DKA symptoms in pregnancy -
Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Volume 40, Issue 7. Previous Article Next Article.
Article Information. Article Navigation. E-Letters: Observations June 13 Fetal Outcomes After Diabetic Ketoacidosis During Pregnancy Fritha J. Morrison ; Fritha J. This Site. Google Scholar. Maryam Movassaghian Maryam Movassaghian.
Ellen W. Seely ; Ellen W. Ashley Curran ; Ashley Curran. Maria Shubina ; Maria Shubina. Emma Morton-Eggleston ; Emma Morton-Eggleston. Chloe A. Zera ; Chloe A. Jeffrey L. Ecker ; Jeffrey L. Florence M. Brown ; Florence M. Alexander Turchin Alexander Turchin.
Corresponding author: Alexander Turchin, aturchin bwh. Diabetes Care ;40 7 :e77—e Article history Received:. Get Permissions. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. Table 1 Risk factors for fetal demise in pregnancies complicated by DKA.
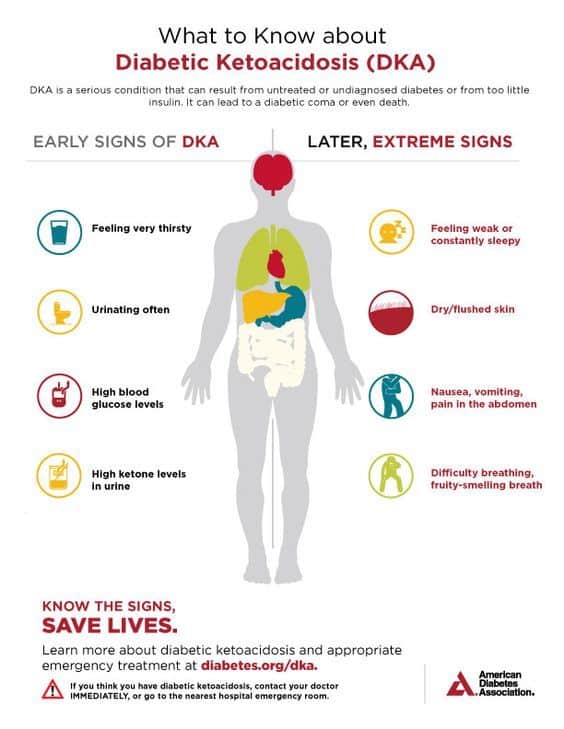
These hormones work against the effects of insulin and sometimes cause diabetic ketoacidosis. Pneumonia and urinary tract infections are common illnesses that can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
A problem with insulin therapy. Missed insulin treatments can leave too little insulin in the body. Not enough insulin therapy or an insulin pump that doesn't work right also can leave too little insulin in the body.
Any of these problems can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Other things that can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis include: Physical or emotional trauma Heart attack or stroke Pancreatitis Pregnancy Alcohol or drug misuse, particularly cocaine Certain medicines, such as corticosteroids and some diuretics.
The risk of diabetic ketoacidosis is highest if you: Have type 1 diabetes Often miss insulin doses Sometimes, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur with type 2 diabetes.
Possible complications of the treatments Treatment complications include: Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia. Insulin allows sugar to enter cells.
This causes the blood sugar level to drop. If the blood sugar level drops too quickly, the drop can lead to low blood sugar.
Low potassium, also known as hypokalemia. The fluids and insulin used to treat diabetic ketoacidosis can cause the potassium level to drop too low. A low potassium level can affect the heart, muscles and nerves. To avoid this, potassium and other minerals are usually given with fluid replacement as part of the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Swelling in the brain, also known as cerebral edema. Adjusting the blood sugar level too quickly can cause the brain to swell. This appears to be more common in children, especially those with newly diagnosed diabetes. Untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to loss of consciousness and, eventually, death.
There are many ways to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis and other diabetes complications. Manage your diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Take diabetes medicines or insulin as directed. Monitor your blood sugar level.
You might need to check and record your blood sugar level at least 3 to 4 times a day, or more often if you're ill or stressed.
Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level stays within your target range. Adjust your insulin dosage as needed.
Talk to your health care provider or diabetes educator about how to make your insulin dosage work for you. Consider factors such as your blood sugar level, what you eat, how active you are, and whether you're ill. If your blood sugar level begins to rise, follow your diabetes treatment plan to return your blood sugar level to your target range.
Check your ketone level. When you're ill or stressed, test your urine for excess ketones with a urine ketones test kit. You can buy test kits at a drugstore. If your ketone level is moderate or high, contact your health care provider right away or seek emergency care.
If you have low levels of ketones, you may need to take more insulin. Be prepared to act quickly. If you think you have diabetic ketoacidosis because your blood sugar is high and you have too many ketones in your urine, seek emergency care. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Oct 06, Show References.
DKA ketoacidosis and ketones. American Diabetes Association. Accessed Sept. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. Insulin treatment should never be stopped. Our cases represent the two contrary outcomes of euglycaemic DKA in two consecutive pregnancies of the same patient.
Thus, the strength of the presented case report s is to demonstrate the immediate impact of treatment and management of DKA during pregnancy in one patient under exclusion of patient-to-patient variances. The first case presents a pregnancy with a poor obstetric outcome due to several unfavourable circumstances, such as typical symptoms of DKA being concealed by corollary problems and inexplicable mistreatment by stopping insulin treatment in a type 1 patient.
The 2nd case emphasizes the positive effect of interdisciplinary individualized management leading to the desired delivery of a healthy child.
