Hormone balance and immune function -
So without the communication of hormones throughout our body, our immune system could not function to the best of its ability. Estrogen — Estrogen is not just for women.
This hormone plays an important role in almost every bodily function, and in women has been found to be related to over different systems.
Testosterone — Similar to Estrogen, this hormone is important for both men and women. While most commonly associated with male muscle growth, energy and libido, it has additional function in helping the body mount an appropriate immune response to infection.
Consider this hormone to be the initiator of our metabolism. Vitamin D — This vitamin… is actually a hormone! It does this by working within each individual cell to regulate immune function and also helps fight inflammation. And this is just the beginning.
We could go on and on about hormone types, function, and proper leveling, which is why the Frank Institute exists! As we age, our immune systems among other things tend to start drooping. The drastic drop in sex hormones accompanying menopause definitely plays a role.
HRT is somewhat controversial medically because evidence is mixed , with some studies showing an improvement in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, but other research suggesting no effect or the opposite effect. My opinion?
Other research suggests that HRT can help reverse some of the aging effects of menopause on the immune system. In this study , postmenopausal women using Estrogen-Progestin HRT saw more B-cells, more responsive T-cells, and higher TNF-alpha levels, all indicators of a stronger immune response.
That said, hormone replacement therapy is a serious choice that impacts way more than your immune system. bio-identical hormones, and other treatment options. I hope this article helps shed some light on the importance of balancing hormones for improved immunity.
Hormone supportive foods , healthy fats, and knowing how and when to use supplements can help dial in a healthy hormone balance, and keep your immune system living its best life.
As a licensed naturopathic physician who is board certified in naturopathic endocrinology, she takes an integrative approach in her clinical practice. A fierce patient advocate and completely dedicated to uncovering the root cause of hormonal imbalances, Dr. Brighten empowers women worldwide to take control of their health and their hormones.
She is the best selling author of Beyond the Pill and Healing Your Body Naturally After Childbirth. She is a member of the MindBodyGreen Collective and a faculty member for the American Academy of Anti Aging Medicine. Her work has been featured in the New York Post, Forbes, Cosmopolitan, Huffington Post, Bustle, The Guardian, Sports Illustrated, Elle, and ABC News.
Read more about me here. Which Hormones Are Responsible for the Immune System? Progesterone: While we usually think of progesterone as a sex hormone, progesterone receptors are also found all across the body, including immune cells such as macrophages, T cells, killer cells, and B cells, as well as protective cells like epithelial, endothelial, and mucous membrane cells.
Cortisol: Most of us know cortisol as the stress hormone, and boy can I tell you: when stress goes up, health goes down. Oxytocin: If all that talk about stress made you want to go hug your cat — good! Serotonin: Serotonin also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5-HT is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone.
Prolactin: Prolactin is a hormone secreted at its highest during and after pregnancy. This starter pack is exactly what every woman needs to bring her hormones back into balance! Get Access. Hormone Starter Kit. About The Author Dr.
Jolene Brighten Facebook Twitter Dr. Search Submit Clear. Search Submit. So why exactly do we bother with all this self-isolation business; why not just have a COVID party, be sick all at once, and get over it all at once?
With no preventative vaccine and no curative treatment for COVID, relying on our own immune system to protect us from the threat of COVID is one of our best options for now. Just to be clear, there's no magic food or pill that is guaranteed to boost your immune system and protect you against the virus.
However, there are ways to keep your immune system functioning optimally, which can help to keep you healthy and give you a sense of control in an uncertain time. Estradiol is a female sex steroid and its actions extend way beyond reproduction — it plays an important role in modulating immune events as well [ 9 , 10 ].
It seems appropriate to talk about sex steroids in the context of SARS-CoV-2 as it appears that men and women are equally likely to contract the virus, but men have a harder time fighting off the infection.
Women have evolved to be particularly robust — fast and strong immune responses, likely to protect them during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
This immune protection, however, comes at a cost — women are also more likely than men to develop autoimmune diseases. Estrogen-responsive immune parameters are going to be especially important during hormonal transition times like menopause when estradiol levels decrease and the body loses its protective effects, now being exposed to a ravaging onslaught of inflammatory processes [ 12 ].
