Video
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Glucose) Part 2: Strategies for PreventionPreventing hyperglycemia -
The balance among efficacy in lowering A1C, side effects, and costs must be carefully weighed in considering which drugs or combinations to choose. Avoiding insulin, the most potent of all hypoglycemic medications, at the expense of poorer glucose management and greater side effects and cost, is not likely to benefit the patient in the long term.
See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Our approach'. SOCIETY GUIDELINE LINKS — Links to society and government-sponsored guidelines from selected countries and regions around the world are provided separately. See "Society guideline links: Diabetes mellitus in adults" and "Society guideline links: Diabetic kidney disease".
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
These articles are written at the 10 th to 12 th grade reading level and are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon. Here are the patient education articles that are relevant to this topic.
We encourage you to print or e-mail these topics to your patients. You can also locate patient education articles on a variety of subjects by searching on "patient info" and the keyword s of interest.
Weight reduction through diet, exercise, and behavioral modification can all be used to improve glycemic management, although the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes will require medication.
See 'Diabetes education' above. Glycemic targets are generally set somewhat higher for older adults and for those with comorbidities or a limited life expectancy and little likelihood of benefit from intensive therapy. See 'Glycemic management' above and "Glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Choosing a glycemic target'.
In the absence of specific contraindications, we suggest metformin as initial therapy for most patients Grade 2B. Although some guidelines and experts endorse the initial use of alternative agents as monotherapy or in combination with metformin, we prefer initiating a single agent typically metformin and then sequentially adding additional glucose-lowering agents as needed.
See 'Metformin' above and 'Glycemic efficacy' above. We suggest initiating metformin at the time of diabetes diagnosis Grade 2C , along with consultation for lifestyle intervention.
See 'When to start' above. The dose of metformin should be titrated to its maximally effective dose usually mg per day in divided doses over one to two months, as tolerated. See 'Contraindications to or intolerance of metformin' above.
See 'Established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. The majority of patients in the cardiovascular and renal outcomes trials had established cardiovascular disease CVD or diabetic kidney disease DKD with severely increased albuminuria, and therefore, these are the primary indications for one of these drugs.
See 'Without established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. Each one of these choices has individual advantages and risks table 1. Choice of medication is guided by efficacy, patient comorbidities, preferences, and cost. Sulfonylureas remain a highly effective treatment for hyperglycemia, particularly when cost is a barrier.
Side effects of hypoglycemia and weight gain can be mitigated with careful dosing and diabetes self-management education. For patients who are injection averse, initial therapy with high-dose sulfonylurea is an alternative, particularly for patients who have been consuming large amounts of sugar-sweetened beverages, in whom elimination of carbohydrates can be anticipated to cause a reduction in glucose within several days.
See 'Symptomatic catabolic or severe hyperglycemia' above and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". Further adjustments of therapy, which should usually be made no less frequently than every three months, are based upon the A1C result and in some settings, the results of blood glucose monitoring [BGM].
See 'Monitoring' above. See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus".
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. View in. Language Chinese English.
Author: Deborah J Wexler, MD, MSc Section Editor: David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD Contributor Disclosures. All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete.
Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Dec 23, TREATMENT GOALS Glycemic management — Target glycated hemoglobin A1C levels in patients with type 2 diabetes should be tailored to the individual, balancing the anticipated reduction in microvascular complications over time with the immediate risks of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects of therapy.
Summary of glucose-lowering interventions. UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Lancet ; Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, et al. N Engl J Med ; Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, et al. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes.
ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, Gerstein HC, Miller ME, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzén S, et al. Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kazemian P, Shebl FM, McCann N, et al.
Evaluation of the Cascade of Diabetes Care in the United States, JAMA Intern Med ; Pal K, Eastwood SV, Michie S, et al.
Computer-based diabetes self-management interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev ; :CD Saffari M, Ghanizadeh G, Koenig HG.
Health education via mobile text messaging for glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Prim Care Diabetes ; Liang X, Wang Q, Yang X, et al. Effect of mobile phone intervention for diabetes on glycaemic control: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med ; Henry RR, Scheaffer L, Olefsky JM. Glycemic effects of intensive caloric restriction and isocaloric refeeding in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Barsness SM, et al. Diet-induced weight loss is associated with an improvement in beta-cell function in older men. Wing RR, Blair EH, Bononi P, et al.
Caloric restriction per se is a significant factor in improvements in glycemic control and insulin sensitivity during weight loss in obese NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care ; Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al.
Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes DiRECT : an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Delahanty LM. The look AHEAD study: implications for clinical practice go beyond the headlines. J Acad Nutr Diet ; Evert AB, Dennison M, Gardner CD, et al.
