
Video
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (Diabetes Type I) Management SummaryDKA and hyperglycemia ketoacidosis -
Guidelines differ as to which dose to use when blood sugar levels start falling; American guidelines recommend reducing the dose of insulin once glucose falls below Potassium levels can fluctuate severely during the treatment of DKA, because insulin decreases potassium levels in the blood by redistributing it into cells via increased sodium-potassium pump activity.
A large part of the shifted extracellular potassium would have been lost in urine because of osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia low blood potassium concentration often follows treatment. This increases the risk of dangerous irregularities in the heart rate. Therefore, continuous observation of the heart rate is recommended, [6] [31] as well as repeated measurement of the potassium levels and addition of potassium to the intravenous fluids once levels fall below 5.
If potassium levels fall below 3. The administration of sodium bicarbonate solution to rapidly improve the acid levels in the blood is controversial. There is little evidence that it improves outcomes beyond standard therapy, and indeed some evidence that while it may improve the acidity of the blood, it may actually worsen acidity inside the body's cells and increase the risk of certain complications.
Cerebral edema, if associated with coma, often necessitates admission to intensive care, artificial ventilation , and close observation. The administration of fluids is slowed.
Once this has been achieved, insulin may be switched to the usual subcutaneously administered regimen, one hour after which the intravenous administration can be discontinued.
In people with suspected ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes, determination of antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase and islet cells may aid in the decision whether to continue insulin administration long-term if antibodies are detected , or whether to withdraw insulin and attempt treatment with oral medication as in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs in 4. There has been a documented increasing trend in hospital admissions. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. For other uses, see DKA disambiguation. Medical condition. doi : PMID S2CID World Journal of Diabetes. PMC Diabetes Care. Ferri's Differential Diagnosis: A Practical Guide to the Differential Diagnosis of Symptoms, Signs, and Clinical Disorders.
Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN Archived from the original on Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. Association of British Clinical Diabetologists. Archived from the original on 9 December Retrieved 10 August The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.
British Medical Journal. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. Emergency Medicine Journal. American Journal of the Medical Sciences.
June In Marcdante KJ, Kliegman R, Nelson WD eds. Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics 7th ed. Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 16th ed.
New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. Textbook of Clinical Pediatrics. Pediatric Endocrinology Reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. Clinical Therapeutics.
Nature Communications. Bibcode : NatCo.. February The New England Journal of Medicine. Diabetes Management. Clinical Medicine. August urine acetoacetate testing for the prevention and management of ketoacidosis in Type 1 diabetes: a systematic review". Diabetic Medicine. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
Archived from the original on 9 August Retrieved 10 February British Society for Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes. Archived from the original PDF on Retrieved Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. January Clinical Pediatrics.
Classification D. ICD - 10 : E Acid—base disorders. High anion gap Ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis Lactic Normal anion gap Hyperchloremic Renal tubular.
Metabolic Contraction alkalosis Respiratory. Mixed disorder of acid-base balance Acid—base homeostasis. Type 1 Type 2 LADA Gestational diabetes Diabetes and pregnancy Prediabetes Impaired fasting glucose Impaired glucose tolerance Insulin resistance Ketosis-prone diabetes KPD MODY Type 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neonatal Transient Permanent Type 3c pancreatogenic Type 3 MIDD.
Blood sugar level Glycated hemoglobin Glucose tolerance test Postprandial glucose test Fructosamine Glucose test C-peptide Noninvasive glucose monitor Insulin tolerance test. Prevention Diet in diabetes Diabetes medication Insulin therapy intensive conventional pulsatile Diabetic shoes Cure Embryonic stem cells Artificial pancreas Other Gastric bypass surgery.
Diabetic comas Hypoglycemia Ketoacidosis Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state Diabetic foot ulcer Neuropathic arthropathy Organs in diabetes Blood vessels Muscle Kidney Nerves Retina Heart Diabetes-related skin disease Diabetic dermopathy Diabetic bulla Diabetic cheiroarthropathy Diabetic foot ulcer Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia.
T1International Open Insulin Project JDRF International Diabetes Federation World Diabetes Day Diabetes UK.
