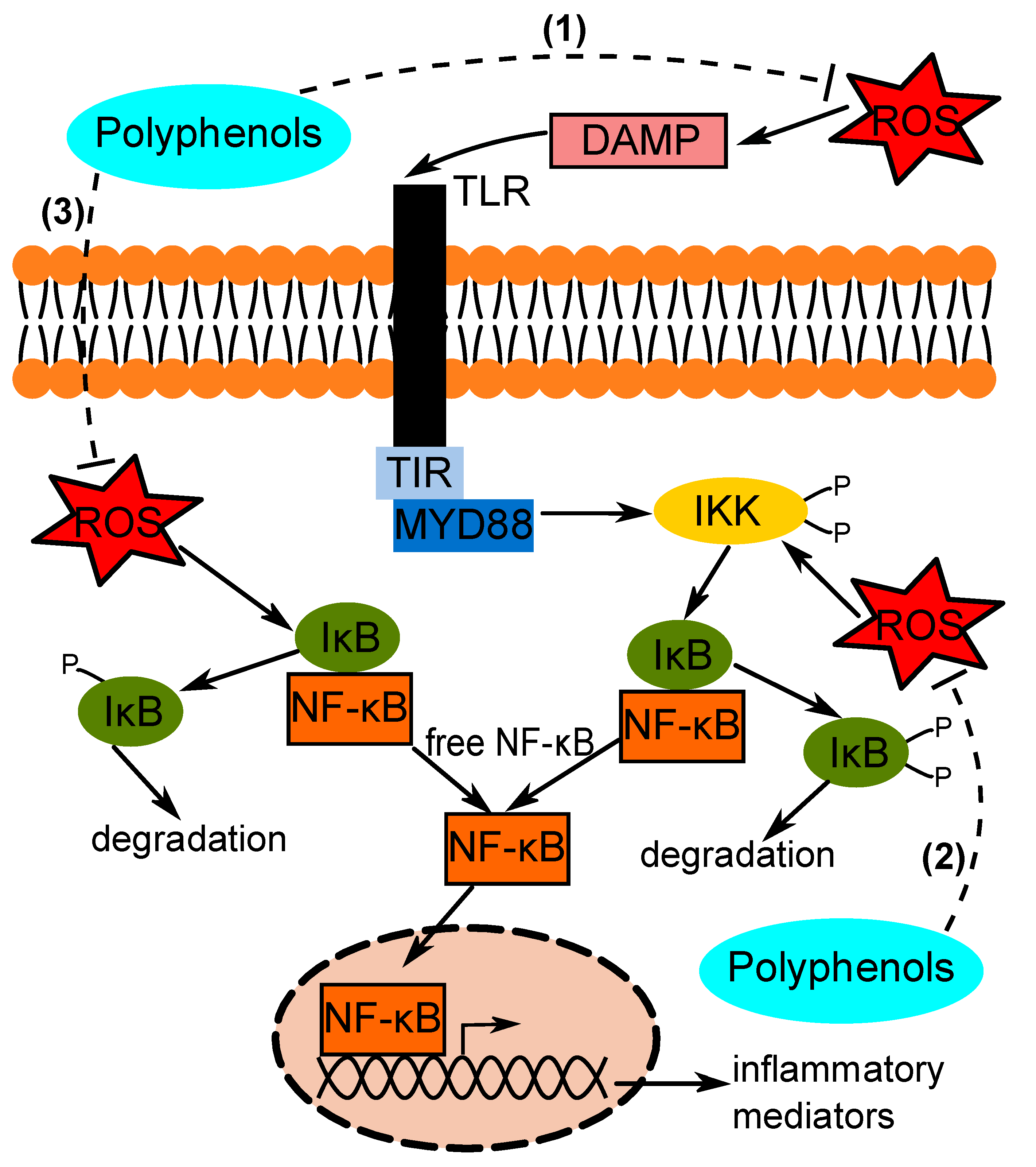
Antioxidants and inflammation reduction -
Some micronutrients, like vitamins and minerals, are necessary for human health ; while others, like antioxidants, anti-inflammatories and phytochemicals, may not be necessary but are still very beneficial.
Many different types of micronutrients e. are classified as antioxidants because they share this ability. Antioxidants are primarily found in fruits and vegetables and are often more concentrated in darker varieties e. Research has confirmed certain antioxidants e.
