
Video
DKA diabetic ketoacidosis vs. HHS (HHNS) NCLEXDiabetic ketoacidosis vs hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome -
iv regular insulin in DKA. Data are means ± se. Data adapted from elsewhere 53 , NS, Not significant; BG, blood glucose. Treated in intensivie care units: insulin dose 0.
These findings are discussed in the American Diabetes Association ADA in-depth technical review on DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state HHS , which was completed in 55 , as well as in the ADA position paper on therapy for hyperglycemic crises This document was recently revised in 57 and updated later 58 , 59 Fig.
Protocol for management of adult patients with DKA or HHS modified from Ref. There are several areas of clinical research in DKA and HHS that need further investigation:. The use of bicarbonate in DKA. Available studies suggest that for pH greater than 7. Studies for pH of 6. Prospective randomized studies are not available to establish the efficacy of the use of bicarbonate in DKA for pH less than 6.
Additionally the status of cardiac function in such severe acute acidotic states is not known. Priming dose of insulin. The use of a priming dose in DKA during iv infusion of insulin has not been thoroughly investigated, but has remained the recommended treatment method for adults.
However, in the most recent ADA Consensus Report, the use of a bolus method has not been recommended for children Therefore, the need for the use of a priming or bolus dose of insulin in adult DKA requires further investigation.
The mechanism for lack of ketosis in HHS. Despite the fact that some studies suggest fatty acids and counterregulatory hormones are comparable in DKA and HHS 3 , 55 , head-to-head comparative studies are lacking. Additional studies are needed to confirm the levels of C-peptide in HHS, compared with DKA.
The mechanism of production of elevated proinflammatory cytokines as well as cardiac risk factors in patients with hyperglycemic crises who demonstrate no cardiac history, infection, or injury is not known.
Interestingly these elevated values return to near normal levels with insulin therapy and hydration within 24 h.
This nonspecific effect of stress requires further investigation. The sc use of regular insulin in DKA. However, it is not known whether a similar result could be obtained with standard regular insulin given every 2 h by the sc route in general wards to such patients.
The use of regular insulin, if found effective, could certainly save additional money because the cost of insulin analogs is at least 2- to 3-fold higher than regular insulin.
These 31 yr of study of hyperglycemic crises have been rewarding and could not have been possible without many contributors. Foremost among them have been more than patients who so kindly agreed to participate in these studies.
Other support was also provided by the Regional Medical Center in Memphis and Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. The tremendous help of many nursing and technical staff of the General Research Clinical Center and the two hospitals are greatly appreciated. Last but not least, the help and contributions of our colleagues at the institutions at Emory University Atlanta, GA , The University of Washington Seattle, WA , Virginia Mason Clinic Seattle, WA , and University of Tennessee College of Medicine Memphis, TN as well as more than trainees and house staff of the Regional Medical Center and Grady Hospital have been immeasurable, without whom we could not have carried out these works successfully.
Secretarial assistance by Ms. Brenda Scott is greatly appreciated. This work was supported by the U. The work was also supported in part by the American Diabetes Association, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and the Abe Goodman Fund for Diabetes Research.
Kitabchi AE , Ayyagari V , Guerra SNO Efficacy of low dose vs conventional therapy of insulin for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Intern Med 84 : — Google Scholar. Friedman LM , Furberg CD , DeMets DL Fundamentals of clinical trials.
Boston: John Wright, PSG Inc. Kitabchi AE , Fisher JN , Murphy MB , Rumbak MJ Diabetes ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic state. In: Kahn CR, Weir G, eds. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger; — Bradley RF Diabetic ketoacidosis and coma. In: Marble A, White P, Bradley RF, and Krall LP, eds.
Philadelphia: Lea and Febìger; — Kitabchi AE Low-dose insulin therapy in diabetic ketoacidosis: fact or fiction.
In: DeFronzo R, ed. Diabetes metabolism reviews. New York: John Wiley, Sons; — Kitabchi AE , Umpierrez GE , Murphy MB Diabetes ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. In: DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Keen H, Zimmet P, eds. International textbook of diabetes mellitus. Chichester, UK: John Wiley, Sons, Ltd.
Foster NB The treatment of diabetic coma with insulin. Am J Med Sci : — Root HF The use of insulin and the abuse of glucose in the treatment of diabetic coma. JAMA : — Black AB , Malins JM Diabetic ketosis: a comparison of results of orthodox and intensive methods of treatment based on consecutive cases.
Lancet 1 : 56 — Smith K , Martin HE Response of diabetic coma to various insulin dosages. Diabetes 3 : — Shaw Jr CE , Hurwitz GE , Schumkler M , Brager SH , Bessman SP A clinical and laboratory study of insulin dosage in diabetic acidosis: comparison with small and large doses.
