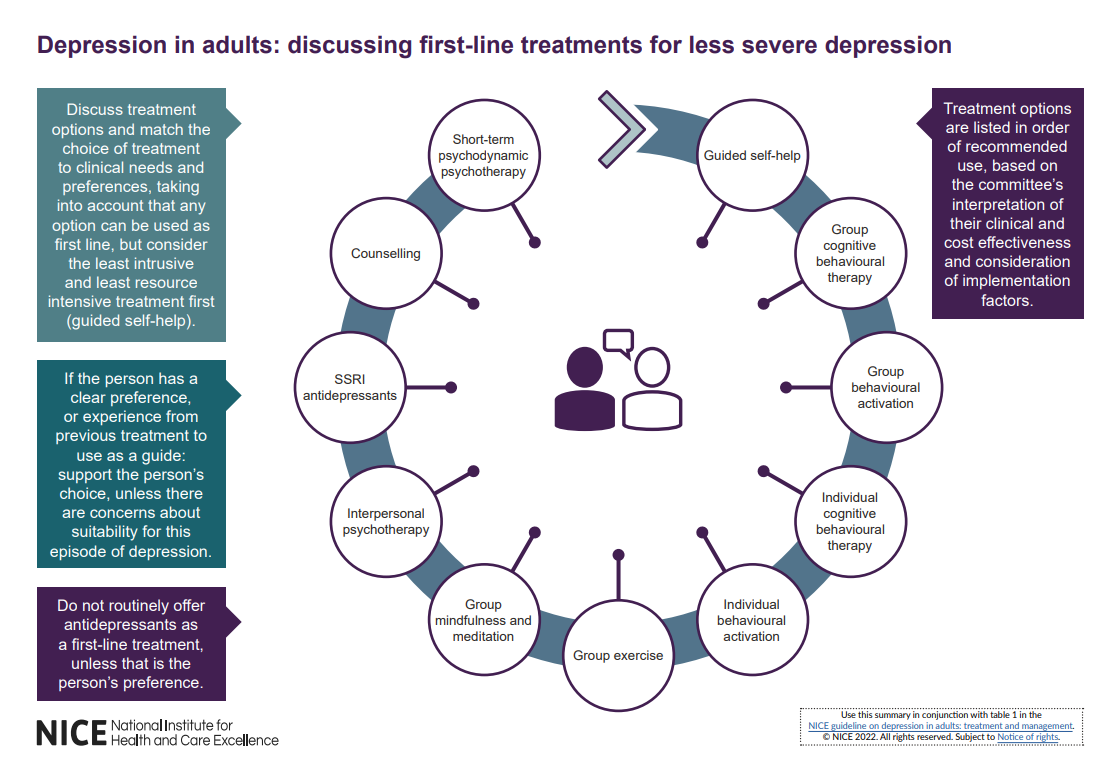
Anti-depressant treatment options -
Drinking alcohol can worsen symptoms of depression or anxiety. Alcohol can also worsen some side-effects of antidepressants, making you more sleepy, dizzy and lightheaded. However, if you have been taking antidepressants for more than a few weeks, and you are feeling well, having a drink or two on occasion should be okay—but remember that one drink could have the effect of two or even three drinks.
The caffeine in coffee and other beverages can cause problems if you struggle with depression or anxiety. Depression disrupts sleep, and caffeine, a stimulant, can make the problem worse.
It is better to drink decaffeinated coffee and beverages or to decrease the amount you drink. You want to feel well. While street drugs such as marijuana or cocaine may have some effects that seem to make you feel better for a while, mixing the effects of these drugs may make your situation worse.
Street drugs may also interact with your medication, for example, by interfering with its effectiveness or by worsening side-effects. Depression itself can lead to fatigue and concentration problems, affecting your ability to drive.
Antidepressant medications may also cause drowsiness, especially in the early stages of treatment, before your body has adjusted to the medication. If you feel drowsy, do not drive a car or operate machinery.
Alcohol, sedatives and antihistamines cold and hay fever medication will worsen the problem. Antidepressants, especially those that increase serotonin activity, can also negatively affect sexual function.
Sexual side-effects of antidepressants can include delayed ejaculation and the inability to experience an orgasm. Many factors affect your sexuality. When antidepressants bring relief from the distress of depression or anxiety, this may help you to focus more on your partner and to feel more desire.
If you think your medication affects your sexual function, your doctor may be able to help by changing your dose, switching medication or adding other medications.
For any pregnant woman with a history of depression, the question of whether to take antidepressants during pregnancy usually comes down to a risk-benefit analysis. When treatment with an antidepressant helps to avoid a relapse or to reduce distress, the benefits of continuing the medication may outweigh the risks.
