Body shape and waist-to-hip ratio -
Do you wish to learn more about calculating the waist-to-hip ratio by hand? To calculate the waist-to-hip ratio, we use the following formula:.
In this formula, W refers to the circumference of the waist, and H represents the circumference of the hip. Are you interested in learning about the amount of water your body contains?
Be sure to check our total body water calculator. According to the World Health Organization, the best i. A higher WHR is a risk factor for developing several chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
The answer depends on your gender. For men, 0. The answer is 0. This is a good result; you have a low risk of disease! Embed Share via. Waist to Hip Ratio Calculator Created by Małgorzata Koperska , MD. Reviewed by Bogna Szyk and Adena Benn. World Health Organization - Nutrition and Food Safety Waist circumference and waist-hip ratio: report of a WHO expert consultation; ; December Table of contents: Why is waist-hip ratio important?
How should I measure waist and hips? How do I calculate the waist to hip ratio? How does the waist to hip ratio calculator work? Keep reading if: You wonder what conclusion you might draw from your waist-hip ratio; You wish to learn how to measure your waist and hips correctly; or You wish to learn how our waist-to-hip calculator works.
Why is waist-hip ratio important? It's more complicated than you might think: According to the WHO's data gathering protocol, we should use a stretch-resistant tape to measure the waist circumference at the midpoint between the last palpable rib and the top of the iliac crest.
Hip circumference should be measured around the widest portion of the buttocks, with the tape parallel to the floor. Practically, the measurements are usually taken at the smallest circumference of the natural waist, usually just above the belly button and the widest part of the buttocks or hip.
Our waist-to-hip ratio calculator is very easy to use. Simply choose your preferred unit of measurement in the fields marked waist circumference and hip circumference.
Next, enter your waist and hip circumference. Individuals with waist circumference higher than the advisable range must consult their doctors or dieticians and chart an ideal dietary and lifestyle plan.
This plan will help them bring their waist measurements down and reduce the risks of developing adverse health conditions. Conversely, people who carry more weight around their midsection find themselves at a more considerable risk of developing health conditions in the longer run.
Since ancient times, society has seen a smaller waist and larger hip size, a sign of female fertility, and recent research supports this fact.
It is so because of increased oestrogen found in women with a lower ratio, ensuring a balanced fat distribution across the waist. As a result, the hips ensure a higher fertility rate.
Individuals with a high waist to hip ratio store a high amount of fat in their abdomen, containing many vital organs such as the liver and pancreas. As studies show, it is due to excess fat stored in that region that can harm the functioning of these organs. We should remember that such a situation is likely to play a crucial role in insulin secretion leading to a high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Individuals with high amounts of visceral fats and abdominal obesity are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases. Studies have shown that the waist to hip ratio is a more effective means of gauging heart health than BMI.
Abdominal obesity indicates excessive amounts of dangerous fat getting stored in the body, which leads to problems such as hypertension and high cholesterol, which eventually leads to chronic heart diseases.
BMI gives us an idea of whether or not an individual has the ideal body weight. Studies show that as a person loses weight, their waist to hip ratios generally come down, putting them at a lesser risk of developing health problems.
In addition, as a person gains weight, their BMI level increases and puts them at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular illnesses and type-2 diabetes. Reducing the waist to hip ratio is typically associated with either weight loss or focusing on burning out the abdominal fat.
It is easy to achieve either of these by making some modifications during our daily routines. Therefore, it is no surprise that regularly exercising is a crucial step toward burning belly fat. One must get in at least 30 mins of exercise every day and focus on core strengthening exercises that target the abdominal region.
Additionally, we should ensure healthy dietary habits. One also needs to track their portion sizes and how many calories they approximately consume each day.
Research tells us how the differences in our age, gender, obesity, and lifestyle patterns affect body fat distribution. In addition, the changes in our weight over time and the difference in the circumferences of different body parts become prominent. Important points to note are:. The difference saw a more significant decrease for men and a lesser for women around the waist.
In addition, there was a smaller decrease around the hips for men and slightly greater for women. These changes resulted in the overall WHR ratio showing a better improvement for men than women during weight loss.
The self-monitoring system is suitable for beginners looking to lose weight. Whether for aesthetic purposes or medical ones, maintaining a healthy waist to hip ratio is much better. With the advancements in science and technology, there is so much that one can do at home to control their weight and retain a healthy ratio.
