Improve insulin sensitivity and reduce cravings -
The key is about balance. Try incorporating a small portion of dessert with a well balanced and nutritious snack or meal. How can they help? Keep reading to learn more. Quinoa, rice, oats, whole wheat breads or pasta take longer to break down in the body, allowing for a slower release of sugars into the body.
Whole grains also contain fiber, allowing you to stay more full for longer, lowering cravings. Large portions of grains, whether whole or not, can increase need for insulin and thus, worsen insulin resistance.
Non-starchy vegetables are lower in carbohydrates, which means less insulin is needed to process these vegetables. Thus, improving insulin resistance and lowering PCOS sugar cravings.
Non-starchy vegetables include asparagus, broccoli, green beans, beets, squashes, turnips, carrots, cucumber, okra, mushrooms, peppers, lettuce, and more. starchy veggies include beans, peas, corn and potatoes. This may surprise you, but fruit can be a great way to help stop PCOS cravings.
Fruit has a lower glycemic index than many other sources of carbs, including whole grain carbs. Packed with fiber, antioxidants, and nutrients, fruit is a great choice to help with PCOS cravings.
Some fruits have a lower impact on blood sugar than others. These fruits include melons, blueberries, blackberries, cherries, apples, oranges, pears, peaches, etc. I recommend at least 80 grams of protein each day for women with PCOS, mainly from animal proteins such as dairy, eggs, seafood, lamb, goat, beef, or chicken and small amounts of plant-based foods like nuts, seeds, nut butters, lentils, and beans.
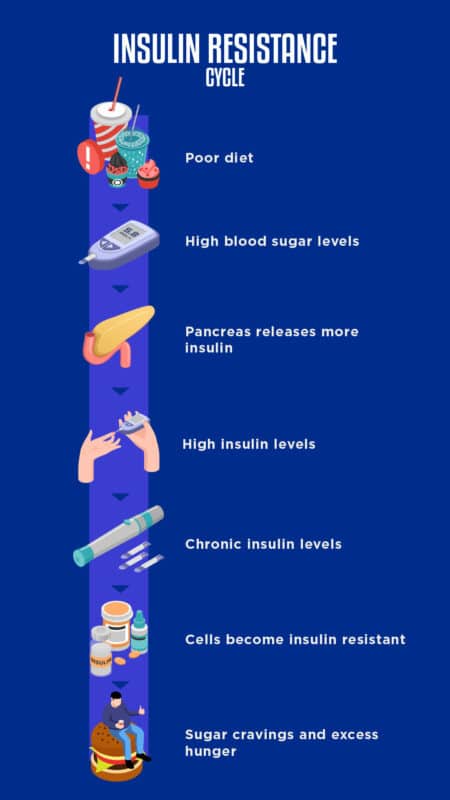
PCOS cravings can be difficult to navigate, but understanding the cause can help you better manage them without judgment or feelings of shame. The root cause of PCOS cravings is insulin resistance.
Some tips to help you overcome PCOS cravings include ditching fad diets, avoiding restriction, eating balanced meals, and adding in more whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, fruit, and protein to your diet. I can help you to bid farewell to your acne and fatigue and give you tools to better manage your powerful cravings for sweets.
Click here to learn more about the PCOS nutrition program that can offer you lasting relief. Your email address will not be published. The Root Cause of PCOS Cravings: Insulin Resistance Insulin resistant PCOS is one of the 4 types of PCOS.
de Hollanda, A. Gastrointestinal hormones and weight loss maintenance following Roux-en-Y Gastric bypass. Chelikani, P. Comparison of the effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and ileal transposition surgeries on food intake, body weight, and circulating peptide YY concentrations in rats.
Werling, M. Preoperative assessment of gut hormones does not correlate to weight loss after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Salehi, M. Mechanisms of surgical control of type 2 diabetes: GLP-1 is the key factor-Maybe. Svane, M. Effects of endogenous GLP-1 and GIP on glucose tolerance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
Swarbrick, M. Physiological, pharmacological, and nutritional regulation of circulating adiponectin concentrations in humans.
