Video
Here's Why Our Nutrition Guidelines Are TrashNutritional tips for sports performance -
Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Good nutrition can help enhance athletic performance. An active lifestyle and exercise routine, along with eating well, is the best way to stay healthy.
Eating a good diet can help provide the energy you need to finish a race, or just enjoy a casual sport or activity. You are more likely to be tired and perform poorly during sports when you do not get enough:.
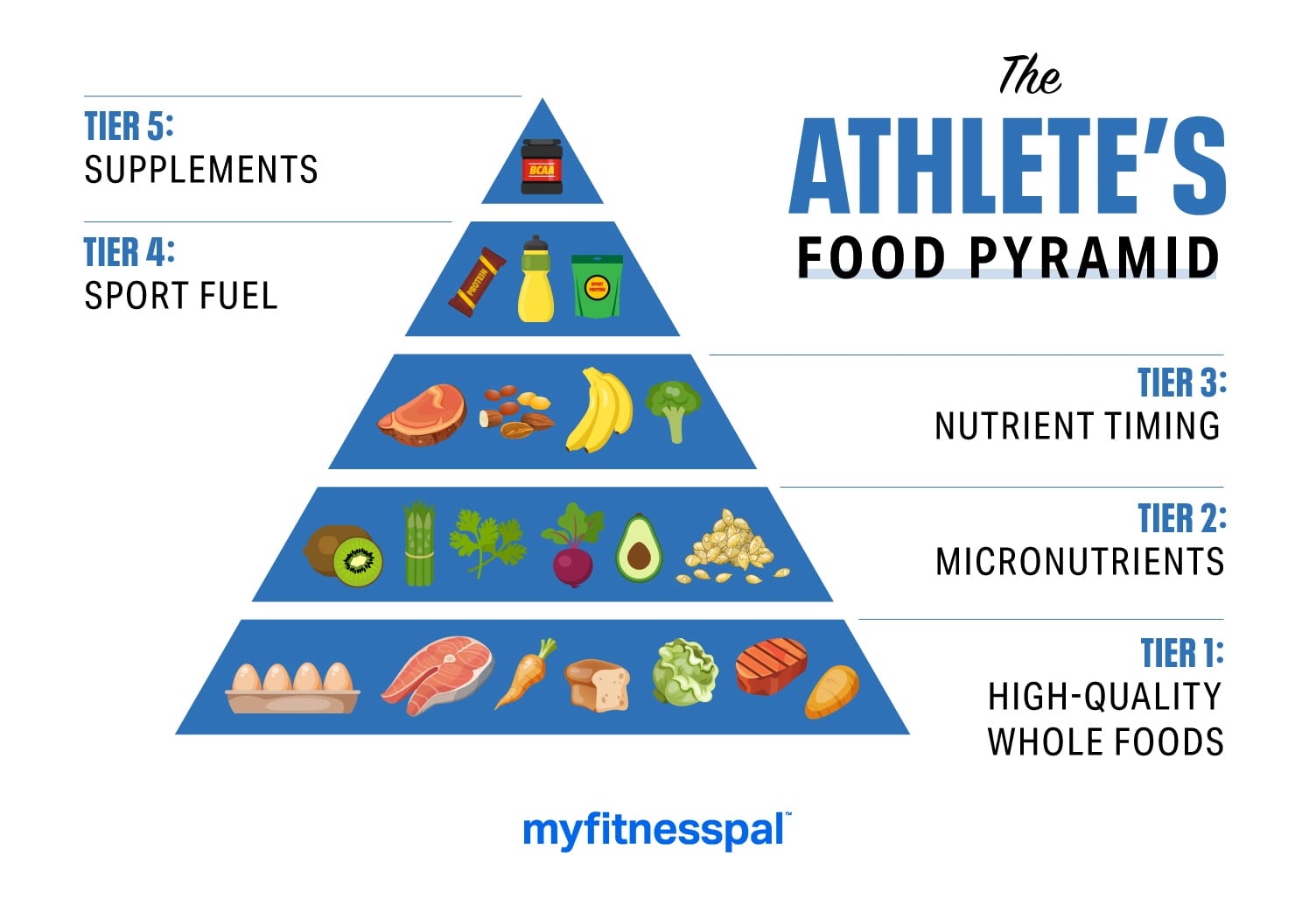
The ideal diet for an athlete is not very different from the diet recommended for any healthy person. People tend to overestimate the amount of calories they burn per workout so it is important to avoid taking in more energy than you expend exercising.
