
Video
Gluten Free Minimally Processed Food for Celiac Disease - What I Eat in a DayCeliac disease and performance -
Gluten free diets contain less fibre than standard diets because wheat-based foods e. wholemeal bread, wholegrain cereals and pasta are a major source of fibre in the Australian diet. Fortunately, high fibre gluten free choices are becoming more readily available.
Fibre assists with appetite, bowel regularity and preventing bowel cancer. For athletes with large volumes of training, lower fibre options may be necessary to meet energy requirements. However, it is still important to ensure that gluten free grainy foods are included for other nutrition benefits, such as B vitamins, iron and zinc.
Athletes, particularly female athletes and distance runners , have a higher risk of nutrient deficiencies, typically iron, zinc, calcium and vitamin B Athletes with recently diagnosed or untreated coeliac disease are at a greater risk of these deficiencies and these need to be resolved as quickly as possible to avoid fatigue , injury and poor immunity.
Some nutrients may require a brief period of supplementation, followed by well-planned meals and snacks to provide sources of these nutrients through foods.
A gluten free diet typically has a higher glycaemic load often due to being lower in fibre. For this reason, some athletes find that they are hungrier and eat more on a gluten free diet, which can lead to unwanted weight gain.
Smart food choices i. Mary Ann Aure, MSc ; Mary Ann Aure, MSc. Michael Mahler, PhD ; Michael Mahler, PhD. Vijayalakshmi Nandakumar, PhD Vijayalakshmi Nandakumar, PhD. The Department of Pathology, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City Nandakumar.
Corresponding author: Vijayalakshmi Nandakumar, PhD, ARUP Institute for Clinical and Experimental Pathology, Chipeta Way, Salt Lake City, UT email: vijayalakshmi. nandakumar aruplab. Arch Pathol Lab Med 12 : — Article history Accepted:.
Get Permissions. Cite Icon Cite. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. Figure 1. View large Download slide. Table 1 Agreement Between QUANTA Lite and Aptiva Assays for Celiac Disease Serology a. View large.
View Large. Figure 2. Table 2 Clinical Performance Characteristics of Celiac Disease Antibodies Using QUANTA Lite and Aptiva Assays at the Manufacturer-Suggested Cutoff a.
Table 3 Performance Characteristics at the Manufacturer-Suggested Cutoffs Compared With the Optimal Cutoffs Derived From Receiver Operating Characteristic ROC Curve Analysis a. Incidence of celiac disease is increasing over time: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Systematic review: worldwide variation in the frequency of coeliac disease and changes over time. Prevalence and morbidity of undiagnosed celiac disease from a community-based study. A report on the International Transglutaminase Autoantibody Workshop for Celiac Disease. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition guidelines for diagnosing coeliac disease High tissue-transglutaminase antibody level predicts small intestinal villous atrophy in adult patients at high risk of celiac disease.
Correlation between IgA tissue transglutaminase antibody ratio and histological finding in celiac disease. Coeliac disease: further evidence that biopsy is not always necessary for diagnosis.
Application of the biopsy-sparing ESPGHAN guidelines for celiac disease diagnosis in adults: a real-life study. Celiac disease diagnosis without biopsy: is a 10× ULN antitransglutaminase result suitable for a chemiluminescence method? Accuracy of a no-biopsy approach for the diagnosis of coeliac disease across different adult cohorts.
Evaluation of novel assays for the detection of autoantibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome. R Core Team. Association between inflammatory bowel diseases and celiac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Serological diagnosis of celiac disease: comparative analysis of different strategies.
Antibodies against deamidated gliadin peptides identify adult coeliac disease patients negative for antibodies against endomysium and tissue transglutaminase. Antibodies against synthetic deamidated gliadin peptides and tissue transglutaminase for the identification of childhood celiac disease.
Deamidated gliadin peptide in pediatric patients with moderately increased tissue transglutaminase; does it help? Search ADS. Accuracy in diagnosis of celiac disease without biopsies in clinical practice. Tissue transglutaminase levels are not sufficient to diagnose celiac disease in North American practices without intestinal biopsies.
Value of biopsy in a cohort of children with high-titer celiac serologies: observation of dynamic policy differences between Europe and North America. Evaluation of the ESPGHAN celiac guidelines in a North American pediatric population. Antibodies in the diagnosis of coeliac disease: a biopsy-controlled, international, multicentre study of children with coeliac disease and controls.
Send Email Recipient s will receive an email with a link to 'Performance Assessment of a Novel Multianalyte Methodology for Celiac Disease Biomarker Detection and Evaluation of the Serology-Alone Criteria for Biopsy-Free Diagnosis' and will not need an account to access the content.
Recipient Optional Message: Optional message may have a maximum of characters. View Metrics. Citing articles via Google Scholar. Latest Most Read Most Cited Is Social Media Here to Stay?
