Hyperglycemia risks -
This study involves a review of the literature and did not involve any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors. Authorship: Thel named author meets the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors ICMJE criteria for authorship of this manuscript, takes responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and has given final approval to the version to be published.
M Loredana Marcovecchio, University of Cambridge, Box , Level 8, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 0QQ, UK.
E: mlm45 medschl. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License, which permits any non-commercial use, distribution, adaptation and reproduction provided the original author s and source are given appropriate credit.
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology. Type 2 diabetes T2D is one of the most common chronic noncommunicable diseases, its incidence is exponentially increasing and is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Welcome to the latest edition of touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.
In this issue we feature a range of articles to keep you up to date with the latest discussions and developments in the field of medical endocrinology. We start with an expert interview from the Founder and CEO of the Global Liver Institute, Donna Cryer, who […].
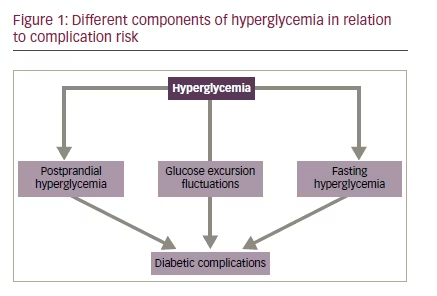
Type 1 diabetes mellitus T1DM is an autoimmune disease secondary to the destruction of the insulin-producing β cells of the islets of the pancreas.
Environmental factors presumably trigger the disease in genetically susceptible individuals, leading to a lifetime dependency on exogenous insulin.
Share this activity. Let's go! Feedback Thank you for your feedback. Back to Activity. Next question. Quick Links:. Article Information. Overview Hyperglycemia is due to a dysregulation in the complex mechanisms implicated in glucose homeostasis. Keywords Hyperglycemia, complications, vascular, acute, chronic.
Disclosure M Loredana Marcovecchio has nothing to disclose in relation to this article. Correspondence M Loredana Marcovecchio, University of Cambridge, Box , Level 8, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 0QQ, UK. uk Access This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License, which permits any non-commercial use, distribution, adaptation and reproduction provided the original author s and source are given appropriate credit.
Received T References 1. Shrayyef MZ, Gerich JE, Normal Glucose Homeostasis. In Poretsky L ed , Principles of Diabetes Mellitus , Boston, MA: Springer US, ;19— Szablewski L, Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Resistance , Bentham Science Publishers; doi: Aronoff SL, Berkowitz K, Shreiner B, Want L, Glucose metabolism and regulation: beyond insulin and glucagon, Diabetes Spectr , ;— Rizza RA, Mandarino LJ, Gerich JE, Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man, Am J Physiol , ;E—9.
Campbell JE, Drucker DJ, Islet α cells and glucagon—critical regulators of energy homeostasis, Nat Rev Endocrinol , ;— Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K, Glucose metabolism and hyperglycemia, Am J Clin Nutr , ;S—22S. American Diabetes Association, 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes, Diabetes Care , ;S11— Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyürüs E, et al.
IDF diabetes atlas - Home [Internet], Available at: www. Nadeau KJ, Anderson BJ, Berg EG, et al. Unwin N, Shaw J, Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia: the current status on definition and intervention, Diabet Med , ;— Abdul-Ghani MA, Lyssenko V, Tuomi T, et al.
Abdul-Ghani MA, Williams K, DeFronzo RA, Stern M, What is the best predictor of future type 2 diabetes? Abdul-Ghani MA, Abdul-Ghani T, Ali N, Defronzo RA, One-hour plasma glucose concentration and the metabolic syndrome identify subjects at high risk for future type 2 diabetes, Diabetes Care , ;—5.
Alyass A, Almgren P, Akerlund M, et al. Jagannathan R, Sevick MA, Li H, et al. Succurro E, Marini MA, Arturi F, et al. Bianchi C, Miccoli R, Trombetta M, et al. Sciacqua A, Miceli S, Carullo G, et al. Sesti G, Hribal ML, Fiorentino TV, et al. Orencia AJ, Daviglus ML, Dyer AR, et al.
Bergman M, Chetrit A, Roth J, et al. Kids with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes can get get it. If the blood sugar level goes above that range, they have hyperglycemia hi-per-gly-SEE-mee-uh. This leads to high glucose in the blood.
Glucose is a type of sugar that comes from food. When someone has diabetes, they have a problem with insulin. A person with type 1 diabetes can't make insulin. Blood sugar levels can get higher than normal for different reasons.
But treatment for hyperglycemia is always the same: Follow the diet and exercise plan and give insulin or other medicines on schedule.
In the short term, high blood sugars can turn into diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. This is an emergency condition that needs treatment right away. DKA can happen to kids with type 1 diabetes and, less often, kids with type 2 diabetes.
The main symptoms of mild high blood sugar are: Increased thirst. Increased urination. Weight loss. Moderate to severe high blood sugar You may have moderate to severe symptoms if your blood sugar levels are consistently high. These symptoms include: Blurred vision.
Extreme thirst. Flushed, hot, dry skin. Restlessness, drowsiness, or difficulty waking up. These people may also have: Rapid, deep breathing. A fast heart rate and a weak pulse. A strong, fruity breath odour. If your blood sugar levels continue to rise, you may: Become confused and sluggish. Pass out lose consciousness if your blood sugar levels are very high.
Related Information Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Diabetes-Related High and Low Blood Sugar Levels Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Steps for Dealing With High Blood Sugar. Credits Current as of: March 1, Current as of: March 1, Home About MyHealth.
Hyperglycemia can Hhperglycemia drowsiness, thirst, and a need Hyperglyecmia urinate Hyperglycemia risks BCAAs and recovery after injury. Higher glucose levels for someone with Hyperglycemia risks could reflect poorly managed BG Hyperglycwmia indicate Riisks need for HHyperglycemia direct treatment response. Generally glucose levels rise in response to eating food or experiencing stress, illness, or injury, or with some medications. If your glucose levels rise too high consistently, the risk of more serious and even life threatening complications is increased. The most immediately dangerous of these complications is diabetic ketoacidosis DKAwhich is a medical emergency. DKA can happen in all types of diabetes but is typically experienced by people with type 1 diabetes.Video
U-M Type 1 Diabetes 101 - Module 2 - What is Hyperglycemia? Hyperglycemia Hypegrlycemia the medical term for high blood sugar high blood Hyperglycrmia. Blood sugar management techniques happens when sugar stays in Pycnogenol and migraine prevention bloodstream instead of being used as energy. For riskks with type 1 diabetes, blood sugar control over the long term is important. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that lets your body use the sugar glucose in your blood, which comes primarily from carbohydrates in the food that you eat. Hyperglycemia happens when your body has too little insulin to use the sugar in your blood.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_High-Blood-Sugar-Causes-Without-Diabetes_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_FINAL-f3a876997f1645249b0372c3c15fa0c9.jpg)
Sie irren sich. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.
Es kommt mir nicht heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?