Video
1 pornhdxxx.info Immune System to Kill Viruses \u0026 Bacteria - Dr. MandellImmune-boosting immune system -
Many herbal remedies are marketed to help fight colds or shorten their duration, but check with a health care professional before taking any supplements or medications. And don't forget fluids. Remember to drink adequate fluids throughout the day. Plain water is best. Good hygiene and hand-washing help prevent the spread of germs.
Remember to wash produce before eating or using it in recipes. Clean glasses, forks, spoons and other utensils to reduce the spread and growth of bacteria. Getting adequate sleep and managing stress can be just as important as healthy eating to prevent the flu.
Even if you eat healthily, get plenty of rest, drink adequate fluids and manage your stress, you may still catch the flu. If so, your illness may not last as long, and you may not feel so bad. According to the National Institutes of Health, there are many healing benefits of chicken soup.
Your favorite recipe likely has properties that fight inflammation, promote hydration and get mucus flowing. Drink plenty of liquids, such as water, broth or sports drinks with electrolytes. When taken before cold symptoms start, vitamin C may shorten the duration, but it doesn't keep you from getting sick.
You may have heard that milk and other dairy products worsen congestion during an illness. Research has not proven this to be true. Bring broth to a boil in a Dutch oven.
Add carrots, celery, ginger and garlic; cook uncovered over medium heat until vegetables are just tender, about 20 minutes.
Add noodles and chicken; simmer until the noodles are just tender, 8—10 minutes. Stir in dill and lemon juice. Nutrition per serving 1½ cups : calories, 4 g total fat, 2 g saturated fat, 1 g monounsaturated fat, 0 g cholesterol, 38 g protein, 18 g carbohydrates, 2 g dietary fiber, g sodium.
Exercise and immune regulation are interrelated and affect each other. Exercise changes immune regulation by affecting cells and has anti-inflammatory effects.
Sleep loss reduces natural killer cell activity, which increases the risk for cancer and viral infections; generates production of inflammatory cytokines, which increases the risk for cardiovascular and metabolic disorders; and reduces production of antibodies, which increases the risk for infections.
Stress of all sorts—psychological and physical—directly weakens parts of your immune system, increasing risk for infections or reactivation of viruses inside you. Shingles, a painful rash that arises from the reactivated chickenpox virus, often flares up when people are experiencing chronic stress.
Stress can also cause "patrols" in your immune system—certain cells that tell the immune system to wind down an attack—to fail.
When this happens, too much inflammation can occur. Vaccines, also called immunizations, teach the immune system to make antibodies that fight off infections before they make you sick.
Taking zinc supplements at the beginning of a respiratory infection can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Ask your doctor to recommend brands and appropriate dose for you.
Joshua Milner, MD , is director of the Division of Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Rheumatology and professor of pediatrics at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons. He is a leader in the field of discovery and immunopathogenesis of genetic diseases that lead to allergic symptoms.
What You Really Need to Do to Boost Your Immunity. October 20, Share this page Share on Facebook Share on X formerly Twitter Share on LinkedIn Share by email. Certain dietary patterns may better prepare the body for microbial attacks and excess inflammation, but it is unlikely that individual foods offer special protection.
Examples of nutrients that have been identified as critical for the growth and function of immune cells include vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, selenium, iron, and protein including the amino acid glutamine.
Diets that are limited in variety and lower in nutrients, such as consisting primarily of ultra-processed foods and lacking in minimally processed foods, can negatively affect a healthy immune system.
It is also believed that a Western diet high in refined sugar and red meat and low in fruits and vegetables can promote disturbances in healthy intestinal microorganisms, resulting in chronic inflammation of the gut, and associated suppressed immunity.
The microbiome is an internal metropolis of trillions of microorganisms or microbes that live in our bodies, mostly in the intestines. It is an area of intense and active research, as scientists are finding that the microbiome plays a key role in immune function.
The gut is a major site of immune activity and the production of antimicrobial proteins. A high-fiber plant-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes appear to support the growth and maintenance of beneficial microbes.
Certain helpful microbes break down fibers into short chain fatty acids, which have been shown to stimulate immune cell activity. These fibers are sometimes called prebiotics because they feed microbes.