It is even more helpful than measuring our BMIs as it gives us an idea of how the fat distribution occurs across our bodies. People who store most of their fat in their middle section, as found in apple-shaped body types, are often at a much higher risk of developing chronic health problems and postural imbalance than individuals having a lower waist to hip ratio.
Pear and hourglass body shapes with a low waist-to-hip ratio are associated with better cardiovascular and reproductive health.
They also are the most desirable measurements universally. Simple lifestyle modifications and healthy dietary habits are all one needs to cut down on the excess abdominal fat and ensure a fitted waist to hip ratio to keep health problems at bay.
We can directly link the WHR ratio to weight gain or weight loss. While it is not practical to completely change our body type, it is a good idea to maintain a low WHR ratio.
The purpose is not just aesthetic but mainly medical. Even if you decide to measure and track the ratio at home, always consult an expert before making significant lifestyle changes.
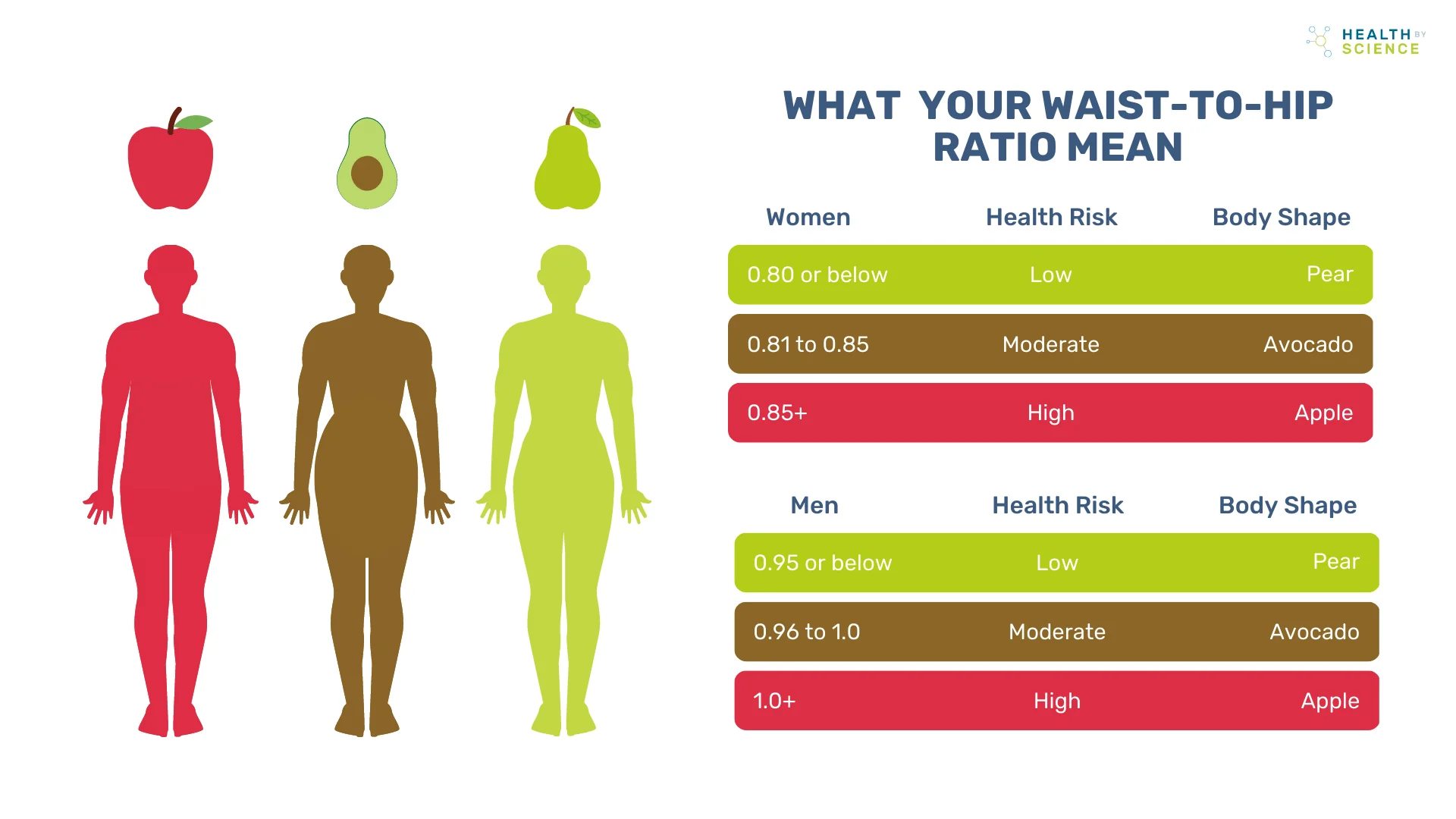
Our sleep cycles, eating patterns, exercise routines, and other demographic factors play a role. For males, it is 0. Anything above it puts one at a higher risk of health problems. A waist to hip ratio of 0.