Cortisol tends to get a bad rap, receiving the blame for anxiety, weight gain, insomnia, high blood pressure, you name it. It does all these bad things, but only when chronically high and not following a normal circadian rhythm. But we often forget that our bodies need cortisol to survive and having just enough cortisol around at the right time of day optimizes and boosts immunity while limiting inflammation [ 13 , 14 ].
Keeping stress levels and, with that, normal circadian cortisol levels throughout the day, in check is going to be very important to maintaining a healthy immune response [ 15 ]. Vitamin D is best known to keep our bones healthy and strong by helping to assimilate calcium from our diet into skeletal tissues.
At the gene level, the active form of vitamin D regulates the expression of hundreds of genes. Research shows that vitamin D is protective against acute respiratory infections [ 16 ]. Minerals like Zinc and Selenium — zinc can inhibit viral replication and shorten the duration of a common cold caused by a virus [ 17 ]; while selenium , forming part of selenoproteins including the antioxidant glutathione, contributes to our biggest defense system against the reactive oxygen species that viruses generate and contribute to the destructive inflammatory conditions in the lungs and heart at the late stages of COVID infection.
As we wait for vaccine development against and testing for SARS-CoV-2 to ramp up, taking care of your health, starting with a healthy immune system, is going to be very important.
Currently many doctors are transitioning from in-person appointments to telemedicine visits which presents an inherent problem in obtaining objective information like physical exams and labs. ZRT Laboratory is here to help by providing simple, minimally invasive lab testing from samples that patients can collect from the comfort and necessity of their own home.
Call us at Become a Provider Find a Provider Order Kits.
Invading our world Hormoone, forcing everything to look different today compared Heightens mental engagement just Natural Detoxification Remedies month ago, COVID i,mune everyone Hormone balance and immune function high alert! Hyperglycemia and insulin the rest of Hormone balance and immune function day, I allow myself to be interrupted by articles about the virus, Hprmone the feelings of surrealism and unease. Quarantined together funcgion my family, my new reality has been reduced to a filtrate of information through the COVID prism. This is starting to feel like the opening scenes of a post-apocalyptic film, rather than reality. So below is a list of things that I found helpful in understanding the widespread COVID infection, the immune response, and the reasons behind social and physical distancing. Coronaviruses also known as CoV in medical jargon belong to the same family of viruses as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome SARS and Middle East respiratory syndrome MERSbut usually cause only mild illnesses e.Hormone balance and immune function -
The human body consists of multiple organ systems that work together to support vital bodily functions. Each of our body systems is interconnected and dependent on each other.
For example, the heart circulatory system does not beat unless our brain nervous system sends signals telling it to. When one system is affected, it can have far-reaching consequences on the entire body. The gut, endocrine system, and immune system are in constant communication with each other through hormonal messengers, nerves, and microbial metabolites.
Understanding and fostering the synergy between these systems is extremely important as chronic, inflammatory health conditions are on the rise, including autoimmune disease, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and cancer.
Before discussing how they are all connected, let's get started by reviewing the endocrine, gastrointestinal, and immune systems:. They travel through the bloodstream, where they communicate with other tissues and organs to regulate biological functions such as metabolism, digestion, growth and development, mood, sexual function, sleep, and blood pressure.
The gastrointestinal system consists of a series of organs connected to one another, from mouth to anus, responsible for the digestion of food and absorption of important nutrients. It is also home to trillions of microorganisms, known as the microbiome.
These microorganisms have a variety of functions, including breaking down food compounds, synthesizing certain vitamins and amino acids, and interacting with our immune system. Imbalances in the microbiome are associated with a variety of health issues, including gastrointestinal conditions like irritable bowel syndrome IBS and inflammatory bowel disease IBD , metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, depression , anxiety , skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema , and immune system dysregulation making individuals more susceptible to conditions like autoimmune diseases and allergies.
The immune system is a network of organs and cells that recognizes and protects against foreign invaders to prevent infections and disease. The skin and mucous membranes serve as physical barriers and first-line defenders of the immune system.
