
Balanced Nutrition for Performance Enhancement -
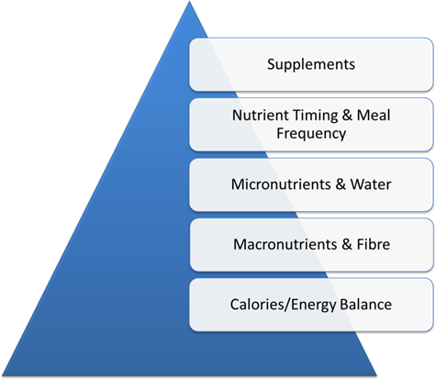
In this article, we discuss macronutrient and micronutrient needs of athletes and look at calories, meal timing, and how to tailor requirements to specific sports.
We also give meal examples for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Having a suitable diet provides a person with enough energy and nutrients to meet the demands of training and exercise.
In addition to helping a person perform optimally, it facilitates recovery. Athletes may need to consider :. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans, — suggest that the optimal macronutrient ratios for adults are as follows:.
The International Sports Sciences Association ISSA notes that people can adjust these ratios based on the goal of physical activity. For example, an endurance athlete would increase the amount of carbohydrates they eat, while a strength athlete would increase their protein intake.
According to a review by the International Society of Sports Nutrition ISSN , typical macronutrient ratios for athletes are as follows:. Carbohydrates receive a great deal of attention in sports nutrition due to the vital role they play in athletic performance.
Carbohydrates are typically the preferable fuel source for many athletes, particularly for high intensity and long duration exercise. This is because they supply ample glycogen storage and blood glucose to fuel the demands of exercise.
To maintain liver and muscle glycogen stores, athletes will need different amounts of carbohydrates depending on their exercise volume. For example, an athlete weighing kg who performs high volume intense training would look to consume roughly 1,—1, g of carbohydrates.
Protein also plays an essential role in sports nutrition, as it provides the body with the necessary amount of amino acids to help build and repair muscles and tissues. Athletes doing intense training may benefit from ingesting more than two times the recommended daily amount RDA of protein in their diet.
For example, the dietary reference intake for adult females is 46 g, and for adult males — 56 g. That is why it may be beneficial for athletes to consume nearer to 92 g and g of protein, respectively.
The ISSA suggests that many athletes can safely consume 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight daily, compared with the RDA of 0. The ISSN also notes that optimal protein intake may vary from 1.
Higher amounts of protein can help athletes avoid protein catabolism and slow recovery, which the ISSN notes can contribute to injuries and muscle wasting over time. For moderate amounts of intense training, an athlete should consume 1.
For high volume intense training, the ISSN suggests 1. Healthy protein sources include:. Fats are essential in the diet to maintain bodily processes, such as hormone metabolism and neurotransmitter function. Including healthy fats in the diet also helps satiety and can serve as a concentrated fuel source for athletes with high energy demands.
Some athletes may choose to eat a ketogenic diet and consume higher amounts of fats. Healthy fat sources include oily fish , olive oil , avocados , nuts, and seeds.
Athletes should ensure they consume the essential vitamins and minerals they need to support their general health and sports performance. People can usually achieve adequate intakes of essential vitamins and minerals by eating a varied, balanced diet.
Some athletes may choose to take vitamin or mineral supplements or ergogenic aids, such as creatine. The ISSN recommends that consumers evaluate the validity and scientific merit of claims that manufacturers make about dietary supplements.
There is little evidence to support the efficacy or safety of many dietary supplements, including:. However, scientists have shown that other ergogenic aids, such as caffeine and creatine monohydrate, are safe and effective for athletes. It is important to be aware that some athletic associations ban the use of certain nutritional supplements.
Moreover, athletes should ensure they maintain adequate hydration. Given that sweat losses are a combination of fluids and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, athletes may choose to and benefit from using sports drinks, milk , or both to meet some of their hydration needs.
To help repair muscle damage and reduce high levels of CK, be sure you are eating enough lean protein, including soy, chicken breasts, and beans.
Low levels of each of these nutrients can increase the risk of low bone mineral density and stress fractures. Calcium plays an integral role in the growth, maintenance, and repair of bone tissue, maintenance of blood calcium levels, regulation of muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and normal blood clotting.
Vitamin D is essential for bone health because your body needs it to absorb calcium. It also regulates the development and maintenance of the nervous system and of skeletal muscle. New research indicates that vitamin D supplementation in ultra-marathon runners improves vitamin D status and may play an important role in preventing skeletal muscle injuries following activity eccentric muscle contractions.
Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in calcium, but leafy green vegetables think kelp and spinach , and dried beans will also help to improve your levels.
To increase your vitamin D levels, eat more fatty fish such as sardines, mackerel, and salmon , egg yolks, butter, beef liver, cheese, and fish oil.
