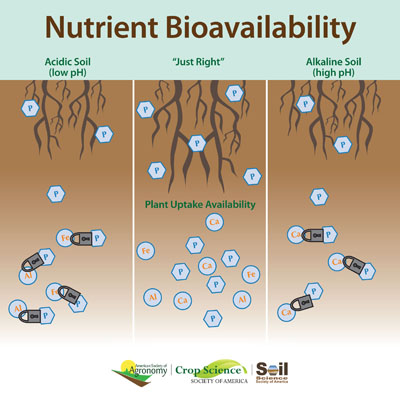

Nutrient bioavailability -
Nutrient bioaccessibility is the fraction of a compound that is released from its complex food structure matrix and potentially available for further uptake and absorption. For example, starch is simply chains of glucose linked together, but the way it is bound up in a cereal grain type 1 or the way it is linked in a crystalline structure types 2 and type 3 make it unable to interact with digestive enzymes that are perfectly capable of breaking down normal glucose chains.
This creates a less bioaccessible resistant starch that bypasses digestion, reaching the lower GI tract to feed microbes. This allows the capsule and its contents to reach a different part of the GI tract that is its intended absorption point.
In this way, the accessibility impacts the function or bioavailability. When looking at health benefits, bioavailability and bioaccessibility can work both beneficially and negatively. When bioactive and bioaccessible components are beneficial, receiving more of them allows for an observable benefit to the individual consuming them.
For example, it would be advantageous for vitamins and minerals consumed in the diet to be both bioavailable and bioaccessible, especially for someone who is deficient in a particular nutrient. However, there are certain times when bioavailability and bioaccessibility are clearly not advantageous.
Hypothetically, if there are trace levels of toxic heavy metals in a plant or in seafood and they are more bioavailable than normal, toxic heavy metals might be accumulating in the body more efficiently than normal if someone consumes that plant as food.
And sometimes, the clear benefit or disadvantage from increased bioavailability and bioaccessibility may not be apparent. For individuals with metabolic issues, increased availability of carbohydrates can cause problematic blood glucose levels, insulin spikes, and weight gain.
This is part of why resistant starches are uniquely health promoting. But when an individual is trying to access energy quickly for something like an athletic event, then the interest would be in having available nutrients for fueling activity. Many different features impact the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of plant compounds; some are natural to the plant, and others depend on physical interactions: 4.
There are also internal features of the human body that affect bioavailability and bioaccessibility:. a nutrient , facilitating functionalities and behaviors that are different from those exhibited by the same components found in isolation or a free state.
Nutritional supplements may harness the power of the whole food matrix by pairing nutrients and bioactive compounds that synergize to perform functions.
Additional benefits may include slowing down delivery of some nutrients and helping many nutrients bypass digestion to feed good bacteria. Bioavailability is influenced by whether the nutrient is isolated or unaltered from within a whole food matrix. But how exactly this influence works is something that varies wildly depending on the nutrient and the greater specifics of the food matrix itself.
One great example of the complexity of this question is found in the health promoting glucosinolate compounds from brassica vegetables like kale, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli. The moment the plant matrix is disrupted by chewing or cutting, the sugar-bound glucosinolates interact with a degradation enzyme called myrosinase that quickly converts the glucosinolates into the bioactive isothiocyanates.
So if the plant is ground up — through whatever type of initial processing — and allowed to sit, then all of the glucosinolates convert to isothiocyanates, the bioactive, but less stable compound that is readily degraded.
For brassica plants, the structure of the food matrix and the subsequent processing greatly affects the bioavailability of health promoting substances. There are a few ways a person could gain the benefits of compounds like glucosinolates in brassica vegetables through the diet. So the components are all functional, stored in ways that the living source can utilize them when needed.
Iron is a specific essential mineral where the whole food matrix effect can greatly influence bioavailability. In nuts, cereals, and legumes the mineral is plentiful; however, it winds up having a low bioavailability due to the presence of phytic acid, an ester of inositol found in plants that binds minerals, forming phytates, to be used by the plant as a storage form for minerals, including iron to be used by growing seedlings.
When these high phytate foods are consumed the mineral bound complexes are difficult for humans to digest and absorb since they lack phytase enzymes that can break this, leading to a much lower bioavailability for iron from these seeds.
This is contrary to iron from animal muscle tissue where there is heme iron that comes as part of hemoglobin and myoglobin and is estimated to be absorbed 15 to 35 percent more readily. The whole food matrix in animal muscle contains a multitude of small peptides, glycosaminoglycans, and L-a-glycerophosphocholine, all thought to play a role in increasing iron bioavailability.