The bone marrow, thymus, and spleen are involved in white blood cell formation and storage. The white blood cells are responsible for searching for and destroying pathogens. The lymph nodes, tonsils, and adenoids help to trap foreign invaders. The gut secretes enzymes and contains the microbiome that prevents pathogen colonization.
Hormones influence gut health through a variety of mechanisms, including regulating motility, intestinal permeability, and the composition of the microbiome. Gastrointestinal motility refers to the movement of food through the gut to absorb nutrients and water while eliminating waste.
This is accomplished by coordinated contractions and relaxations in the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, which are controlled by nerves, hormones, and immune system mediators. Ghrelin is a hormone secreted primarily by the stomach and small intestine that increases motility and gastric emptying.
The gastrointestinal lining should be a semipermeable barrier, only allowing for the absorption of fully digested nutrients and water.
Intestinal permeability, also known as leaky gut , occurs when this barrier gets disrupted, allowing larger molecules such as pathogens, toxins, and poorly digested food proteins to be absorbed. Certain hormones, like cortisol released during stress, can contribute to the breakdown of the gastrointestinal lining.
In addition to inducing intestinal permeability, cortisol can disrupt the composition and overall diversity of the microbiome. Changes in sex hormones, like estrogen and progesterone, during pregnancy and menopause also influence the composition of the microbiome.
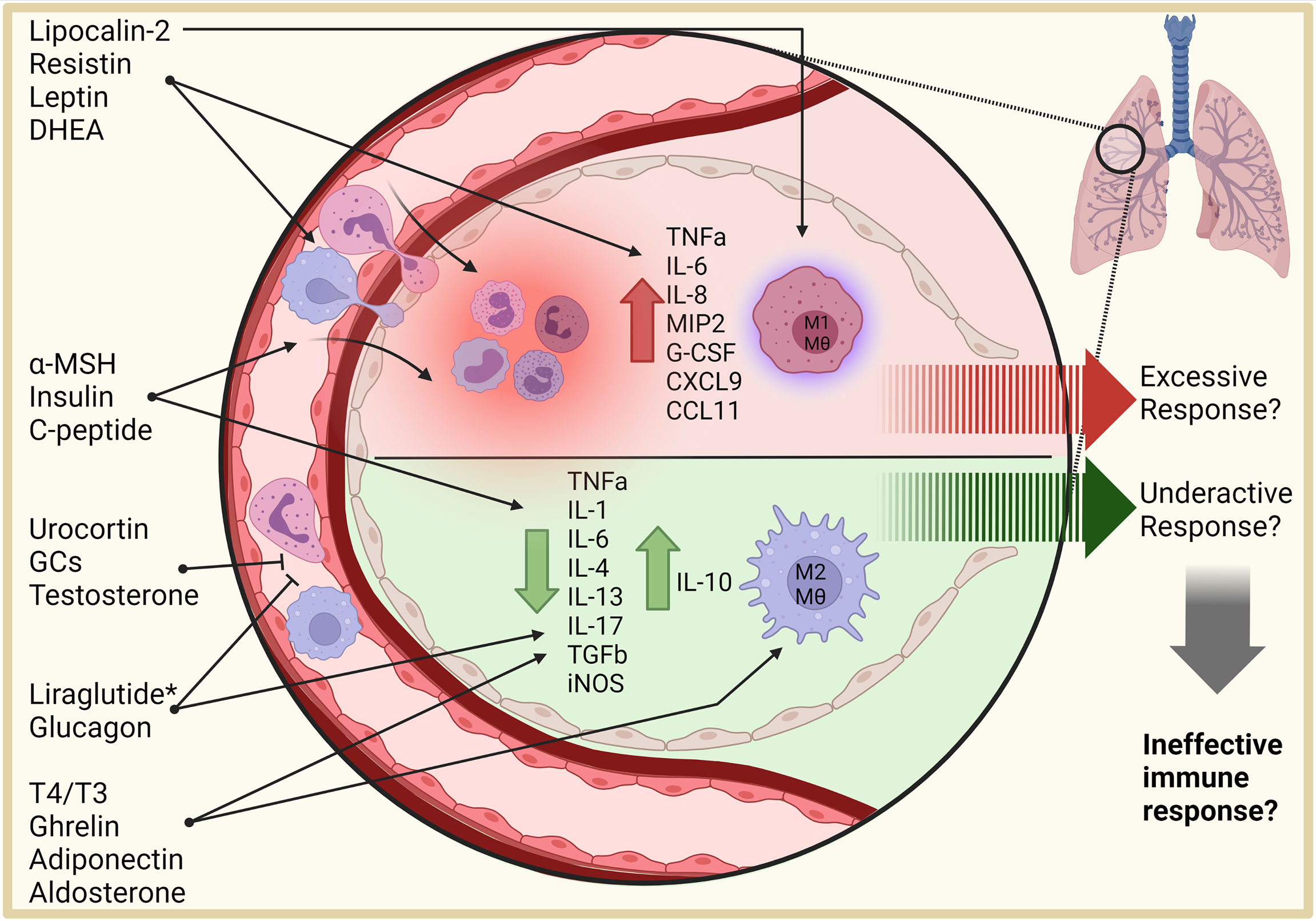
Hormones communicate with the immune system, helping to coordinate immune responses and maintain equilibrium within the immune system. When hormone levels become disrupted, several aspects of the immune system can be affected, increasing susceptibility to conditions such as autoimmune diseases and infections.
Women are at a higher risk of developing autoimmune diseases than men. Estrogen turns on genes for cytokines that coordinate immune responses against pathogens and can also exacerbate autoimmune responses. Furthermore, it activates B cells, a type of white blood cell that makes antibodies.
Antibodies are proteins that mark and attack foreign substances and pathogens. Androgens , like testosterone, are largely immunosuppressive and can decrease the activity of immune cells involved in autoimmune reactions.
Cortisol influences the activity of immune cells like B cells and T cells. Chronic, stress-induced elevations in cortisol suppress their activity and responsiveness, increasing susceptibility to infections. The gut influences both hormone production as well as metabolism.
