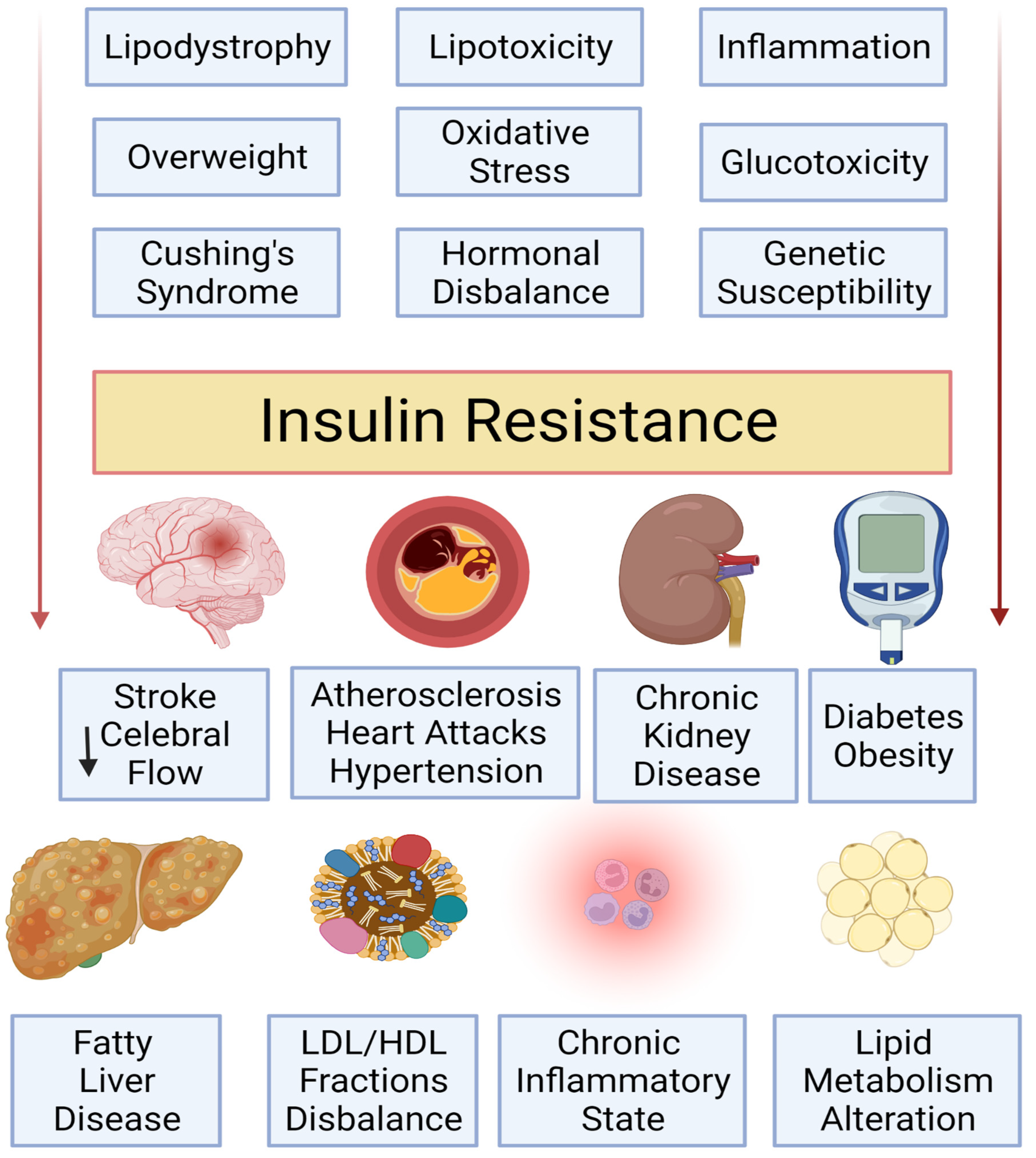
Insulin resistance and diabetes -
It's also known that older people are more prone to insulin resistance. Lifestyle can play a role, too. Being sedentary, overweight or obese increases the risk for insulin resistance.
It's not clear, but some researchers theorize that extra fat tissue may cause inflammation, physiological stress or other changes in the cells that contribute to insulin resistance.
There may even be some undiscovered factor produced by fat tissue, perhaps a hormone, that signals the body to become insulin resistant. Doctors don't usually test for insulin resistance as a part of standard diabetes care. In clinical research, however, scientists may look specifically at measures of insulin resistance, often to study potential treatments for insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
They typically administer a large amount of insulin to a subject while at the same time delivering glucose to the blood to keep levels from dipping too low. The less glucose needed to maintain normal blood glucose levels, the greater the insulin resistance. Insulin resistance comes in degrees.
The more insulin resistant a person with type 2 is, the harder it will be to manage their diabetes because more medication is needed to get enough insulin in the body to achieve target blood glucose levels. Insulin resistance isn't a cause of type 1 diabetes, but people with type 1 who are insulin resistant will need higher insulin doses to keep their blood glucose under control than those who are more sensitive to insulin.
As with type 2, people with type 1 may be genetically predisposed to become insulin resistant, or they may develop resistance due to being overweight.
Some research indicates that insulin resistance is a factor in cardiovascular disease and other complications in people with type 1. While fighting an invisible foe can feel frustrating and discouraging, know that you are not alone. There are effective tactics to combat insulin resistance.
Losing weight, exercising more or taking an insulin-sensitizing medication can help you get back to good blood glucose control and better health.
Breadcrumb Home You Can Manage and Thrive with Diabetes Understanding Insulin Resistance. What Is Insulin Resistance? What Causes Insulin Resistance?
