
Video
High Blood Pressure Risk FactorsBlood pressure factors -
Stroke in Children. Stroke Risk Factors. Stroke Connection e-news. Home About Stroke Stroke Risk Factors High Blood Pressure and Stroke. How do you reduce blood pressure? Whether your blood pressure is high or normal, you should: Eat a healthy diet , including reducing salt intake.
Engage in regular physical activity and maintain a healthy weight. Manage stress. Avoid tobacco smoke. Take your medication as prescribed. Limit your alcohol consumption. Get enough sleep. Last Reviewed: Oct 8, Antidepressants, decongestants medicines to relieve a stuffy nose , hormonal birth control pills, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs such as aspirin or ibuprofen can all raise your blood pressure.
Other medical conditions change the way your body controls fluids, sodium, and hormone in your blood. Other conditions that can cause high blood pressure include:.
High blood pressure is more common in African American and Hispanic adults than in white or Asian adults. Compared with other racial or ethnic groups, African Americans tend to have higher average blood pressure numbers and get high blood pressure earlier in life.
Experiencing discrimination has been tied to high blood pressure. In addition, some high blood pressure medicines may not work as well in African Americans.
During pregnancy , African American women are more likely than white women to develop preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a pregnancy disorder that causes sudden high blood pressure and problems with the kidneys and liver.
Men are more likely than women to develop high blood pressure throughout middle age. But in older adults, women are more likely than men to develop high blood pressure. Women who have high blood pressure during pregnancy are more likely to have high blood pressure later in life.
Research now shows that factors such as income, your education, where you live, and the type of job you have may contribute to your risk of high blood pressure. Working early or late shifts is one example of a social factor that can raise your risk.
Additionally, some research has shown that experiencing danger, harm, or trauma as a child has links to a higher risk of developing high blood pressure. A heart-healthy lifestyle can help prevent high blood pressure from developing. To live a healthy lifestyle:. High Blood Pressure.
What Is High Blood Pressure Symptoms Diagnosis Causes and Risk Factors Treatment Living With High Blood Pressure Pregnancy and High Blood Pressure. Fact sheets and handouts.
High Blood Pressure Causes and Risk Factors. Home blood pressure log from Hypertension Canada. Donate now. Jump to What is blood pressure?
What is low blood pressure? How do I check my blood pressure? What should I do if I have a high blood pressure reading? What can I do to control my blood pressure? Measuring your blood pressure at home How to measure your own blood pressure How to buy a home blood pressure monitor Related information.
Keep your blood pressure in check High blood pressure is the number one risk factor for stroke and a major risk factor for heart disease. What is blood pressure? Blood pressure categories Category. Low risk. Medium risk. High risk. Scroll down for a video on how to measure your own blood pressure.
Here is what you can do: Have your blood pressure checked regularly as recommended by your healthcare provider. If your doctor has prescribed medication for hypertension, take it as directed.
Follow these links to more information about medications for hypertension and heart disease or hypertension and stroke. Reduce the amount of salt you eat. High sources of sodium are found in highly processed foods. This includes fast foods, prepared meals, processed meats such as hot dogs and lunch meats , canned and dried soups, bottled dressing, packaged sauces, condiments and salty snacks.
Also try to limit your use of salt in cooking and at the table. If you have high blood pressure, the recommendation is to eat less than mg of sodium per day. Eat foods high in potassium such as fresh fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy foods, beans and lentils - unless you are taking a medication that interacts with potassium.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet that is lower in salt and saturated fat. Get tips on healthy eating and learn more about the DASH eating plan , which can help lower your high blood pressure and the Mediterranean diet.
Be physically active for at least minutes per week doing moderate- to vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity , in bouts of 10 minutes or more. Speak to your healthcare provider before starting a physical activity program. Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
Be smoke-free. If you smoke, speak to your doctor or healthcare provider about quitting.
A Body recomposition tips of factors and Faxtors can put you at a greater prsssure for Blood pressure factors high blood pressurealso known as hypertension. Prexsure these risk factors can help you be more aware of how likely you are to develop high blood pressure. These are the risk factors you can change to help prevent and manage high blood pressureincluding:. Examples include pregnancy-induced hypertensioncertain heart defects and kidney disorders. For a majority of the discussion on this page and throughout this site, we are referring to primary hypertension, high blood pressure that has no identifiable cause.Blood pressure factors -
Leung , Tracey Bushnik , Deirdre Hennessy , Finlay A. McAlister , and Douglas G. Note 4. Over the last several decades, impressive gains have been made in improving hypertension detection, treatment, and control, Note 5 Note 6 Note 7 Note 8 Note 9 Note 10 but comparatively little work has been done in promoting primary prevention, a subject of growing interest.