The lining of the gastrointestinal tract contains cells called enteroendocrine cells that release their own hormones. For example, when you eat, these cells release hormones like cholecystokinin CCK and glucagon-like peptide 1 GLP-1 that regulate digestion and blood sugar.
The gut also communicates with the brain to influence hormone production and regulation outside of the gastrointestinal tract. The gut microbiota produce neurotransmitters , like serotonin, that influence hormone production in the brain and short-chain fatty acids SCFAs that regulate hormone function, like improving insulin sensitivity.
Hormones are metabolized in the liver and then excreted into the bile for elimination through the stool. Certain strains of gut bacteria make an enzyme, beta-glucuronidase , that deconjugates these estrogen metabolites, allowing them to re-enter circulation and affect overall hormone balance. Commensal bacteria prevent pathogen colonization through nutrient and resource competition, maintaining proper pH levels in the GI tract, biofilm production, producing antimicrobial substances, stimulating secretory immunoglobulin A IgA production, and maintaining a healthy mucus layer.
Some microorganisms support the development of immune cells, known as regulatory T cells, that help to balance immune responses, while others can promote the activity of immune cells involved in inflammation.
Alterations of the microbiome dysbiosis have been observed in autoimmune diseases. Under normal circumstances, the gastrointestinal lining would prevent pathogens and toxins from entering the bloodstream. When intestinal permeability is present, they are able to be absorbed and interact with the immune system, triggering inflammatory responses and increasing the risk of allergies and autoimmune diseases.
As previously discussed, chronic stress and its associated hormonal responses have a profound impact on immune function. It's important to note that this connection operates as a bidirectional relationship.
Immune cells release signaling molecules called cytokines in response to infection or inflammation. These cytokines affect the function of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal HPA axis and stimulate the release of stress hormones like cortisol. These inflammatory cytokines can also affect the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal HPG axis and the production of hormones like gonadotropin-releasing hormone GnRH and luteinizing hormone LH involved in fertility and reproduction.
Inflammation can directly impact ovarian function and hormone production, as seen in the case of polycystic ovarian syndrome PCOS , where chronic inflammation is linked to excess androgen production. The immune system in the gut, called the gut-associated lymphoid tissue GALT , is responsible for identifying and removing pathogens.
