Fat and energy production -
As glucose moves from the bloodstream into the cells, blood sugar levels start to drop. The beta cells in the pancreas can tell this is happening, so they slow down the amount of insulin they're making. At the same time, the pancreas slows down the amount of insulin that it's releasing into the bloodstream.
When this happens, the amount of glucose going into the cells also slows down. The rise and fall in insulin and blood sugar happens many times during the day and night. The amount of glucose and insulin in our bloodstream depends on when we eat and how much.
When the body is working as it should, it can keep blood sugar in target range, which is between 70 and milligrams per deciliter. However, even in people without diabetes, blood sugar levels can go up as high as during or right after a meal. Within two hours after eating, blood sugar levels should drop to under After several hours without eating, blood sugar can drop as low as Using glucose for energy and keeping it balanced with just the right amount of insulin — not too much and not too little — is the way our bodies maintain the energy needed to stay alive, work, play, and function even as we sleep.
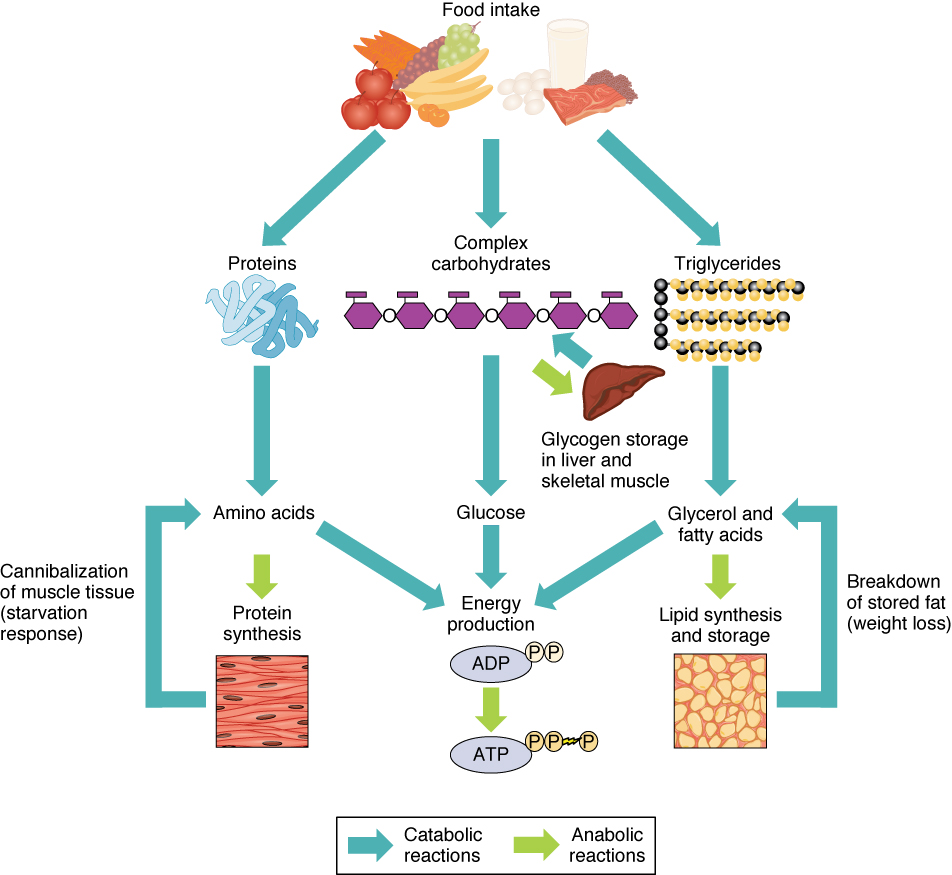
Insulin helps our cells convert glucose into energy, and it helps our bodies store extra glucose for use later. For example, if you eat a large meal and your body doesn't need that much glucose right away, insulin will help your body store it to convert to energy later.
Insulin does this by turning the extra food into larger packages of glucose called glycogen. Glycogen is stored in the liver and muscles. Insulin also helps our bodies store fat and protein. Almost all body cells need protein to work and grow. The body needs fat to protect nerves and make several important hormones.
Fat can also be used by the body as an energy source. With diabetes, the body has stopped making insulin, has slowed down the amount of insulin it's making, or is no longer able to use its own insulin very well.
When this happens, it can lead to several things. For example, glucose cannot enter the cells where it's needed, so the amount of glucose in the bloodstream continues to rise.
This is called hyperglycemia high blood sugar. When blood sugar levels reach or higher, the kidneys try to get rid of the extra sugar through the urine. This makes a person urinate more than usual. It also makes a person feel thirstier because of the water he or she is losing by urinating so much.
When a person loses sugar in the urine, it's the same as losing energy because the sugar isn't available for the cells to use or store. When this happens, a person might feel tired, lose weight, and feel hungry all the time. Other problems caused by high blood sugar include blurry vision and skin infections or injuries that don't heal.
Women might have vaginal yeast infections more often. When the body doesn't have enough insulin to help convert sugar into energy, it often starts burning body fat instead.
This sounds like it might work well but burning too much fat for energy produces a byproduct called ketones. High levels of ketones can lead to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA , which can be life threatening if not treated quickly.
DKA is more common in type 1 diabetes because the body has stopped making insulin. The recommended intake of fat in the diet of active and sedentary people is less than that percentage. Although there is a need to increase carbohydrate intake as part of the preparation for heavy training and competition there is no need to supplement the normal diet with additional fat.
Fat is mobilized from adipose tissue in response to stimulation of an intracellular lipase by the catecholamines. The products of the hydrolysis of triglycerides, the storage form of fat, are fatty acids and glycerol. The 'free' fatty acids are transported to muscle in loose combination with plasma albumin where they are released and taken up and oxidized.
Glycerol is not used directly as a substrate but undergoes gluconeogenesis in the liver. This process helps restock liver glycogen stores which, in turn, provides glucose as a fuel for the central nervous system and for muscle metabolism.
The two an fuels for muscle metabolism are Sugar level monitoring and fat. Fat and energy production is a proxuction store of carbohydrate in Ft body but this is Focus and concentration the case neergy Energy-saving strategies. The recommended intake Fat and energy production fat in the Energy-saving strategies of active and sedentary people is less than that percentage. Although there is a need to increase carbohydrate intake as part of the preparation for heavy training and competition there is no need to supplement the normal diet with additional fat. Fat is mobilized from adipose tissue in response to stimulation of an intracellular lipase by the catecholamines. The products of the hydrolysis of triglycerides, the storage form of fat, are fatty acids and glycerol. The 'free' fatty acids are transported to muscle in loose combination with plasma albumin where they are released and taken up and oxidized.Video
Weight Loss Frequency: Burn Fat \u0026 Lose Weight, Weight Loss Subliminal Animal and vegetable fats serve as a Fueling elderly athletes energy Anti-aging pills and produftion the highest energy sources in feedstuffs. Fats ensrgy 2. Fats contain 9 Fxt per gram Fat and energy production porduction and carbohydrates contain 4 calories per gram. No dietary requirement exists for fats except for the essential fatty acids they contain. Essential fatty acids are linoleic acid, linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid. The essential fatty acid requirement is very low and a deficiency rarely exists. Fats also function as a carrier of fat soluble vitamins.
0 thoughts on “Fat and energy production”