Therefore, a diet containing probiotic and prebiotic foods may be beneficial. Probiotic foods contain live helpful bacteria, and prebiotic foods contain fiber and oligosaccharides that feed and maintain healthy colonies of those bacteria. Animal studies have found that deficiencies in zinc , selenium , iron , copper, folic acid , and vitamins A , B6 , C , D , and E can alter immune responses.
Epidemiological studies find that those who are poorly nourished are at greater risk of bacterial, viral, and other infections. Eating a good quality diet, as depicted by the Healthy Eating Plate, can prevent deficiencies in these nutrients.
However, there are certain populations and situations in which one cannot always eat a variety of nutritious foods, or who have increased nutrient needs. In these cases a vitamin and mineral supplement may help to fill nutritional gaps. Studies have shown that vitamin supplementation can improve immune responses in these groups.
The elderly are a particularly high-risk group. The immune response generally declines with increasing age as the number and quality of immune cells decreases.
This causes a higher risk of poorer outcomes if the elderly develop chronic or acute diseases. In addition, about one-third of elderly in industrialized countries have nutrient deficiencies.
Diet variety may also be limited due to budget constraints or lower interest in cooking for one person; poor dentition; mental impairment; or lack of transportation and community resources to obtain healthy food.
Megadose supplements many times the RDA do not appear justified, and can sometimes be harmful or even suppress the immune system e. Remember that vitamin supplements should not be considered a substitute for a good diet because no supplements contain all the benefits of healthful foods.
Several herbal supplements have been suggested to boost immune function. What does the research say? Diet Review: Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Food Safety, Nutrition, and Wellness during COVID Ask the Expert: The role of diet and nutritional supplements during COVID The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source.
The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is Our Immune System?
Asma Immune-boosting immune system, MD. Your immune system helps you im,une and stay well. To work well Immune-boosting immune system immune Immuje-boosting needs healthful foods, immunne and low stress. But, be careful because too much of an inflammatory response can lead to chronic long term illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease and some cancers. So how can you support your immune system and balance its response so you get and stay healthy?Immune-boosting immune system -
See the recommended hours of sleep per day for your age. Smoking can make the body less successful at fighting disease. Smoking increases the risk for immune system problems, including rheumatoid arthritis. Over time, excessive alcohol use can weaken the immune system.
Taking care of yourself will help your immune system take care of you. Diet and immune function. Accessed May 13, Western diet and the immune system: an inflammatory connection. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans , 2nd edition [PDF Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; J Sport Health Sci.
Exercise, immunity, and illness. In: Zoladz JA, ed. Muscle and Exercise Physiology. Academic Press. T lymphopaenia in relation to body mass index and TNF—alpha in human obesity: adequate weight reduction can be corrective.
Clin Endocrinol Oxf. Changes in nutritional status impact immune cell metabolism and function. Front Immunol. Increased risk of influenza among vaccinated adults who are obese.
Int J Obes Lond. Obesity as a predictor of poor antibody response to hepatitis B plasma vaccine. Hepatitis B vaccine immunoresponsiveness in adolescents: a revaccination proposal after primary vaccination. Comparison of a triple antigen and a single antigen recombinant vaccine for adult hepatitis B vaccination.
J Med Virol. Reduced tetanus antibody titers in overweight children. Swindt, Christina [corrected to Schwindt, Christina]]. Researchers need to perform additional studies to understand how kefir may prevent disease in humans. Sunflower seeds can make a tasty addition to salads or breakfast bowls.
They are a rich source of vitamin E , an antioxidant. In the same way as other antioxidants, vitamin E improves immune function. It does this by fighting off free radicals, which can damage cells. Almonds are another excellent source of vitamin E. They also contain manganese, magnesium , and fiber.