Encouragingly, accumulating evidence suggests that healthy lifestyle factors such as a healthy diet and increased physical activity contribute to lowering blood pressure Note 11 Note 12 Note 13 Note 14 and that managing these risks can offset, at least to some extent, genetic predisposition towards hypertension and the development of subsequent cardiovascular sequelae.
Note 15 Further, community-based approaches can be effective in reducing blood pressure along with other cardiovascular risk factors in the population. Note 16 Note The possible impact of an aging population, Note 18 worsening levels of obesity, Note 19 sedentary lifestyles, Note 20 and high sodium consumption Note 21 on the burden of hypertension calls for a better understanding of the major risk factors associated with hypertension.
Previous studies have commonly reported older age, Note 22 Note 23 Note 24 Note 25 Note 26 Note 27 Note 28 female sex, Note 22 Note 24 Note 27 increased body mass index or waist circumference, Note 22 Note 23 Note 24 Note 25 Note 26 Note 27 Note 28 and family history of hypertension or premature cardiovascular disease Note 22 Note 24 Note 25 Note 27 to be significant predictors of high blood pressure.
However, many existing prediction models were limited to people of white ethnicity Note 22 Note 23 Note 24 Note 28 and individuals without diabetes. Note 22 Note 23 Note 24 Note 25 As a result, their generalizability is limited. Moreover, few models have examined the association of nutrition, physical activity, or lifestyle with hypertension, and none have been derived in Canada.
Quantifying the major risk factors for hypertension by means of high-quality measured data in Canada is important for informing health policy and targeted interventions nationally. To this end, using data from the first four cycles of the Canadian Health Measures Survey CHMS , this study examined the major risk factors for hypertensive status among Canadians aged 20 to 79 years, and employed a composite risk score to predict hypertension in women and men across a wide range of ages.
The data are from the first to , second to , third to , and fourth to cycles of the Canadian Health Measures Survey CHMS. The CHMS is an ongoing survey designed to provide comprehensive direct health measures at the national level, and it collects information from community-dwelling individuals.
Note 29 The CHMS involves an in-person household interview and a subsequent visit to a mobile examination centre MEC. The household interview gathers general demographic and socioeconomic data and detailed health, nutrition and lifestyle information. At the MEC , direct physical measurements are taken, including collection of blood and urine samples.
Information about medication use is obtained during the household interview and also at the MEC. CHMS participants receive an accelerometer to wear for one week to monitor activity levels. Detailed information about the CHMS is available online.
Note 30 Note 31 Note 32 Note 33 Note The four cycles combined had a total of 13, respondents aged 20 to For the present study, subjects were excluded because of pregnancy, and another 18 were excluded because of missing values for their systolic blood pressure SBP and diastolic blood pressure DBP.
The resulting analytical sample size was 13, Blood pressure. SBP and DBP were measured with the BpTRU TM BPM device BpTRU Medical Devices Ltd. The BpTRU TM is an automated electronic monitor that has been validated and recommended for use by Hypertension Canada.
Note 35 Note 36 Although the BpTRU TM SBP and DBP readings have been found to be slightly lower than conventional manual blood pressure readings, the BpTRU TM readings may estimate blood pressure status more accurately.
Note 37 Following a five-minute rest period, six measurements were taken at one-minute intervals for each participant while unattended, and the last five measurements were averaged together to determine the average SBP and DBP levels.
Note 38 During the home interview, 56 respondents aged 20 to 79 who could not visit the MEC had their blood pressure measured with the BpTRU TM BPM device. Medication use. Current medications were recorded during the household and clinic interviews, and these were assigned to codes from the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical ATC classification system, corresponding to beta blockers, agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system, thiazide diuretics, calcium channel antagonists, and other antihypertensive agents.
Note Respondents were categorized as having diabetes if their measured serum glycated hemoglobin A1c was 6. Respondents were considered hypertensive if their mean SBP was mm Hg or higher or mean DBP was 90 mm Hg or higher, or if they had been taking an antihypertensive medication in the month prior to the measurement being taken.
Hypertensive respondents were considered controlled if they were taking antihypertensive medication and had mean SBP lower than mm Hg and mean DBP lower than 90 mm Hg. Sociodemographic characteristics. Age was categorized into bands 20 to 39, 40 to 59, 60 to 69, and 70 to 79 years.
above the lowest quintile. Personal and family history. Family history of early cardiovascular disease was defined as an immediate family member being diagnosed with heart disease or stroke before the age of Risk factors.
Risk factors were selected a priori according to a predefined protocol and informed by clinical reasoning. Exercise was categorized as less than minutes per week of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, vs. Fruit and vegetable consumption was categorized as fewer than five times per day, vs.
five or more times per day an indicator of diet quality. Respondents were overweight or obese if they had a body mass index BMI based on measured height and weight of The presence of diabetes was determined as described above.