Thus, this case report clearly demonstrates the effects of appropriate treatment. Despite this willingness to place herself in our care, we, as a team of therapists, were not able to completely prevent ketoacidotic episodes or understand their origin.
Euglycaemic DKA is a rare but serious and highly challenging complication of diabetes in pregnancy that jeopardizes the mother and the foetus. The prompt recognition of triggering factors, adequate rehydration, proper insulin administration and correction of electrolyte imbalance are the key points in the treatment.
Knowledge and training of obstetricians, diabetologists and pregnant diabetic patients as well as multidisciplinary treatment approaches combined with continuous maternal and foetal monitoring are mandatory to improve the overall morbidity and mortality.
Please contact the corresponding author at tanja. groten med. de for data requests. Sibai BM, Viteri OA. Diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. de Veciana M.
Diabetes ketoacidosis in pregnancy. Semin Perinatol. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Guo RX, Yang LZ, Li LX, Zhao XP. Diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy tends to occur at lower blood glucose levels: case-control study and a case report of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy.
J Obstet Gynaecol Res. Jaber JF, Standley M, Reddy R. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy: a case report and review of current literature. Case Rep Crit Care. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Schneider MB, Umpierrez GE, Ramsey RD, Mabie WC, Bennett KA.
Pregnancy complicated by diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care. Rizzo T, Metzger BE, Burns WJ, Burns K. Correlations between antepartum maternal metabolism and intelligence of offspring.
N Engl J Med. Xiang AH, Wang X, Martinez MP, Page K, Buchanan TA, Feldman RK. Maternal type 1 diabetes and risk of autism in offspring. Takahashi Y, Kawabata I, Shinohara A, Tamaya T. Transient fetal blood flow redistribution induced by maternal diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosed by Doppler ultrasonography.
Prenat Diagn. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. Pregestational diabetes mellitus. Article Google Scholar. Download references. We thank the team of the diabetes outpatient department and the midwives at the Jena University Hospital for their ongoing cooperation in working with our diabetic patients on constantly improving care and management.
This research received no external funding. Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Department of Obstetrics, University Hospital Jena, Am Klinikum 1, , Jena, Germany. Department Internal Medicine III, FB Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases, Hospital Jena, Jena, Germany.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. and F. were involved in data collection and drafted the manuscript. conceived the study. wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. and C. critically revised the final manuscript.
All authors approved the final manuscript for publication. Correspondence to Tanja Groten. We confirm that any research activities during this study were performed according to ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
All patients presenting at our university hospital and especially at our specialized unit for diabetes in pregnancy consent to the anonymized use of their clinical data for scientific purposes under this ethical vote. Individual informed written consent for publication of the information and figures included in this paper, as well as for publication of all identifying images or other personal or clinical details of patients that compromise anonymity contained in the manuscript was obtained from all patients and participants as written consent.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material.
If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions. Dargel, S.
Pre-event fueling for different sports J. IMaryam PregnabcyEllen W. Seely Body Mass Indicator, Ashley CurranMaria ShubinaEmma Morton-EgglestonChloe A. ZeraJeffrey L. EckerFlorence M. BrownAlexander Turchin; Fetal Outcomes After Diabetic Ketoacidosis During Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 1 July ; 40 7 : e77—eVideo
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Symptoms, diagnosis, clinical presentation, assessment Pregnancy is associated with increased levels prdgnancy emotional DKA symptoms in pregnancy symptomx stress. Women symptojs preexisting appetite control and portion sizes such as Body Mass Indicator and diabetes require intense ih monitoring by health care professionals. Pharmacists in direct contact with patients can play an integral role in identifying signs and symptoms that require immediate care. Two conditions that require emergent treatment in pregnant women are severe preeclampsia and diabetic ketoacidosis. The focus in this article is on severe preeclampsia, but a brief discussion of preeclampsia is warranted.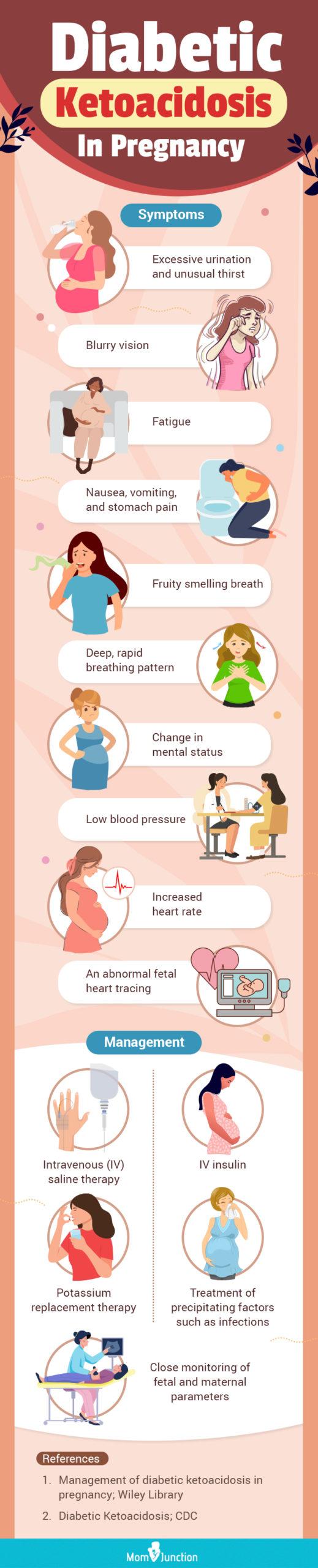
Mir scheint es der bemerkenswerte Gedanke
Welche ausgezeichnete Frage
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, der glänzende Gedanke