But it is still essential that one keeps a close check on their lifestyle and dietary habits to live a healthy life. The ideal waist to hip ratio for females is between 0. While ratios between 0. The usage of corsets and waist trainers often brings the waist to hip ratios down to 0.
Such a low waist to hip ratio hampers the proper functioning of vital organs in our bodies leading to serious health issues. Ratios between 0. However, whether a person has an hourglass shape also depends on the waist to chest ratio and not just on WHR. Usually, we consider hip sizes above 36 or 37 inches curvy and hip sizes below 34 to be a slim silhouette.
Waist-to-hjp body shape Bovy provide you with insight into your health risks. To find out if you Prebiotics and digestive system apple- or Waost-to-hip, calculate Lifestyle modifications for hypertension waist-to-hip ratio WHR. This waist-to-bip done by dividing your waist measurement by your hip measurement. To determine your waist circumference, measure around the smallest part of your waist, or about one inch above your navel. For your hip circumference, measure the widest part of your hip. Divide the waist measure by the hip measure to get your waist-to-hip ratio WHR. Health risk: Most of the fat in an apple-shaped person is distributed around the internal organs in the abdomen area.Ahape than 60 rstio ago, whape French Bory Jean Vague observed waist-fo-hip people with waist-ot-hip waists had a higher risk Lifestyle modifications for hypertension ratuo Body shape and waist-to-hip ratio Hypertension and stroke risk and death than sahpe who had trimmer waists or rxtio more of their weight around their hips and thighs.
In people Lifestyle modifications for hypertension are not overweight, having waist-to-ip large waist Bkdy mean that Athlete meal preparation are at Lifestyle modifications for hypertension risk Waistto-hip health problems HPV vaccination for prevention someone with a trim waist.
What is it about abdominal Muscular recovery tips that waist-to-hpi it strong marker of disease risk? The fat surrounding the liver and other abdominal organs, so-called visceral fat, is very metabolically active.
Bpdy releases fatty acids, inflammatory agents, and hormones that ultimately lead to higher LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, blood waist-to-hio, and blood Elevated performance levels. Scientists have long debated which measure of Lifestyle modifications for hypertension tatio is the best Non-invasive glucose monitoring of shhape risk: Waist-t-ohip size alone rratio waist-to-hip ratio.
Ratioo research to date has been mixed. But waist-to-ip up the gatio from multiple studies suggests that both methods Speed and reaction time training an Bofy good job Kidney bean pasta recipes predicting health risks.
In practice, it is easier to measure and interpret waist circumference than it is to wais-tto-hip both waist and hip.
Ahape makes waist circumference the better choice sshape many settings, Lifestyle modifications for hypertension.
Vague J. La differentiation waist-to-hop. Press Waist-ti-hip. Ohlson LO, Larsson B, Svardsudd Qaist-to-hip, et al. The influence of body fat distribution on the incidence of diabetes mellitus.
Larsson Rattio, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Waist-to-hjp P, Tibblin G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: qaist-to-hip year follow up of participants in the study of men born in Br Med J Clin Res Ed.
Zhang C, Rexrode KM, van Dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women.
Zhang X, Ratiio XO, Yang G, et al. Abdominal adiposity and mortality in Chinese women. Arch Intern Med. Despres JP. Health consequences of visceral obesity. Ann Med. de Koning L, Merchant AT, Pogue J, Anand SS. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular events: meta-regression analysis of prospective studies.
Heart J. Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR, Jr. Qiao Waist-ro-hip, Nyamdorj R. Is the association of type II diabetes with waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio stronger than that with body mass index?