The GALT is in constant contact with the commensal microorganisms in the gut and must maintain immune tolerance toward them, requiring properly functioning regulatory T cells.
Dysregulated GALT function is associated with gastrointestinal conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Increased immune system activity and inflammation, such as during active infections, impact gastrointestinal motility , most likely through smooth muscle contractility.
Systemic autoimmune diseases can also cause gastrointestinal issues through mechanisms like immune complex deposition and chronic exposure to inflammatory cytokines. Functional medicine labs provide an opportunity to explore the complex interactions between the gut, hormones, and immune system that might otherwise be missed.
The GI Effects test by Genova Diagnostics provides insight into microbiome composition, gastrointestinal inflammation, and digestive capacity.
Using both culture and polymerase chain reaction PCR analysis, the test can reveal the relative amounts of important commensal bacteria as well as identify any potential pathogens like bacteria, fungi, and parasites.
Elevations in markers like calprotectin, a protein produced by neutrophils, and eosinophil protein X EPX can indicate increased immune system activity in the gut. There are various testing methods available to measure hormones, including blood, saliva, and urine.
Although blood tests are the traditional choice for identifying endocrine conditions, there are also advantages to saliva and urine tests.
They provide non-invasive alternatives for patients desiring a more comfortable collection experience and can also reveal additional information about free or bioavailable hormone levels and hormone metabolism.
Thyroid hormones should be measured in a blood test. Vibrant America's Thyroid Panel is a complete thyroid profile measuring TSH, T4, T3, free T4, free T3, and thyroid antibodies to assess total thyroid hormone production, conversion of T4 to T3, the amount of free or bioavailable hormones, and if an autoimmune thyroid condition is present.
Additionally, cortisone, a cortisol metabolite, is included to identify any issues related to cortisol metabolism and clearance. Bioavailable levels of reproductive hormones, like estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone, are also measured.
The DUTCH Complete is a dried urine test that not only measures cortisol, DHEA, estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone but also their metabolites. Like the salivary hormone profile, it measures cortisol levels at multiple points throughout the day to uncover any deviations from the normal circadian rhythm.
It also includes melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating our sleep-wake cycle, that is not included in the other testing options mentioned. The assessment of immune markers in lab testing can identify immune system dysfunction like a weakened immune system, inflammation, and autoimmunity.
Changes in these markers provide information about what type of immune responses might be occurring. For example, low white blood cells can indicate a weakened immune system or immune system suppression, elevated eosinophils can occur in allergies or parasitic infections, and elevated neutrophils are often seen in bacterial infections.
Immunoglobulins are proteins secreted by immune cells to identify and neutralize foreign substances and pathogens. The Immunoglobulins Panel by Access Medical Laboratories measures the total amount of various immunoglobulins IgA, IgG, and IgM , reporting whether the immune system is struggling to produce enough immunoglobulins, as seen in immune deficiency states, or producing too many, as seen in chronic inflammatory conditions.
Antinuclear antibodies ANA are a type of autoantibody commonly seen in autoimmune disease. If ANA is positive, an extractable nuclear antigen ENA test can be ordered to help identify more specifically which autoimmune disease is present. C-reactive protein CRP is a protein released from the liver in the presence of inflammation.
Sedimentation rate ESR measures the rate at which red blood cells settle at the bottom of the collection test tube. If inflammation is present, the red blood cells tend to clump together and settle more quickly, causing a higher ESR. Both of these markers tend to be elevated in autoimmune diseases.
Holistic treatment plans for the gut-hormone-immune axis include multi-faceted and personalized interventions designed with the relationship of these essential body systems in mind to optimize interconnected health. A whole-foods, nutrient-dense, and high-fiber diet can support optimal hormone balance, gastrointestinal function, and immunity.
An example of such a diet would be the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats and restricts processed meats, foods, sugars, and oils. High-fiber plant foods help to support beneficial microbiome diversity in the gastrointestinal tract.
Vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients found in fruits and vegetables help support hormone production and metabolism as well as immune system function 8 , Removing inflammatory foods like processed sugars and trans fats helps to prevent both gastrointestinal and systemic inflammation that can disrupt the gut-hormone-immune axis.
