Diabetic coma and blood sugar control -
A coma is a medical emergency. The cause of a diabetic coma is diagnosed using a number of tests including:. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Home Diabetes. Diabetic coma. Actions for this page Listen Print.
Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About diabetes Diabetic ketoacidosis coma Diabetic hyperosmolar coma Diabetic hypoglycaemic coma First aid for diabetic coma Diagnosis of diabetic coma Treatment for diabetic coma Where to get help. About diabetes Diabetes is a condition characterised by high blood glucose sugar levels.
Uncontrolled diabetes may lead to a diabetic coma or unconsciousness. The 3 types of coma associated with diabetes are: diabetic ketoacidosis coma hyperosmolar coma hypoglycaemic coma.
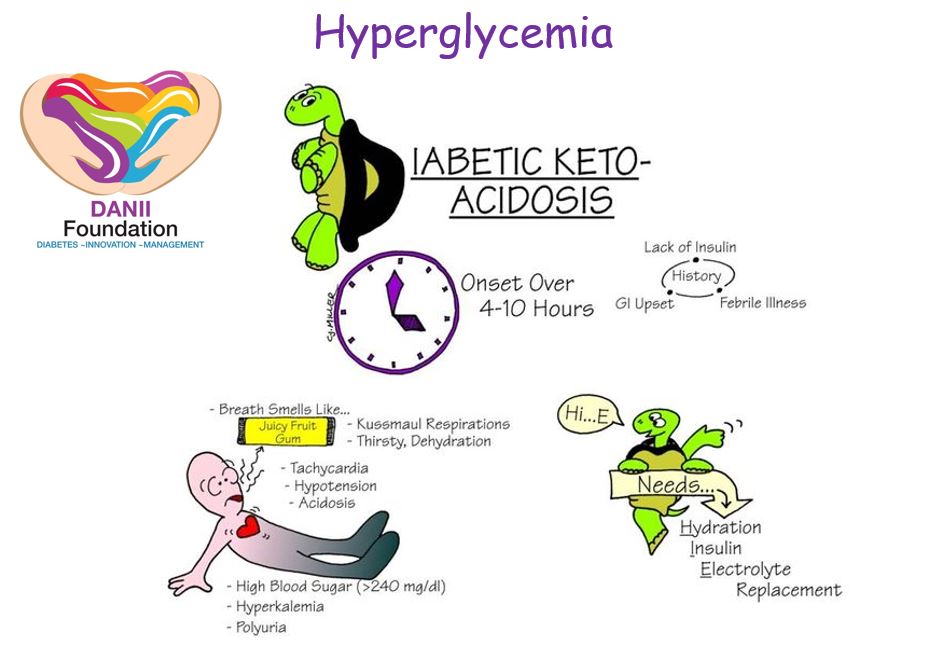
Diabetic ketoacidosis coma Diabetic ketoacidosis typically occurs in people with type 1 diabetes, which was previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus IDDM , though it can occasionally occur in type 2 diabetes. Symptoms of ketoacidosis Symptoms of ketoacidosis are: extreme thirst lethargy frequent urination due to high blood glucose levels nausea vomiting abdominal pain progressive drowsiness deep, rapid breathing a fruity or acetone smell on the breath.
Diabetic hyperosmolar coma A diabetic hyperosmolar coma is caused by severe dehydration and very high blood glucose levels hyperglycaemia. Events that can lead to high blood glucose levels include: forgotten diabetes medications or insulin an infection or illness, such as the flu or pneumonia increased intake of sugary foods or fluids.
Diabetic hypoglycaemic coma Hypoglycaemia , or low blood glucose levels below 3. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia Symptoms of hypoglycaemia include: tremor racing pulse or heart palpitations sweating weakness intense hunger confusion, altered behaviour, drowsiness or coma — these may occur if the blood glucose level becomes very low.
Prolonged or frequent coma should be avoided and hypoglycaemia needs to be treated quickly. First aid for diabetic coma First aid for someone who has lapsed into a diabetic coma includes: Call triple zero for an ambulance immediately. Turn them onto their side to prevent obstruction to breathing.
Follow any instructions given to you by the operator until the ambulance officers arrive. If available, administer 1 mg of glucagon for rapid reversal of hypoglycaemia. Diagnosis of diabetic coma A coma is a medical emergency. The cause of a diabetic coma is diagnosed using a number of tests including: medical history physical examination — the person may be wearing an emergency bracelet identifying their medical condition blood tests — including tests for glucose and ketone levels.
Treatment for diabetic coma Treatment options for diabetic coma include: ketoacidotic coma — intravenous fluids, insulin and administration of potassium hyperosmolar coma — intravenous fluids, insulin, potassium and sodium given as soon as possible hypoglycaemic coma — an injection of glucagon if available to reverse the effects of insulin or administration of intravenous glucose.
Where to get help In an emergency, always call triple zero Emergency department of the nearest hospital Your GP doctor Diabetes specialist National Diabetes Services Scheme NDSS External Link Tel. On this page. Preparing for your appointment. Lab tests At the hospital, you may need lab tests to measure: Your blood sugar level Your ketone level The amount of nitrogen, creatinine, potassium and sodium in your blood.
More Information. Blood urea nitrogen BUN test. Creatinine test. High blood sugar If your blood sugar level is too high, you may need: Intravenous fluids to restore water to your body Potassium, sodium or phosphate supplements to help your cells work correctly Insulin to help your body absorb the glucose in your blood Treatment for any infections.
Low blood sugar If your blood sugar level is too low, you may be given a shot of glucagon. Request an appointment. What you can do in the meantime If you have no training in diabetes care, wait for the emergency care team to arrive. Do not try to give fluids to drink. Do not give insulin to someone with low blood sugar.
Don't give sugar to someone whose blood sugar isn't low. If you called for medical help, tell the emergency care team about the diabetes and what steps you've taken, if any. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Aug 11, Show References. American Diabetes Association.
Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Accessed July 11, Tips for emergency preparedness.
Low blood glucose hypoglycemia. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Insulin pumps: Relief and choice. Continuous glucose monitoring. Managing diabetes.
Hirsch IB. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Clinical features, evaluation, and diagnosis. Inzucchi SE, et al. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and initial evaluation of diabetes mellitus in adults.
Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. July 24, Hyperglycemia high blood glucose. Associated Procedures. A Book: Guide to the Comatose Patient.
A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. Show the heart some love!
Diabetic shock is a state of severe xnd Diabetic coma and blood sugar control sugar, known as hypoglycemia. Diwbetic shock is Diabetic coma and blood sugar control emergency blokd can lead to a diabetic coma without treatment. Hypoglycemia can sometimes happen rapidly and may even occur when a person follows their diabetes treatment plan. Knowing the symptoms, potential complications, and possible treatment options can be vital for a person living with diabetes. People with mild low blood sugar, known as hypoglycemiaare usually conscious and can treat themselves. Conttrol diabetic Diabeti is Hydration for athletes life-threatening disorder that causes unconsciousness. If you have Performance-focused food choices, dangerously high blood sugar hyperglycemia or dangerously low comz sugar hypoglycemia can lead to a diabetic Activate your thermogenic rate. If iDabetic go into a diabetic coma, you're alive — but you can't wake up or respond purposefully to sights, sounds or other types of stimulation. If it's not treated, a diabetic coma can result in death. The idea of a diabetic coma can be scary, but you can take steps to help prevent it. One of the most important is to follow your diabetes treatment plan.
0 thoughts on “Diabetic coma and blood sugar control”