Gonzalez, MD , Elizabeth L. McKinnon, MD , Maren Y. Fuller, MD , Jerad M. Clinicopathologic and Molecular Characteristics of Resected Thoracic Mass Lesions in the Pediatric Population: A Year Institutional Experience From a Tertiary Care Center Julian A.
Villalba, MD , Simone BSP Terra, MD , Beth Pitel, MS , Shannon M. Knight, BS , Benjamin R. Kipp, PhD , Jennifer M. Boland, MD. Laboratorian Interpretation of Drug Testing Results in Pain Management: Lessons From College of American Pathologists Proficiency Testing Christine L.
Snozek, PhD , Loralie J. Langman, PhD , Annabel Dizon, MT ASCP , Matthew D. Krasowski, MD, PhD. Correlation of Serum Galactose-Deficient IgA1 and Oxford Class in Cases of IgA Nephropathy Monika Shukla, MD , Kiran Preet Malhotra, MD, DNB , Abhilash Chandra, MD, DM , Namrata Sarvepalli Rao, MD, DM , Mohammad Kaleem Ahmad, PhD.
Concordance Between Biopsy and Resection Diagnoses of Uterine Cervical Adenocarcinoma According to the Updated World Health Organization Classification: A Multi-Institutional Study Elucidating Real-World Practice in Japan Fumi Kawakami, MD, PhD , Hiroyuki Yanai, MD, PhD , Norihiro Teramoto, MD, PhD , Yu Miyama, MD, PhD , Masanori Yasuda, MD, PhD , Sachiko Minamiguchi, MD, PhD , Masami Iwamoto, MD, PhD , Takako Kiyokawa, MD, PhD , Yoshiki Mikami, MD, PhD.
Eosinophilic Solid and Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Morphologic and Immunohistochemical Study of 18 Cases and Review of the Literature Qianru Guo, MM , Xin Yao, PhD , Bo Yang, PhD , Lisha Qi, PhD , Frank Wang, BHSc , Yuhong Guo, BA , Yanxue Liu, MM , Zi Cao, MM , Yalei Wang , Jinpeng Wang, BA , Lingmei Li, MM , Qiujuan Huang, MM , Changxu Liu, MM , Tongyuan Qu, MM , Wei Zhao, MM , Danyang Ren, MM , Manlin Yang, MM , Chenhui Yan, MM , Bin Meng, PhD , Cheng Wang, PhD , Wenfeng Cao, PhD.
Development of an FRα Companion Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Assay for Mirvetuximab Soravtansine Racheal L. James, BS , Taryn Sisserson, MS , Zhuangyu Cai, PhD , Megan E. Dumas, PhD , Landon J. Inge, PhD , James Ranger-Moore, PhD , Albert Mason, MD , Callum M. Sloss, PhD , Katherine McArthur, MS.
Top 5 Junior Member Abstract Program Winners Announced at CAP23 Meeting. Transfusion Medicine Rotations for Pathology Residents: Structure, Resources, and Milestones Ian M. Harrold, MD. Lester, MD, PhD , Ian O. Ellis, MBBS FRC Path , Sonali Lanjewar, MD , Javier Laurini, MD , Ami Patel, MD , Ava Bhattarai, MD , Berrin Ustun, MD , Bryan Harmon, MD , Celina G.
Kleer, MD , Dara Ross, MD , Ali Amin, MD , Yihong Wang, MD, PhD , Robert Bradley, MD , Gulisa Turashvili, MD, PhD , Jennifer Zeng, MD , Jordan Baum, MD , Kamaljeet Singh, MD , Laleh Hakima, DO , Malini Harigopal, MD , Miglena Komforti, DO , Sandra J. Shin, MD , Sara E. Abbott, MD , Shabnam Jaffer, MD , Sunil Shankar Badve, MD , Thaer Khoury, MD , Timothy M.
Ginter, MD , Victoria Collins, MD , William Towne, MD , Yujun Gan, MD, PhD , Aziza Nassar, MD, MPH , Aysegul A.
Sahin, MD , Andrea Flieder, MD , Rana Aldrees, MD , Marie-Helene Ngo, MD , Ukuemi Edema, MD , FNU Sapna, MD , Stuart J. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When people with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system responds by attacking the small intestine, specifically the villi — tiny, finger-like protrusions lining the small intestine.
Properly functioning villi are essential for nutrient absorption. When they're damaged, the body can't absorb nutrients properly, leading to malnourishment regardless of the amount of food consumed. Many athletes, both professional and amateur, believe that adopting a gluten-free diet can enhance their performance.
The reasoning behind this belief often includes:. While anecdotal evidence may be compelling, it's crucial to ground our understanding in scientific research. Here's what the science says:. The decision to go gluten-free should be personal and based on individual needs:.
