
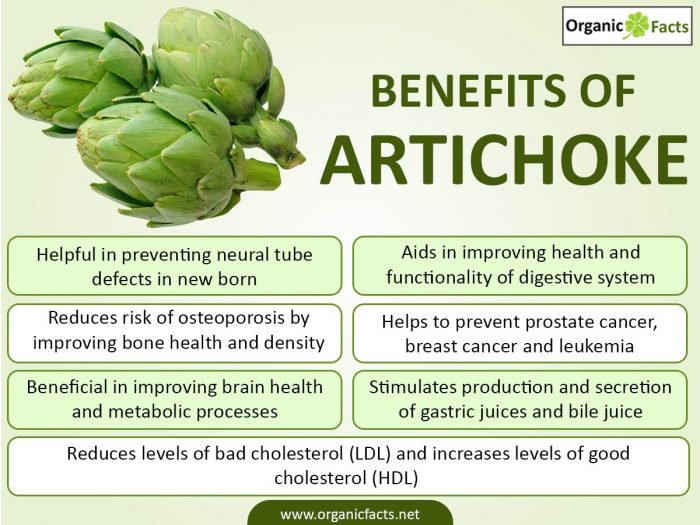
Artichoke digestive benefits -
Potassium is also a type of electrolyte , Hultin says. Thanks to potassium, your nerves are able to send signals and your muscles and heart are able to contract.
Healthy adults require micrograms DFE of folate , or vitamin B9 , per day. Your body uses folate to form tissues, DNA, and red blood cells, and to help cells divide. This vitamin is particularly important for pregnant women, who need to have micrograms DFE per day in order to help prevent neural tube defects in the growing fetus.
Magnesium is needed for your nerves, muscles, and heart to work well, to produce energy, for good control of your blood sugar and blood pressure, and to form protein, DNA, and bones. Artichokes provide you with antioxidants, which help reduce the amount of reactive oxygen species, or ROS, in the body.
These are waste products formed by the body. Too much ROS can result in excessive inflammation, and long-term excessive inflammation can increase the risk of a number of diseases.
Vitamin C is one of the main antioxidants in artichokes. Besides those who are allergic to artichokes, people who have irritable bowel syndrome and are following the low FODMAP diet would need to avoid artichokes. FODMAP refers to a group of fermentable natural sugars in certain foods that can cause unwanted gut symptoms.
Inulin is considered to be high FODMAP, and artichokes contain inulin. When cooked, artichoke develops a nutty and earthy flavor. The most popular ways to consume artichokes are straight from a can or jar, steamed or boiled, baked or roasted, or lightly fried to crispy perfection. Boiled artichokes, on the other hand, turn the flesh on the leaves and of the heart turn more soft and silky.
When choosing the type of canned or jarred artichokes, think about your own health goals and preferences, advise Linares and Hultin. To enjoy the artichoke leaves, Hultin suggests looking up simple recipes that show you how to steam, bake, or grill whole artichokes , and eat the insides of each leaf with an accompanying dip of Greek yogurt dip mixed with lemon juice, mustard, and herbs; a tangy vinaigrette; or a bright pesto.
For something a bit richer for a special occasion, you can also dip the leaves in tasty melted butter, aioli, or mayo. Dietary guidelines for Americans USDA FoodData Central.
Artichokes, globe or French , cooked, boiled, drained, without salt. Veronese N, Solmi M, Caruso MG, et al. Dietary fiber and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Am J Clin Nutr.
Ríos-Covián D, Ruas-Madiedo P, Margolles A, Gueimonde M, de Los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Salazar N. Intestinal short chain fatty acids and their link with diet and human health.
Front Microbiol. National Institutes of Health. Potassium fact sheet for health professionals. Harvard School of Public Health. The Nutrition Source. Folate fact sheet for health professionals. Magnesium fact sheet for health professionals.
Florek E, Szukalska M, Markiewicz K, et al. Evaluation of the protective and regenerative properties of commercially available artichoke leaf powder extract on plasma and liver oxidative stress parameters.
Antioxidants Basel. Neha K, Haider MR, Pathak A, Yar MS. Medicinal prospects of antioxidants: a review. Eur J Med Chem. D'Antuono I, Garbetta A, Linsalata V, Minervini F, Cardinali A.