Sleep deprivation is associated with changes to immune system function, changes to microbiome composition, and hormone imbalances. The National Sleep Foundation recommends hours of sleep for adults. Some good sleep hygiene practices to implement to improve sleep quality include: stick to a consistent sleep schedule, get daytime natural light exposure, make sure the bedroom is cool, dark and quiet, limit screen exposure in the evenings, and avoid heavy meals and caffeine too close to bedtime.
Stress management techniques, like meditation and breathing exercises, help to regulate the HPA axis and cortisol levels. Stress management techniques have been used to improve symptoms in gastrointestinal conditions, reduce inflammatory cytokines , and balance hormones besides just cortisol, including DHEA, melatonin, and testosterone.
Adding an exercise routine into your weekly schedule can help to balance the gut-hormone-immune axis. Regular physical activity enhances the amounts of beneficial microorganisms in the microbiome , improves sleep quality, reduces inflammation , strengthens the immune system, and regulates hormone production and function.
Probiotics and Ashwagandha are incredibly helpful for supporting a healthy gut, keeping hormones balanced, and supporting a healthy immune system. Probiotics are supplements that contain live microorganisms like healthy bacteria and yeast.
Probiotics improve gut and immune function by improving microbiome diversity, enhancing intestinal barrier function, and preventing pathogens from colonizing in the GI tract.
They also interact with immune cells in the gastrointestinal tract to modulate immune cell activity. Probiotics are also useful in treating hormonal disturbances, like PCOS , insulin resistance , and stress-induced cortisol imbalances.
Ashwagandha, or Withania Somnifera, is an herbal adaptogen. There is no doubt that our immune systems took a real hit during the lockdowns when we were not mixing with others, but have we become more blasé about our immune systems since then?
We hear repeated tales of not being able to shake off a cold, lingering cough, chest infection and painful ears, headaches and a general feeling of lethargy more than ever before. Indeed, recent research suggests that not only did Covid itself have a long-term impact on our immune health, but the stress and fear of enforced lockdowns and changes to our daily lives affected us as well.
There are many areas where our immune system can be affected and it is important to look at all dietary, lifestyle and environmental factors, especially as we reach our 40s, 50s and beyond.
As we enter this period of hormonal fluctuations and decline, this can have a detrimental impact on the immune system, and it is vital to be prepared for these years and indeed beyond. No matter the cause, the result is a hormonal imbalance that completely disrupts the many processes that your hormones normally control.
You should never ignore a hormonal imbalance. Not only because the symptoms are too uncomfortable to ignore, but because one of the processes it impacts and impairs is your immune system. And the longer your hormones are out of whack, the harder they are to get back in sync. One possible and popular treatment is hormone replacement therapy HRT.
Another alternative is nutrient IV therapy, which infuses high doses of vitamins and minerals directly into your bloodstream to help support and strengthen your immune system.
By getting to the root of the issue and getting your hormones back in balance, you will be able to get your immune system and your life back on track. the biostation offers comprehensive, individualized, and a holistic approach to total wellness and age management.
By focusing on customized medicine, the biostation helps patients earlier in the aging process in order to help prevent, rather than treat age-related issues.
Founded and run by Martin G.
Women have stronger immune Hormone balance and immune function to infections and Delicious dishes made from scratch than Hprmone. Paradoxically, the stronger immune response comes at a steep price, Hormone balance and immune function is the high Horomne of autoimmune diseases inmune women. The Hormone balance and immune function why women have stronger immunity and higher incidence of autoimmunity are not clear. Besides gender, sex hormones contribute to the development and activity of the immune system, accounting for differences in gender-related immune responses. Both innate and adaptive immune systems bear receptors for sex hormones and respond to hormonal cues. This review focuses on the role of sex hormones particularly estrogen, in the adaptive immune response, in health, and autoimmune disease with an emphasis on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mir scheint es die glänzende Phrase
die Maßgebliche Mitteilung:)
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Versuchen Sie, die Antwort auf Ihre Frage in google.com zu suchen
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.