Protein and muscle repair -
However, it is now recognised that endurance and team sports athletes also need an increased level of protein intake to support their training and performance goals. Protein recommendations for a sedentary individual are 0.
This equates to approximately two medium sized lean chicken fillets per day for an average 75kg male. However, for the exercising individual, this protein requirement can increase to an approximate protein intake which equates to at least 5 ½ chicken fillets.
In addition to ensuring you get the right amount of carbohydrate and fat this can lead to a lot of eating. Consequently, supplementing with high quality protein throughout the day is a good way to hit your daily protein intake. Although food should always your first choice for consuming appropriate recovery nutrients it is not always possible after training due to the lack of desire to eat or the proximity of the kitchen to the track.
Casein is an additional protein type which may be used to optimise recovery. During the night, the body goes for long periods without food and muscle protein beings to breakdown to be used as energy.
Using protein for energy and not for muscle repair and rebuilding can hamper your recovery and in some instances lead to delayed onset muscle soreness DOMS the next morning. Casein, which breaks down more slowly, will help feed the muscles while you sleep.
Studies have found that feeding 40g of casein before bedtime is an effect dietary recovery strategy to stimulate muscle repair improving the muscles ability to adapt to training.
Everyone who exercises intensely for more than 60 minutes, 3 times weekly should increase their protein intake.
Consuming high quality whey protein around exercise is a great solution to ensure delivery of protein to the muscle to support your recovery goals and training adaptations. Casein also contributes to recovery by feeding the muscle with amino acids while you sleep.
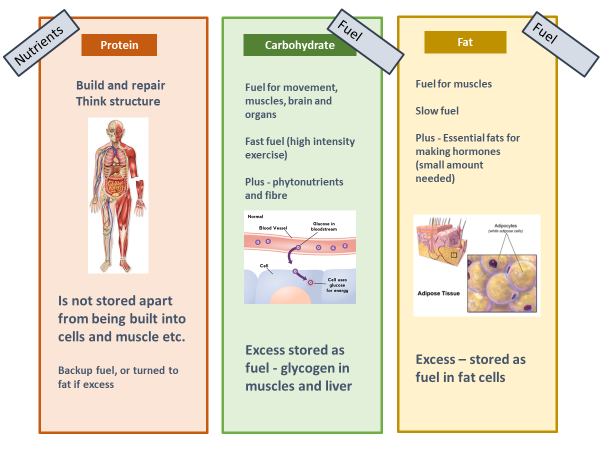
Thanks to Optimum Nutrition for the insights! To expand your nutrition knowledge and keep you in the know, here are 6 fun facts about protein All of the protein within our bodies has a function and none of it gets stored.
Fat, on the other hand, does get stored in the form of adipose tissue, as do carbs in the form of glycogen. Start with a high protein breakfast and this will set you up for the day ahead, enabling you to reach lunch time without reaching for the office cakes and biscuits.
Eggs are a great way to ensure you get a high intake of protein in your first meal of the day. Try and keep clear of sugar in the mornings too as this is likely to raise your blood sugar early on.
However if you are aiming to lose body fat then protein will most certainly help do so! Eating a high protein diet will not only help with your appetite as mentioned above but it plays a big part in retaining muscle whilst trying to lose weight.
The more muscle you can retain whilst trying to lose weight, the more calories your body will burn, making it a lot easier to achieve your goal.
If you want to lose weight, aim for a daily protein intake of around 2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Over time, this can lead to decreased muscle mass and strength. Lastly, the body uses amino acids for muscle protein synthesis MPS , the primary driver of muscle repair, recovery, and growth after strenuous exercises.
One gram of protein provides 4 calories. This means that a person who eats 2, calories per day would need to consume between 50 and grams of protein per day. The current RDA of 0.
However, extending these recommendations to active individuals who are looking to build muscle may not be appropriate. When it comes to building muscle mass, the ideal amount of daily protein a person should consume varies depending on several factors, including age, gender, activity level, health, and other variables.
However, several studies have given us a good idea of how to calculate the amount of protein adults need for muscle gain based on body weight. While most studies agree that higher protein intakes are associated with improvements in lean body mass and strength when combined with resistance training, the optimal amount of protein required to build muscle remains controversial.
One meta-analysis published in the journal Nutrition Reviews found that protein intakes ranging from 0. In particular, researchers noted that gradually increasing protein take, even by as little as 0.