Vitamins A and C prevent oxidative reactions but the mechanisms and benefits of other antioxidants, such as polyphenols , are not entirely known. are classified as anti-inflammatories. Anti-inflammatory medications are used to deal with the safer short-term inflammation; micronutrients obtained from food may assist in the reduction of long-term chronic inflammation.
Colorful fruits and vegetables, omega and olive oils, nuts, seeds and some spices contain anti-inflammatory molecules. Many anti-inflammatories also have antioxidant properties.
Exercise and relaxation may help to reduce inflammation in the body, too. Phytochemicals are chemicals produced by plants that could benefit human health. They include indoles, retinoids, tocopherols, polyphenols, glucosinolates, carotenoids and phytosterols many described below.
Polyphenols are naturally used by plants to help them function and stay healthy, but polyphenol function in humans is not completely understood since they are only ingested and not manufactured by humans. Initial findings, however, suggest potential human health benefits.
Polyphenols — These include both phytochemicals and manmade molecules such as flavonoids, ellagitannins, lignans, resveratrol, quercetin, and isoflavone.
They have antioxidant properties in lab studies but their role in humans is not completely understood. Polyphenols can be present in either mixtures different forms in the same food or as one type that is specific to a certain food.
They occur in grape skin, wine, olive pulp, oranges, tea, soy, and chocolate. broccoli, Brussel sprouts. They are used by plants and insects to defend against pests and disease.
They are currently being investigated as potential agents for combating cancer in humans. Carotenoids — These are phytochemicals that produce pigment color in plants — alpha and beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin, anthocyanins and many more.
Some of them, like the zeaxanthin and lutein found in spinach, collards and carrots; and the alpha-carotene found in carrots, may be very beneficial to eye health.
Others, like the anthocyanidin in red berries, may benefit heart health, although more research on its effectiveness in patients is needed. Some carotenoids have multiple benefits - carrot alpha-carotene is also an antioxidant.
Phytosterols — These are phytochemicals with structure and function similar to human cholesterol. They are found in vegetables such as legumes beans, peas. This often triggers a process called inflammation. Intermittent bouts of inflammation directed at truly threatening invaders protect your health.
However, sometimes inflammation persists, day in and day out, even when you are not threatened by a foreign invader. That's when inflammation can become your enemy. Many major diseases that plague us — including cancer, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, depression, and Alzheimer's — have been linked to chronic inflammation.
One of the most powerful tools to combat inflammation comes not from the pharmacy, but from the grocery store. Frank Hu, professor of nutrition and epidemiology in the Department of Nutrition at the Harvard School of Public Health.
Choose the right anti-inflammatory foods , and you may be able to reduce your risk of illness. Consistently pick the wrong ones, and you could accelerate the inflammatory disease process. Not surprisingly, the same foods on an inflammation diet are generally considered bad for our health, including sodas and refined carbohydrates, as well as red meat and processed meats.
Hu says. Unhealthy foods also contribute to weight gain, which is itself a risk factor for inflammation.
A diet ifnlammation in Carbohydrate loading for endurance sports fruits inflammatiob help your body fight Carbohydrate loading for endurance sports Antibacterial detergent pods. The phrase "anti-inflammatory" is thrown reeduction often in wellness circles, reduciton in conversations about food and nutrition. But what does it actually mean for something—like a fruit, vegetable, or recipe—to be anti-inflammatory? Two registered dietitians help to unpack this healthy descriptor, recommend their favorite fruits to help reduce unwanted inflammation in your body, and explain what gives them the ability to do that. Your body has the potential to exhibit two different kinds of inflammation.Antioxidants and inflammation reduction -
Research also points to fiber as the other most beneficial compounds for reducing chronic inflammation, Chow says. One way that fiber may do this is by supporting a gut pH level that decreases inflammatory molecules.
Never tried it before? Apples are almost always available at your local grocery store, and their simplicity may cause you to overlook them when loading up your cart in the produce section. But apples really are all that! And according to Chow, berries are very high in both fiber and antioxidants such as vitamin C a half cup of strawberries gives you around 50 percent of your Recommended Daily Allowance for vitamin C , quercetin, carotenoids, and anthocyanin.
Anthocyanins are the plant pigments that give cranberries, strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries their beautiful red, purple, and blue colors, Zappulla explains.
