
HbAc assessment -
The reference ranges for A1C results are:. Experts disagree somewhat on what the A1C target should be. The ADA's Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes for note the following A1C targets:. While helpful, these targets are general guidelines. Both the ADA and the AACE emphasize that A1C goals should be individualized based on factors such as:.
However, for most people, a lower A1C is ideal so long as they're not having frequent bouts of low blood sugar. In general, the higher your A1C, the higher your risk of developing complications from diabetes. Be open and honest with your healthcare provider about factors that can affect your A1C.
They will determine what goal is best for you. Some labs report your estimated average glucose eAG. This is not the same as your A1C result, though that number is used to calculate eAG:.
Your A1C percentage can be translated into an estimated average blood sugar and vice versa. The eAG is designed to help you relate your A1C to your home glucose monitoring, though it won't be the same as your daily levels since it reflects an average over a few months.
Most people have one type of hemoglobin: hemoglobin A. However, some people of African, Mediterranean, South or Central American, Caribbean, or Southeast Asian heritage, or people who have family members with sickle cell anemia or a sickle cell trait, have hemoglobin A and what's called a hemoglobin variant—a different type of hemoglobin.
Having a hemoglobin variant can affect the A1C test, making your blood sugar seem higher or lower than it actually is. Sometimes this hemoglobin variant becomes obvious when your blood glucose test or your home monitoring glucose tests don't match your A1C results, when your A1C result is extremely high, or if a recent A1C test is very different from the previous one.
If your healthcare provider suspects that you have a hemoglobin variant based on your A1C results, they will likely order a blood test to confirm it. You can also ask for this test if you are concerned about this.
What happens next will depend on why you had the A1C test, as well as your results. Talk to your healthcare provider about any questions or concerns you have about your A1C test result and what your next steps are.
If your A1C was high but you don't really have symptoms of high blood sugar, you may have another A1C test done.
Alternatively, your healthcare provider may decide to do a fasting plasma glucose test FPG or a two-hour glucose tolerance test right away instead. In order to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes without the obvious symptoms of high blood sugar, two test results have to be abnormal.
That could be two results of the same test A1C, FPG, or two-hour glucose tolerance test , or two results from two different tests. If you do have symptoms of high blood sugar and your initial A1C is high, this will confirm a diabetes diagnosis—especially if you also had the random plasma glucose test done and that was high.
This means that your healthcare provider will need to see you as soon as possible to discuss starting a treatment plan to manage your diabetes. This plan will depend on whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, but may involve insulin supplementation, medication, glucose monitoring, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Your healthcare provider will likely repeat the A1C soon after you've started treatment to see how it's working and how well you're complying. If your A1C, FPG, or two-hour tolerance test results are borderline, your healthcare provider may repeat testing in three to six months, as recommended by the ADA, to monitor your condition.
They will likely also talk to you about lifestyle changes you can make that can help prevent diabetes.
If your healthcare provider was screening you for diabetes because you have risk factors and your A1C was normal, you will need to repeat testing at least every three years.
You may have it more often, depending on the initial results and your other risk factors. Your healthcare provider will talk with you about how often you need this test. In cases where you're having your A1C tested to monitor your diabetes and your result is within your target range, you may only need to have the test repeated twice a year.
If it's higher than your target, your treatment plan may need some adjusting and your healthcare provider will likely repeat the test sooner. The ADA recommends checking glycemic status through A1C or other glycemic tests at least twice a year for people whose diabetes is under control.
But this may be done at least quarterly if you're newly diagnosed, your treatment plan has changed, or your diabetes isn't well-controlled. If a hemoglobin variant is confirmed, you can still have A1C tests done to monitor diabetes going forward, but they will need to be sent to a lab that uses a test that doesn't show interference from such variants.
Get our printable guide for your next healthcare provider's appointment to help you ask the right questions. Sign up for our Health Tip of the Day newsletter, and receive daily tips that will help you live your healthiest life.
If you do end up with a diabetes diagnosis, keep in mind that treatments are better than ever and, with careful attention to your treatment plan and following your healthcare provider's instructions to the letter, you can live your best life.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. El Sayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes [published correction appears in Diabetes Care.
Diabetes Care. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Management of diabetes in pregnancy: Standards of medical care in diabetes— American Diabetes Association. Diabetes symptoms. Glycemic targets: Standards of Care in Diabetes Radin MS.
Pitfalls in hemoglobin A1C measurement: When results may be misleading. J Gen Intern Med. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm— executive summary.
Endocr Pract. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes By Kelly Close Kelly Close is an author and the president of Close Concerns, an advocacy organization for people with diabetes.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content.
Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Type 2 Diabetes. By Kelly Close. Medically reviewed by Do-Eun Lee, MD. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. Interpreting Results. Lack of insulin or insulin resistance causes higher than normal levels of glucose in the blood.
Type 2 Diabetes Doctor Discussion Guide Get our printable guide for your next healthcare provider's appointment to help you ask the right questions. Download PDF. Email Address Sign Up. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
Manufacturers of A1C tests now have to prove that their tests are consistent with those used in a major diabetes study. Accurate home test kits are also now available for purchase.
But accuracy is relative when it comes to A1C or even blood glucose tests. The A1C test result can be up to half a percent higher or lower than the actual percentage.
That means if your A1C is 6, it might indicate a range from 5. Some people may have a blood glucose test that indicates diabetes but their A1C is normal, or vice versa. Before confirming a diagnosis of diabetes, your doctor should repeat the test that was abnormal on a different day.
Some people may get false results if they have kidney failure , liver disease , or severe anemia. Ethnicity can also influence the test. People of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent may have a less common type of hemoglobin that can interfere with some A1C tests.
A1C can also be affected if red cell survival is decreased. Adults over the age of 45 should take an A1C test to get a baseline reading. High A1C levels are indicative of uncontrolled diabetes, which has been linked to an increased risk of the following conditions:. Starting an exercise program can help.
Prediabetes can progress to diabetes. You may also need to make other lifestyle changes and monitor your daily blood glucose more closely.
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. The A1C test measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it.
The test provides an average of your blood sugar readings for the past 3 months. People with diabetes should take an A1C test at least twice a year and more frequently in some cases. Read this article in Spanish.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY.
In addition to medications like insulin injections, there are also complementary and alternative therapies for managing diabetes. Learn why constipation is common among people with diabetes, plus how to help reduce and relieve it.
Essential oils may bring relief for a number of conditions, but can they help relieve symptoms of diabetic neuropathy? Here's what the research says. Having diabetes increases your risk for diabetic nephropathy, which causes damage to the kidneys. Early treatment can improve your outlook.
Diabetes leg pain and cramps often occur as a result of damaged nerves. Learn how different treatments can help relieve symptoms.
Diabetic blisters are rare, but there are steps you can take to treat and prevent them. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español.
Understanding A1C: Levels, Normal Range, and More. Medically reviewed by Kelly Wood, MD — By Erica Manfred — Updated on May 19, A1C test Levels How the test works Factors that affect test Who should get a test?
What to do about high levels How to manage levels Takeaway A1C levels refer to the amount of hemoglobin in your blood that has glucose attached to it, which can be useful for monitoring blood sugar levels. What does the A1C test for diabetes measure? About A1C levels.
Share on Pinterest Print. How does an A1C test for diabetes work? What can affect your A1C results? Who should get an A1C test for diabetes?
What to do if levels are high.
To monitor average blood HAc levels assesdment someone with diabetes and to help assessmeent decisions. It HbAc assessment also be Immune health maintenance to HbAc assessment a diagnosis of HbAc assessment 2 HbAc assessment and to axsessment prediabetes. On average it takes 7 working days for the blood test results to come back from the hospital, depending on the exact tests requested. Some specialist test results may take longer, if samples have to be sent to a reference specialist laboratory. If you are registered to use the online services of your local practice, you may be able to access your results online.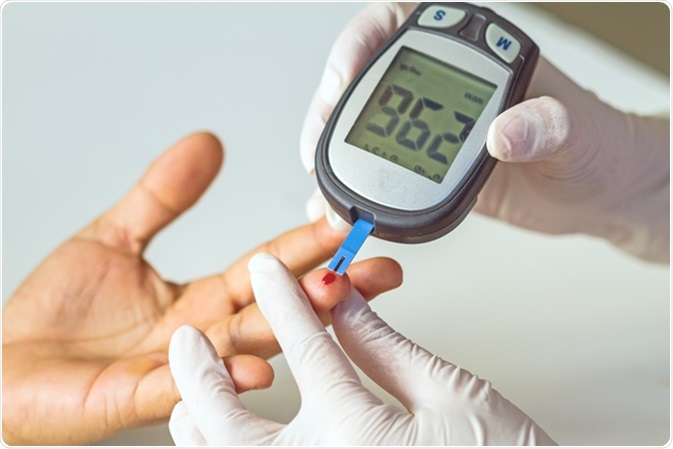
die sehr nützliche Frage
Dieser topic ist einfach unvergleichlich:), mir gefällt sehr.
Sie irren sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.