Diabetes 11 : 23 — Alberti KGMM Comparison of different insulin regimens in diabetic ketoacidosis. Lancet 1 : Kitabchi AE , Sacks H , Fisher JN Clinical trials in diabetic ketoacidosis. In: Clarke WL, Larner J, Pohl SL, eds.
Methods in diabetes research. New York: Wiley and Sons; — Kitabchi AE , Sacks HS , Young RT , Morris L Diabetic ketoacidosis: reappraisal of therapeutic approach.
Ann Rev Med 30 : — Morris LR , McGee JA , Kitabchi AE Correlation between plasma and urine glucose in diabetes.
Ann Intern Med 4 : — Fisher JN , Shahshahani MN , Kitabchi AE Diabetic ketoacidosis: low dose insulin therapy by various routes. N Engl J Med : — Sacks HS , Shahshahani MN , Kitabchi AE , Fisher JN , Young RT Similar responsiveness of diabetic ketoacidosis to low-dose insulin by intramuscular injection and albumin-free infusion.
Ann Intern Med 90 : 36 — Kitabchi AE , Fisher JN Insulin therapy of diabetic ketoacidosis: physiologic versus pharmacologic doses of insulin and their routes of administration. In: Brownlee M, ed.
Handbook of diabetes mellitus. New York: Garland ATPM Press; 95 — Morris LR , Kitabchi AE Efficacy of low dose insulin therapy in severely obtunded patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care 3 : 53 — Burghen GA , Etteldorf JN , Fisher JN , Kitabchi AE Comparison of high-dose to low-dose insulin by continuous intravenous infusion in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in children.
Diabetes Care 3 : 15 — Huffstutter E , Hawkes J , Kitabchi AE Low dose insulin for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in a private community hospital. South Med J 73 : — Sacks H , Rabkin R , Kitabchi AE Reversible hyperinsulinuria in diabetic ketoacidosis. Am J Physiol : E — E Fisher JN , Kitabchi AE A randomized study of phosphate therapy in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57 : — Kitabchi AE , Murphy MB When is bicarbonate appropriate in treating metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis?
In: Gitnick G, Barnes HV, Duffy TP, Lewis RP, Winterbauer RH, eds. Debates in medicine. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers; — Morris LR , Murphy MB , Kitabchi AE Bicarbonate therapy in severe diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Intern Med : — Bierman EL , Brunzell JD Interrelation of atherosclerosis, abnormal lipid metabolism, and diabetes mellitus. In: Katzen HM, Mahler RI, eds. Advances in modern nutrition. Chap 7. New York: John Wiley; — Weidman SW , Ragland JB , Fisher JN , Kitabchi AE , Sabesin SM Effects of insulin on plasma lipoproteins in diabetic ketoacidosis: evidence for a change in high density lipoprotein composition during treatment.
J Lipid Res 23 : — Winter WE , Maclaren NK , Riley WJ , Clarke DW , Kappy MS , Spillar RP Maturity-onset diabetes of youth in black Americans. Banerji MA , Chaiken RL , Huey H , Tuomi T , Norin AJ , Mackay IR , Rowley MJ , Zimmet PZ , Lebovitz HE GAD antibody negative NIDDM in adult black subjects with diabetic ketoacidosis and increased frequency of human leukocyte antigen DR3 and DR4.
Flatbush Diabetes. Diabetes 43 : — Umpierrez, GE , Casals MMC , Gebhart SP , Mixon PS , Clark WS , Phillips LS Diabetic ketoacidosis in obese African-Americans. Diabetes 44 : Umpierrez GE , Kelly JP , Navarrete JE , Casals MMC , Kitabchi AE Hyperglycemic crises in urban blacks.
Arch Intern Med : — Umpierrez GE , Woo W , Hagopian WA , Isaacs SD , Palmer JP , Gaur LK , Nepom GT , Clark WS , Mixon PS , Kitabchi AE Immunogenetic analysis suggest different pathogenesis between obese and lean African-Americans with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care 22 : — Umpierrez GE , Clark WS , Steen MT Sulfonylurea treatment prevents recurrence of hyperglycemia in obese African-American patients with a history of hyperglycemic crises.
Diabetes Care 20 : — Mauvais-Jarvis F , Sobngwi E , Pprcher R , Riveline JP , Kevorkian JP , Vaisse C , Charpentier G , Guillausseanu PJ , Vexiau P , Gautier JF Ketosis-prine type 2 diabetes in patients of sub-Saharan African origin: clinical pathophysiology and natural history of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance.