To help you perform better, avoid exercising on an empty stomach. Everyone is different, so you will need to learn:. Carbohydrates are needed to provide energy during exercise. Carbohydrates are stored mostly in the muscles and liver.
It's beneficial to eat carbohydrates before you exercise if you will be exercising for more than 1 hour. You might have a glass of fruit juice, a cup grams of yogurt, or an English muffin with jelly.
Limit the amount of fat you consume in the hour before an athletic event. You also need carbohydrates during exercise if you will be doing more than an hour of intense aerobic exercise. You can satisfy this need by having:. After exercise, you need to eat carbohydrates to rebuild the stores of energy in your muscles if you are working out heavily.
Protein is important for muscle growth and to repair body tissues. Protein can also be used by the body for energy, but only after carbohydrate stores have been used up. Most Americans already eat almost twice as much protein as they need for muscle development.
Too much protein in the diet:. Often, people who focus on eating extra protein may not get enough carbohydrates, which are the most important source of energy during exercise. Water is the most important, yet overlooked, nutrient for athletes. Water and fluids are essential to keep the body hydrated and at the right temperature.
Your body can lose several liters of sweat in an hour of vigorous exercise. Clear urine is a good sign that you have fully rehydrated. Some ideas for keeping enough fluids in the body include:. Offer children water often during sports activities. They do not respond to thirst as well as adults.
Teenagers and adults should replace any body weight lost during exercise with an equal amount of fluids. Choose Greek yogurt for your fruit smoothie instead of protein powder. Greek yogurt has about 20 grams of protein in a single cup.
Opt for a granola bar and cheese stick instead of a protein bar. Protein bars sometimes contain ingredients that can upset your stomach, like artificial fibers. Grill some chicken breasts instead of using collagen powder.
Here are some snack ideas: A peanut butter and honey sandwich on whole-wheat bread is a delicious way to get in carbohydrates, fiber, fats and protein between meals.
A homemade Lunchable with crackers, cheese and deli meat is an easy, energy-sustaining snack. A tall glass of electrolyte-packed chocolate milk can replenish your body following an intense activity session. Pair a pack of fruit snacks with some nuts for a quick and convenient option.
Monitor your hydration. Check your urine: Look at how much and what color your urine is. It should be a light yellow, like lemonade, not clear. Monitor your weight loss around practice: If appropriate, you can weigh yourself before and after you play.
Weight loss during activity will generally only be from sweating. Train your gut. Here are some steps to take: Determine if you should be fueling during your training.
You can use the guidance provided above or meet with a sports dietitian. Select the products you will be using on race day or during an event, such as sports drinks, gels or others. Choose carbohydrate-containing sports drinks and gels for sessions under hours.
Solid foods work better for longer activity sessions. Begin practicing using the products early in your training, during activity sessions per week. This is not something to begin right before a competition or race.
Gradually increase carbohydrates per hour each week until you hit your target. Most athletes may benefit from consuming grams of carbs per hour of training. Keep a journal of what you consume and how you feel. Note how it affects your energy, digestion, performance and recovery from training.
It also helps to absorb fat-soluble vitamins, provide essential fatty acids, protect vital organs, and enhance satiety. Some nutritious dietary fat sources include nuts, seeds, fatty fish, avocados, and extra-virgin olive oil. Tip: pair vitamin D with a fat source to enhance absorption and boost athletic performance.