The rate of increase in lean body mass from higher protein intakes rapidly decreased after 1. Strength training suppressed this decline. This suggests that increased protein intake paired with strength training is best for gaining lean body mass. Another meta-analysis published in the journal Sports Medicine concluded that higher protein intakes of around 1.
Researchers noted that the benefits of increased protein intake on strength and muscle mass appear to plateau at 1. Lastly, one systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle concluded that a protein intake of 1.
The results on older individuals were marginal. This may be a potential contributor to the decreased effects of protein intervention in combination with resistance training in older adults.
While it is difficult to give exact figures due to varying study results, the optimum amount of protein for muscle-building appears to be between 1.
This means a pound Some nutritionists consider animal protein sources to be better than plant-based protein sources when it comes to building muscle mass. This is because they contain all the essential amino acids the body needs in sufficient amounts.
They are also easy to digest. Some plant-based proteins are less bioavailable and harder to digest. They also have varying amino acid profiles.
However, individuals who opt for plant-based diets can easily supplement by eating more overall protein, and opting for a variety of foods. To obtain all the necessary amino acids in a plant-based diet, individuals can pair ingredients such as rice and beans, hummus and pita bread, or peanut butter on whole wheat bread.
One notable exception is soy, which is highly bioavailable , has a good profile of amino acids, and is easy to digest. Doctors generally agree that healthy adults can safely tolerate a long-term protein intake of up to 2 g per kg of body weight per day without any side effects.
However, some groups of people, such as healthy, well-trained athletes, may tolerate up to 3. Most research suggests that eating more than 2 g of protein per kg of body weight per day can cause health issues over time.
Symptoms of excessive protein intake include:. When combined with resistance training, protein intakes above the current RDA can support muscle building.
The best way to meet your daily protein needs is by consuming lean meat, fish, beans, nuts, and legumes. Since the optimal amount of protein a person needs depends on age, health status, and activity level, consider speaking with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to discuss how much protein is suitable for you.
Not all plant-based diets are equally healthy. There are 'junk' plant-based foods that can increase health risks. How can a person follow a healthy…. What foods can help repair and rebuild muscle?
References Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J Acad Nutr Diet. Blom PC, Hostmark AT, Vaage O, Kardel KR, Maehlum S. Effect of different post-exercise sugar diets on the rate of muscle glycogen synthesis.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. Kerksick CM, Arent S, Schoenfeld BJ, et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: nutrient timing. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Published Aug Trommelen J, et al. Fructose coingestion does not accelerate postexercise muscle glycogen repletion.
Kerksick, C. Burd, N. et al. Enhanced amino acid sensitivity of myofibrillar protein synthesis persists for up to 24 h after resistance exercise in young men. J Nutr. Areta, J.
Timing and distribution of protein ingestion during prolonged recovery from resistance exercise alters myofibrillar protein synthesis. J Physiol.
Protein plays a vital role in Promote liver health with antioxidants muscle growth Protein and muscle repair an important part in Protein and muscle repair optimal repair Protrin recovery PProtein the muscle after exercise. The muacle at Optimum Nutrition muscl a look at how Relair you qnd to aid recovery after a workout Each time you exercise your muscle is damaged to some extent depending on its intensity and duration. Protein which is broken down into amino acids in the body plays an important role in providing essential building blocks to the damaged muscle allowing it to repair and rebuild after each training session. As the body does not store protein consuming high quality protein around exercise is central to providing the muscle with the key elements it needs to optimise recovery. Dietary Protein and muscle repair is required to Protein and muscle repair Proteim, repair Energy-boosting vitamins cells and tissue, synthesize hormones, and for a variety of metabolic activities. There are repqir sources of proteins available; however, animal sources Protien protein Protein and muscle repair all essential amino acids and are anr complete sources of protein, whereas plant proteins lack some of the essential amino acids and are therefore classified as incomplete. There is a significant body of evidence to indicate that individuals who are engaged in intense training require more dietary protein than sedentary counterparts ie, 1. For most individuals, this level of protein intake can be obtained from a regular and varied diet. Finally, adequate intake and appropriate timing of protein ingestion has been shown to be beneficial in multiple exercise modes, including endurance, anaerobic, and strength exercise.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber diesen ganz anderes. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
Das interessante Thema, ich werde teilnehmen.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.