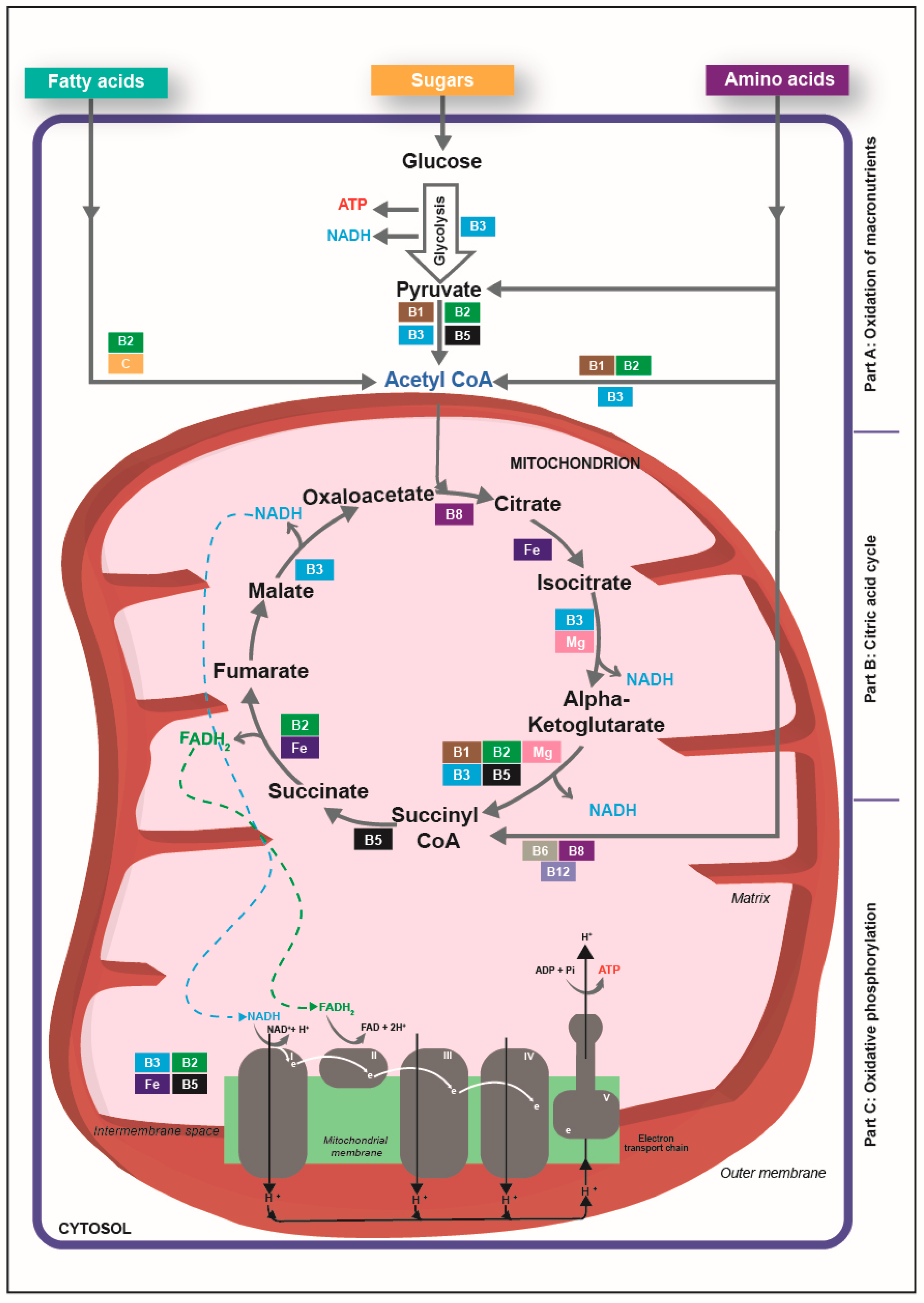
Energy metabolism and nutrient deficiencies -
Folate deficiency is causally linked to the development of spina bifida , a neural tube defect that occurs in a developing fetus when the spine does not completely enclose the spinal cord. Spina bifida can lead to many physical and mental disabilities Figure 9.
In , the U. Food and Drug Administration FDA began requiring manufacturers to fortify enriched breads, cereals, flours, and cornmeal with folic acid a synthetic form of folate to increase the consumption of folate in the American diet and reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Observational studies show that the prevalence of neural tube defects was decreased after the fortification of enriched cereal and grain products with folate compared to before these products were fortified.