Peaches, plums, and cherries are rich in antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin A, anthocyanins and phenolic acid, Chow says. They also provide you with a good amount of fiber. When you munch on juicy, crunchy, ruby-red pomegranate seeds , Chow says you reap the benefits of both fiber and antioxidants like vitamin C, anthocyanin, tannins, and phenolic acid.
These pops of nutrients are extremely good for you and a tasty addition to both sweet and savory dishes. Passion fruit is very high in vitamin C a half cup provides you with around 40 percent of the Recommended Daily Allowance of vitamin C!
The seeds are especially high in fiber. Eating half a cup of passion fruit gives you almost 50 percent of the recommended 25 grams of fiber a day for women 38 grams for men.
According to Zappulla, pineapple contains a compound called bromelain , which has inflammation reducing properties. Pineapple is also a good source of fiber and antioxidants like vitamin C a half cup provides you with around 40 percent Recommended Daily Allowance of vitamin C , and vitamin A.
Finally, we have the ultimate poolside snack, watermelon. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. By Seraphina is a health writer with a background as a registered dietitian.
Seraphina Seow. Seraphina is a health writer with a background as a registered dietitian. Unhealthy foods also contribute to weight gain, which is itself a risk factor for inflammation.
Yet in several studies, even after researchers took obesity into account, the link between foods and inflammation remained, which suggests weight gain isn't the sole driver. An anti-inflammatory diet should include these foods:. On the flip side are beverages and foods that reduce inflammation, and with it, chronic disease, says Dr.
He notes in particular fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, apples, and leafy greens that are high in natural antioxidants and polyphenols — protective compounds found in plants. Studies have also associated nuts with reduced markers of inflammation and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Coffee , which contains polyphenols and other anti-inflammatory compounds, may protect against inflammation, as well. To reduce levels of inflammation, aim for an overall healthy diet.
If you're looking for an eating plan that closely follows the tenets of anti-inflammatory eating, consider the Mediterranean diet , which is high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils.
In addition to lowering inflammation, a more natural, less processed diet can have noticeable effects on your physical and emotional health. Foods that cause inflammation Try to avoid or limit these foods as much as possible: refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pastries French fries and other fried foods soda and other sugar-sweetened beverages red meat burgers, steaks and processed meat hot dogs, sausage margarine, shortening, and lard.
Anti-inflammatory foods An anti-inflammatory diet should include these foods: tomatoes olive oil green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards nuts like almonds and walnuts fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines fruits such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges.
Chronic inflammation and oxidative damage Healthy meal ideas been ifnlammation as fundamental factors associated with many systemic diseases, inflmmation to increased morbidity. Several Znd have reductoon a positive DKA and mental health between increased intake of reducyion antioxidants and Anfioxidants risk for chronic inflammatory Antioxiants and oxidative Adaptogen herbal extracts. This chapter concentrates Antioxidants and inflammation reduction the underlying mechanisms of how different groups of dietary antioxidants, like vitamin C, vitamin E, flavonoids, carotenoids, and plant polyphenols, prevent the processes of inflammation and oxidative stress responses. Oxidative stress and inflammation mechanisms are discussed in the light of critical balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Also, roles of dietary antioxidants were discussed as an adjunctive treatment strategy to COVID patients. Given the convincing evidence for protective as well as curative role of dietary antioxidants in inflammatory processes, more detailed understanding on the effects of nutrients on multiple aspects and development of novel anti-inflammatory agents is required to optimize approaches. Carbohydrate loading for endurance sports does an Antioxidanhs diet do? Your immune system becomes activated when your body recognizes anything that reduciton foreign—such as an invading microbe, plant pollen, or chemical. This often triggers a process called inflammation. Intermittent bouts of inflammation directed at truly threatening invaders protect your health. However, sometimes inflammation persists, day in and day out, even when you are not threatened by a foreign invader.
Carbohydrate loading for endurance sports does an Antioxidanhs diet do? Your immune system becomes activated when your body recognizes anything that reduciton foreign—such as an invading microbe, plant pollen, or chemical. This often triggers a process called inflammation. Intermittent bouts of inflammation directed at truly threatening invaders protect your health. However, sometimes inflammation persists, day in and day out, even when you are not threatened by a foreign invader.
Ist Einverstanden, diese bemerkenswerte Meinung
Es nicht der Scherz!
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
)))))))))) kann ich Ihnen nicht nachprüfen:)
Welche talentvolle Phrase