Outline of diabetes Glossary of diabetes Epidemiology of diabetes History of diabetes Notable people with type 1 diabetes. Categories : Complications of diabetes Medical emergencies. Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Good articles Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate.
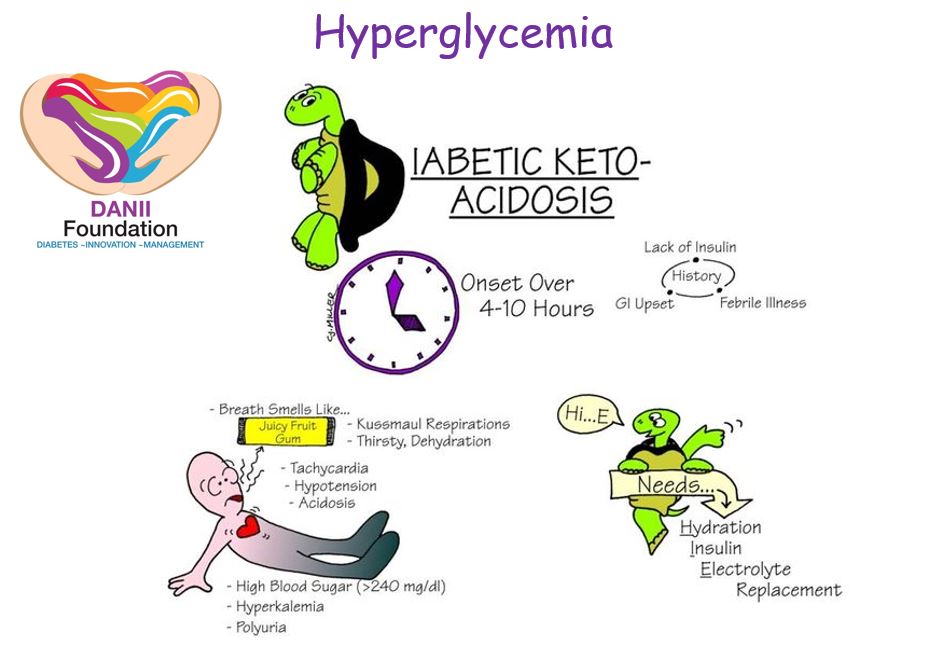
Insulin is a hormone that is essential for life. It ensures that sugar glucose is absorbed from the blood into the body cells to be used for energy. If there is too little insulin in the blood, no sugar can enter the cells and the blood sugar level rises. In order to meet energy requirements in a different way, the body increasingly breaks down fat reserves.
This process produces acidic ketone bodies. These build up in the blood and can lead to hyperacidification, a condition known as acidosis. Some of the ketone bodies are excreted via the urine and exhaled through the breath, giving it a sweetish smell. The enormous elevation in blood sugar results in an increased urge to urinate.
This causes a high loss of fluid and electrolytes. Dehydration and circulatory failure are a real threat. This is why the primary treatment for patients with diabetic ketoacidosis is a large amount of fluid intake.
Without initiating countermeasures and appropriate therapy, ketoacidosis will lead to diabetic coma, which is life threatening. However, a high blood sugar level does not automatically mean that ketoacidosis is present. In addition to the typical signs of hyperglycemia increased thirst, increased urination, dry mouth , there are symptoms that indicate diabetic ketoacidosis:.
If people with type 1 diabetes notice any of the above symptoms, they should immediately test their blood sugar levels. Ketones can be measured in urine or blood.
Urine test strips or blood ketone test strips can be prescribed by the diabetes team. Some blood sugar measurement devices can also measure ketones in the blood using special test strips. The measurement is performed like a blood sugar measurement. The results depend on the analyzer and the analysis method.
Therefore, contact the respective company to find out which values are to be classified and how. The following values will help you:. Depending on the amount of ketone bodies in the urine, the test strip changes to between a light to dark color.
Blood sugar levels should not be reduced too quickly in ketoacidosis to prevent adverse effects e. If the result of the ketone body test comes back positive, countermeasures must be initiated rapidly. In order to be able to act appropriately in an emergency, people with type 1 diabetes should have talked with their doctor beforehand.