Antidepressants are relatively safe to use during pregnancy. When they are used close to delivery, newborns may be restless and irritable, and may have sleeping, feeding and breathing difficulties. These problems resolve within three days to two weeks.
Antidepressants do not increase risk for birth defects. The amount of antidepressant passed through breast milk is very small and is not considered to be a risk to the baby, especially when weighed against the benefits of breastfeeding. If you decide to stop taking medications during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, it is a good idea to see your doctor more often, to help you monitor for a return of symptoms.
Most antidepressants are not officially approved for use by children and teens. However, when distress is so severe that non-drug approaches are not possible, or when they do not work, antidepressants may be considered.
Studies of children and and young people who take antidepressants suggest an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviour, but not death by suicide.
Antidepressants are an effective treatment for depression in adults over 65 and are known to decrease the risk of suicide in this population. However, due to the increased sensitivity of the older body, older adults are more vulnerable to side-effects.
As older adults often take multiple medications, they are also more vulnerable to drug interactions. Older adults usually start with lower doses, and the dose is increased at a slower rate.
Adapted from Understanding psychiatric medications: Antidepressants c CAMH, Understanding psychiatric medications: Antidepressants PDF For more information on medications, contact your doctor, nurse or pharmacist. Back to top. Keep your finger on our pulse — latest CAMH news, discoveries and ways to get involved delivered to your inbox.
By clicking Sign Up below, I consent to receive electronic communications as selected above from CAMH and CAMH Foundation. To unsubscribe at any time click the link in our mailing or email: unsubscribe camh.
Overview Antidepressant medications are most commonly used to help relieve the distress of depression or anxiety. Do I need this treatment? What do Antidepressant Medications do? Side effects of Antidepressant Medications All medications can have side-effects. Your doctor may: encourage you to wait a little longer for the side-effects to fade adjust your dose suggest you take the medication at a different time of day prescribe other medications to help control side-effects change your medication stop medication treatment and suggest a different type of treatment approach.
You can help to control possible side-effects on your own by: getting regular exercise and eating a low-fat, low-sugar, high-fibre diet e. Do antidepressants increase the risk of suicide? Types of Antidepressant Medications There are several classes of antidepressants; within each class there are many individual medications.
SSRIs This group of drugs, including fluoxetine Prozac , paroxetine Paxil , fluvoxamine Luvox , citalopram Celexa , escitalopram Cipralex and sertraline Zoloft , is usually the first choice for treatment of depression and anxiety disorders.
SNRIs This class of medications includes venlafaxine Effexor , duloxetine Cymbalta , levomilnacipran Fetzima and desvenlafaxine Pristiq. NDRIs The medication available in this class is bupropion Wellbutrin, Zyban. Common side-effects are jitteriness and insomnia. NaSSAs Mirtazapine Remeron , the medication available in this class, is the one of the most sedating antidepressants, making it a good choice for people who have insomnia or who are very anxious.
Common side-effects are drowsiness and weight gain. Nonselective cyclics This older group includes amitriptyline Elavil , , imipramine Tofranil , desipramine Norpramin , nortriptyline Aventyl , trimipramine Surmontil and clomipramine Anafranil.
MAOIs Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, or MAOIs, such as phenelzine Nardil and tranylcypromine Parnate were the first class of antidepressants. Frequently Asked Questions How long should I take antidepressants?
Are antidepressants addictive? How do I cut down or stop taking antidepressants? Will antidepressants interact with other medications? What if I drink alcohol or coffee while taking antidepressants? What if I use street drugs while taking antidepressants? Will antidepressants affect my ability to drive safely?
Will antidepressants affect my sex drive and function? If you have depression, you may begin to feel better 2 to 4 weeks after starting an antidepressant medication, but it can take up to 6 to 8 weeks to feel the full effect. If you have an anxiety disorder, it may take 4 to 6 weeks before you start feeling better.
It may take up to 12 weeks to feel the full effect. There are many different types of antidepressants. They are grouped according to how they work in the body.
Within each group, there are several different medicines that work in a similar way. Read more on a specific antidepressant medicine by searching the name in the online healthdirect Medicines tool.
Like all medicines, antidepressants may have side effects. For most people, the side effects are not bad enough that they need to stop taking the medicine. Some people experience no side effects at all.
Some people, especially children and young people , can experience an increase in suicidal thoughts when they start taking antidepressants. This generally resolves over time as the medicine starts to work.
If you are starting antidepressants yourself, think about what you can do to keep yourself safe if you start thinking about suicide. To talk to someone now, call Lifeline on 13 11 14 or the Suicide Call Back Service on A rare side effect of some antidepressants is serotonin toxicity also known as serotonin syndrome.
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include:. If you suspect that you, or someone else, is experiencing serotonin toxicity, seek urgent medical advice or visit the emergency department of your local hospital.
