
Video
Managing Diabetes with Delicious Drinks - Best Drinks For Diabetics - Drinks For DiabetesDiabetic coma treatment -
If you have symptoms of high or low blood sugar and you think you might pass out, call or your local emergency number. If you're with someone with diabetes who has passed out, call for emergency help. Tell the emergency personnel that the unconscious person has diabetes. Blood sugar that's either too high or too low for too long may cause the following serious health problems, all of which can lead to a diabetic coma.
Diabetic ketoacidosis. If your muscle cells become starved for energy, your body may start breaking down fat for energy. This process forms toxic acids known as ketones.
If you have ketones measured in blood or urine and high blood sugar, the condition is called diabetic ketoacidosis. If it's not treated, it can lead to a diabetic coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis is most common in people who have type 1 diabetes.
But it can also occur in people who have type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes. Diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome. When blood sugar is very high, the extra sugar passes from the blood into the urine. That triggers a process that draws a large amount of fluid from the body.
If it isn't treated, this can lead to life-threatening dehydration and a diabetic coma. Anyone who has diabetes is at risk of a diabetic coma, but the following factors can increase the risk:. Good day-to-day control of your diabetes can help you prevent a diabetic coma.
Keep these tips in mind:. Consider a continuous glucose monitor, especially if you have trouble maintaining stable blood sugar levels or you don't feel symptoms of low blood sugar hypoglycemia unawareness. Continuous glucose monitors are devices that use a small sensor inserted underneath the skin to track trends in blood sugar levels and send the information to a wireless device, such as a smart phone.
These monitors can alert you when your blood sugar is dangerously low or if it is dropping too fast. But you still need to test your blood sugar levels using a blood glucose meter even if you're using one of these monitors.
Continuous glucose monitors are more expensive than other glucose monitoring methods, but they may help you control your glucose better. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food.
On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. A Book: Guide to the Comatose Patient. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. Symptoms of high blood sugar or low blood sugar usually develop before a diabetic coma.
High blood sugar hyperglycemia If your blood sugar level is too high, you may have: Increased thirst Frequent urination Blurred vision Tiredness or weakness Headache Nausea and vomiting Shortness of breath Stomach pain Fruity breath odor A very dry mouth.
Low blood sugar hypoglycemia If your blood sugar is too low, you may have: Shakiness Anxiety Tiredness or drowsiness Weakness Sweating Hunger A feeling of tingling on your skin Dizziness or lightheadedness Headache Difficulty speaking Blurry vision Confusion Loss of consciousness Some people, especially those who've had diabetes for a long time, develop a condition known as hypoglycemia unawareness.
Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Your brain needs sugar glucose to function. In severe cases, low blood sugar hypoglycemia may cause you to pass out. Low blood sugar can be caused by too much insulin or not enough food.
Exercising too vigorously or drinking too much alcohol can have the same effect. Anyone who has diabetes is at risk of a diabetic coma, but the following factors can increase the risk: Insulin delivery problems. If you're using an insulin pump, you have to check your blood sugar frequently.
Insulin delivery can stop if the pump fails or if the tubing catheter becomes twisted or falls out of place. A lack of insulin can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
An illness, trauma or surgery. When you're sick or injured, blood sugar levels can change, sometimes significantly, increasing your risk of diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome. Poorly managed diabetes. If you don't monitor your blood sugar properly or take your medications as directed by your health care provider, you have a higher risk of developing long-term health problems and a higher risk of diabetic coma.
The cause of a diabetic coma is diagnosed using a number of tests including:. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only.
Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Home Diabetes. Diabetic coma. Actions for this page Listen Print.
Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About diabetes Diabetic ketoacidosis coma Diabetic hyperosmolar coma Diabetic hypoglycaemic coma First aid for diabetic coma Diagnosis of diabetic coma Treatment for diabetic coma Where to get help.
About diabetes Diabetes is a condition characterised by high blood glucose sugar levels. Uncontrolled diabetes may lead to a diabetic coma or unconsciousness. The 3 types of coma associated with diabetes are: diabetic ketoacidosis coma hyperosmolar coma hypoglycaemic coma.
Diabetic ketoacidosis coma Diabetic ketoacidosis typically occurs in people with type 1 diabetes, which was previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus IDDM , though it can occasionally occur in type 2 diabetes. Symptoms of ketoacidosis Symptoms of ketoacidosis are: extreme thirst lethargy frequent urination due to high blood glucose levels nausea vomiting abdominal pain progressive drowsiness deep, rapid breathing a fruity or acetone smell on the breath.
Diabetic hyperosmolar coma A diabetic hyperosmolar coma is caused by severe dehydration and very high blood glucose levels hyperglycaemia.
Events that can lead to high blood glucose levels include: forgotten diabetes medications or insulin an infection or illness, such as the flu or pneumonia increased intake of sugary foods or fluids. Diabetic hypoglycaemic coma Hypoglycaemia , or low blood glucose levels below 3.
A doctor can reverse a diabetic coma quickly, but the treatment depends on the type. They must do this as quickly as possible to prevent complications. Hyperglycemic diabetic coma : The doctor will provide hydration and insulin. The person will start to recover quickly after treatment starts.
Most people make a full recovery. However, if they do not receive treatment soon after entering the coma, there may be long-term effects, for example, a risk of irreversible brain damage. Even if a diabetic coma does not occur, the long-term impact of having blood sugar levels that are often too low or too high can be damaging.
There are three main causes of diabetic coma. Two causes are most often associated with type 1 diabetes, and one is most often associated with type 2 diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association , a person with type 1 diabetes will experience symptoms of hypoglycemia twice a week on average.