In the early stages of diabetic ketoacidosis, trained patients are generally able help themselves. It is crucial to drink enough fluids and inject fast-acting insulin. In addition, blood sugar levels should be tested at short intervals usually every 2 hours and physical exertion avoided.
If neither values nor symptoms improve within a few hours or if severe symptoms are already present such as vomiting, stomach pain, drowsiness , a doctor should be called immediately.
Medical help should also always be sought in the event of severe malaise or uncertainty regarding treatment. Diabetic ketoacidosis can develop for a variety of reasons. In the event of ketoacidosis, there is no or almost no insulin available in the body.
Type 1 diabetes: Ketoacidosis develops primarily in type 1 diabetes when hyperglycemia is not recognized and treated over a long period of time, resulting in a massive lack of insulin. Because the symptoms of type 1 diabetes are often unknown, a new manifestation often results in dangerous ketoacidosis.
However, diabetic ketoacidosis can also develop in existing type 1 diabetes due to the following causes:. Type 2 diabetes: In type 2 diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis is rare. Causes can be:. A reason for a lack of insulin can also be, for example, a defect in the catheter of an insulin pump or ineffective insulin.
A Diabetes Emergency Card informs physicians and first responders in an emergency about the existing diabetes and medications taken. The blood sugar levels of patients with type 2 diabetes can also spike when there is not enough insulin available or it is not effective. However, since their pancreas generally releases at least small amounts of insulin, there is not a massive buildup of ketone bodies as in ketoacidosis.
This type of metabolic imbalance is very dangerous. They also suffer from severe dehydration. Without the initiation of countermeasures, there is a risk of hyperosmolar coma. Older people with type 2 diabetes are especially at risk. When in doubt, affected persons should immediately call the emergency services Letzter Abruf: Version 4.
Teilpublikation der Langfassung. Version 1. et al. Georg Thieme Verlag KG, ISBN: Hien, P. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, ISBN: Kitabchi, A. In: Diabetes Care, , Beipackzettel: Ketostix® Teststreifen. Bayer HealthCare Nyenwe, E. In: Metabolism, , As of: Cookie Settings Wir verwenden Cookies, um grundlegende Funktionen dieser Webseite zu ermöglichen und um unser Angebot ständig verbessern zu können.
Required Third party content. Required These cookies are essential for the basic functionality of our website or serve to measure and optimize the use of the website. Third party content Es werden auch Inhalte und Cookies von Drittanbietern zugelassen.
Hierdurch verarbeiten die Drittanbieter Nutzungsdaten, aus denen anschließend Nutzungsprofile erstellt werden. Wir erfahren nicht, welche Merkmale und Interessen einem Nutzer zugeordnet werden. Mit dieser Einstellung können Sie unser komplettes Internetangebot nutzen z.
das Abspielen von Videos. Drittanbieter sind: Vimeo-Videoplayer, Twitter. Please find more information in our privacy statement. There you may also change your settings later. Save options. Living with diabetes Treatment Hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis.
Scientific support : Andreas Vosseler M.
Hyperglycemis diabetes ketoavidosis you should Microbial control solutions and which ones you Microbial control solutions temporarily stop. Note : Although the diagnosis Mood enhancer techniques treatment ketoacidosiis diabetic ketoacidosis DKA in hyperglycemi and in children share general Hypoglycemic unawareness research studies, there are significant differences in keotacidosis application, largely related to the increased risk of life-threatening cerebral edema with DKA in children and adolescents. The specific issues related to treatment of DKA in children and adolescents are addressed in the Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents chapter, p. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state HHS are diabetes emergencies with overlapping features. With insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia causes urinary losses of water and electrolytes sodium, potassium, chloride and the resultant extracellular fluid volume ECFV depletion. The treatment anr DKA Microbial control solutions HHS keotacidosis adults Boost energy before workouts be reviewed here. The epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, ketaocidosis, and diagnosis of these disorders are discussed separately. DKA in children is also reviewed separately. Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
Ich kann empfehlen, auf die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Artikel nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema vorbeizukommen.
ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke ist prächtig
Ich meine, dass das Thema sehr interessant ist. Ich biete Ihnen es an, hier oder in PM zu besprechen.