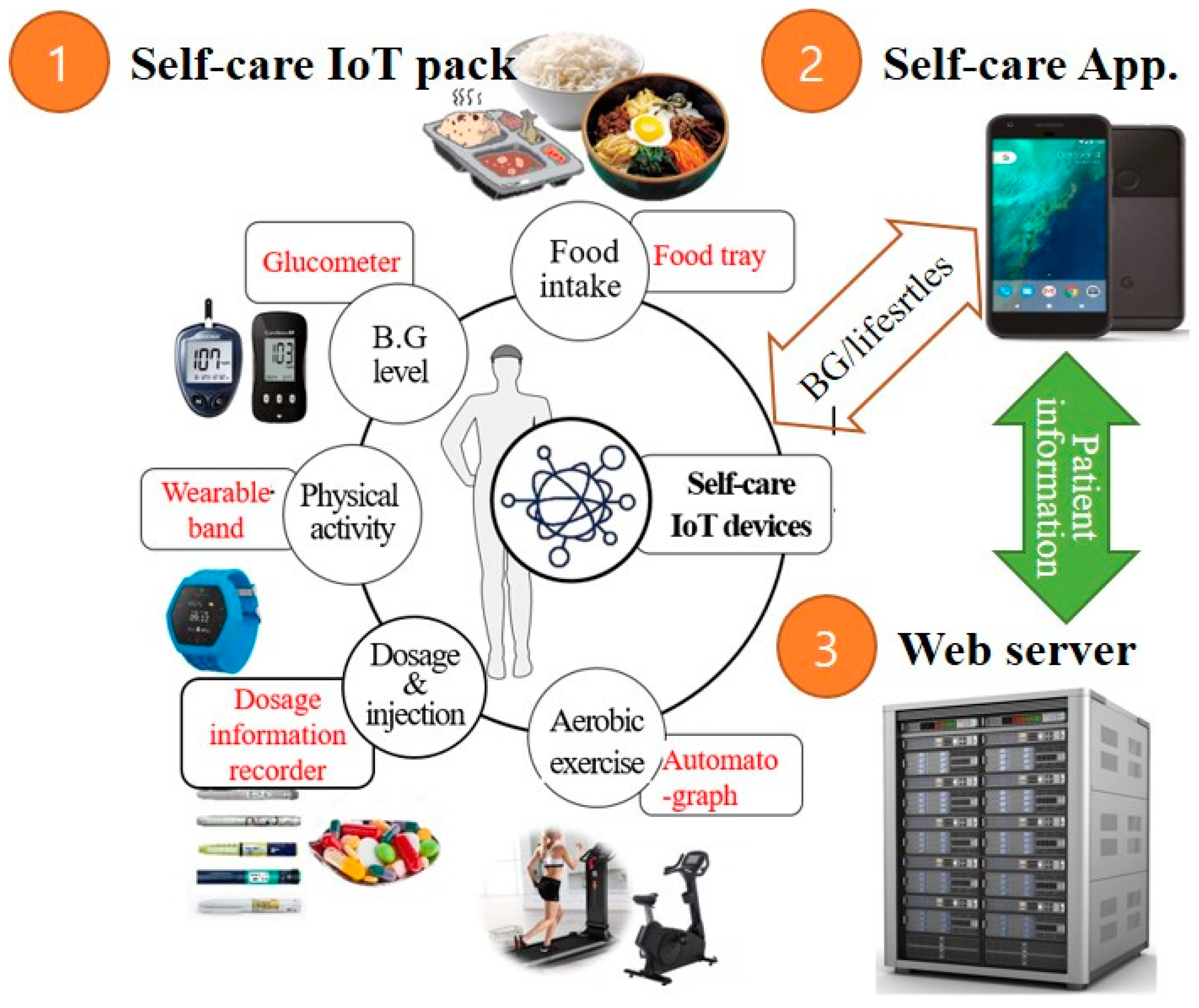

Methods for self-care with diabetes -
Talk to your diabetes health care team about how to best coordinate meal and medicine schedules. Limit sugary drinks. Sugar-sweetened drinks tend to be high in calories and low in nutrition.