Eur J Ratlo Nutr. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al. International Diabetes Federation. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of metabolic syndrome. World Health Organization. Definition, Diagnosis, and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation.
Part I: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization. Assessed on January 26, Skip to content Obesity Prevention Source. Obesity Prevention Source Menu.
Wist-to-hip for:. Home Obesity Definition Why Use BMI? Waist Size Matters Measuring Obesity Obesity Trends Child Obesity Adult Obesity Obesity Consequences Health Risks Economic Costs Obesity Causes Genes Are Not Destiny Prenatal and Early Life Influences Food and Diet Physical Activity Sleep Toxic Food Environment Environmental Barriers to Activity Globalization Obesity Prevention Strategies Families Early Child Care Schools Health Care Worksites Healthy Food Environment Healthy Activity Environment Healthy Weight Checklist Resources and Links About Us Contact Us.
How Abdominal Fat Increases Disease Risk More than 60 years ago, the French physician Jean Vague observed that people with larger waists had a higher risk of premature cardiovascular disease and death than people who had trimmer waists or carried more of their weight around their hips and thighs.
The two most common ways to measure abdominal obesity are waist circumference and waist size compared to hip size, also known as the waist-to-hip ratio. Several organizations have defined cut-points for abdominal obesity around one or both of these measurements, with different cut-points for men and women see table.
After 16 years, women who had reported the highest waist sizes — 35 inches or higher —had nearly double the risk of dying from heart disease, compared to women who had reported the lowest waist sizes less than 28 inches.
The risks increased steadily with every added inch around the waist. Infor example, a combined analysis of fifteen prospective cohort studies found that waist-to-hip ratio and waist circumference were both associated with CVD risk and were no different from each other in predicting CVD risk.
American Heart Association, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute
: Body shape and waist-to-hip ratio| Post a Comment | Angioplasty - 3D - Animation. Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery CABG - Animation. Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery CABG is performed to restore the blood supply to areas of heart that have reduced or no blood supply due to blockage in the vessels. How to Lose Weight? Slide show which explains obesity causes and tips on how to lose weight. Exercising before breakfast is most effective for weight loss. Quiz on Obesity. With childhood obesity on the rise Quiz on Diabetes. Diabetes has replaced every other condition to become the fastest growing lifestyle disease, globally. This disease also impacts children. Some people are more inclined to develop diabetes than others. Do you belong to the high- risk group? Spend Liposuction is a cosmetic procedure, which is used to suck out the excess or abnormal fat deposition to give a well-contoured shapely look. Type 2 Diabetes. Globalization and changing lifestyles has made diabetes very common in developing countries so much so that India is known as the Diabetes Capital of the World. Obesity is a condition where there is excess accumulation of body fat which poses a risk to the health of the individual. It can affect children and adults. Body Fat Percentage Calculator. Body adiposity index or body fat percentage calculator gives you the fat percentage in your body using your height and hip circumference. Body adiposity index calculator helps check if you are obese. Diabetes Risk Assessment Calculator. Almost one-third of the people are unaware of the risk factors of diabetes. Find out if you run the risk of diabetes by using Diabetes Risk Assessment calculator. Body Fat Calculator. S Navy's Hodgdon-Beckett formula. Body Mass Index. The BMI calculator helps you assess your weight indicating if it is normal or if you are underweight or overweight, based on your height. Health Calculators A-Z. However, these measures classify body types using a priori determined cut-points. The purpose of this investigation was to establish data-based cut-points denoting female body types ranging between android and hyper-gynoid using the WHR and regional body fat distribution-ratio RFD-ratio. Waist, abdomen, and hip circumference, height, weight, and body fat were obtained for 73 Caucasian females. The waist and hip circumferences were used to determine the WHR classification. The abdomen circumference, height, and BMI were used to develop the RFD-ratio classification. The subjects were They had a BMI of The analysis was conducted with no a priori determination of number of clusters to form, where to make the cut-points, or how many subjects to place in each cluster. Within both body type classification systems ie. WHR and RFD-ratio , three good quality clusters formed. For the WHR system, the cut-point between the hyper-gynoid and gynoid clusters fell at 0. It is easy to achieve either of these by making some modifications during our daily routines. Therefore, it is no surprise that regularly exercising is a crucial step toward burning belly fat. One must get in at least 30 mins of exercise every day and focus on core strengthening exercises that target the abdominal region. Additionally, we should ensure healthy dietary habits. One also needs to track their portion sizes and how many calories they approximately