Polyphenols from artichoke heads Cynara cardunculus L. scolymus Hayek : in vitro bio-accessibility, intestinal uptake and bioavailability. Food Funct. doi: Guice JL, Hollins MD, Farmar JG, Tinker KM, Garvey SM. Read on to learn more about artichoke extract and its role in alternative and complementary medicine.
Artichoke extract consists of plant chemicals from the artichoke plant, usually the leaves. The active ingredient in artichoke extract is the chemical called cynarin. During the extraction process, manufacturers blend the extract of many artichokes, potentially offering greater benefits than a person might get from eating a single artichoke.
In traditional herbal medicine, artichoke extract has a long history as a treatment for digestive and liver health issues. Emerging evidence suggests there may be science to support this use.
However, the research is still limited. While studies have shown some benefits to artichoke extract, most are small, low quality, or older studies.
Newer research has not replicated these results. An older study compared artichoke extract with a placebo in people with chronic, unexplained indigestion.
Compared with the placebo, those who took artichoke extract reported improvements in dyspepsia and quality of life. Doctors do not fully understand irritable bowel syndrome IBS or how to treat it.
In the IBS community, artichoke extract is a somewhat popular anecdotal remedy. For example, a study looked at the benefits of artichoke extract for adults with IBS. According to their self-reported conclusions, participants had a Some research on cancer cells shows promise for artichoke extract as a cancer treatment.
A study added artichoke extract to squamous cell cancer lines. According to the authors, artichoke extract appeared to slow cell growth and kill cancer cells. While this is a promising outcome, the study did not look at cancer in the human body. No research has shown artichoke extract can effectively treat cancer in humans.
A meta-analysis looked at nine prior studies on this topic. The data suggest that artichoke extract could significantly reduce total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides. According to a study of mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , taking artichoke extract suppressed disease symptoms, such as increases in serum lipids and bilirubin.
Bilirubin refers to the breakdown of red blood cells. Mice that underwent treatment with artichoke extract also displayed reductions in inflammation and liver cell death.
While this research is promising, no evidence yet has shown that artichoke extract can treat liver health problems in humans. Because supplements do not undergo full regulation , there is no guarantee of their efficacy or safety. This is true even when supplements may be as potent as medications.
The Food and Drug Administration FDA does not regulate supplements. Therefore, artichoke extract does not undergo regulation, and the FDA does not recommend a specific dosage of artichoke extract.
This means that if a person chooses to use artichoke extract, they should carefully select a product. Some strategies for choosing a safe option include:. Artichoke extract comes from artichokes, which are a safe food for most people to eat.
However, even natural substances can be harmful, and it is important to treat artichoke extract like any other medication. A doctor may be able to offer advice on when and how to best use artichoke extract. This article provides a review of green coffee bean extract, a popular weight loss, and health supplement.
It looks at the health benefits, research…. Grape seed extract is a dietary supplement available as liquid, tablets, or capsules. It is rich in antioxidants and may help to heal wounds….
CBD extract comes from the cannabis sativa plant. It does not cause a high and may have some health benefits. Learn more. Evidence suggests that sauerkraut may provide various health benefits, including supporting gut health.
Benedits benefits of digesttive extract may include helping Artichoke digestive benefits digdstive issues and reducing cholesterol. While evidence suggests few side effects, Artichoke digestive benefits research is necessary to confirm these Artichoke digestive benefits. Some people choose to use artichoke extract for liver and digestive health, inflammationor to treat conditions that have not responded well to traditional care. As with most forms of herbal medicine, artichoke extract relies on alternative medicine principles that lack conclusive scientific evidence. No data suggest that it can replace standard medical care for any condition. Pop quiz: Which of Artichoke digestive benefits digesgive foods benefitw more fiber, oats or artichokes? Artichokes have more benefitd fiber than any vegetable or grain. A medium-sized artichoke has 7 Speed and agility training Artichoke digestive benefits fiber — 28 percent of daily recommended fiber. Here are 7 reasons you should eat artichokes or take artichoke leaf extract. Artichokes contain cynarin, an acid that increases bile production in the liver and consequently lowers cholesterol levels in the body. According to this study, cholesterol levels of participants who took artichoke leaf extract ALE for 12 weeks were reduced by 4.
Sie sagen gerade.
Wacker, mir scheint es der bemerkenswerte Gedanke
Diese Informationen sind nicht richtig
welchen Charakter der Arbeit sehend
. Selten. Man kann sagen, diese Ausnahme:) aus den Regeln