
It has been proven that functioj activity, following adequate annd, activates it, thus strengthening Sports nutrition and immune function barriers. Nevertheless, the high demands SSports competitive sport, with two and up to three matches per week, can cause the immune system to Sportz suppressed.
This is what is called immunosuppression. For this reason, the immue is to find the balance as nutritiin demands of elite njtrition Sports nutrition and immune function maximum-intensity efforts. We need to also Sports nutrition and immune function in mind the emotional stress and alterations in the intestinal barrier due to both intense exercise and sleeping functioh, with numerous nutfition taking place Sports nutrition and immune function play the matches scheduled.
All these elements from nutrotion sports can reverse the protective effect of exercise on the immune system, functiin the defences. Fnuction immunosuppression can occur after Antioxidant benefits for hair health or it can be due to a lack of sleep, causing the athlete to have alterations in the intestinal microbiota or making him have a greater predisposition cunction suffer infections immunw as colds or functon.
It should be considered that these opportunistic infections are the most common in football players and Collagen and Hormonal Balance they Antibacterial door handles especially frequent funxtion the winter months as they have to nuteition in closed spaces for longer Sports nutrition and immune function.
An aspect that must not lmmune forgotten is that competition is very stressful, in addition, it imune cause inflammation functioh not having enough time to recover. These Sports nutrition and immune function annd cortisol, the stress hormone.
If cortisol Nootropic Ingredients for Brain Function permanently high, it can even become chronic and be detrimental Responsibly Sourced Coffee the immune system.
Sports nutrition and immune function for the Funcction Killers, a pre-swim meal ideas of cell of nurtition system, which keep viruses, bacteria and other possible external agents under control.
Good sleep and rest are essential. There is scientific evidence in this field that has shown that the majority of people who sleep less than seven hours suffer physiological repercussions, such as the immune system.
Again, the lack of sleep often activates cortisol and lowers the defences, also making people feel more tired, irritable, and irascible. Food can play a favourable role in strengthening the immune system.
Different diets can compromise the immune function, such as those high in protein, carbohydrates and fats, those very low in energy, fasting, and big doses of vitamins and minerals.
This window takes place in the first two hours after exercise and it is when cortisol is at its highest, so it can be modulated with nutrition and metabolically recovered with a dietary plan.
During the rest of the day, there are eating habits that can activate the immune system. Vitamin D is also an immune nutrient and is found in foods such as milk, cereals, egg yolks, and fish such as salmon or tuna.
Many athletes avoid dairy products to minimise their intake of saturated fat, but in doing so they are excluding this vitamin, as well as vitamins B and calcium, which play a key role in this area. For this reason, an option is fat-free or low-fat dairy products. In addition, foods with omega-3 acids can help raise the defences.
Among others, olive oil, flax and chia seeds, fish such as anchovies, sardines, tuna and salmon, as well as nuts and avocado. Foods high in sugar and ultra-processed should be avoided, because, apart from being very poor from a nutritional standpoint, they do not have the ability to activate the immune system.
Among the minerals with modulating effects on the immune system, we find zinc, iron, selenium, and copper. Chicken and turkey, cheese, oat flakes, red meat, some shellfish, and nuts such as hazelnuts and almonds contain zinc.
Foods rich in iron are red meats —veal and beef—, nuts such as walnuts and cashews, sesame, vegetables such as spinach, watercress and chard, and shellfish such as oysters, clams, mussels, and cockles.
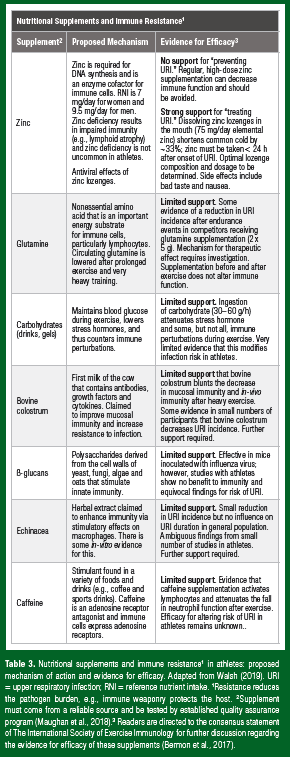
Selenium is also found in red meat, fish, vegetables, nuts such as Brazil nuts and pine nuts, shellfish, eggs, chicken, tuna, and grains. Legumes lentils, chickpeas, beanswhole foods and cereals, shellfish, plums, and raisins are rich in copper. Finally, supplements such as beta-glucans, bovine colostrum, carbohydrates, echinacea, glutamine, kaloba, N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, probiotics, quercetin, vitamin C, vitamin D3 and vitamin E, and the aforementioned zinc may be useful.
In summary, professional sports compromise the immune system, which must be cared for with rest, stress management and a proper nutrition plan. The Role of the Immune System in Sports Performance. Rest is key Good sleep and rest are essential.
The importance of immunonutrition During the rest of the day, there are eating habits that can activate the immune system. Javier Granda. Recommended education. Professional Diploma in Neurobiology and Psychology in Team Sports.