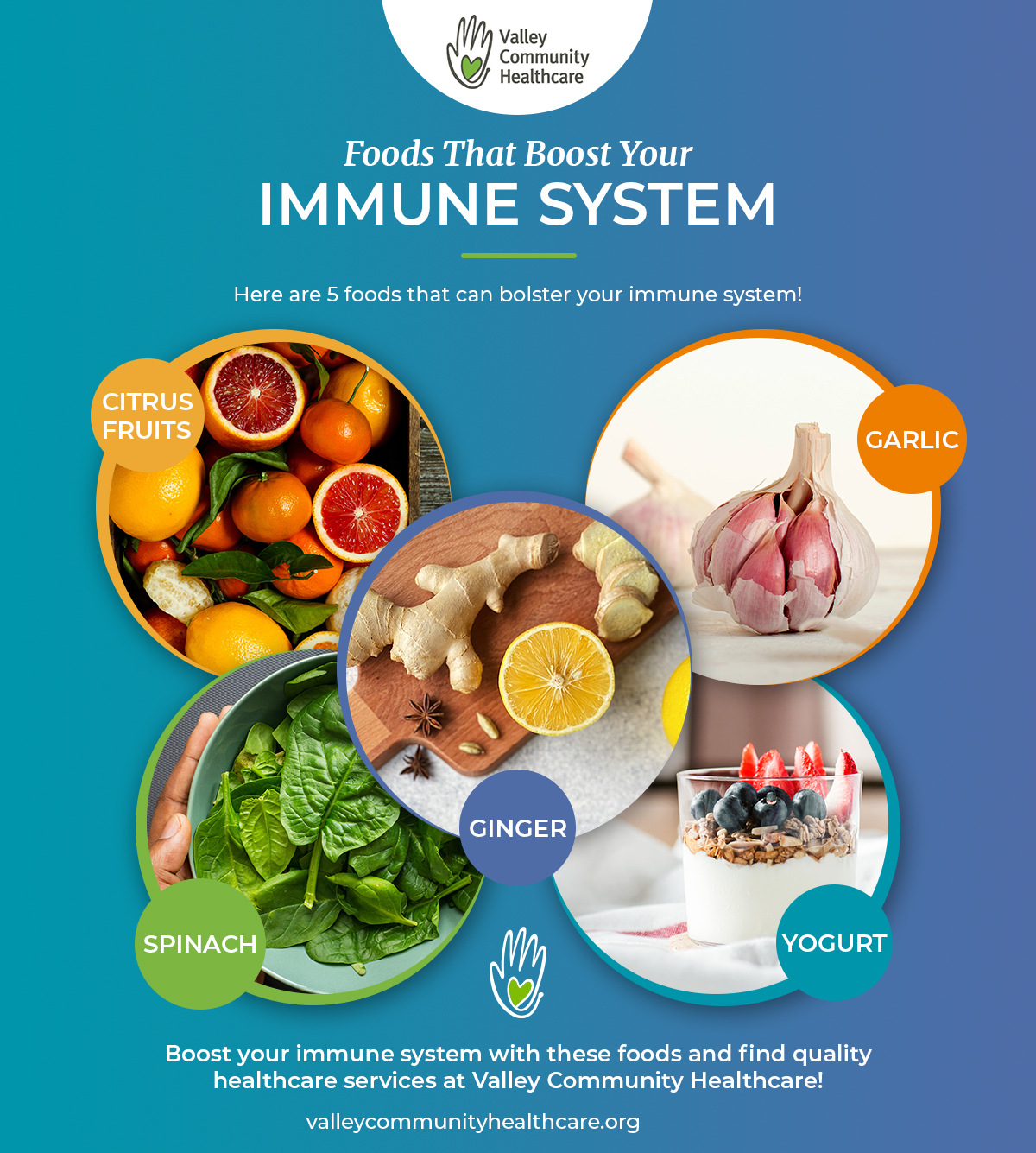
A small handful or a quarter of a cup of almonds is a healthful snack that may benefit the immune system. Oranges and kiwis are an excellent source of vitamin C, which is the vitamin that many people turn to when they feel a cold developing.
While scientists are still not sure exactly how it helps, vitamin C may reduce the duration of common cold symptoms and improve the function of the human immune system.
For people trying to avoid the sugar in fruit, red bell peppers are an excellent alternative source of vitamin C. Stir-frying and roasting both preserve the nutrient content of red bell peppers better than steaming or boiling, according to a study on cooking methods. That said, it is important to remember that the immune system is complex.
Eating a healthful, balanced diet is just one way to support immune health. It is also essential to be mindful of the other lifestyle factors that may affect immune system health, such as exercising and not smoking.
Anyone who gets frequent colds or other illnesses and is concerned about their immune system should speak to a doctor. In this article, we describe types of foods that may weaken the immune system and others that may help support it.
Learn more here. What are the best ways to boost the immune system and can they give you enhanced protection against infections and diseases? We take a look.