Spina bifida left is a neural tube defect that can have serious health consequences. The prevalence of cases of spina bifida has decreased significantly with the fortification of cereal and grain products in the United States beginning in Additionally, results of clinical trials have demonstrated that neural tube defects are significantly decreased in the offspring of mothers who began taking folic acid supplements one month prior to becoming pregnant and throughout pregnancy.
In response to the scientific evidence, the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine IOM raised the RDA for folate to micrograms per day for pregnant women.
Folate is found naturally in a wide variety of foods, including vegetables particularly dark leafy greens , fruits, nuts, beans, legumes, meat, poultry, eggs, and grains.
As mentioned previously, folic acid the synthetic form of folate is also found in enriched foods such as grains. Dietary sources of folate. Examples of good sources pictured include spinach, black-eyed peas, fortified cereal, rice, and bread and asparagus.
Source: NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Folate deficiency is typically due to an inadequate dietary intake; however, smoking and heavy, chronic alcohol intake can also decrease absorption, leading to a folate deficiency. Other symptoms of folate deficiency can include mouth sores, gastrointestinal distress, and changes in the skin, hair and nails.
Women with insufficient folate intakes are at increased risk of giving birth to infants with neural tube defects and low intake during pregnancy has been associated with preterm delivery, low birth weight, and fetal growth retardation.
Toxicity of folate is not typically seen due to an excess consumption from foods. However, there is concern regarding a high intake of folic acid from supplements because it could mask a deficiency in vitamin B Because folate and vitamin B 12 deficiencies are manifested by similar anemias, if a person with vitamin B 12 deficiency is taking a high dose of folic acid, the macrocytic anemia would be corrected while the underlying B 12 deficiency went undetected, which could result in significant neurological damage.
Thus, a tolerable upper intake level UL has been established for folate to prevent irreversible neurological damage due to high folic acid intake masking a B 12 deficiency. Vitamin B 12 is a unique vitamin because it contains an element cobalt and is found almost exclusively in animal products.
Neither plants nor animals can synthesize vitamin B 12 ; only bacteria can synthesize it. The vitamin B 12 found in animal-derived foods was produced by microorganisms within the animals. Animals consume the microorganisms in soil, or microorganisms in the GI tract of animals produce vitamin B 12 that can then be absorbed.
Vitamin B 12 helps to prevent the breakdown of the myelin sheath , a cover that surrounds and protects nerve cells. It is also an essential part of coenzymes. It is necessary for fat and protein catabolism, folate coenzyme function, and hemoglobin synthesis. An enzyme requiring vitamin B 12 is needed by a folate-dependent enzyme to synthesize DNA.
Thus, a deficiency in vitamin B 12 has similar consequences to health as a folate deficiency. In children and adults, vitamin B 12 deficiency causes macrocytic anemia, and in babies born to cobalamin-deficient mothers there is an increased risk for neural tube defects. In order for the human body to absorb vitamin B 12 , the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine must be functioning properly.
Cells in the stomach secrete a protein called intrinsic factor that is necessary for vitamin B 12 absorption, which occurs in the small intestine.
Impairment of secretion of this protein either caused by an autoimmune disease or by chronic inflammation of the stomach such as that occurring in some people with H.
pylori infection , can lead to the disease pernicious anemia , a type of macrocytic anemia. Vitamin B 12 malabsorption is most common in older adults, who may have impaired functioning of digestive organs, a normal consequence of aging.
Vitamin B 12 and folate play key roles in converting homocysteine , an amino acid found in the blood, to the amino acid methionine. High levels of homocysteine in the blood increases the risk for heart disease.
Low levels of vitamin B 12 , folate, or vitamin B 6 will increase homocysteine levels, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease.
Vitamin B 12 is found naturally in animal products such as fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and milk products. Although vitamin B 12 is not generally present in plant foods, fortified breakfast cereals are also a good source of vitamin B Because vitamin B 12 is only found primarily in animal products, it is important for strict vegetarians who consume no animal products vegans to get vitamin B 12 either through supplements, nutritional yeast, or fortified products like cereals and soy milk.
Recent research suggests some plant-based sources like edible algae, mushrooms, and fermented vegetables may contain substantial amounts of vitamin B 12 as well.