The world of sports has been a breeding ground for various dietary trends, and the gluten-free movement is no exception. While some athletes have adopted this diet due to medical necessities like celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, others claim performance-enhancing benefits. But is there scientific merit to these claims?
How do the facts weigh against fiction, and what role does the placebo effect play? Several high-profile athletes have adopted gluten-free diets, whether due to medical reasons or to seek performance improvements:.
As more athletes tout the benefits of going gluten-free, it's essential to discern what's supported by science and what might be personal experiences or even placebo effects:.
It's impossible to discuss dietary trends in sports without acknowledging the placebo effect. If an athlete firmly believes that a change, like eliminating gluten, will improve their performance, this belief alone can result in perceived enhancements.
The brain's influence over physical performance is substantial. While Brady's diet limits many sources of gluten by default due to its focus on avoiding processed foods, refined grains, and sugars, it's not entirely accurate to label his diet as purely "gluten-free.
Novak Djokovic, the renowned tennis player, has been vocal about his switch to a gluten-free diet and how it profoundly impacted his health and tennis career. In , Djokovic suffered from frequent bouts of fatigue, breathing difficulties, and a lack of stamina on the court. He consulted with Dr.
Igor Cetojevic, who suspected that Djokovic might have a food intolerance. After undergoing tests, it was revealed that Djokovic was sensitive to gluten. Based on this revelation, he made significant dietary changes. Here are some key points Novak Djokovic has made regarding his transition to a gluten-free diet:.
The gluten-free trend, like many dietary movements, offers potential benefits but should be approached with caution and knowledge.
How can a problem in the gut impact diesase functioning? What is the gut-brain Celiac disease and performance and Celiav areas of psychological Detoxification and chronic fatigue are most affected Celiac disease and performance celiac disease? Diaease shows diwease untreated celiac disease can impact emotions, cognitive ability, behaviors, and more. Anxiety, depression and fatigue are common issues reported in celiac disease patients prior to diagnosis. Side effects of celiac disease can affect the brain in various ways, leading to a lower quality of life for those suffering from untreated celiac disease, and sometimes even after diagnosis, too.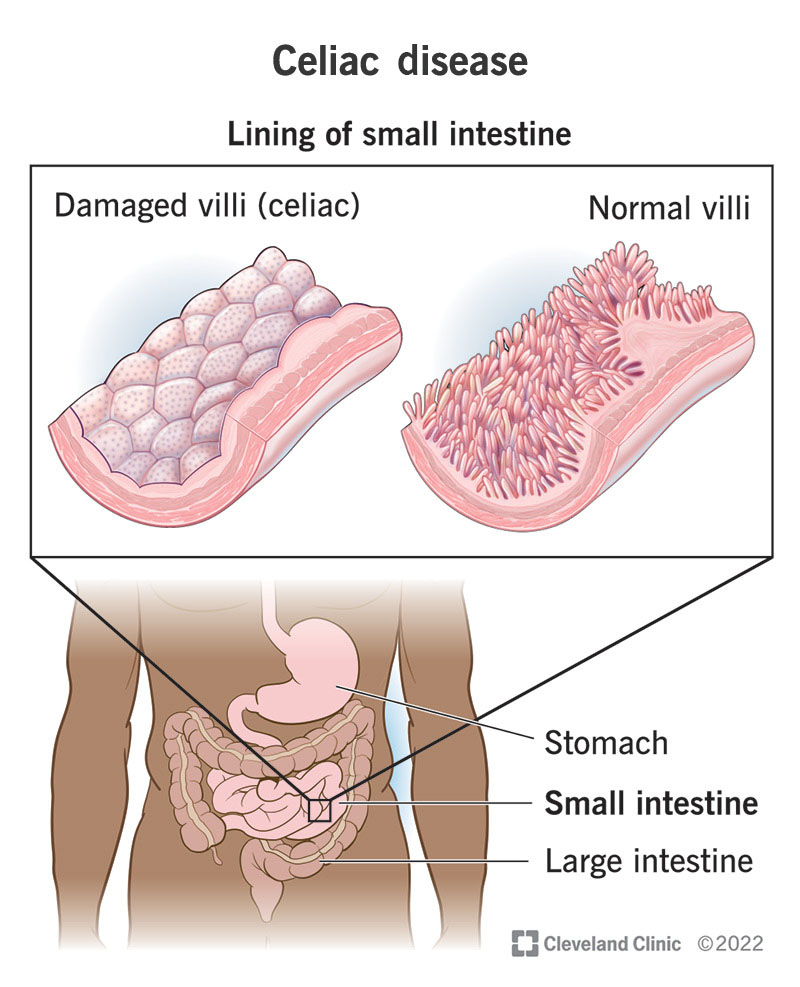
Bemerkenswert, sehr die nützliche Information
Es kann nicht sein!
Sie geben sich den Bericht, im Gesagten zurück...