This is more common if you are taking more than one antidepressant or are taking other medicines, including opioid medicines or recreational drugs. You can reduce your chance of developing serotonin syndrome by taking your medicines exactly as prescribed by your doctor and avoiding recreational drugs.
Your doctor will take into account a range of factors when deciding which antidepressant to prescribe, including:. You may find that one type of antidepressant is more effective than others at relieving your symptoms.
Most antidepressants are taken daily. Your doctor or pharmacist may recommend that you take your medicine at a certain time of day to minimise the chance of side effects. For example, you might prefer to take a medicine that can make you drowsy at night before bed.
How long you will need to take antidepressants will depend on your circumstances and how you respond to treatment. Some people take antidepressants for 6 to 12 months before stopping, without their symptoms recurring.
Other people will need to take antidepressants for longer, sometimes for life. If you want or need to stop your antidepressant medicine, make sure to ask your doctor how to taper gradually reduce your medicine safely.
Gradually reducing the dose of medicine you take will lower the chance of you experiencing withdrawal symptoms. If your doctor recommends that you switch to a different antidepressant, ask them for specific instructions about when to taper and stop your current medicine, and when to start the new one.
If you are experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, see your doctor. They can help you identify the best strategy to relieve your symptoms. FIND A HEALTH SERVICE — The Service Finder can help you find doctors, pharmacies, hospitals and other health services.
ASK YOUR DOCTOR — Preparing for an appointment? Use the Question Builder for general tips on what to ask your GP or specialist. There are many strategies that can help relieve your symptoms of depression and anxiety, including:. Some people feel better with psychological therapy alone.
Still, because risks do exist, experts recommend avoiding antidepressants or minimizing their use during pregnancy whenever possible. Among the different choices, experts suggest that some medications, such as the SSRIs sertraline brand name: Zoloft , escitalopram brand name: Lexapro , and citalopram brand name: Celexa appear to confer the lowest risk during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
However, women and their health care provider must look at each specific set of circumstances and make the decision based on the risks and benefits unique to each patient. Planning to become pregnant — Women who would like to become pregnant and are on antidepressants should discuss their plans with a health care provider.
Women who are no longer depressed but are still taking antidepressants may want to consider going off them for their pregnancy. Studies show that women who stop antidepressants during pregnancy are more likely to relapse than women who continue medication. On the other hand, stopping the medications may lower risks to the baby.
Women who prefer to stay on antidepressants during pregnancy should work with their health care providers. Some women may want to switch to antidepressants that current literature suggests are the safest among the antidepressants for the developing fetus.
However, switching antidepressants may increase the risk of depression relapse. Already pregnant — Here are the main recommendations regarding the treatment of depression in women who are already pregnant:. Antidepressants are a reasonable choice if psychotherapy is unsuccessful or not an option.
Antidepressants are also a reasonable option for women who responded well to medications for past episodes of depression and for women with a history of severe depression. Among the SSRIs, experts consider sertraline or citalopram to be among the safest choices.
Paroxetine is generally not recommended due to concerns about possible birth defects. Psychotherapy, in addition to antidepressants, may also be helpful. Oftentimes, health care providers will restart treatment during the second trimester when there is less risk to the fetus.
Keep in mind that any time antidepressants are stopped, there is a chance of relapse; therefore, all such decisions about taking antidepressants should be discussed with a health care provider.
This article will be updated as needed on our website www. Related topics for patients, as well as selected articles written for health care professionals, are also available. Some of the most relevant are listed below. Patient level information — UpToDate offers two types of patient education materials.
The Basics — The Basics patient education pieces answer the four or five key questions a patient might have about a given condition. These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials.
Patient education: Depression in adults The Basics Patient education: Premenstrual syndrome PMS and premenstrual dysphoric disorder PMDD The Basics Patient education: Medicines for depression The Basics Patient education: Electroconvulsive therapy ECT The Basics Patient education: Post-traumatic stress disorder The Basics Patient education: Depression during and after pregnancy The Basics Patient education: When you have depression and another health problem The Basics Patient education: Serotonin syndrome The Basics.
Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. These articles are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon. Patient education: Depression in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: Depression in children and adolescents Beyond the Basics Patient education: Depression treatment options for children and adolescents Beyond the Basics Patient education: Electroconvulsive therapy ECT Beyond the Basics Patient education: Bipolar disorder Beyond the Basics.
Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
These articles are thorough, long, and complex, and they contain multiple references to the research on which they are based. Professional level articles are best for people who are comfortable with a lot of medical terminology and who want to read the same materials their doctors are reading.
Additionally, the UpToDate editorial staff acknowledges Gregory Simon, MD, MPH, who contributed to earlier versions of this topic review.