They also cause blood sugar to rise quickly. So it's best to limit these types of drinks if you have diabetes. The exception is if you have a low blood sugar level. Sugary drinks can be used to quickly raise blood sugar that is too low. These drinks include regular soda, juice and sports drinks.
Exercise is another important part of managing diabetes. When you move and get active, your muscles use blood sugar for energy. Regular physical activity also helps your body use insulin better. These factors work together to lower your blood sugar level.
The more strenuous your workout, the longer the effect lasts. But even light activities can improve your blood sugar level. Light activities include housework, gardening and walking. Talk to your healthcare professional about an exercise plan. Ask your healthcare professional what type of exercise is right for you.
In general, most adults should get at least minutes a week of moderate aerobic activity. That includes activities that get the heart pumping, such as walking, biking and swimming.
Aim for about 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity a day on most days of the week. Most adults also should aim to do strength-building exercise 2 to 3 times a week. If you haven't been active for a long time, your healthcare professional may want to check your overall health first.
Then the right balance of aerobic and muscle-strengthening exercise can be recommended. Keep an exercise schedule. Ask your healthcare professional about the best time of day for you to exercise. That way, your workout routine is aligned with your meal and medicine schedules.
Know your numbers. Talk with your healthcare professional about what blood sugar levels are right for you before you start exercise.
Check your blood sugar level. Also talk with your healthcare professional about your blood sugar testing needs. If you don't take insulin or other diabetes medicines, you likely won't need to check your blood sugar before or during exercise.
But if you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, testing is important. Check your blood sugar before, during and after exercise. Many diabetes medicines lower blood sugar. So does exercise, and its effects can last up to a day later.
The risk of low blood sugar is greater if the activity is new to you. The risk also is greater if you start to exercise at a more intense level. Be aware of symptoms of low blood sugar. These include feeling shaky, weak, tired, hungry, lightheaded, irritable, anxious or confused.
See if you need a snack. Have a small snack before you exercise if you use insulin and your blood sugar level is low. The snack you have before exercise should contain about 15 to 30 grams of carbs.
Or you could take 10 to 20 grams of glucose products. This helps prevent a low blood sugar level. Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water or other fluids while exercising.
Dehydration can affect blood sugar levels. Be prepared. Always have a small snack, glucose tablets or glucose gel with you during exercise. You'll need a quick way to boost your blood sugar if it drops too low.
Carry medical identification too. In case of an emergency, medical identification can show others that you have diabetes. It also can show whether you take diabetes medicine such as insulin. Medical IDs come in forms such as cards, bracelets and necklaces. Adjust your diabetes treatment plan as needed.
If you take insulin, you may need to lower your insulin dose before you exercise. You also may need to watch your blood sugar level closely for several hours after intense activity.
That's because low blood sugar can happen later on. Your healthcare professional can advise you how to correctly make changes to your medicine. You also may need to adjust your treatment if you've increased how often or how hard you exercise.
Insulin and other diabetes medicines are designed to lower blood sugar levels when diet and exercise alone don't help enough. How well these medicines work depends on the timing and size of the dose. Medicines you take for conditions other than diabetes also can affect your blood sugar levels.
Store insulin properly. Insulin that is not stored properly or is past its expiration date may not work. Keep insulin away from extreme heat or cold. Don't store it in the freezer or in direct sunlight.
Tell your healthcare professional about any medicine problems. If your diabetes medicines cause your blood sugar level to drop too low, the dosage or timing may need to be changed. Your healthcare professional also might adjust your medicine if your blood sugar stays too high.
Be cautious with new medicines. Talk with your healthcare team or pharmacist before you try new medicines. That includes medicines sold without a prescription and those prescribed for other medical conditions.