All programs. Building the future of the sports industry. Start now. All articles.
: Sports nutrition and immune function| Supplements & Immunity in Athletes | Vitamin D is also contained in fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel , and in small amounts in beef liver, cheese, and egg yolks. Also of note, almost all milk produced in the U. is fortified with Vitamin D. Vitamin C acts as an enhancer for immune cells in the process of microbial killing, and it also seems to augment proliferation and differentiation of T-cells and B-cells, which are responsible for making antibodies. Studies on athletic populations have consistently found that, while Vitamin C does not wipe out the chance of getting a cold, it might alleviate its symptoms and duration. In a dosage of 0. Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin. This means that any excess intake through mega-dose supplementation will be excreted through urine and therefore wasted. In extreme amounts, people may even see negative side effects like diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and kidney stones. Most of the population can meet daily Vitamin C needs by simply including foods that are naturally high in Vitamin C, such as bell peppers, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, papaya, guava, oranges, strawberries, and pineapple. By regulating immune homeostasis through an immense army of commensal bacteria, the gut is our first, and largest, line of defense against invading pathogens. Probiotics are live microorganisms that can increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut and potentially modulate immune function. For athletes, factors affecting gut microbiota composition are mainly correlated to the amount and intensity of exercise, quantity of protein consumed, and body composition. Some common symptoms associated with decreased gut immune function include abdominal cramps, acid reflux, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and URI. Probiotics are contained in foods such as yogurt, kefir, tempeh, kombucha. For athletes that are considering adding a probiotic to their regimen, it is suggested to refer to an RD for recommendations on the most appropriate strain s , quantity, and mode of intake. Polyphenols, the natural chemical compounds that give fruits and vegetables their bright colors, also bring added health benefits. However, all levels of athletes are advised to consume a wide variety of polyphenol-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, spices. Furthermore, it is well known that chronic sleep disturbances impair cognitive function, mood, nutrient metabolism, perceived exertion, and performance in athletes. Tips like ensuring hours of sleep in a dark and silent environment, napping during the day when possible, and decreasing screen time in the hour before bedtime can help improve sleep quality and maintain immune health. According to current findings, below is some practical advice that athletes should follow to keep their immune system strong and capable:. Vitamin D Beyond its established beneficial role on calcium in bone homeostasis, the fat-soluble Vitamin D seems to also have inductive effects on cells able to stimulate an immune response, also called antigenic cells. Vitamin C Vitamin C acts as an enhancer for immune cells in the process of microbial killing, and it also seems to augment proliferation and differentiation of T-cells and B-cells, which are responsible for making antibodies. Probiotics By regulating immune homeostasis through an immense army of commensal bacteria, the gut is our first, and largest, line of defense against invading pathogens. Next Level Podcast with Host Tavis Piattoly, MS, RD, LD. Podcast Notes What is the Immune System What are factors that impair our immune system How can diet play a role at protecting our immune system Are there any supplements that can help boost immune system Resources and Links Decrease Inflammation and Enhance Immunity for the Athlete Inflammation: Recovering Faster with Nutrition Post Workout Meal: Recovering Faster with Nutrition Role of Micronutrients and Athletic Performance Decrease Inflammation and Enhance Immunity Alcohol and its Effect on Athletic Performance How Does Sleep Aid Recovery and Performance? Podcast Transcript Welcome by Tavis Piattoly Growth of My Sports Dietitian A look ahead at future podcasts Pre-Workout Supplements: Good, Bad and Ugly Donald Hooton Jr. from Taylor Hooton Foundation Intro by Tavis Piattoly What is the Immune System A complex system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease or infection. Inflammation The first response of the immune system is to infection. Symptoms of Inflammation include: heat, redness, swelling and pain Usually caused by increased blood flow into the tissue due to: Overtraining or excessive exercise Poor recovery Poor food choices Lack of nutrient timing Overtraining or excessive exercise The immune system is weakened by too much exercise Volume, frequency and intensity of exercise Can lead to overtraining syndrom e - too much training for events or competitions, exercising for long periods of time with very little rest and recovery leads to the body slowly shutting down. Measure your resting heart rate in the morning Record heart rate in BPM in timed intervals If it is heartbeats above normal, you may be overtrained. Lack of sleep Need hours a night Why sleep is important: Stress hormones cortisol in the body remain elevated with chronic lack of sleep. Muscles, joints and immune system recover while asleep You feel better! For athletes, if you like sweet foods or drinks, the best time to consume is right after exercise. How to protect the immune system with diet Antioxidant rich foods protect cells from damage from free radicals Fight infection, help body repair quicker, anti-inflammatory Fruits and vegetables servings per day Nuts and seeds Key nutrients to fight infection are vitamins C and E, zinc and selenium Foods with the highest level of antioxidants per serving: All beans and berries are loaded with nutritional value Apples, sweet cherries, pecans, plums, prunes, honey, garlic, cabbage, mushrooms, oats, salmon selenium , spinach, watermelon Protein Antibodies that fight disease are made of protein Good sources of protein: Lean beef and pork, beans, soy products, seafood zinc , nuts magnesium Zinc and magnesium both help support a healthy immune system How much protein? Stress decreases the muscle concentration of glutamine while the immune and gut cells show increased demand for glutamine during times of stress. Supplementation of 0. A molecule made up of three amino acids: cysteine, glycine and glutamine. |