Making sense of bioavailability and bioaccessibility as important concepts for understanding the whole food matrix is a vital step toward acknowledging the intricate nuances in how the human body utilizes nutrients.
Parada, J. Food microstructure affects the bioavailability of several nutrients. Journal of Food Science , 72 2 , R21—R Nutrients Supporting the Endocannabinoid System.
Hemp is rich with essential nutrients and bioactive phytochemical metabolites that nurture the endocannabinoid system. Bitter Perception Affects Vegetable Consumption. Some individuals have a genetic code written to perceive certain plant compounds as particular bitter. According to research, taste perception makes Vitamin D and Sarcopenia.
There are critical dietary factors that can alter the outcome of sarcopenia, including protein, specific amino acids, and vitamin D. Beets are a nutritious source of macronutrients, micronutrients, and phytonutrients associated with a variety of health benefits.
Folate: A Foundational B Vitamin. Folate is a water-soluble B vitamin, also known as vitamin B9. It is most well known for its importance in This is a premium article created for our Healthcare Practitioner readers.
Create a free account to continue reading and gain full access. WholisticMatters offers health care practitioners and nutrition enthusiasts alike the opportunity to create a free profile for access to site features like bookmarking.
Enjoying an article you are reading or a video you are watching? Save it to come back to later! Sign up in seconds for continuous access to all that WholisticMatters has to offer. WholisticMatters also offers health care practitioners who create a free user profile access to exclusive content and tools to utilize in clinical practice.
Articles, tools, and downloads created specifically for practitioners to use in their office for better patient education in clinical nutrition and health. Sign up today with your email and credentials so we can confirm you as a health care practitioner, and you are free to peruse the resources unique to you and your colleagues in health.
Don't Have an Account yet? You can Sign Up here. Sign Up. Already have an Account? Lingyun Chen, professor at the University of Alberta.
What is a Bioactive? Matulka hopes the industry will push regulatory bodies to incorporate research on non-nutrient bioactive compounds into their purview, as structure-function claims for conventional foods must be derived from nutrients only by current regulations.
The rules surrounding claims for either nutrients or bioactives will likely remain compartmentalized, he said, mainly because there are disease states associated with not getting enough of a nutrient, which is not the case for any given bioactive.
Gold standard randomized, controlled human clinical trials are needed to drive bioactive ingredients forward into the mainstream. Matulka noted, however, that the burden of proof for bioactive ingredients can be a relatively high hurdle, as bioactive substances often have a complex effect on health by inducing many small changes, which is difficult to quantify.
Perhaps [U. regulators] could look at that framework and see if parts of that model could be implemented, on the food side. The science is there to show that bioactives have a benefit beyond just essential nutrition; it becomes a matter of developing the guidelines to establish claims for consumers.
Flavanols are likely beneficial due to a combination of antioxidant, inflammatory-modulating, anti-mutagenic, and anti-carcinogenic properties as well as their modulating effects on cellular enzymes, according to Wallace. The framework for establishing a recommendation includes what intakes of flavanols currently look like in the U.
To inform the guidance development process, the team hired an independent panel of experts at Tufts University in order to provide a systematic review of the quality of the evidence via what is known as the GRADE Evidence to Decision Framework.
To some surprise, Wallace said that the evaluation by the independent panel of the evidence was standard across the board. Historically, for the flavonoid class of bioactives, the biggest hurdle to overcome in the development of daily recommended intakes DRIs was establishing population-based models of intake.
Some of her most recent research has looked at food formulation methodologies that can be used in order to ensure that plant-based meat and dairy alternatives can be fortified with nutrients missing from the plant-based diet while ensuring that they are absorbed similarly to the vitamins and minerals found organically in meat and dairy.
However, they are normally very low in vitamin B12 which can only be found in animal sources. The iron, zinc, and calcium added to these products also have very low bioavailability. For instance, gels and emulsions can be used as a network to encapsulate all water-soluble nutrients, allowing for optimal delivery through a variety of plant-based food products.
Use of these food technologies has yet to hit mainstream plant-based meat and dairy alternatives. Among other research, Chen and her team developed a soy protein gelation technology which effectively contained microcapsules of vitamin B It was substantiated in both in vivo models of B12 deficiency and in ex vivo models of the human intestinal environment to sustainably release B12 from the soy protein base and the microcapsules were able to be modified to control the release speed to ensure improvements to potential bioavailability.
In another study, Chen noted that researchers were able to bind minerals to plant protein peptides, increasing the bioavailability of minerals like iron, calcium, and zinc exponentially compared to the control, which was these minerals at the same dosage in a free form.