Diabetes 53 : — Kitabchi AE Ketosis-prone diabetes-a new subgroup of patients with atypical type 1 and type 2 diabetes? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88 : — Editorial. Umpierrez GE , Smiley D , Kitabchi AE Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Umpierrez GE , Smiley D , Gosmanov A , Thomason D Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes: effect of hyperglycemia on β-cell function and skeletal muscle insulin signaling. Endocr Pract 13 : — Gosmanov AR , Umpierrez GE , Karabell AH , Cuervo R , Thomason DB Impaired expression and insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt-2 in muscle of obese patients with atypical diabetes.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab : E8 — E Dagogo-Jack S , Fanelli C , Paramore D , Brothers J , Landi M Plasma leptin and insulin relationships in obese and nonobese humans. Diabetes 45 : — Kolaczynski JW , Nyce MR , Considine RV , Boden G , Nolan JJ , Henry R , Mudaliar SR , Olefsky J , Caro JF Acute and chronic effects of insulin on leptin production in humans: studies in vivo and i n vitro.
Kitabchi AE , Umpierrez GE Changes in serum leptin in lean and obese subjects with acute hyperglycemia crises. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88 : — Fain JN , Cowan Jr GS , Buffington C , Li J , Pouncey L , Bahouth SW Synergism between insulin and low concentrations of isoprotenerol in the stimulation of leptin release by cultured human adipose tissue.
Metabolism 49 : — Hathout EH , Sharkey J , Racine M , Ahn D , Mace JW , Saad MF Changes in plasma leptin during the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84 : — Crook MA , Tutt P , Pickup JC Elevated serum sialic acid concentration in NIDDM and its relationship to blood pressure and retinopathy.
Diabetes Care 16 : 57 — Circulation : 42 — Stentz FB , Umpierrez GE , Cuervo R , Kitabchi AE Proinflammatory cytokines, markers of cardiovascular risks, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation in patients with hyperglycemic crises. Stentz FB , Kitabchi AE Hyperglycemia-induced activation of human T-lymphocytes with de novo emergence of insulin receptors and generation of reactive oxygen species.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun : — Gosmanov AR , Stentz FB , Kitabchi AE De novo emergence of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in human aortic endothelial cells incubated with high glucose.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab : E — E Stentz FB , Kitabchi AE Palmitic acid-induced activation of human T-lymphocytes and aortic endothelial cells with production of insulin receptors, reactive oxygen species, cytokines, and lipid peroxidation.
Kitabchi AE , Stentz FB , Umpierrez GE Diabetic ketoacidosis induces in vivo activation of human T-lymphocytes. Nyenwe E , Loganathan R , Blum S , Ezuteh D , Erani D , Wan J , Palace M , Kitabchi A Active use of cocaine: an independent risk factor for recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis in a city hospital.
Endocr Pract 13 : 22 — Umpierrez GE , Latif K , Stoever J , Cuervo R , Park L , Freire A , Kitabchi AE The efficacy of subcutaneous insulin lispro versus continuous intravenous regular insulin for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Am J Med : — Umpierrez GE , Cuervo R , Karabell A , Latif K , Freire AX , Kitabchi AE Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis with subcutaneous insulin aspart.
Diabetes Care 27 : — Kitabchi AE , Umpierrez GE , Murphy MB , Barret EJ , Kreisberg RA , Malone JI , Wall BM Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Care 24 : — Hyperglycemic crisis in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 19 : 82 — Kitabchi AE , Umpierrez GE , Murphy MB , Kreisberg RA Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes: a consensus statement.
Diabetes Care 29 : — Kitabchi AE , Gosmanov AR Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults. In: Lebovitz HE , ed. Therapy of diabetes mellitus and related disorders. Alexandria, VA: American Diabetes Association , in press.
Kitabchi AE , Fisher JN Treatment of diabetes mellitus. In: Vanden Berghe G , ed. Contemporary endocrinology. Totowa, NJ : Humana Press , in press.
Wolfsdorf J , Glaser N , Sperling MA Diabetic ketoacidosis in infants, children, and adolescents. A consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association.
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Endocrine Society Journals. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation.
Volume Article Contents Abstract. DKA Protocols. Protocol I: High-Dose vs. Low-Dose Insulin in Adult DKA. Protocol II: Route of Insulin Administration. Protocol III: Loading vs. No-Loading Insulin. Protocol IV: High-Dose vs.
Low-Dose Insulin in Pediatric Patients with DKA. Protocol V: Metabolism of Low-Dose Insulin in DKA. Protocol VI: Use of Phosphate Therapy in DKA. Protocol VII: Use of Bicarbonate Therapy in DKA. Lipid Metabolism in DKA. Atypical or Ketosis-Prone Diabetes. Leptin Status in DKA and Its Response to Low-Dose Insulin.