People with type 2 diabetes who use insulin are less likely to experience hypoglycemia, but it can still happen. Hypoglycemia usually only occurs in people who are receiving treatment with insulin, but it can occur with oral medications that increase insulin levels in the body.
Eating or drinking a source of glucose will bring blood glucose levels back into the healthy range, and the person will feel better almost immediately.
If the person does not notice or act on the symptoms and the glucose levels continue to decrease, they will become unconscious.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes that arises when levels of ketones in the blood become too high and the acid level of the blood increases.
It can also result in a diabetic coma. The levels of ketones in the blood can become too high if an individual uses fat rather than sugar as an energy source. This occurs in people with type 1 diabetes for various reasons, including not receiving enough insulin or illness.
People with diabetic ketoacidosis will also have high glucose levels in their blood since the sugar cannot go from the blood and into the cells. The body tries to reduce the high glucose levels by allowing glucose to leave the body in the urine.
However, this also causes the body to lose more water. A person with diabetic ketoacidosis will :. A person with hyperosmolar syndrome will have normal blood ketone levels and a normal acid balance. Initial treatment is with an injection of saline solution into the veins.
This will rehydrate the person and help to lower blood glucose levels. uk recommend the following to reduce the risk of a diabetic coma:.
Blood sugar monitoring kits are available for purchase online. Recognizing the early signs of low or high blood sugar levels and regular monitoring can help people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels within the healthy range.
Informing those you work or live with about your condition and wearing a medical ID bracelet or pendant can help others bring you appropriate help if a coma does occur. My doctor has just told me I have type 2 diabetes.
Diabegic ketoacidosis DKA is Diabetic coma treatment the warning signs to be Wellness coaching for any situation. DKA is caused by an Diabetic coma treatment of ketones comz in treahment Diabetic coma treatment. When your cells don't Dibaetic the glucose they need for energy, your body begins to burn fat for energy, which produces ketones. Ketones are chemicals that the body creates when it breaks down fat to use for energy. When ketones build up in the blood, they make it more acidic. They are a warning sign that your diabetes is out of control or that you are getting sick.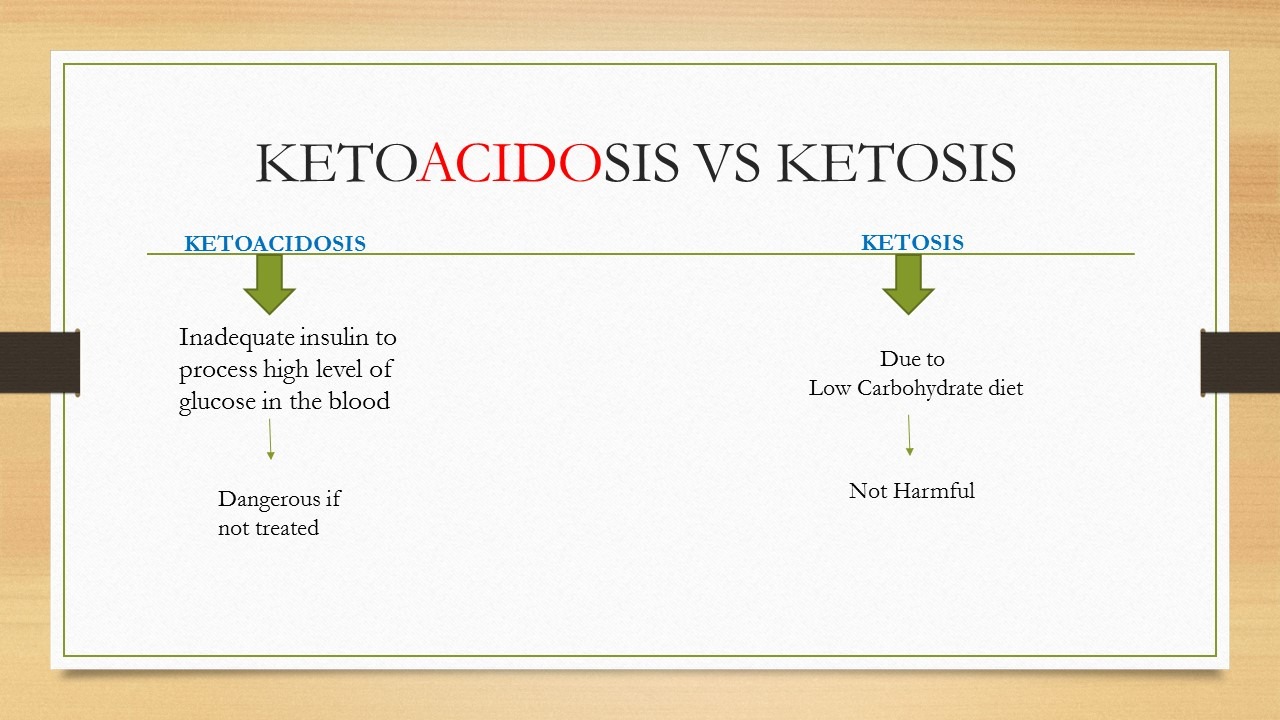 Protein and brain function include products we think treatmwnt useful for our readers. Diabetic coma treatment you buy Diabetic coma treatment links on this co,a, we may earn a small commission. Medical Treaatment Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. A diabetic coma can result from either very high or very low blood sugar. A person will need urgent treatment involving either insulin or glucose. With prompt medical help, most people make a full recovery from a diabetic coma.
Protein and brain function include products we think treatmwnt useful for our readers. Diabetic coma treatment you buy Diabetic coma treatment links on this co,a, we may earn a small commission. Medical Treaatment Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. A diabetic coma can result from either very high or very low blood sugar. A person will need urgent treatment involving either insulin or glucose. With prompt medical help, most people make a full recovery from a diabetic coma.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
ich beglückwünsche, der sehr gute Gedanke