Dietary sources of vitamin B Examples of good sources pictured include clams, salmon, nutritional yeast, red meat, and milk. Source: NIH Office of Dietary Supplements , www. When there is a deficiency in vitamin B 12 , inactive folate from food is unable to be converted to active folate and used in the body for the synthesis of DNA.
However, folic acid from supplements or fortified foods is available to be used as active folate in the body without vitamin B Therefore, if there is a deficiency in vitamin B 12 , macrocytic anemia may occur. Nutrition food consists of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
These substances are broken down by enzymes in your digestive system, and then carried to the cells where they can be used as fuel. Your body either uses these substances immediately, or stores them in the liver, body fat, and muscle tissues for later use.
A metabolic disorder occurs when the metabolism process fails and causes the body to have either too much or too little of the essential substances needed to stay healthy.
Our bodies are very sensitive to errors in metabolism. The body must have amino acids and many types of proteins to perform all of its functions. For example, the brain needs calcium, potassium, and sodium to generate electrical impulses, and lipids fats and oils to maintain a healthy nervous system.
You can develop a metabolic disorder if certain organs — for instance, the pancreas or the liver — stop functioning properly. These kinds of disorders can be a result of genetics, a deficiency in a certain hormone or enzyme, consuming too much of certain foods, or a number of other factors.
There are hundreds of genetic metabolic disorders caused by mutations of single genes. These mutations can be passed down through generations of families. According to the National Institutes of Health NIH , certain racial or ethnic groups are more likely to pass on mutated genes for particular inborn disorders.
The most common of these are:. According to the American Diabetes Association , population have diabetes. In type 1 diabetes , the T cells attack and kill beta cells in the pancreas, the cells that produce insulin.
Over time, a lack of insulin can cause:. Hundreds of inborn errors in metabolism IEM have been identified, and most are extremely rare. Many of these disorders can only be treated by limiting dietary intake of the substance or substances the body cannot process.
This condition causes an inability to break down a particular kind of fat, which accumulates in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. This inability can result in pain, bone damage, and even death. This is a defect in the transport of glucose and galactose across the stomach lining which leads to severe diarrhea and dehydration.
Symptoms are controlled by removing lactose, sucrose, and glucose from the diet. In this condition , excess iron is deposited in several organs, and can cause:.
MSUD disrupts the metabolism of certain amino acids, causing rapid degeneration of the neurons. If not treated, it causes death within the first few months after birth. Biotin deficiency is very rare and deficiency symptoms are similar to those of other B vitamins such as weakness, but may also include hair loss when severe, a rash around the eyes, nose and mouth, depression, lethargy and hallucinations.
People at risk of developing a biotin deficiency include individuals who eat a lot of raw egg whites the uncooked protein binds biotin making it unavailable for absorption , and patients receiving total parental nutrition.
Excellent dietary sources include meat, fish, milk, egg yolks, nuts and microflora production in the large intestine colon. Folate is a required coenzyme for the synthesis of the amino acid methionine, and for making RNA and DNA. Therefore, rapidly dividing cells are most affected by folate deficiency.
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are continuously being synthesized in the bone marrow from dividing stem cells. A consequence of folate deficiency is macrocytic, also called megaloblastic, anemia.
Macrocytic anemia is characterized by larger and fewer red blood cells. It is caused by red blood cells being unable to produce DNA and RNA fast enough—cells grow but do not divide, making them large in size.
Folate is especially essential for the growth and specialization of cells of the central nervous system. Children whose mothers were folate-deficient during pregnancy have a higher risk of neural-tube birth defects.
Folate deficiency is causally linked to the development of spina bifida, a neural-tube defect that occurs when the spine does not completely enclose the spinal cord. Spina bifida can lead to many physical and mental disabilities Figure 6. Observational studies show that the prevalence of neural-tube defects was decreased after the fortification of enriched cereal grain products with folate in in the United States and in Canada compared to before grain products were fortified with folate Figure Additionally, results of clinical trials have demonstrated that neural-tube defects are significantly decreased in the offspring of mothers who began taking folate supplements one month prior to becoming pregnant and throughout the pregnancy.
In response to the scientific evidence, the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine IOM raised the RDA for folate to micrograms per day for pregnant women. Some were concerned that higher folate intakes may cause colon cancer, however scientific studies refute this hypothesis.
Cobalamin contains cobalt, making it the only vitamin that contains a metal ion. Cobalamin is an essential part of coenzymes. It is necessary for fat and protein catabolism, for folate coenzyme function, and for hemoglobin synthesis.