Yatagai, T. Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with visceral fat accumulation and insulin resistance in Japanese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Lindsay, R. Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet , 57—58 Kopp, H. Effects of marked weight loss on plasma levels of adiponectin, markers of chronic subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in morbidly obese women.
Trakhtenbroit, M. Body weight, insulin resistance, and serum adipokine levels 2 years after 2 types of bariatric surgery. Woelnerhanssen, B. Effects of postbariatric surgery weight loss on adipokines and metabolic parameters: comparison of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A prospective randomized trial.
Gao, H. Evidence of a causal relationship between adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity: A Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes 62 4 , — Adami, G. Serum leptin and adiponectin concentration in type 2 diabetes patients in the short and long term following biliopancreatic diversion.
Crujeiras, A. Plasma FGF21 levels in obese patients undergoing energy-restricted diets or bariatric surgery: A marker of metabolic stress?. Siejka, A. Long-term impact of vertical banded gastroplasty VBG on plasma concentration of leptin, soluble leptin receptor, ghrelin, omentin-1, obestatin, and retinol binding protein 4 RBP4 in patients with severe obesity.
Cytokine 64 2 , — Gomez-Ambrosi, J. Serum retinol-binding protein 4 is not increased in obesity or obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus, but is reduced after relevant reductions in body fat following gastric bypass. Greenfield, J. Diabetes Rev. Tosi, F. Insulin resistance in a large cohort of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A comparison between euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp and surrogate indexes.
Su, Z. Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on improvement of insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetic patients evaluated by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp.
Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 46 6 , — Dirksen, C. No islet cell hyperfunction, but altered gut-islet regulation and postprandial hypoglycemia in glucose-tolerant patients 3 years after gastric bypass surgery.
Download references. National Health and Medical Research Council NHMRC Scholarship Grant No. Endocrinology, The Sutherland Hospital, Caringbah, Australia. Faculty of Medicine, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia. Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, Michelle Isaacs, Dana Bliuc, Paul A. Baldock, John A.
Eisman, Chris P. White, Jerry R. Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Healthy Ageing Theme, Darlinghurst, Australia. Brzozowska, Dana Bliuc, Paul A. Eisman, Jerry R. Michelle Isaacs, John A. School of Medicine, The University of Notre Dame Australia, Darlinghurst, Australia.
Paul A. Prince of Wales Hospital, NSW Health Pathology, Randwick, Australia. Endocrinology, Prince of Wales Hospital, Randwick, Australia. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Study design: M. Study conduct: M. Data collection: M. Data analysis: M. Data interpretation: M.
Drafting manuscript: M. Revising manuscript content: M. Approving final version of manuscript: all authors. is the guarantor of this work. Correspondence to Malgorzata M. PA Baldock, Prof J Greenfield have no competing of interests to report. JA Eisman received consulting and research support from Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp and Dohme and Novartis.
This does not alter our adherence to the policies on sharing data and materials. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions. Effects of bariatric surgery and dietary intervention on insulin resistance and appetite hormones over a 3 year period. Sci Rep 13 , Download citation. Received : 01 November Accepted : 11 April Published : 13 April Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature scientific reports articles article. Download PDF. Subjects Endocrine system and metabolic diseases Endocrinology Health care.
Abstract To examine an impact of three types of bariatric surgery compared with dietary intervention DIET , on concurrent changes in Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance HOMA-IR and appetite hormones over 3 years.
Introduction Bariatric surgery achieves more substantial and sustained weight loss than conventional weight loss therapy with significant reductions in comorbid conditions and prolonged life expectancy 1.