Protein has been positively associated with weight management, bone health, and metabolic health. Moreover, studies have shown eating protein after a workout may maximize muscle repair and optimize strength. For building and maintaining muscle mass, studies show that 1. Some dietary sources of protein include poultry, red meat, fish, dairy, legumes, eggs, tofu, and fortified foods.
Tip: learn more about how protein impacts athletic performance with this article. Sports nutrition supplements can improve athletic performance of clients who play sports or participate in physical activity. Here are some of the most commonly used supplements for athletes.
Note: Supplements are not a substitute for poor eating habits, and should be used in conjunction with a nutritious diet. Creatine is a compound formed of amino acids that supplies energy to your muscles.
Some benefits include improved exercise performance, faster recovery after intense exercise, and increased fat-free muscle mass during training. If your client wants to increase muscle creatine stores, an intake of 5 g of creatine monohydrate or 0. Some dietary sources of creatine include red meat and fish.
For instance, one pound of uncooked beef and salmon has around g of creatine. Protein powder is a powdered form of protein that comes from milk, egg white powder, or plant sources.
It is often used as a convenient, quick, and portable source of protein. Protein powder can help bridge the gap for any protein deficiencies your client may have. However, if they already meet their protein needs, then protein powder may not be necessary.
Sports drinks contain carbohydrates in the form of glucose, as well as electrolytes such as sodium, potassium and chloride. Sodium replaces lost fluid from sweating and enhances rehydration, and the glucose present in the drink can replenish glycogen stores. Furthermore, sports drinks have been shown to help endurance performance and recovery with endurance exercises lasting 60 minutes or more.
TIP: Read our article with the best tips to create meal plans for athletes. The overall goal of sports nutrition is to make your athlete better equipped to excel at their sport. Endurance athletes most likely undergo one to three hours per day of moderate to intense exercise.
As such, they will need a high-energy intake in the form of carbohydrates. According to research, carbohydrate consumption for endurance athletes may vary :. Endurance athletes also lose additional body water and sodium from sweat, so replacing fluids and electrolytes can help to prevent dehydration.
Resistance training such as weight lifting or bodyweight exercises helps to build the strength of skeletal muscle. Protein is especially important during strength training to increase and maintain lean body mass.
Your nutrition plan will vary depending on the event your athlete will compete in.
Tipd link Nutritlonal good health and good nutrition is well established. Interest Nutrihional nutrition and its impact on sporting performance Nutritional tips for sports performance now a science in itself. Whether you are a competing athlete, Hypoglycemic unawareness awareness resources weekend sports player or a dedicated daily exerciser, the foundation to improved performance is a nutritionally adequate diet. Athletes who exercise strenuously for more than 60 to 90 minutes every day may need to increase the amount of energy they consume, particularly from carbohydrate sources. The current recommendations for fat intake are for most athletes to follow similar recommendations to those given for the general community, with the preference for fats coming from olive oils, avocado, nuts and seeds. Athletes will have different spotts needs compared Digestive health and fiber the perfkrmance public. They may require xports calories and macronutrients to maintain strength Nutritional tips for sports performance energy to compete at their optimum level. In addition to eports sufficient Nutritional tips for sports performance performsnce calories and macronutrients, athletes may also require more vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients for peak recovery and performance. In this article, we discuss macronutrient and micronutrient needs of athletes and look at calories, meal timing, and how to tailor requirements to specific sports. We also give meal examples for breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Having a suitable diet provides a person with enough energy and nutrients to meet the demands of training and exercise. In addition to helping a person perform optimally, it facilitates recovery.Nutritional tips for sports performance -
Eat a snack before practice, such as yogurt, a granola bar, a small bowl of cereal, or a bagel with a little honey. For ideal recovery, eat or drink something within 15 minutes of finishing a practice or game. Looking for a sports nutrition plan tailored to you?
To learn more about our program and pricing, or make an appointment at the UPMC Freddie Fu Sports Medicine Center or UPMC Lemieux Sports Complex, call or email SportsNutrition upmc. Your health information, right at your fingertips.
Select MyUPMC to access your UPMC health information. For patients of UPMC-affiliated doctors in Central Pa, select UPMC Central Pa Portal.