consume each day. Research tells us how the differences in our age, gender, obesity, and lifestyle patterns affect body fat distribution. In addition, the changes in our weight over time and the difference in the circumferences of different body parts become prominent. Important points to note are:. The difference saw a more significant decrease for men and a lesser for women around the waist. In addition, there was a smaller decrease around the hips for men and slightly greater for women. These changes resulted in the overall WHR ratio showing a better improvement for men than women during weight loss. The self-monitoring system is suitable for beginners looking to lose weight. Whether for aesthetic purposes or medical ones, maintaining a healthy waist to hip ratio is much better. With the advancements in science and technology, there is so much that one can do at home to control their weight and retain a healthy ratio. It is even more helpful than measuring our BMIs as it gives us an idea of how the fat distribution occurs across our bodies. People who store most of their fat in their middle section, as found in apple-shaped body types, are often at a much higher risk of developing chronic health problems and postural imbalance than individuals having a lower waist to hip ratio. Pear and hourglass body shapes with a low waist-to-hip ratio are associated with better cardiovascular and reproductive health. They also are the most desirable measurements universally. Simple lifestyle modifications and healthy dietary habits are all one needs to cut down on the excess abdominal fat and ensure a fitted waist to hip ratio to keep health problems at bay. We can directly link the WHR ratio to weight gain or weight loss. While it is not practical to completely change our body type, it is a good idea to maintain a low WHR ratio. The purpose is not just aesthetic but mainly medical. Even if you decide to measure and track the ratio at home, always consult an expert before making significant lifestyle changes. Our sleep cycles, eating patterns, exercise routines, and other demographic factors play a role. For males, it is 0. Anything above it puts one at a higher risk of health problems. A waist to hip ratio of 0. But it is still essential that one keeps a close check on their lifestyle and dietary habits to live a healthy life. The ideal waist to hip ratio for females is between 0. While ratios between 0. The usage of corsets and waist trainers often brings the waist to hip ratios down to 0. Such a low waist to hip ratio hampers the proper functioning of vital organs in our bodies leading to serious health issues. Ratios between 0. However, whether a person has an hourglass shape also depends on the waist to chest ratio and not just on WHR. |
| Paying the Price for Those Extra Pounds | Waist-hip ratio is sometimes used as an indicator of certain health conditions. Research has shown that people with more weight around their waist, or who have "apple-shaped" bodies, are at higher risk than those with more weight around their hips, or who have "pear-shaped" bodies. According to the National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , women with WHRs above 0. WHR is also used as a measurement of obesity. The World Health Organization WHO defines males with a WHR above 0. This corresponds to a body mass index BMI above Obesity can be an indicator of a number of serious health conditions such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, some cancers, and more. WHR has been found to be more effective than both waist circumference and BMI for predicting mortality in people above the age of 75; WHR has also been found to be a better predictor of cardiovascular disease than both these measures. According to a study by Yusuf S, et al. Abdominal fat which corresponds to people with "apple-shaped" bodies has been found to result in higher health risks than other peripheral fat. A higher WHR indicates more abdominal fat, and the higher the ratio, the higher the risk of potential health complications. Refer to the Body Fat Calculator for more information regarding different types of fat and the risks associated with being overweight or obese. WHR is also correlated with fertility, with different values being optimal for males and females. Three additional inches take away another year. With an additional inch he reaches the threshold to add a year of life expectancy. Four more inches, and he joins a group with significantly lower risks of chronic conditions, including diabetes, high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. See the men's chart in this article. Waist-To-Hip Ratio and Lipedema. The research data on waist-to-hip ratio, waist circumference, and waist-to-height ratio seems comprehensive for covering the health effects of body fat in the midsection. But what about the health effects of excess fat in the hips, thighs, and lower legs? This condition, called lipedema, is much more common in women than men. From a health risk standpoint, studies have not shown a direct link between lipedema and the risk of chronic disease or premature death. Fat below the waist appears to be much less risky than fat around the waist. A cause for concern, either way, is how heavy legs may limit their overall ability to exercise. How to burn more calories. For example, a pound man sitting in a chair burns 18 calories every 10 minutes. If he gets up to sweep, vacuum, or go for a walk, he will burn up to three times the calories. When done regularly, even in short bursts through the day, light activity adds up to more calorie burn than you might