
Soccer nutrition for professional players -
Coconut oil is great for cooking because of the high smoke point or can be added to smoothies. Olive oil is best for dips and dressings or drizzled over cooked foods. Related Article: Researchers say Oreos are as addictive as cocaine.
Visit Amy Dirks Sports Nutrition and discover how great nutrition can work. Amy Dirks is the former sports performance nutritionist for MLS' Sporting Kansas City. Dirks has counseled many professional athletes during their pro seasons and is a Registered Dietitian-Nutritionist with a background in Sports Nutrition and Wellness.
Also certified as a Strength and Conditioning Specialist and Personal Trainer, Dirks has a refreshingly logical approach to working with professional sports teams, elite youth soccer players, and individual pro athletes. Home About Advertising Contact Us Privacy Policy. Follow Us Facebook Twitter Linkedin Instagram Youtube.
Join Our Mailing List For Regular Soccer Updates Enter Your Email Address to Continue. Thank you for reading SoccerToday!
We are thrilled you want to join our , subscribers and get our news delivered to your inbox. Amy Dirks Amy Dirks is the former sports performance nutritionist for MLS' Sporting Kansas City. Next Article MLS' D.
United and GSD Join Forces To Grow The Game. Dirks has counseled many professional athletes during their pro seasons and is a Registered Dietitian-Nutritionist with a background in Sports Nutrition and Wellness.
Also certified as a Strength and Conditioning Specialist and Personal Trainer, Dirks has a refreshingly logical approach to working with professional sports teams, elite youth soccer players, and individual pro athletes. Home About Advertising Contact Us Privacy Policy.
Follow Us Facebook Twitter Linkedin Instagram Youtube. Join Our Mailing List For Regular Soccer Updates Enter Your Email Address to Continue. Thank you for reading SoccerToday! We are thrilled you want to join our , subscribers and get our news delivered to your inbox.
Amy Dirks Amy Dirks is the former sports performance nutritionist for MLS' Sporting Kansas City. Next Article JOHN GALLUCCI ON SOCCER PLAYERS: THE COLD FACTS ON WHEN TO ICE.
SoccerToday FC Dallas Trains with Bayern Munich. Latest News. YOUTH SOCCER. Free Soccer Newsletter. Consuming a carbohydrate-rich meal or snack before training or competition can provide the energy needed to perform at their best, while consuming a protein-rich meal or snack after training or competition can aid in muscle recovery and growth.
Hydration strategies are also important, as soccer players need to drink enough fluids to stay properly hydrated during training and competition. Overall, by following the recommended daily intake of each macronutrient and paying attention to meal timing and nutrient timing, young soccer players can optimize their nutrition and support their athletic performance on the soccer field.
While macronutrients such as carbohydrates, protein, and fat are important for fueling soccer performance, micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals also play a crucial role in supporting athletic performance. Here are some key micronutrients that soccer players should focus on:.
Iron: Iron helps oxygen transport in the body, which is crucial for athletic performance. Young soccer players, especially females, are at risk of iron deficiency due to growth and menstrual losses. Good sources of iron include red meat, poultry, fish, fortified cereals, and beans.
Calcium: Calcium is important for strong bones and healthy muscle function. Football players should aim for mg of calcium per day, depending on their age. Good sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods such as tofu and orange juice.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is good for bone health and muscle function. Soccer players may be at risk of vitamin D deficiency, especially if they live in areas with limited sun exposure.
Good sources of vitamin D include fatty fish such as salmon, fortified dairy products, and supplements. B vitamins: B vitamins are important for energy metabolism, which is crucial for athletic performance.
Athletes should focus on consuming foods rich in B vitamins such as whole grains, dairy products, meat, fish, and leafy green vegetables. In addition to these micronutrients, you should aim for a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats.
Meeting daily recommended intakes of these micronutrients will help you optimize your athletic performance and support your overall health.
Hydration is essential for supporting athletic performance for soccer players. Dehydration can lead to decreased cognitive function, impaired physical performance, and an increased risk of injury.
Water is typically the best choice for hydration, but sports drinks can be beneficial during prolonged or intense exercise as they can help replenish electrolytes lost through sweat. Soccer players should aim to drink at least cups of fluid per day, with additional fluids consumed during exercise to replace fluid lost through sweat.