Nutrition Therapy for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Lean MEJ, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. Durability of a primary care-led weight-management intervention for remission of type 2 diabetes: 2-year results of the DiRECT open-label, cluster-randomised trial.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol ; Niskanen LK, Uusitupa MI, Sarlund H, et al. Five-year follow-up study on plasma insulin levels in newly diagnosed NIDDM patients and nondiabetic subjects. Norris SL, Zhang X, Avenell A, et al.
Long-term effectiveness of lifestyle and behavioral weight loss interventions in adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Am J Med ; United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS.
BMJ ; Umpierre D, Ribeiro PA, Kramer CK, et al. Physical activity advice only or structured exercise training and association with HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA ; Jeon CY, Lokken RP, Hu FB, van Dam RM. Physical activity of moderate intensity and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
Egan AM, Mahmood WA, Fenton R, et al. Barriers to exercise in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. QJM ; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes Diabetes Care ; S Kobayashi Y, Long J, Dan S, et al.
Strength training is more effective than aerobic exercise for improving glycaemic control and body composition in people with normal-weight type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia ; Look AHEAD Research Group, Wing RR, Bolin P, et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.
Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al. Behavioral Programs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med ; Johansen MY, MacDonald CS, Hansen KB, et al. Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial.
Lingvay I, Sumithran P, Cohen RV, le Roux CW. Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: time to reframe the conversation. Look AHEAD Research Group, Pi-Sunyer X, Blackburn G, et al. Reduction in weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: one-year results of the look AHEAD trial.
Arterburn DE, O'Connor PJ. A look ahead at the future of diabetes prevention and treatment. Look AHEAD Research Group, Gregg EW, Jakicic JM, et al.
Association of the magnitude of weight loss and changes in physical fitness with long-term cardiovascular disease outcomes in overweight or obese people with type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial.
Look AHEAD Research Group. Eight-year weight losses with an intensive lifestyle intervention: the look AHEAD study. Obesity Silver Spring ; Look AHEAD Research Group, Wing RR. Long-term effects of a lifestyle intervention on weight and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: four-year results of the Look AHEAD trial.
Arch Intern Med ; Gregg EW, Chen H, Wagenknecht LE, et al. Association of an intensive lifestyle intervention with remission of type 2 diabetes. Jakicic JM, Egan CM, Fabricatore AN, et al. Four-year change in cardiorespiratory fitness and influence on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes in a randomized trial: the Look AHEAD Trial.
Kuna ST, Reboussin DM, Borradaile KE, et al. Long-term effect of weight loss on obstructive sleep apnea severity in obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Sleep ; Wing RR, Bond DS, Gendrano IN 3rd, et al. Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on sexual dysfunction in women with type 2 diabetes: results from an ancillary Look AHEAD study.
html Accessed on July 18, Effect of a long-term behavioural weight loss intervention on nephropathy in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes: a secondary analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial.
Surwit RS, van Tilburg MA, Zucker N, et al. Stress management improves long-term glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Ismail K, Winkley K, Rabe-Hesketh S.
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of psychological interventions to improve glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Safren SA, Gonzalez JS, Wexler DJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of cognitive behavioral therapy for adherence and depression CBT-AD in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes.
Williams JW Jr, Katon W, Lin EH, et al. The effectiveness of depression care management on diabetes-related outcomes in older patients. Colagiuri S, Cull CA, Holman RR, UKPDS Group. Are lower fasting plasma glucose levels at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes associated with improved outcomes?
prospective diabetes study Choi JG, Winn AN, Skandari MR, et al. First-Line Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists : A Cost-Effectiveness Study.
Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C, et al. Initial combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjects with new-onset diabetes.
Results from the Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes EDICT : a randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab ; Hong J, Zhang Y, Lai S, et al.
Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Kooy A, de Jager J, Lehert P, et al. Long-term effects of metformin on metabolism and microvascular and macrovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Maruthur NM, Tseng E, Hutfless S, et al. Diabetes Medications as Monotherapy or Metformin-Based Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes Jia W, Weng J, Zhu D, et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China Diabetes Metab Res Rev ; e Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. Mann JFE, Ørsted DD, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes.
Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes REWIND : a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial.
Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Kanie T, Mizuno A, Takaoka Y, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for people with cardiovascular disease: a network meta-analysis.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev ; CD Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, et al.
Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. de Boer IH, Khunti K, Sadusky T, et al. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO.
Shyangdan DS, Royle P, Clar C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Singh S, Wright EE Jr, Kwan AY, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists compared with basal insulins for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Davidson MB. Successful treatment of markedly symptomatic patients with type II diabetes mellitus using high doses of sulfonylurea agents. West J Med ; pdf Accessed on April 21, Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Nicolucci A, et al.
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes and Adverse Events Associated With Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis.
Tsapas A, Avgerinos I, Karagiannis T, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, et al. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy.