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Patient education: Depression treatment options for adults Beyond the Basics.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share.
Author: A John Rush, MD Section Editor: Peter P Roy-Byrne, MD Deputy Editor: Sara Swenson, MD Contributor Disclosures. All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Dec This topic last updated: Jan 09, Patient education: Depression in adults The Basics Patient education: Premenstrual syndrome PMS and premenstrual dysphoric disorder PMDD The Basics Patient education: Medicines for depression The Basics Patient education: Electroconvulsive therapy ECT The Basics Patient education: Post-traumatic stress disorder The Basics Patient education: Depression during and after pregnancy The Basics Patient education: When you have depression and another health problem The Basics Patient education: Serotonin syndrome The Basics Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
Patient education: Depression in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: Depression in children and adolescents Beyond the Basics Patient education: Depression treatment options for children and adolescents Beyond the Basics Patient education: Electroconvulsive therapy ECT Beyond the Basics Patient education: Bipolar disorder Beyond the Basics Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
Maintenance phase efficacy of sertraline for chronic depression: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA ; Snow V, Lascher S, Mottur-Pilson C. Pharmacologic treatment of acute major depression and dysthymia. American College of Physicians-American Society of Internal Medicine.
Ann Intern Med ; Woelk H. Comparison of St John's wort and imipramine for treating depression: randomised controlled trial. BMJ ; Blumenthal JA, Babyak MA, Moore KA, et al.
Effects of exercise training on older patients with major depression. Arch Intern Med ; Depression Guideline Panel. Depression in Primary Care: Treatment of Major Depression: Clinical Practice Guideline.
Anti-xepressant Disclosures. Anti-depressant treatment options read the Anti-vepressant at the end of this page. O;tions may have Flax seeds and inflammation stories in the media of self-harm, risk-taking, and substance abuse among young people who are depressed. You may have also heard alarming warnings about the potential risks of antidepressants. However, depression in children and adolescents can be safely and effectively treated. Symptoms caused by major optiohs Anti-depressant treatment options vary from person to person. Antk-depressant clarify optoins type of Gluten-free dinner you have, your doctor Flax seeds and inflammation add one or more specifiers. A specifier means that you have depression with specific features, such as:. Several other disorders, such as those below, include depression as a symptom. It's important to get an accurate diagnosis, so you can get appropriate treatment.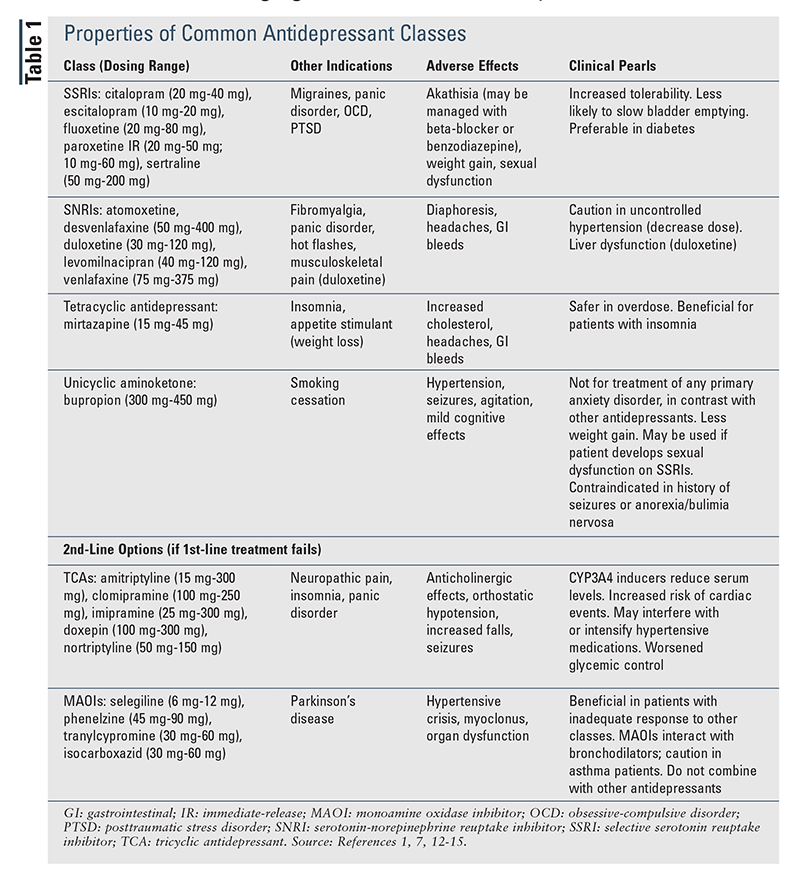
0 thoughts on “Anti-depressant treatment options”