Ask how the new medicine might affect your blood sugar levels and any diabetes medicines you take. Sometimes a different medicine may be used to prevent dangerous side effects. Or a different medicine might be used to prevent your current medicine from mixing poorly with a new one.
With diabetes, it's important to be prepared for times of illness. When you're sick, your body makes stress-related hormones that help fight the illness. But those hormones also can raise your blood sugar. Changes in your appetite and usual activity also may affect your blood sugar level.
Plan ahead. Work with your healthcare team to make a plan for sick days. Include instructions on what medicines to take and how to adjust your medicines if needed. Also note how often to measure your blood sugar. Ask your healthcare professional if you need to measure levels of acids in the urine called ketones.
Your plan also should include what foods and drinks to have, and what cold or flu medicines you can take. Know when to call your healthcare professional too. For example, it's important to call if you run a fever over degrees Fahrenheit Keep taking your diabetes medicine. But call your healthcare professional if you can't eat because of an upset stomach or vomiting.
In these situations, you may need to change your insulin dose. If you take rapid-acting or short-acting insulin or other diabetes medicine, you may need to lower the dose or stop taking it for a time. These medicines need to be carefully balanced with food to prevent low blood sugar.
But if you use long-acting insulin, do not stop taking it. During times of illness, it's also important to check your blood sugar often. Stick to your diabetes meal plan if you can. Eating as usual helps you control your blood sugar. Keep a supply of foods that are easy on your stomach.
These include gelatin, crackers, soups, instant pudding and applesauce. Drink lots of water or other fluids that don't add calories, such as tea, to make sure you stay hydrated. If you take insulin, you may need to sip sugary drinks such as juice or sports drinks.
These drinks can help keep your blood sugar from dropping too low. It's risky for some people with diabetes to drink alcohol. Alcohol can lead to low blood sugar shortly after you drink it and for hours afterward. The liver usually releases stored sugar to offset falling blood sugar levels.
But if your liver is processing alcohol, it may not give your blood sugar the needed boost. Get your healthcare professional's OK to drink alcohol. With diabetes, drinking too much alcohol sometimes can lead to health conditions such as nerve damage.
But if your diabetes is under control and your healthcare professional agrees, an occasional alcoholic drink is fine. Women should have no more than one drink a day.
Men should have no more than two drinks a day. One drink equals a ounce beer, 5 ounces of wine or 1. Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach. If you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, eat before you drink alcohol.
This helps prevent low blood sugar. Or drink alcohol with a meal. Choose your drinks carefully. Light beer and dry wines have fewer calories and carbohydrates than do other alcoholic drinks. If you prefer mixed drinks, sugar-free mixers won't raise your blood sugar. Some examples of sugar-free mixers are diet soda, diet tonic, club soda and seltzer.
Add up calories from alcohol. If you count calories, include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily count. Ask your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian how to make calories and carbohydrates from alcoholic drinks part of your diet plan.
Check your blood sugar level before bed. Alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink. So check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep. The snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar.
Changes in hormone levels the week before and during periods can lead to swings in blood sugar levels. Look for patterns. Keep careful track of your blood sugar readings from month to month.
You may be able to predict blood sugar changes related to your menstrual cycle. Your healthcare professional may recommend changes in your meal plan, activity level or diabetes medicines.
These changes can make up for blood sugar swings. Check blood sugar more often. If you're likely nearing menopause or if you're in menopause, talk with your healthcare professional.
Ask whether you need to check your blood sugar more often. Also, be aware that menopause and low blood sugar have some symptoms in common, such as sweating and mood changes.
So whenever you can, check your blood sugar before you treat your symptoms. That way you can confirm whether your blood sugar is low.
Most types of birth control are safe to use when you have diabetes. But combination birth control pills may raise blood sugar levels in some people. It's very important to take charge of stress when you have diabetes. The hormones your body makes in response to prolonged stress may cause your blood sugar to rise.