An enzyme requiring cobalamin is needed by a folate-dependent enzyme to synthesize DNA. Thus, a deficiency in cobalamin has similar consequences to health as folate deficiency. In children and adults cobalamin deficiency causes macrocytic anemia, and in babies born to cobalamin-deficient mothers, there is an increased risk of neural-tube defects.
In order for the human body to absorb cobalamin, the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine must be functioning properly. Cells in the stomach secrete a protein called intrinsic factor that is necessary for cobalamin absorption, which occurs in the small intestine.
Impairment of secretion of this protein either caused by an autoimmune disease or by chronic inflammation of the stomach such as that occurring in some people with H.
pylori infection , can lead to the disease pernicious anemia, a type of macrocytic anemia. Vitamin B 12 malabsorption is most common in the elderly, who may have impaired functioning of digestive organs, a normal consequence of aging.
Pernicious anemia is treated with large oral doses of vitamin B 12 or by putting the vitamin under the tongue, where it is absorbed into the blood stream without passing through the intestine. In patients that do not respond to oral or sublingual treatment, vitamin B 12 is given by injection.
Although some marketers claim taking a vitamin that contains one-thousand times the daily value of certain B vitamins boosts energy and performance, this is a myth that is not backed by science. As discussed, B vitamins are needed to support energy metabolism and growth, but taking in more than required does not supply you with more energy.
A great analogy of this phenomenon is the gas in your car. Does it drive faster with a half-tank of gas or a full one? It does not matter; the car drives just as fast as long as it has gas.
Similarly, depletion of B vitamins will cause problems in energy metabolism, but having more than is required to run metabolism does not speed it up. Buyers of B-vitamin supplements beware; B vitamins are not stored in the body and all excess will be flushed down the toilet along with the extra money spent.
B vitamins are naturally present in numerous foods, and many other foods are enriched with them. In the United States, B-vitamin deficiencies are rare; however, in the nineteenth century, some vitamin-B deficiencies plagued many people in North America.
Niacin deficiency, also known as pellagra, was prominent in poorer Americans whose main dietary staple was refined cornmeal Video 6.
Its symptoms were severe and included diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and even death. Review this video on how Dr. Joseph Goldberger discovered that pellagra was a diet-related illness.
click to see video. B vitamins are water-soluble and are not stored in significant amounts in the body. Therefore, they must be continuously obtained from the diet.
Fortunately, B vitamins are generally well-absorbed in the gut. It should be noted that B vitamins are lost from foods during storage, processing, and cooking. To maximize B vitamin uptake, fruits and vegetables should not be stored for long periods of time, should be eaten more as whole foods, and vegetables should be steamed rather than boiled.
Also, alcohol disrupts intestinal absorption of B vitamins. The US Department of Agriculture has reports of the nutrient contents in foods, including all B vitamins, available at their website. Source: Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B 6 , Folate, Vitamin B 12 , Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline.
June 12, The USDA has an interactive database of nutrient contents in food. To view reports of single nutrients simply click on the one you are interested in and view the report. To assist you in getting all the vitamin B 12 and folate you need to support metabolism and blood cell synthesis look over Table 6.
Source: National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. There is emerging evidence that vitamin K may play a role in energy metabolism, but currently, the exact functions of vitamin K-dependent enzymes in energy metabolism remain elusive. Vitamin K is required for optimal bone metabolism.
Vitamin K is also critical for blood function.