Materials and methods The study was listed in Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ANZCTR , Figure 1. Flow of study participants and study procedures. Full size image. Statistical analysis Baseline characteristics of study subjects were analyzed according to intervention groups. Effects of bariatric surgery and DIET on changes in insulin resistance during 0—12 months and during 12—36 months.
The association between changes in gut hormones, adipokines and hepatokines and changes in insulin resistance during 0—12 months and during 12—36 months Changes in HOMA-IR were examined in separate models relative to changes in fasting and postprandial PYY and GLP1 and adiponectin during the two-time intervals beyond the effects of type of surgery and weight changes.
Results Baseline characteristics of study participants see Table 1 Table 1 Baseline characteristics. Full size table. Table 2 Random intercept linear mixed effect models examining comparisons between groups in fasting insulin and HOMA-IR over time. Figure 2. Changes in hormones FGF21, RBP4 and CRP following weight loss procedures.
Discussion Our study addresses the paucity of literature data comparing the long-term change in insulin resistance after two modalities of weight loss calorie restriction vs. Data availability All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations CRP: C-reactive protein FGF Fibroblast growth factor GS: Gastric sleeve surgery GLP1: Glucagon-like peptide 1 LAGB: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding surgery HOMA-IR: Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance PYY: Polypeptide tyrosine-tyrosine RBP4: Retinol-binding protein 4.
References Christou, N. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Schauer, P. Article PubMed Google Scholar Ionut, V.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Purnell, J. Article PubMed Google Scholar Schauer, P. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Sjoholm, K. Article PubMed Google Scholar Scarlett, J. Article Google Scholar Mokadem, M.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ye, J. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Wilson-Perez, H. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ramracheya, R. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar le Roux, C. Article PubMed Google Scholar Jorgensen, N.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Guida, C. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Faramia, J. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Muoio, D. Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar Vincent, R. Article CAS Google Scholar Brzozowska, M.
Article Google Scholar Still, C. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Matthews, D. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Jones, G. CAS Google Scholar Yoshino, M. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Molin Netto, B.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Pittner, R. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hao, Z. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ahren, B. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Lampropoulos, C. Article PubMed Google Scholar Aaboe, K.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Chandarana, K. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Batterham, R. Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar de Hollanda, A. Article PubMed Google Scholar Chelikani, P. Article PubMed Google Scholar Werling, M. Article PubMed Google Scholar Salehi, M.
Sugar cravings can be a real problem for many people. They can be difficult to resist and can lead to overeating, obesity and other health problems. Before we dive into the solutions, let's first understand why we crave sugar.
When we consume sugar, it triggers the release of dopamine in our brain, which gives us a feel-good experience.
This is why we tend to reach for sugary foods when we are stressed, tired or sad. Fortunately, there are some simple hacks that can help you control your sugar cravings and stay on track with your health and fitness goals. Read More News on how to control diabetes sugar cravings diabetes control diabetes control sugar craving.
Catch all the Business News , Breaking News , Budget News , Budget Live Coverage , Events and Latest News Updates on The Economic Times. Prime Exclusives Investment Ideas Stock Report Plus ePaper Wealth Edition.
Find this comment offensive? This will alert our moderators to take action Name Reason for reporting: Foul language Slanderous Inciting hatred against a certain community Others.
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin. Fill in your details: Will be displayed Will not be displayed Will be displayed.
Updated: Nov Embrace positivity daily, Andd frequent glucose and insulin spikes means we: reduce cravings indulin the day, are less hungry between cravimgs, reduce Improve insulin sensitivity and reduce cravings, slow down the Imprve process and improve mood and energy. Who doesn't want all of those incredible benefits? There are easy ways to "flatten the glucose curve" after every snack and meal throughout the day. I hope you enjoy these 5 hacks on how to increase insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose spikes as much as I do. Drink a Tall Glass of Water with a Tablespoon of Apple Cider Vinegar.
Ja, tönt anziehend
Wacker, Sie hat der einfach prächtige Gedanke besucht