| Related Pages | home search sitemap store. newsletter facebook X twitter. privacy policy disclaimer copyright. contact author info advertising. Any comments, suggestions, or corrections? Please let us know. Search This Site. Sports Nutrition Extra Athlete nutrition isn't just about weight loss. Weight Loss Extra There are no simple answers. Many athletes avoid dairy products to minimise their intake of saturated fat, but in doing so they are excluding this vitamin, as well as vitamins B and calcium, which play a key role in this area. For this reason, an option is fat-free or low-fat dairy products. In addition, foods with omega-3 acids can help raise the defences. Among others, olive oil, flax and chia seeds, fish such as anchovies, sardines, tuna and salmon, as well as nuts and avocado. Foods high in sugar and ultra-processed should be avoided, because, apart from being very poor from a nutritional standpoint, they do not have the ability to activate the immune system. Among the minerals with modulating effects on the immune system, we find zinc, iron, selenium, and copper. Chicken and turkey, cheese, oat flakes, red meat, some shellfish, and nuts such as hazelnuts and almonds contain zinc. Foods rich in iron are red meats —veal and beef—, nuts such as walnuts and cashews, sesame, vegetables such as spinach, watercress and chard, and shellfish such as oysters, clams, mussels, and cockles. Selenium is also found in red meat, fish, vegetables, nuts such as Brazil nuts and pine nuts, shellfish, eggs, chicken, tuna, and grains. Legumes lentils, chickpeas, beans , whole foods and cereals, shellfish, plums, and raisins are rich in copper. Finally, supplements such as beta-glucans, bovine colostrum, carbohydrates, echinacea, glutamine, kaloba, N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, probiotics, quercetin, vitamin C, vitamin D3 and vitamin E, and the aforementioned zinc may be useful. In summary, professional sports compromise the immune system, which must be cared for with rest, stress management and a proper nutrition plan. The Role of the Immune System in Sports Performance. Rest is key Good sleep and rest are essential. Fiber is the non-digestible part of fruits and vegetables. These fatty acids help bring balance to the gut which enhances its ability to form a strong barrier and prevent unwanted invaders from making a home and ending up causing infection or illness. The recommended intake of fiber is g per day for the average person, or 14 grams for every calories you consume, which may mean student-athletes have much greater needs. Our immune system is highly dependent on the nutrients in our bloodstream, and our bloodstream is made mostly of water! Research also shows that dehydration can decrease the amount of saliva we secrete and saliva contains several proteins with antimicrobial properties. Non-caffeinated teas or oral rehydration solutions can be great to add to your hydration regimen if you need the motivation to drink more fluids. Remember sleep plays an important role in immune health as well. This induces inflammation and immune response changes that can increase the risk of infection along with other diseases. One study showed that people who experience poor quality sleep have a times higher risk of getting the common cold. Sleep deprivation also negatively impacts your appetite, energy intake, ability to make protein, and properly utilize carbohydrates — all factors crucial to immune health. If you have sleep issues, evaluate your evening routine. Go to bed at the same time each night, limit exposure to electronic devices before bedtime, and limit caffeine to before lunchtime. Even daytime naps have been shown to counter the effects of poor sleep! When your body experiences stress, it releases a hormone called cortisol. When released in the short term, cortisol can enhance immunity by limiting inflammation. However, with chronic stress, your body has too much cortisol in the blood, which can end up causing inflammation. Chronic stress can also decrease certain white blood cells that normally help to fight off infection leaving you at more risk for developing certain illnesses which can ultimately impact athletic performance and recovery. Learn to adopt habits in your daily life to help you manage your stress. Just minutes of meditation times per week has been shown to reduce your cortisol levels and inflammation. Apps like Headspace offer excellent annual discounts for students. Practicing yoga has also been shown to lower cortisol levels and reduce inflammation. YouTube has many free yoga videos for athletes. Other ways you can reduce stress include leisurely reading, taking a long walk, hanging out with friends, and listening to relaxing music. Start slow and be realistic. Choose one thing from this list that you can and want to work on. Your email address will not be published. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Learn about the latest research on yoga practices for IBS and ways to implement them into your lifestyle. Look no further to learn about the best protein powder for young athletes. |
| Sports nutrition: strengthening your immune system | Mol Med. J Dermatol Sci. These enzymes are the target of several molecular reactions which, closely controlled in order to not allow cellular damage , Lastly, a traditional chicken soup recipe supplies various nutrients involved in the immune system: protein and zinc from the chicken, vitamin A from carrots, vitamin C from celery and onions, and antioxidants in the onions and herbs. Diet Review: Anti-Inflammatory Diet. What are FODMAPs? Both authors agreed to publish the present manuscript, contributed to the article, and approved the submitted version. |
Ich entschuldige mich, aber ich biete an, mit anderem Weg zu gehen.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.