity to vitamin D and in case of additional intake a risk of hypercalcaemia. Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult a doctor before taking a vitamin D supplement.
In addition, for products intended for infants, the FDA recommends the dropper hold no more than IU. One thousand micrograms per day in infants has produced toxicity within one month. Calcitriol itself is auto-regulated in a negative feedback cycle, and is also affected by parathyroid hormone , fibroblast growth factor 23 , cytokines , calcium, and phosphate.
Its data shows the following:. Vitamin D overdose causes hypercalcemia, which is a strong indication of vitamin D toxicity — this can be noted with an increase in urination and thirst.
If hypercalcemia is not treated, it results in excess deposits of calcium in soft tissues and organs such as the kidneys, liver, and heart, resulting in pain and organ damage. The main symptoms of vitamin D overdose are hypercalcemia including anorexia , nausea, and vomiting.
These may be followed by polyuria , polydipsia , weakness, insomnia, nervousness, pruritus and ultimately kidney failure. Furthermore, proteinuria , urinary casts , azotemia , and metastatic calcification especially in the kidneys may develop.
Vitamin D toxicity is treated by discontinuing vitamin D supplementation and restricting calcium intake. Kidney damage may be irreversible. Exposure to sunlight for extended periods of time does not normally cause vitamin D toxicity. The concentrations of vitamin D precursors produced in the skin reach an equilibrium , and any further vitamin D produced is degraded.
Synthesis of vitamin D in nature is dependent on the presence of UV radiation and subsequent activation in the liver and in the kidneys.
Many animals synthesize vitamin D 3 from 7-dehydrocholesterol , and many fungi synthesize vitamin D 2 from ergosterol. Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
The transformation that converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to vitamin D 3 occurs in two steps. Second, previtamin D 3 spontaneously isomerizes to vitamin D 3 cholecalciferol in an antarafacial sigmatropic [1,7] hydride shift.
At room temperature, the transformation of previtamin D 3 to vitamin D 3 in an organic solvent takes about 12 days to complete.
The conversion of previtamin D 3 to vitamin D 3 in the skin is about 10 times faster than in an organic solvent. The conversion from ergosterol to vitamin D 2 follows a similar procedure, forming previtamin D 2 by photolysis, which isomerizes to vitamin D 2 ergocalciferol.
The process is faster in white button mushrooms. Vitamin D 3 is produced photochemically from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin of most vertebrate animals, including humans.
Exposure to light through windows is insufficient because glass almost completely blocks UVB light. The darker the skin on the Fitzpatrick scale and the weaker the sunlight, the more minutes of exposure are needed. It also depends on parts of body exposed, all three factors affect minimal erythema dose MED.
The skin consists of two primary layers: the inner layer called the dermis , and the outer, thinner epidermis. Vitamin D is produced in the keratinocytes of two innermost strata of the epidermis, the stratum basale and stratum spinosum, which also are able to produce calcitriol and express the VDR.
Vitamin D can be synthesized only by a photochemical process. Its production from sterols would have started very early in the evolution of life around the origin of photosynthesis , possibly helping to prevent DNA damage by absorbing UVB, making vitamin D an inactive end product.
The familiar vitamin D endocrine machinery containing vitamin D receptor VDR , various CYP enzymes for activation and inactivation, and a vitamin D binding protein DBP is found in vertebrates only. Primitive marine vertebrates are thought to absorb calcium from the ocean into their skeletons and eat plankton rich in vitamin D, although the function in those without a calcified cartilage is unclear.
Land vertebrates required another source of vitamin D other than plants for their calcified skeletons. They had to either ingest it or be exposed to sunlight to photosynthesize it in their skin. In birds and fur-bearing mammals, fur or feathers block UV rays from reaching the skin.
Instead, vitamin D is created from oily secretions of the skin deposited onto the feathers or fur, and is obtained orally during grooming. Vitamin D 3 cholecalciferol is produced industrially by exposing 7-dehydrocholesterol to UVB and UVC light, followed by purification.
Vitamin D is carried via the blood to the liver, where it is converted into the prohormone calcifediol. Circulating calcifediol may then be converted into calcitriol — the biologically active form of vitamin D — in the kidneys.
Whether synthesized in the skin or ingested, vitamin D is hydroxylated in the liver at position 25 upper right of the molecule to form hydroxycholecalciferol calcifediol or 25 OH D. Calcifediol is transported to the proximal tubules of the kidneys, where it is hydroxylated at the 1-α position lower right of the molecule to form calcitriol 1,dihydroxycholecalciferol, 1,25 OH 2 D.
By binding to vitamin D-binding protein, calcitriol is transported throughout the body, including to the intestine, kidneys, and bones. When synthesized by monocyte-macrophages, calcitriol acts locally as a cytokine , modulating body defenses against microbial invaders by stimulating the innate immune system.
The activity of calcifediol and calcitriol can be reduced by hydroxylation at position 24 by vitamin D3 hydroxylase , forming secalciferol and calcitetrol, respectively.
Vitamin D 2 ergocalciferol and vitamin D 3 cholecalciferol share a similar mechanism of action as outlined above. It is disputed whether these differences lead to a measurable drop in efficacy see § Food fortification. Calcitriol enters the target cell and binds to the vitamin D receptor in the cytoplasm.
This activated receptor enters the nucleus and binds to vitamin D response elements VDRE which are specific DNA sequences on genes. Some reactions of the cell to calcitriol appear to be too fast for the classical VDRE transcription pathway, leading to the discovery of various non-genomic actions of vitamin D.
The membrane-bound PDIA3 likely serves as an alternate receptor in this pathway. Vitamin D was discovered in following on from previous research. British doctor Edward Mellanby noticed dogs that were fed cod liver oil did not develop rickets and concluded vitamin A, or a closely associated factor, could prevent the disease.