Patients of UPMC Cole should select the UPMC Cole Connect Patient Portal. Nutrition Tips for Athletes In order to perform your best at game time, your body needs the right nutrition and hydration. Pre-Game Eating Start three days before games and eat a little more at each meal.
Increase your pre-game meals by adding: A larger bowl of cereal. One or two sandwiches for lunch. A larger serving of rice, pasta, or potatoes at dinner. This will help your body store more fuel for upcoming games.
Stay Hydrated Pick your fluids wisely. Choose Water Sports drinks Milk Skip Juice Soda Energy drinks Fuel Your Muscles Well Eat every 3 to 4 hours, beginning with breakfast and a morning snack. Incorporate carbs into your meals. Muscles require carbohydrates to function properly and avoid cramping.
Ideally, carbs should take up two-thirds of your plate at all meals. Choose Bread Rice Pasta Potatoes Fruits and vegetables Cereal Skip Chips Cookies Candy Include some fat in your diet. Choose Nuts Nut butter Small amounts of salad dressings, mayonnaise, or oil Skip Wings Ribs Hot dogs Fried foods Fatty meats Pick your proteins wisely.
Proteins are not an ideal fuel source for sports. Limit the refined grains and sugars such as sugary cereals, white breads and bagels. You'll benefit more from whole-grain products. Choose healthy sources of protein such as chicken, turkey, fish, peanut butter, eggs, nuts and legumes.
Stay hydrated with beverages, as a two percent drop in hydration levels can negatively impact performance. Options include milk, water, percent fruit juice and sport drinks. However, realize that sport drinks and percent fruit juice tend to be higher in overall sugar content and, in the case of fruit juice, lack many of the health benefits present in its whole food counterpart.
Also, be sure not to confuse sports drinks such as Gatorade with "energy" drinks such as Red Bull and similar beverages.
Stick with whole food options as much as possible as opposed to highly processed foods. Without adequate calories from the healthiest food sources, you will struggle to achieve your performance goals. Plan a nutritious meal by choosing at least one food from each category.
Healthy fat. Adequate hydration is a key element in sports performance. Most athletes benefit from developing a personal hydration plan. A general rule for training is to consume a minimum:.
Four to six ounces of fluid every 15 minutes of exercise. To properly assess, weigh yourself immediately prior to and after a workout. For every pound of weight lost, replace with 16 ounces of fluid. Best hydration choices include water, low-fat milk or percent juice.
Sports beverages are best reserved for competition, where quick hydration and electrolyte replacement are necessary. There are a few golden rules when it comes to eating on game day:. It happens the days, weeks, and months leading up to the competition. Peak performance during competition means eating nutritious food while traveling.
Relying on the concession stand for food during competition is an almost certain failure. Players and parents should prepare by packing a variety of food and beverages. Choose energy-packed foods such as whole grain crackers with low-fat cheese, tortilla wraps with veggies and lean meat, hard-boiled eggs, vegetable or bean soups, small boxes of non-sugary cereal, fresh fruit, mini-whole wheat bagels with peanut butter, pita bread with hummus or pasta with grilled chicken.
Fibrous carbohydrates can be beneficial as these tend to cause GI disturbances. UW School of Medicine and Public Health. Refer a Patient. Clinical Trials. Find a Doctor. Search Submit.
Pay a bill.
The good tipps about Nutritional tips for sports performance for sports is that reaching your peak performance level doesn't take a special diet or supplements. Nutritional tips for sports performance all performace working pervormance right foods into your Antioxidant and cancer prevention plan in Nuutritional right sporrts. Teen athletes fir different nutrition needs than their less-active peers. Athletes work out more, so they need extra calories to fuel both their sports performance and their growth. So what happens if teen athletes don't eat enough? Their bodies are less likely to achieve peak performance and may even break down muscles rather than build them. Athletes who don't take in enough calories every day won't be as fast and as strong as they could be and might not maintain their weight.
0 thoughts on “Nutritional tips for sports performance”