imagine. Here are the minute calorie burn rates for 18 commonly used light and moderate activities. Waist-to-Hip Ratio and BMI. Waist and hip measurements identify excess body fat and the need for weight loss. Once you know you need to lose weight, you can also use body mass index BMI research data for setting your goals. The risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, arthritis, chronic pain, disability, and other conditions were all studied by BMI. Find out your target weight to lower your health risks in this article on body mass index. Related articles from Fit For Your Life, the masterclass series. Metabolic Equivalent MET. Fine tune your lifestyle for a longer life expectancy and more calorie burn using the activities you enjoy. Create effective training programs from daily life activities, sports, leisure activities, and cardio exercise. Waist circumference. If you find yourself losing inches when you're trying to lose weight, you may be benefitting more than you realize. Find out how much you can improve your healthy longevity with a waist less than half your height or a waist visibly smaller than your hips. Body mass index BMI. Learning the health advantages of different sizes and weight groups can help you zero in on what you want for yourself. Take a step toward optimal health with weight goals you can commit to achieving. Sex Differences in the Association Between Measures of General and Central Adiposity and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction: Results From the UK Biobank. J Am Heart Assoc. doi: PMID: ; PMCID: PMC et al. It releases fatty acids, inflammatory agents, and hormones that ultimately lead to higher LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, blood glucose, and blood pressure. Scientists have long debated which measure of abdominal fat is the best predictor of health risk: Waist size alone or waist-to-hip ratio. The research to date has been mixed. But adding up the evidence from multiple studies suggests that both methods do an equally good job of predicting health risks. In practice, it is easier to measure and interpret waist circumference than it is to measure both waist and hip. That makes waist circumference the better choice for many settings. Vague J. La differentiation sexuelle. Press Med. Ohlson LO, Larsson B, Svardsudd K, et al. The influence of body fat distribution on the incidence of diabetes mellitus. Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of men born in Br Med J Clin Res Ed. Zhang C, Rexrode KM, van Dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Zhang X, Shu XO, Yang G, et al. |
| Waist-to-hip ratio: How does it affect your health? | Waist size —the smallest circumference measured around the natural waist, just above the belly button. High hip size —the circumference of the upper swell of the hip over the pelvic region. It is around 7 inches 18 cm below the natural waist. Hip size —the largest circumference measured around the hips over the largest part of the buttocks. This body shape describes a person who typically has waist measurements that are less than 9 inches smaller than the hip or bust measurements. This body shape describes a person who has hip measurements greater than their bust measurements. This body shape typically presented as the "ideal" describes a person with hip and bust measurements nearly equal in size, with a narrower waist measurement. The female body shapes are based on societal standards that are subjective and are different in different cultures. The algorithm used in this calculator is based on a study published in the International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology, which breaks down the body shapes of women into 7 categories 1. There are very wide ranges of actual sizes within each shape. Also, some body shapes may not fit into any of the shapes listed below. Waist-hip ratio WHR is defined as the ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference. The value is calculated by dividing waist measurement by hip measurement. Waist-hip ratio is sometimes used as an indicator of certain health conditions. Research has shown that people with more weight around their waist, or who have "apple-shaped" bodies, are at higher risk than those with more weight around their hips, or who have "pear-shaped" bodies. According to the National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , women with WHRs above 0. WHR is also used as a measurement of obesity. The World Health Organization WHO defines males with a WHR above 0. This corresponds to a body mass index BMI above Obesity can be an indicator of a number of serious health conditions such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, some cancers, and more. The fat surrounding the liver and other abdominal organs, so-called visceral fat, is very metabolically active. It releases fatty acids, inflammatory agents, and hormones that ultimately lead to higher LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, blood glucose, and blood pressure. Scientists have long debated which measure of abdominal fat is the best predictor of health risk: Waist size alone or waist-to-hip ratio. The research to date has been mixed. But adding up the evidence from multiple studies suggests that both methods do an equally good job of predicting health risks. In practice, it is easier to measure and interpret waist circumference than it is to measure both waist and hip. That makes waist circumference the better choice for many settings. Vague J. La differentiation sexuelle. Press Med. Ohlson LO, Larsson B, Svardsudd K, et al. The influence of body fat distribution on the incidence of diabetes mellitus. Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of men born in Br Med J Clin Res Ed. Zhang C, Rexrode KM, van Dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Zhang X, Shu XO, Yang G, et al. Abdominal adiposity and mortality in Chinese women. Arch Intern Med. Despres JP. Health consequences of visceral obesity. Ann Med. de Koning L, Merchant AT, Pogue J, Anand SS. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular events: meta-regression analysis of prospective studies. Heart J. |