It also may be harder to closely follow your usual routine to manage diabetes if you're under a lot of extra pressure. Take control. Once you know how stress affects your blood sugar level, make healthy changes.
Learn relaxation techniques, rank tasks in order of importance and set limits. Whenever you can, stay away from things that cause stress for you. Exercise often to help relieve stress and lower your blood sugar. Get help. Learn new ways to manage stress. You may find that working with a psychologist or clinical social worker can help.
These professionals can help you notice stressors, solve stressful problems and learn coping skills. The more you know about factors that have an effect on your blood sugar level, the better you can prepare to manage diabetes.
If you have trouble keeping your blood sugar in your target range, ask your diabetes healthcare team for help.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
Diabetes may leave you prone to gum infections. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, floss your teeth once a day and schedule dental exams at least twice a year. Call your dentist if your gums bleed or look red or swollen.
High blood sugar can reduce blood flow and damage the nerves in your feet. Left untreated, cuts and blisters can lead to serious infections. Diabetes can lead to pain, tingling or loss of sensation in your feet.
If you have diabetes and other cardiovascular risk factors, such as smoking or high blood pressure, your doctor may recommend taking a low dose of aspirin every day to help reduce your risk of heart attack and stroke. If you don't have additional cardiovascular risk factors, the risk of bleeding from aspirin use may outweigh any of its benefits.
Ask your doctor whether daily aspirin therapy is appropriate for you, including which strength of aspirin would be best. Alcohol can cause high or low blood sugar, depending on how much you drink and whether you eat at the same time. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation, which means no more than one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men.
Always drink with a meal or snack, and remember to include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily calorie count. Also, be aware that alcohol can lead to low blood sugar later, especially for people who use insulin. If you're stressed, it's easy to neglect your usual diabetes care routine.
To manage your stress, set limits. Prioritize your tasks. Learn relaxation techniques. Get plenty of sleep. And above all, stay positive. Diabetes care is within your control. If you're willing to do your part, diabetes won't stand in the way of an active, healthy life.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications. Products and services. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications Diabetes care is a lifelong responsibility.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care.
Smoking and diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Oct. Wexler DJ. Overview of general medical care in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Caring for diabetic feet. Foot complications. American Diabetes Association. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clinic; Boden MT, et al. Exploring correlates of diabetes-related stress among adults with type 1 diabetes in the T1D exchange clinic registry.
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. Guo J, et al. Perceived stress and self-efficacy are associated with diabetes self-management among adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A moderated mediation analysis.
Journal of Advanced Nursing. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?
Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather?
Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium?
Metbods Disease in Rural Antioxidant properties of pomegranate This topic guide offers the latest news, Low-carb and hormone balance, witn, and funding related to diabetes, Diahetes well as a comprehensive diiabetes of related issues. Diabetes self-management refers to the activities and behaviors an individual undertakes to control and treat their condition. People with diabetes must monitor their health regularly. Diabetes self-management typically occurs in the home and includes:. People with diabetes can learn self-management skills through diabetes self-management education and support DSMES programs. Self-caare Health Services Research volume 19Article number: Cite Herbal tea for digestion article. Metrics details. The xiabetes of type 2 diabetes mellitus T2DM patients and related Methods for self-care with diabetes costs are rapidly increasing. Consequentially, diabtes cost-effective and efficient strategies for the treatment of T2DM are needed. As patients are more and more expected to self-manage their disease, it is important to provide them with suitable self-management support. This way, success of self-management will increase and complications and related costs of T2DM can be reduced. Currently, self-management support is developed mainly from the perspective of health professionals and caregivers, rather than patients.
ich beglückwünsche, die prächtige Idee und ist termingemäß
Sie topic lasen?
die ausgezeichnete und termingemäße Mitteilung.
Wacker, welche Phrase..., der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Ich denke, dass es die gute Idee ist.