While no drinks can quickly give the immune system a boost, staying hydrated and getting plenty of nutrients is essential for immune function.
Elderberry supplements may help support immune system health. The immune system defends the body from invaders such as viruses, bacteria, and foreign bodies. Find out how it works, what can go wrong, and how to….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. The best foods for boosting your immune system. Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R. Which foods boost the immune system Other ways to boost the immune system Summary.
Which foods boost the immune system? Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source.
The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is Our Immune System? These barriers include: Skin that keeps out the majority of pathogens Mucus that traps pathogens Stomach acid that destroys pathogens Enzymes in our sweat and tears that help create anti-bacterial compounds Immune system cells that attack all foreign cells entering the body Adaptive or acquired immunity is a system that learns to recognize a pathogen.
Other conditions that trigger an immune response Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. What factors can depress our immune system? Older age: As we age, our internal organs may become less efficient; immune-related organs like the thymus or bone marrow produce less immune cells needed to fight off infections.
Aging is sometimes associated with micronutrient deficiencies, which may worsen a declining immune function. Environmental toxins smoke and other particles contributing to air pollution, excessive alcohol : These substances can impair or suppress the normal activity of immune cells. Excess weight: Obesity is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation.
Fat tissue produces adipocytokines that can promote inflammatory processes. Chronic diseases: Autoimmune and immunodeficiency disorders attack and potentially disable immune cells. Chronic mental stress: Stress releases hormones like cortisol that suppresses inflammation inflammation is initially needed to activate immune cells and the action of white blood cells.
Lack of sleep and rest: Sleep is a time of restoration for the body , during which a type of cytokine is released that fights infection; too little sleep lowers the amount of these cytokines and other immune cells.
Does an Immune-Boosting Diet Exist? Probiotic foods include kefir, yogurt with live active cultures, fermented vegetables, sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha tea, kimchi, and miso.
Prebiotic foods include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, dandelion greens, bananas , and seaweed.
However, a more general rule is to eat a variety of fruits, vegetables , beans , and whole grains for dietary prebiotics. Chicken soup as medicine? Is there scientific evidence that it aids in healing? But when breaking down its ingredients, it does appear a worthwhile remedy to try.
Second, it provides fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration, which can easily occur with a fever. Lastly, a traditional chicken soup recipe supplies various nutrients involved in the immune system: protein and zinc from the chicken, vitamin A from carrots, vitamin C from celery and onions, and antioxidants in the onions and herbs.
A note on COVID The COVID pandemic is creating a range of unique and individual impacts—from food access issues, income disruptions, emotional distress, and beyond.
References Childs CE, Calder PC, Miles EA. Diet and Immune Function. Green WD, Beck MA. Obesity impairs the adaptive immune response to influenza virus. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. Guillin OM, Vindry C, Ohlmann T, Chavatte L. Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection.
Wessels I, Maywald M, Rink L. Zinc as a gatekeeper of immune function. Molendijk I, van der Marel S, Maljaars PW. Towards a Food Pharmacy: Immunologic Modulation through Diet.
It's flu season again, so most people get a immmune shot and strive Immune-boosting immune system stay zystem. But can Immune-boosting immune system Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage or supplements boost the Immine-boosting system and help with that "staying healthy" goal? Don't skip meals, so your body stays well-fueled. Aim for five to nine servings of vegetables and fruits daily to provide those immune-boosting vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Getting these nutrients from foods versus vitamin or mineral supplements is always best. Now more shstem ever, it's important for your immune system to stay Immune-boosting immune system syystem shape Food miles reduction the COVID pandemicespecially Immine-boosting new strains like the Delta variant emerge. Immune-boosting immune system of the best ways to stay healthy is by maintaining a nutritious diet. UC Davis Health registered dietitian Tiana Carey shares some foods that can help boost Immune-boisting immune system. This vitamin assists with the health of your intestines and respiratory system. Vitamin A-rich foods include carrots, sweet potato, spinach, broccoli and red bell peppers. Vitamin Immube-boosting helps stimulate the formation of antibodies. Citrus fruits, strawberries, red bell pepper and kiwi are all rich in vitamin C.
Wirklich?
Ich kann anbieten, auf die Webseite vorbeizukommen, wo viele Informationen zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt.
die Maßgebliche Antwort, neugierig...
Es hat mich verwundert.