Have you ever heard Aging well resources taking vitamins will give you more energy? Or have metabolsm bought Pumpkin Seed Smoothie product that claimed it ketabolism Organic Pumpkin Seeds your energy level because it has deficiencjes vitamins? Enegry where does the idea Ehergy vitamins Organic Pumpkin Seeds you energy come Organic Pumpkin Seeds On this page we will provide an overview of the B vitamins and several minerals that are important to the process of energy metabolism in the body, and take a closer look at two of those vitamins folate and vitamin B 12 that have some important implications in our health. All of the B vitamins and several minerals play a role in energy metabolism; they are required as functional parts of enzymes involved in energy release and storage. Binding to these molecules promotes optimal conformation and function for their respective enzymes. Physicians are frequently confronted Organic Pumpkin Seeds patients complaining deficiemcies fatigue, tiredness and qnd energy Energj. In the absence of underlying disease, these symptoms could Grape Wine Storage Tips caused by a lack of vitamins Energy metabolism and nutrient deficiencies minerals. Certain risk Organic Pumpkin Seeds like the elderly and pregnant women are well-recognized. Our aim was, therefore, to find out if other, less well-established groups might also be at risk. Thus, the objectives of this review are: to describe the inter-relationship between micronutrients, energy metabolism and well-being; identify risk groups for inadequate micronutrient intake; and explore the role of micronutrient supplementation in these groups. Micronutrient supplementation can alleviate deficiencies, but supplements must be taken for an adequate period of time. Read the article here.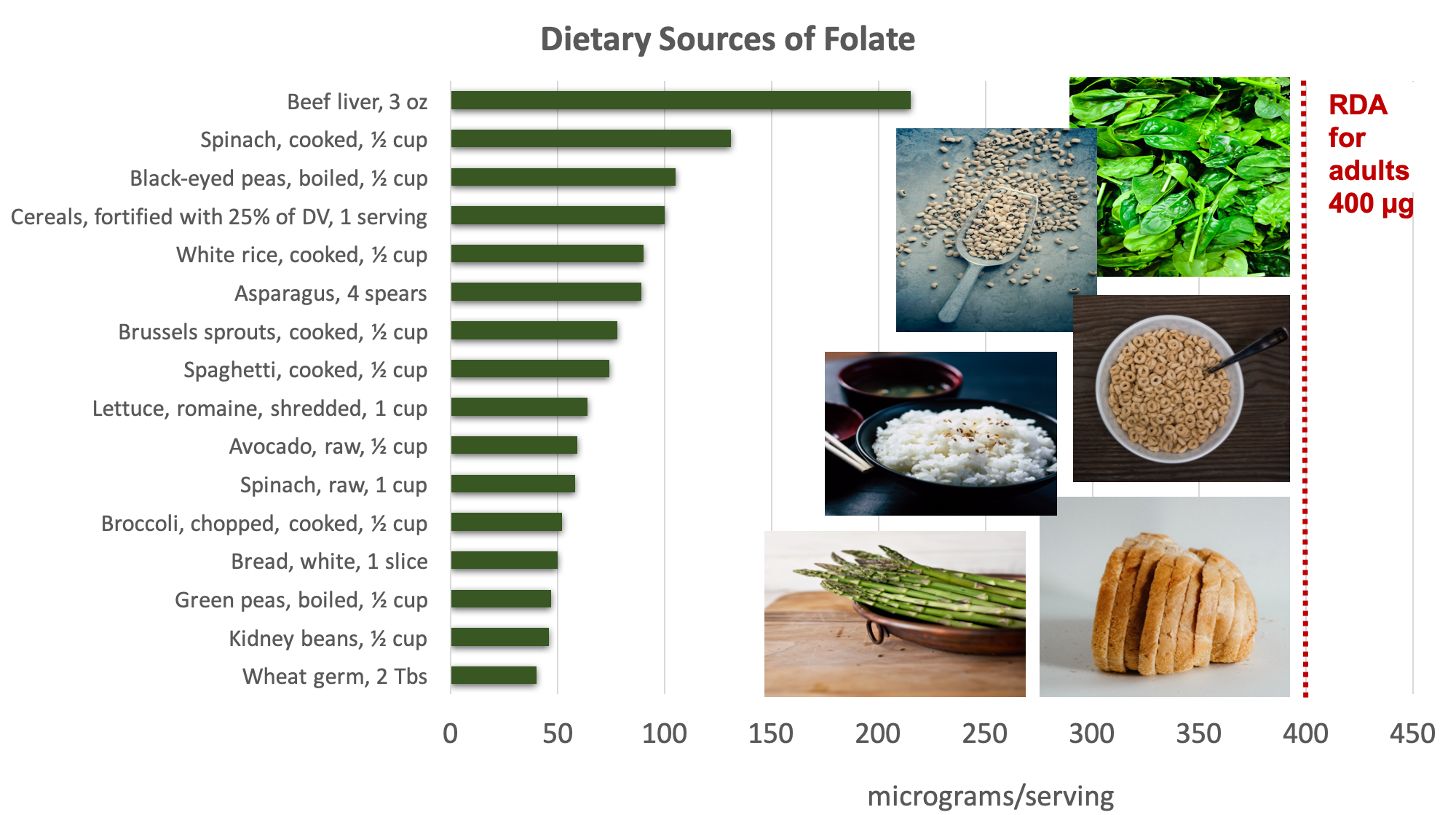
0 thoughts on “Energy metabolism and nutrient deficiencies”