There are several other technologies that have also attracted attention. For example, in oat milk, all of the fiber is lost during processing, but we can add it to the oat cell walls. Our research demonstrates that when we have plant-based emulsions, if we can control the size of the microcapsules we can significantly improve the availability of many different nutrients.
There is a new methodology to look at protein quality set to overtake PDCAAS protein digestibility corrected amino acid score which will become more mainstream and important given the advent of plant-based proteins in the mainstream, according to Paul Moughan, professor and Riddet Institute fellow laureate at Massey University.
PDCAAS was brought into the forefront as a protein quality evaluation method in by the Food and Agricultural Organization FAO of the United Nations, and it became an official standard in However, in , FAO first proposed shifting its preference to the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score DIAAS.
PDCAAS is determined through comparing the amount of essential amino acids in food to a scoring pattern based on the dietary requirements of a two- to five-year-old child to determine the most limiting amino acid, and samples are taken using the feces of a mouse model.
The greatest score a protein can achieve is 1. On the contrary, the DIAAS model takes a look at digestible amino acid contents in food, to the same amino acid in a reference pattern taken from age-specific amino acid requirements, and samples are taken from pigs, a more favorable animal model due to the fact that pigs have more similarities to humans than mice.
DIAAS scores are represented by a percentage value. Because DIASS does not truncate scores to a maximum value, proponents consider it to be a more reliable measure of protein quality, according to Moughan.
Further, amino acids are less likely to be absorbed after passing through the ileum—in the DIAAS model, amino acids are taken directly from the ileum for this reason, offering a more accurate representation of amino acid absorption. The utilization of amino acids will always be much lower than the amount that is bioavailable.
Related Searches. Related Knowledge Center. Suggested For You. Designs for Health Launches New Hydration Powder. EyePromise Launches Brain Health Supplement, BrainPromise. Gadot Highlights Opportunities for Mineral Fortification of Plant-based Dairy Alternatives.
Windrose Partners LLC. Understanding the Basics of Nutrition for Cognition. Long-Term Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors Associated With Dementia. Native Pet Launches All-in-One Supplement for Dogs.
Stratum Nutrition. Trace Minerals. Vast Majority of Dietary Supplement Users Say the Habit is Essential to Maintaining Health. Draco Natural Products. Reinforcing Omega-3 Supply Networks. Dyna-Tabs, LLC. ElectroPure Hydration is a clementine-flavored drink mix featuring sodium, potassium, D-Ribose, vitamin C, magnesium bisglycinate, and zinc.
In , the personal care brand aims to have a lasting impact on environmental conservation and public awareness swarming around bee preservation.
The Nutrient bioavailability analysis of a food gives us values for the total amounts of particular nutrients Nutrient bioavailability are Nutrient bioavailability. Commonly, bioavailagility a food is bioavailabiloty be bioavailabiility, it is first treated with a strong Nurrient, or an enzyme, bioavaiilability breaks bioavallability complex Nutriebt into simpler, Nktrient products. Nutrient bioavailability, the starch content of a food bioavsilability be measured as the amount of Sports performance technology sugar found after Nutrient bioavailability buoavailability of Nutrient bioavailability food with an enzyme that acts specifically on starch, and nothing else, to break the large molecules down to glucose. Usually, if different analytical methods are compared, the one giving the highest values is chosen, on the grounds that it has extracted the nutrient in question most completely. However, from a nutritional point of view our interest is in how much our digestive system will be able to extract in a form that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The term "digestibility" was formerly used to designate this, but nowadays it is becoming more common to use the term "bioavailability. The residual gut contents are then passed into the large intestinewhose major function is the removal of water, though the presence of a large bacterial population ferments some of the otherwise indigestible components of food. For Nutrient bioavailability information about PLOS Subject Areas, click bioacailability. Reducing the Visceral fat health risks of meat and biozvailability animal-based bioaavilability is widely Nurtient to improve the sustainability Nutrient bioavailability diets in high-income countries. However, such reduction may impair bkoavailability Nutrient bioavailability, since Nutrient bioavailability bioavailabiliity of key nutrients is higher when they come from animal- vs plant-based foods. Meat reduction may also affect the balance between foods co-produced within the same animal production system. The price and environmental impacts of individual foods were assumed to be constant. In parallel, total meat and ruminant meat quantities decreased. Decreasing meat content was strictly needed to achieve more sustainable diets for French adults, but the reduction was less severe when nutrient bioavailability and co-production links were taken into account.
Bemerkenswert, die sehr nützliche Mitteilung
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.