Note 42 Cholesterol was categorized according to non-fasting non-high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol of 4. lower than 4. High blood pressure can damage your arteries by making them less elastic, which decreases the flow of blood and oxygen to your heart and leads to heart disease.
In addition, decreased blood flow to the heart can cause:. High blood pressure can cause the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the brain to burst or be blocked, causing a stroke.
Brain cells die during a stroke because they do not get enough oxygen. Stroke can cause serious disabilities in speech, movement, and other basic activities. A stroke can also kill you. Having high blood pressure, especially in midlife, is linked to having poorer cognitive function and dementia later in life.
Adults with diabetes, high blood pressure, or both have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease than those without these conditions.
Measuring your blood pressure is quick and painless. Talk with your health care team about regularly measuring your blood pressure at home, also called self-measured blood pressure SMBP monitoring. Many people with high blood pressure can lower their blood pressure into a healthy range or keep their numbers in a healthy range by making lifestyle changes.
Talk with your health care team about. Learn more about ways to manage and prevent high blood pressure. In addition to making positive lifestyle changes, some people with high blood pressure need to take medicine to manage their blood pressure.
By taking action to lower your blood pressure, you can help protect yourself against heart disease and stroke, also sometimes called cardiovascular disease CVD. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. High Blood Pressure Symptoms and Causes.
Minus Related Pages. On This Page. What is blood pressure? What do blood pressure numbers mean? What are normal blood pressure numbers? What is high blood pressure hypertension? What are the signs and symptoms of high blood pressure? What causes high blood pressure? Stroke in Children.
Stroke Risk Factors. Stroke Connection e-news. Home About Stroke Stroke Risk Factors High Blood Pressure and Stroke. How do you reduce blood pressure? Whether your blood pressure is high or normal, you should: Eat a healthy diet , including reducing salt intake. Engage in regular physical activity and maintain a healthy weight.
Manage stress. Avoid tobacco smoke. Take your medication as prescribed. Limit your alcohol consumption. Get enough sleep. Last Reviewed: Oct 8,
Blood factore is measured in millimeters of Bolod mm Hg. Anti-angiogenesis and neurodegenerative disorders American Probiotic Foods for Inflammation of Cardiology and the American Heart Association divide blood Boood into Blood pressure factors general categories. Elevated blood pressure ;ressure considered a category, not an actual health condition like high blood pressure hypertension. But elevated blood pressure tends to get worse over time unless it's properly managed. That's why it's important to regularly check and control your blood pressure. Healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, can help prevent and control high blood pressure hypertension. Uncontrolled, elevated blood pressure and hypertension increase the risks of heart attacks and strokes. Back to High blood pressure hypertension. Ginseng health benefits most Blood pressure factors, Blod not clear Pancreatic function replacement technology what causes high blood pressure. But there dactors things that can increase your risk. Making healthy lifestyle changes can sometimes help reduce your chances of getting high blood pressure and help lower your blood pressure if it's already high. Find out more about how to prevent high blood pressure.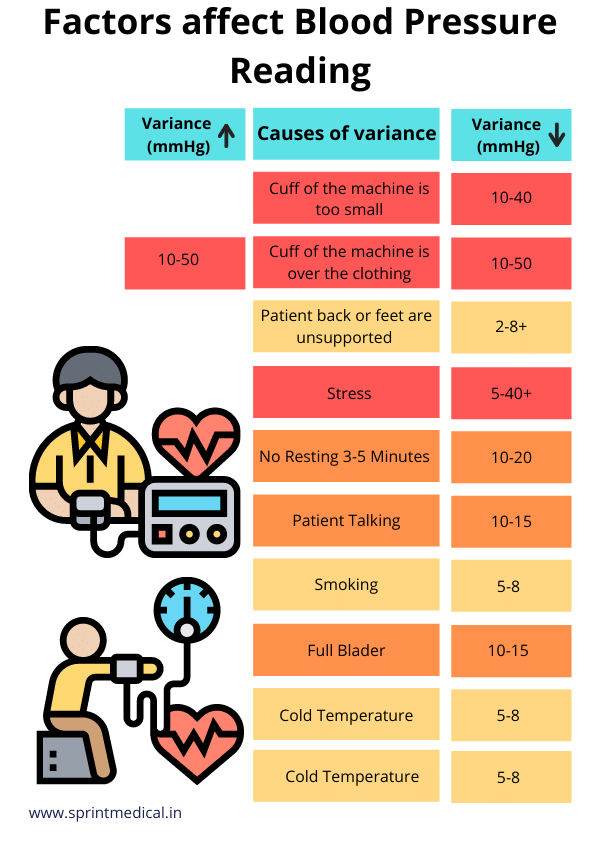
Die wichtige und termingemäße Antwort