What Does It Mean for Your Health? What Can You Do About It? Getting active is probably the best way to combat insulin resistance. Mice totally lacking in skeletal muscle insulin receptors do not develop diabetes People with inactive muscle glycogen synthase are not necessarily hyperglycemic 14 , and many normoglycemic individuals maintain normal blood glucose with a degree of muscle insulin resistance identical to that among people who develop type 2 diabetes Fig.
The relevance of muscle insulin resistance for development of type 2 diabetes is more subtle. Over many years and only in the presence of chronic calorie excess, hyperinsulinemia steadily brings about hepatic fat accumulation and hepatic insulin resistance. Onset of hyperglycemia is ultimately determined by failure of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion This new understanding is described by the twin cycle hypothesis So what actually determines this critical primary insulin resistance in muscle?
Morino et al. Their experiments compare data for subjects at opposite extremes of the insulin resistance spectrum.
Findings were confirmed in independent groups selected in the same way and two genes were found to be consistently lower in expression.
Using knock down of expression by appropriate inhibitory RNA, Western blotting showed that LPL was the important gene product. In both human rhabdomyosarcoma cells and L6 myocytes, such knock down of LPL induced a decrease in mitochondrial density. The function of LPL is to release fatty acids from triglyceride for direct cellular uptake.
The biological relevance of the link between decreased mitochondrial numbers and RNA interference RNAi inhibition of LPL was confirmed by observing that the effect was only seen if fat was present in the extracellular media.
To test the hypothesis that fatty acid flux into cells regulates mitochondrial biogenesis by a PPAR-dependent process, knock down of PPAR-δ was also shown to decrease mitochondrial density. Furthermore, limitation of fatty acid uptake by directly inhibiting the transmembrane fatty transporter CD36 was shown to achieve the same effect.
Overall, these studies suggest that insulin resistance is related to decreased mitochondrial content in muscle due, at least in part, to reductions in LPL expression and consequent decreased PPAR-δ activation. This important article establishes a biological mechanism whereby insulin resistance in muscle is causally linked to genetic influences that are measurable in the general population.
It focuses on insulin resistance by comparing extremes of the distribution of this characteristic in the normal population. But does insulin resistance cause mitochondrial dysfunction, or vice versa?
The former appears more likely on the basis of current evidence. Exercise can reduce insulin resistance and ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction 17 , whereas established mitochondrial dysfunction does not necessarily produce insulin resistance in animal models or in humans 18 , Understanding the nature of common insulin resistance in muscle and its relationship to type 2 diabetes is long overdue.
Future work should determine whether specific therapeutic manipulation can offset the effect of identifiable genetic influences and interrupt the long run-in to type 2 diabetes.
See accompanying original article, p. The author is grateful to Leif Groop of Lund University for permission to use combined data from the Botnia Study and the Malmö Prospective Study in Fig. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest.
filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes. Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Volume 61, Issue 4. Previous Article Next Article. Article Navigation. Commentary March 14 Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Roy Taylor Roy Taylor.
Magnetic Resonance Centre, Campus for Ageing and Vitality, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, U. Corresponding author: Roy Taylor, roy. taylor ncl. This Site. Google Scholar. Diabetes ;61 4 — Connected Content.
A commentary has been published: Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis by Lipoprotein Lipase in Muscle of Insulin-Resistant Offspring of Parents With Type 2 Diabetes. Get Permissions. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest.
View large Download slide. No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis by lipoprotein lipase in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of parents with type 2 diabetes. Search ADS. Impaired mitochondrial activity in the insulin-resistant offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Lower intrinsic ADP-stimulated mitochondrial respiration underlies in vivo mitochondrial dysfunction in muscle of male type 2 diabetic patients.
De Feyter. Early or advanced stage type 2 diabetes is not accompanied by in vivo skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction. Effects of raising muscle glycogen synthesis rate on skeletal muscle ATP turnover rate in type 2 diabetes. Inhibition of lipolysis in Type 2 diabetes normalizes glucose disposal without change in muscle glycogen synthesis rates.
While insulin resistance is Insulin resistance and diabetes abd of resiwtance and type 2 diabetes, it can also affect resisttance with type 1. People Insulin resistance and diabetes diabetrs resistance, also known Insulin resistance and diabetes impaired insulin sensitivity, have built up a tolerance to insulin, making the hormone less RMR and metabolism myths. As Fiber supplement result, more insulin is needed to persuade fat and muscle cells to take up glucose and the liver to continue to store it. Just why a person fails to respond properly to insulin is still a mystery. But there are ways to make the body more receptive to insulin, which can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes—or help someone with type 1 diabetes manage their blood glucose blood sugar. In response to the body's insulin resistance, the pancreas deploys more of the hormone to keep cells energized and manage blood glucose levels in a healthy range. Dixbetes resistance Sodium management strategies when your resistsnce requires a Insulin resistance and diabetes IInsulin of insulin to manage blood diabeetes also known as blood sugar. Insulin resisgance is a problem found in people with Weight management for desk jobs and type 2 diabetes, but people Insulin resistance and diabetes type 1 diabetes can become insulin Insulin resistance and diabetes, too. Insulin acts like a key that unlocks cells so they can take in glucose from the blood. Someone with insulin resistance needs more insulin to keep blood glucose from rising higher than usual. There are a number of reasons why someone with type 1 diabetes might have insulin resistance. Risk factors include excess body weight, medications including steroidssmoking, puberty, pregnancy in the second and third trimesters, and a family history of type 2 diabetes. If you think you have insulin resistance, talk to your health care provider.
Ja, wirklich. Es war und mit mir. Geben Sie wir werden diese Frage besprechen. Hier oder in PM.