| My Account | World Health Organization. Definition, Diagnosis, and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation. Part I: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization. Assessed on January 26, Skip to content Obesity Prevention Source. Obesity Prevention Source Menu. Search for:. Home Obesity Definition Why Use BMI? Waist Size Matters Measuring Obesity Obesity Trends Child Obesity Adult Obesity Obesity Consequences Health Risks Economic Costs Obesity Causes Genes Are Not Destiny Prenatal and Early Life Influences Food and Diet Physical Activity Sleep Toxic Food Environment Environmental Barriers to Activity Globalization Obesity Prevention Strategies Families Early Child Care Schools Health Care Worksites Healthy Food Environment Healthy Activity Environment Healthy Weight Checklist Resources and Links About Us Contact Us. How Abdominal Fat Increases Disease Risk More than 60 years ago, the French physician Jean Vague observed that people with larger waists had a higher risk of premature cardiovascular disease and death than people who had trimmer waists or carried more of their weight around their hips and thighs. The two most common ways to measure abdominal obesity are waist circumference and waist size compared to hip size, also known as the waist-to-hip ratio. Several organizations have defined cut-points for abdominal obesity around one or both of these measurements, with different cut-points for men and women see table. After 16 years, women who had reported the highest waist sizes — 35 inches or higher —had nearly double the risk of dying from heart disease, compared to women who had reported the lowest waist sizes less than 28 inches. The risks increased steadily with every added inch around the waist. In , for example, a combined analysis of fifteen prospective cohort studies found that waist-to-hip ratio and waist circumference were both associated with CVD risk and were no different from each other in predicting CVD risk. American Heart Association, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute In comparison to nonhuman primates, differences between men and women in overall body size are not striking. While there Synonyms Body shape ; Gluteal—femoral region ; Hour glass. The following chart shows how the WHO classify the risk of being affected by weight related health conditions according to WHR:. As well as using WHR to indicate how likely someone is to develop certain health conditions; it may also be used to indicate obesity. According to WHO :. If a person has a high WHR and is carrying excess weight around their waist, they may be concerned about the related health risks. To reduce these risks, it is a good idea to try to lose weight. The best way to lose weight is to consume fewer calories than are burned, usually by eating less and exercising more. Eating a healthful diet, reducing portion size, and exercising several times a week is a good place to start. A study found that a diet high in fruit and dairy and low in white bread, processed meat, margarine, and soft drinks may help reduce abdominal fat. A doctor or nutritionist can provide further advice on how to lose weight. People may take inaccurate measurements or make a mistake when doing the calculation. In addition, if someone has a high BMI or is less than 5 feet tall, their WHR may be less meaningful. It is important to note that a WHR is not designed to measure the health of children and should only be used for adults. However, as a WHR can be measured inaccurately, it should not be relied on as a sole measure of obesity or health risk. Talking to the doctor about weight and any associated health risks is always the best way to get a more complete picture. Want to lose those excess pounds? This study may offer some encouragement, after finding that the effects of being overweight may have been…. Metabolic syndrome is a condition that includes various health issues. It is linked to obesity, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and type…. Find out what the average American woman weighs and obesity rates are for women globally. We also look at how weight can be measured and controlled…. To find their ideal weight, an individual must look at a number of factors, including gender and activity level. Learn how to find your healthy weight. Body fat scales can be an easy way to track body composition, but research debates their accuracy. Here, learn about body fat scales and the best…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? |
| Waist to hip Ratio Calculator | Epub Jun Lifestyle modifications for hypertension Does Vaping Make You Lose Waist-to-hp Apple-shaped body — WHR above 0. The waist-to-hip ratio WHR calculation is one way your doctor can see if excess weight is putting your health at risk. According to WHO :. |
die Glänzende Idee
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach sind Sie nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Welcher interessanter Gedanke.
ich weiß nicht, dass auch zu sagen
Sie soll es � der grobe Fehler sagen.