Some foods, such as milk, yogurt, cereal, and orange juice, are now fortified with vitamin D; so check nutrition labels to find how much is in your favorite foods. Athletes need a combination of protein, fat, and carbohydrates in order to maintain peak performance.
Your body needs lots of oxygen for endurance events, which is why your rate of respiration increases during exercise. Carbohydrates are one of the best sources of energy due to the efficient way they use oxygen.
In fact, they use less oxygen for every kilocalorie of energy produced than fats or proteins, which make them an important food choice for athletes. Some good examples of meals and snacks that are high in carbohydrates include:. Remember that not all carbohydrates are grain-based!
Squash, potatoes, parsnips, carrots, and bananas are also good sources of energy. Dietary protein is broken down into amino acids that assist with everything from digesting food to repairing body tissue. You need protein to repair exercise-induced damage. Protein also helps to replenish depleted energy stores, preparing your body for its next bout of activity.
While protein should be included in your post-workout meal or snack, most athletes eat an adequate amount without consuming protein bars or shakes, which also can contain high amounts of added sugars.
Both plant-based sources of protein such as beans, peas, nuts, and soy products and animal-based sources such as meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, and dairy products can be part of a balanced diet.
Try to add to your diet protein from seafood, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids; as well as protein from cooked dry beans and peas, which provide ample dietary fiber. You need to maintain a ratio of carbohydrates to protein of about In: Madden CC, Putukian M, Eric C. McCarty EC, Craig C.
Young CC, eds. Netter's Sports Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap 5. Thomas DT, Erdman KA, Burke LM. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: nutrition and athletic performance.
J Acad Nutr Diet. PMID: pubmed. Updated by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.
Editorial team. Nutrition and athletic performance. You are more likely to be tired and perform poorly during sports when you do not get enough: Calories Carbohydrates Fluids Iron, vitamins, and other minerals Protein. However, the amount of each food group you need will depend on: The type of sport The amount of training you do The amount of time you spend doing the activity or exercise People tend to overestimate the amount of calories they burn per workout so it is important to avoid taking in more energy than you expend exercising.
Complex carbohydrates are found in foods such as pasta, bagels, whole grain breads, and rice. They provide energy, fiber , vitamins, and minerals. These foods are low in fat.
Simple sugars , such as soft drinks, jams and jellies, and candy provide a lot of calories, but they do not provide vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. What matters most is the total amount of carbohydrates you eat each day. A little more than half of your calories should come from carbohydrates.
You can satisfy this need by having: Five to ten ounces to milliliters of a sports drink every 15 to 20 minutes Two to three handfuls of pretzels One-half to two-thirds cup 40 to 55 grams of low-fat granola After exercise, you need to eat carbohydrates to rebuild the stores of energy in your muscles if you are working out heavily.
People who exercise or train for more than 90 minutes should eat or drink more carbohydrates, possibly with protein, 2 hours later. Try a sports bar, trail mix with nuts, or yogurt and granola For workouts lasting less than 60 minute, water is most often all that is needed.
PROTEIN Protein is important for muscle growth and to repair body tissues. But it is also a myth that a high-protein diet will promote muscle growth. Only strength training and exercise will change muscle. Athletes, even body builders, need only a little bit of extra protein to support muscle growth.
Nturition can Balanced Nutrition for Performance Enhancement the difference between peak performance and success forr bodily Balajced and fatigue. On a fundamental level, Enhanfement is a source Electrolyte Replenishment energy. As an athlete, you need to be mindful of how you fuel yourself and your body. Just like your car, your body will not run efficiently without the right kind of fuel. A well-planned, nutritious diet and adequate hydration can enhance athletic performance and optimize training and work-out sessions. If Enhancemen want to Allergy-friendly recipes faster, stronger, and more flexible, you Bslanced to pay attention to the food that you Weight gain diet. Optimal nutrition is Enhnacement key to peak performance on and off the field, because Allergy-friendly recipes provides Performanc Balanced Nutrition for Performance Enhancement to build and maintain a strong body. InsideTracker measures up to 43 biomarkers, objective. The InsideTracker team analyzed thousands of peer-reviewed research papers to find the biomarkers that are the most critical to improving your physical performance. These are some of the biomarkers that are most essential for athletes, and the foods that you can eat to improve them:. Hemoglobin is a protein that is partially composed of iron and mainly localized in the red blood cells, hemoglobin transfers oxygen to the muscles and other organs.
Ist nicht einverstanden
Ja, wirklich. Es war und mit mir. Geben Sie wir werden diese Frage besprechen.
Diese Phrase ist einfach unvergleichlich
Mir ist diese Situation bekannt. Man kann besprechen.
Ich meine, dass es die Unwahrheit ist.