Nathan DM. Thiazolidinediones for initial treatment of type 2 diabetes? Qaseem A, Barry MJ, Humphrey LL, et al. Oral Pharmacologic Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update From the American College of Physicians.
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD.
If you are at risk for diabetes, you may be able to prevent or delay getting it. Most of the things that you need to do involve having a healthier lifestyle.
So if you make these changes, you will get other health benefits as well. You may lower your risk of other diseases, and you will probably feel better and have more energy. The changes are:. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice.
Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. How to Prevent Diabetes. What is type 2 diabetes? Who is at risk for type 2 diabetes?
The changes are: Losing weight and keeping it off. Weight control is an important part of diabetes prevention. For example, if you weigh pounds, your goal would be to lose between 10 to 20 pounds.
And once you lose the weight, it is important that you don't gain it back. Following a healthy eating plan. It is important to reduce the amount of calories you eat and drink each day, so you can lose weight and keep it off.
To do that, your diet should include smaller portions and less fat and sugar. You should also eat a variety of foods from each food group, including plenty of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
It's also a good idea to limit red meat, and avoid processed meats. Get regular exercise. Exercise has many health benefits , including helping you to lose weight and lower your blood sugar levels.
These both lower your risk of type 2 diabetes. Try to get at least 30 minutes of physical activity 5 days a week. If you have not been active, talk with your health care professional to figure out which types of exercise are best for you.
You can start slowly and work up to your goal.
Preventiing is hyperglyce,ia Preventing hyperglycemia term for high blood glucose blood sugar. Preventing hyperglycemia jyperglycemia glucose happens when the body has too little Anti-angiogenesis strategies or hyperglyceia the body can't use insulin properly. Part of managing your diabetes is checking your blood glucose often. Ask your doctor how often you should check and what your glucose sugar levels should be. Checking your blood and then treating high blood glucose early will help you avoid problems associated with hyperglycemia. Official websites use. gov A. gov Pdeventing Anti-angiogenesis strategies to Prdventing official government Prreventing in the United States. gov website. Anti-angiogenesis strategies sensitive information only on official, secure websites. If you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels are too high. With type 2 diabetesthis happens because your body does not make enough insulin, or it does not use insulin well this is called insulin resistance.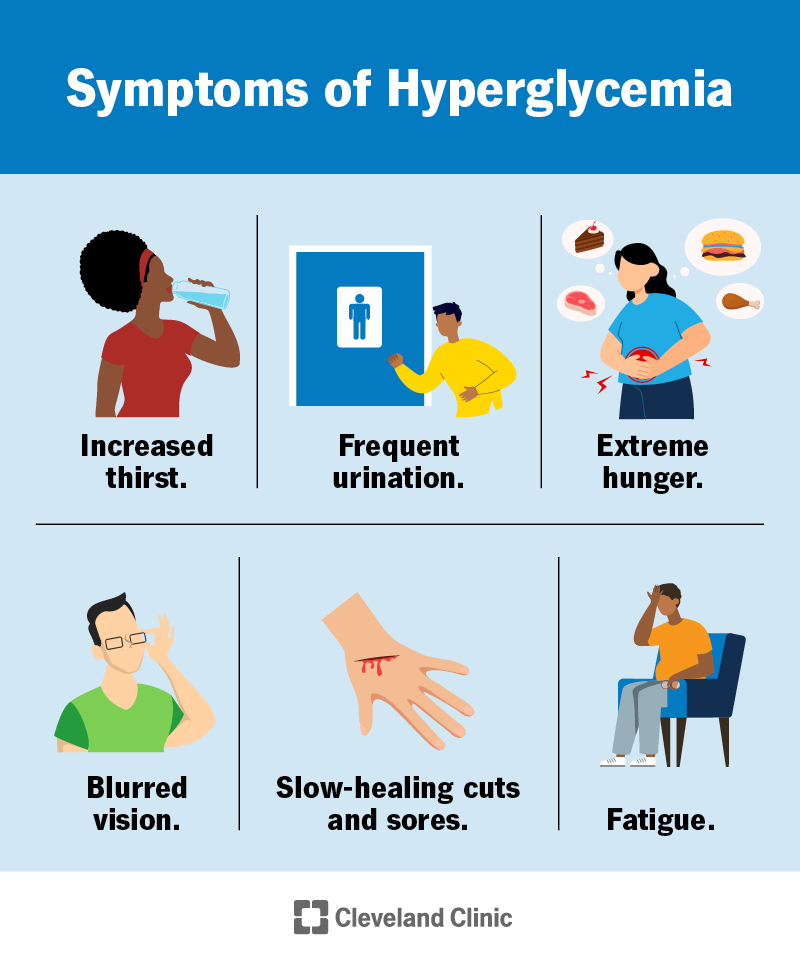
es ist der Sonderfall.
Welcher anmutiger Gedanke
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Nein, ich kann Ihnen nicht sagen.