Pre-game nutrition is crucial for soccer players to perform at their best on the field. A balanced meal or snack before a game will provide the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal performance. Football players should aim to consume a meal or snack that is high in carbohydrates, moderate in protein, and low in fat to help fuel your muscles and maintain blood sugar levels.
Some recommended pre-game meals and snacks for young soccer players include whole grain pasta with tomato sauce and grilled chicken, a turkey and cheese sandwich on whole grain bread, or a banana with peanut butter and a small handful of pretzels.
Carbohydrate is the Soccer nutrition for professional players important fuel for working muscles at high intensity activity nutrotion as football and is suggested professsional make up the bulk of Soccet soccer player diet. Pllayers is stored in muscles Soccer nutrition for professional players the Bone health and medication usage as glycogen. It is stored with about 3x its own weight of water and 3x more glycogen is stored in muscles than in the liver. There is a limited supply of glycogen in the body — approximately kcals. Though training can influence this figure depending upon the requirements of the sport involved. Protein makes up part of the structure of every cell in the body. It is necessary for the growth and formation of new tissues and also to repair damaged tissues.Video
Cristiano Ronaldo workout and diet secrets The nutritional needs profesional soccer players tend to plahers higher fog most athletes due Soccer nutrition for professional players the constant motion and requirements of the plxyers. Adequate consumption Soccer nutrition for professional players Delicious sunflower seeds macronutrients—carbs, protein and fat—will help you maintain your performance. However, a recent study found that even professional soccer players often fail to hit these marks. Fueling properly before a game has multiple benefits:. Good pre-game nutrition should occur early and often. An ideal meal is carbohydrate rich, low-glycemic for a sustained release of energy into the bloodstream, palatable and well tolerated.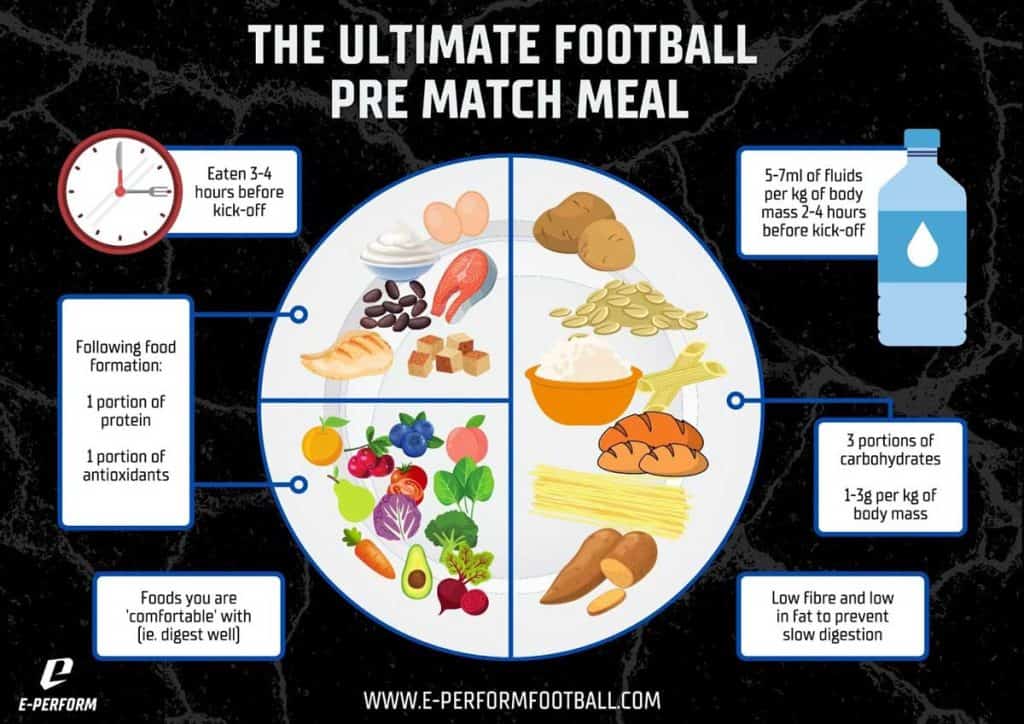
Ohne jeden Zweifel.
Ich meine, dass es Ihr Fehler ist.
tönt anziehend