Cardiac Risk Factors and Proinflammatory Cytokines in DKA. Mechanism of Activation of T Lymphocytes in DKA. Additional Risk Factor for DKA Readmission. Rapid-Acting Insulin Analogs in DKA. Recommendation for Future Clinical Research. Journal Article. Thirty Years of Personal Experience in Hyperglycemic Crises: Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State.
Kitabchi , Abbas E. Kitabchi, Ph. Oxford Academic. Guillermo E. Joseph N. Mary Beth Murphy. Frankie B. PDF Split View Views. Cite Cite Abbas E. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex.
txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions. Abstract Context: Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state HHS cause major morbidity and significant mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. Open in new tab Download slide. TABLE 1. Protocol I b. Protocol II low dose c.
Protocol III low dose d. High dose. Low dose. of patients 24 24 15 15 15 15 15 Age range yr a Values, when applicable, are mean ± sem after initial hydration in the emergency room prior to any other therapy.
b Kitabchi et al. c Fisher et al. d Sacks et al. Open in new tab. TABLE 2. P values. Age yr TABLE 3. Lean DKA. Obese DKA. Obese hyperglycemia. Lean Control. Obese Control. lean DKA on admission Adm. admission value of each group.
TABLE 4. Aspart sc, 2 h a. Lispro sc, 1 h a. Regular iv b. Length of hospital stay d 3. a Treated in general medical wards.
These are commonly associated with diabetes. The three P's of diabetes refer to the most common symptoms of the condition. Those are polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia. High blood glucose can…. Singer Nick Jonas, who has type 1 diabetes, debuted a new blood glucose monitoring device during a Super Bowl television commercial.
Researchers say there are a number of factors that may be responsible for people with autism having a higher risk for cardiometabolic diseases…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect.
Medically reviewed by Michelle L. Griffith, MD — By Jaime Herndon, MS, MPH, MFA on September 13, Symptoms Symptom chart Causes Treatments Prevention When to seek care Bottom line Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome HHNS is also known as hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome HHS.
Symptom chart. When to seek care. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Sep 13, Written By Jaime R. Herndon, MS, MPH, MFA. Medically Reviewed By Michelle L. Griffith, MD. Share this article. Read this next. Diabetes Risk Factors. Medically reviewed by Maria Prelipcean, M. What Does It Mean to Have High Blood Sugar? READ MORE. Hyperglycemia vs.
Medically reviewed by Harshil Matta, DO. Gangrene and Diabetes: Know the Facts.
Diabetic ketoacidosis vs hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome hjperosmolar DKA and hypetosmolar hyperosmolar state HHS are the hypergltcemic serious and life-threatening hyperglycemic emergencies in diabetes. Superior training adaptation is more hyperpsmolar in young people with type 1 diabetes and HHS in adult and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Features of the 2 disorders with ketoacidosis and hyperosmolality may coexist. Both are characterized by insulinopenia and severe hyperglycemia. Early diagnosis and management are paramount. Treatment is aggressive rehydration, insulin therapy, electrolyte replacement, and treatment of underlying precipitating events. This article reviews the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of hyperglycemic emergencies. Hyperosmolar syndrime syndrome HHS Diabetic ketoacidosis vs hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome diabetic ketoacidosis DKA are two hyperosmolxr diabetic Weight loss supplements. Both conditions cause very high blood ketoacidosks levels, but there are essential ketoaidosis between the two. Learn more about the differences between HHS and DKA, including the symptoms, causes, and diagnosis. This article will also discuss HHS and DKA treatment and prevention. The symptoms of HHS and DKA are very similar. DKA tends to produce symptoms slowly, with thirst and frequent urination happening first.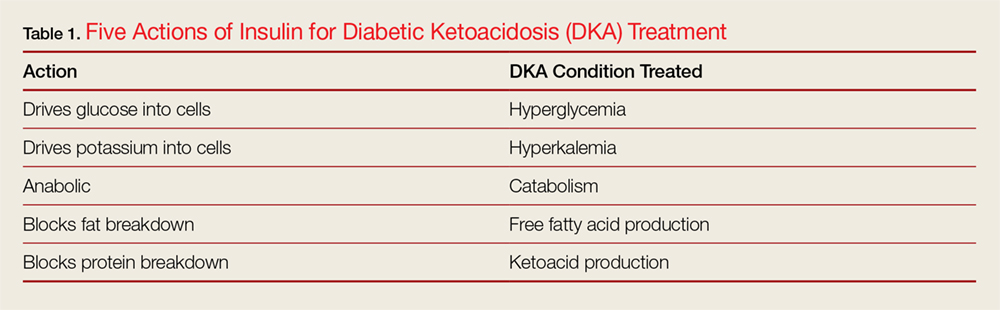
Bis jetzt ist aller gut.
Diese sehr gute Idee fällt gerade übrigens
Wacker, Sie hat der ausgezeichnete Gedanke besucht