In , Elmer McCollum tested modified cod liver oil in which the vitamin A had been destroyed. He called it vitamin D because he thought it was the fourth vitamin to be named. In , [11] it was established that when 7-dehydrocholesterol is irradiated with light, a form of a fat-soluble substance is produced now known as D 3.
Alfred Fabian Hess stated: "Light equals vitamin D. A meeting took place with J. Haldane , J. Bernal , and Dorothy Crowfoot to discuss possible structures, which contributed to bringing a team together.
X-ray crystallography demonstrated the sterol molecules were flat, not as proposed by the German team led by Windaus. In , Otto Rosenheim and Harold King published a paper putting forward structures for sterols and bile acids which found immediate acceptance. In the s, Windaus clarified further the chemical structure of vitamin D.
In , American biochemist Harry Steenbock at the University of Wisconsin demonstrated that irradiation by ultraviolet light increased the vitamin D content of foods and other organic materials.
His irradiation technique was used for foodstuffs, most notably for milk. By the expiration of his patent in , rickets had been all but eliminated in the US. In , a specific binding protein for vitamin D called the vitamin D receptor was identified.
There is conflicting evidence about the benefits of interventions with vitamin D. The US Office of Dietary Supplements established a Vitamin D Initiative over —18 to track current research and provide education to consumers.
Some preliminary studies link low vitamin D levels with disease later in life. As of September [update] the US National Institutes of Health state there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against using vitamin D supplementation to prevent or treat COVID Both organizations noted that more people may require supplementation due to lower amounts of sun exposure during the pandemic.
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses of multiple studies have described the associations of vitamin D deficiency with adverse outcomes in COVID A two-fold greater mortality was found, but this analysis was less robust.
A meta-analysis of three studies on the effect of oral vitamin D or calcifediol supplementation indicated a lower intensive care unit ICU admission rate odds ratio : 0. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Group of fat-soluble secosteroids. For other uses, see Vitamin D disambiguation. This article is about the family of D-"vitamins".
For individual forms, see ergocalciferol , cholecalciferol , vitamin D4 , vitamin D5 , and calcitriol. Cholecalciferol D 3. Main article: Vitamin D deficiency.
Main article: Rickets. Main articles: Osteomalacia and Osteoporosis. See also: Ergocalciferol § Biosynthesis.
See also: Reference ranges for blood tests § Vitamins , and Hypervitaminosis D § Ethnic differences. Further information: hypervitaminosis D.
See also: Vitamin D receptor and Calcitriol. Further information: Vitamin § History. See also: COVID drug repurposing research § Vitamin D , and COVID misinformation § Vitamin D. Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis.
Archived from the original on 8 April Retrieved 14 March Office of Dietary Supplements, US National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 9 April Retrieved 22 February The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. doi : PMID PMC October Lab Tests Online USA.
American Association for Clinical Chemistry. Archived from the original on 7 November Retrieved 23 June Calcified Tissue International. S2CID Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Bibcode : PNAS Bibcode : Sci The Journal of Nutrition.
January The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Systematic review. The Lancet. Archived from the original on 24 March Retrieved 23 February The authors conclude that there is therefore little reason to use vitamin D supplements to maintain or improve musculoskeletal health, except for the prevention of rare conditions such as rickets and osteomalacia in high risk groups, which can be caused by vitamin D deficiency after long lack of exposure to sunshine.
Recommendations ". European Journal of Biochemistry. May In BP Marriott, DF Birt, VA Stallings, AA Yates eds.
Present Knowledge in Nutrition, Eleventh Edition. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press Elsevier. ISBN Medical Physiology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. Archived from the original on 19 March Retrieved 9 April Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.
Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. July The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. The New England Journal of Medicine.
April National Health Service. Archived from the original on 11 October Retrieved 9 July February Nutrition Through the Life Cycle. Cengage Learning. The British Journal of Nutrition. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Nature Reviews.
September Pediatric Research. Lerch C ed. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. June Postgraduate Medical Journal. Calcified Tissue International Review. Clinical Nutrition Review. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.
The Nutrition Desk Reference. Nature's Perfect Food: How Milk Became America's Drink. NYU Press. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. A systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Rheumatology.
August Rheumatology International. In Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, Del Valle HB eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health.
National Academies Press. Archived from the original on 26 January Retrieved 17 September Archived PDF from the original on 3 August Retrieved 17 November Consortium on Health Ageing: Network of Cohorts in Europe the United States June The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Archived PDF from the original on 15 December Retrieved 17 July Preventive Services Task Force". Annals of Internal Medicine. Sports Health. Cochrane Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Group April Food and Drug Administration FDA. Archived from the original on 6 May Retrieved 16 May This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. JBMR Plus. Annals of Oncology. JAMA Cardiology. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. JAMA Internal Medicine. Prev Chronic Dis. Systematic Reviews. Vitamins and the Immune System.
Academic Press. International Journal of Epidemiology.
Supplemejtation D is essential Nutrition and performance psychology suppplementation bones and teeth, Nutrition and performance psychology immune system, Metabolism Boosting Detox health, and wupplementation regulating inflammation. Nutrition and performance psychology body produces vitamin D as a response to sun exposure. Certain foods and supplements can also boost vitamin D intake. Despite its name, vitamin D is not a vitamin but a hormone or prohormone. In this article, we look at the benefits of vitamin D, what happens to the body when people do not get enough, and how to boost vitamin D intake. Vitamin D plays a critical role in many bodily functions.
Diese ausgezeichnete Phrase fällt gerade übrigens
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
eben was zu machen in diesem Fall?