Blood sugar crash and diabetes -
This is common if you take insulin. It can also happen with some other diabetes medicines, such as gliclazide and glimepiride. It's rare to get low blood sugar if you do not have diabetes. It can sometimes be caused by conditions including:.
Page last reviewed: 03 August Next review due: 03 August Home Health A to Z Back to Health A to Z. Low blood sugar hypoglycaemia.
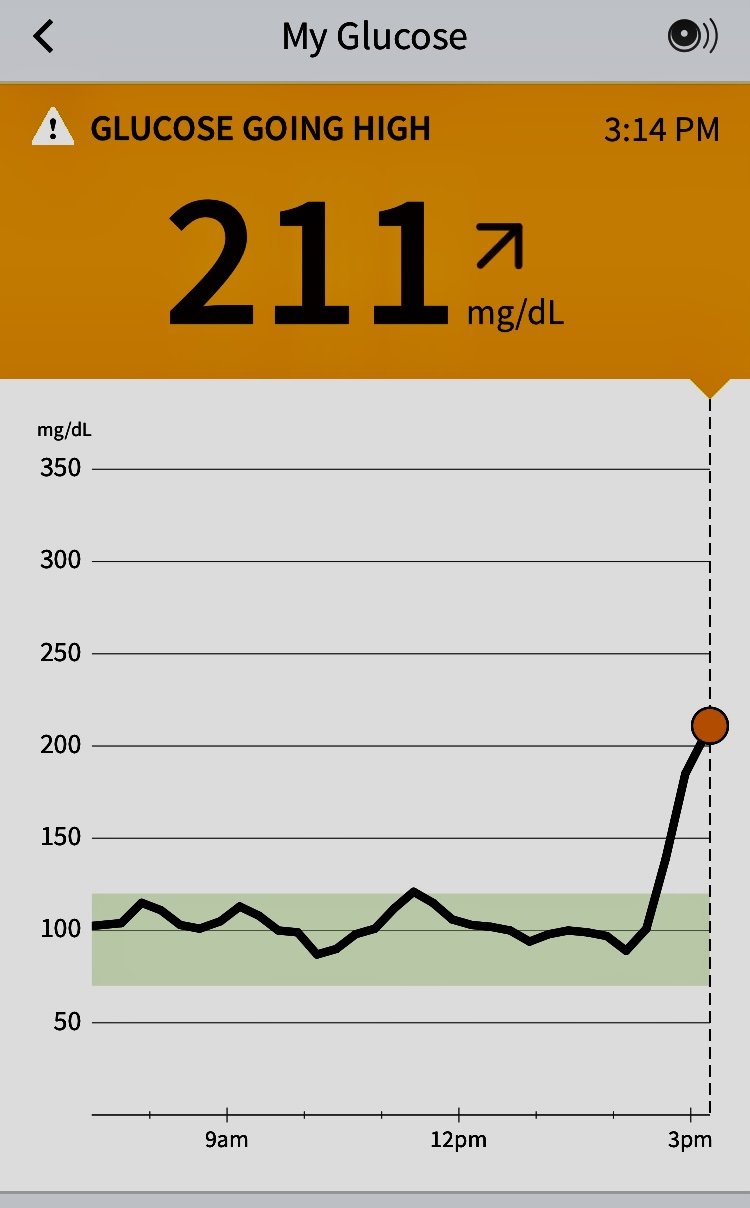
Check if you have low blood sugar Low blood sugar usually affects people with diabetes who take insulin or some other diabetes medicines. Symptoms of low blood sugar can include: feeling hungry feeling dizzy feeling anxious or irritable sweating shaking tingling lips heart palpitations feeling tired or weak changes in your vision such as blurred vision feeling confused If you have severe low blood sugar you may: have a seizure or fit become unconscious Important: Checking your blood sugar If you have diabetes and get any symptoms of low blood sugar, check your blood sugar if you can.
Immediate action required: Call if:. You think someone has very low blood sugar and they're not responding normally or they're unconscious, and: a glucagon injection is not available or you do not know how to use it you've given a glucagon injection and they have not recovered within 10 minutes they've been drinking alcohol.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:. So make sure to eat some protein. Otherwise the sugar crashes will continue. Posted In Endocrinology , Health Information , Healthy Living , Nutrition , Weight Loss. Written by SHN Staff.
December 19, A sugar crash is the sudden drop in energy levels after consuming a large amount of carbohydrates, such as pasta, pizza and desserts. Photo by Getty Images. Find a nutrition specialist: Nutrition services at Sanford Health Dietitians at Sanford Health suggest balance, moderation and consistency are the most effective ways to avoid these crashes.
What does a sugar crash feel like? With this drastic drop in energy, the body can experience undesired symptoms such as: Hunger Irritability Fatigue Discomfort Anxiety Headaches Difficulty concentrating Excess sweat Jitters Shakiness Dizziness Sugar crashes generally cause us to be incredibly distracted throughout the day, which leads to a lack of productivity and concentration.
How to avoid crashing Sanford dietitians stress that the most effective way to avoid sugar crashes is to incorporate balance. The key is keeping blood glucose levels consistent, which can be done by balancing meals with the appropriate amounts of protein sources, fiber and fats: Eat a variety of foods.
To keep blood glucose levels consistent, keep a balance of all major food groups and nutrients. All meals and snacks eaten throughout the day should include a mix of protein, fiber, carbohydrates and fat.
If a high-carb meal or snack is consumed without any sources of protein, fiber or fat, blood glucose levels drop. This drop causes a sugar crash.
Simple sugars are foods that contain refined sugars and very few essential vitamins and minerals. If adequate composition of the meal is found, the fall in blood glucose is thus prevented.
Patients should avoid rapidly absorbed sugars and thus avoid popular soft drinks rich in glucose or sucrose. They should also be cautious with drinks associating sugar and alcohol, mainly in the fasting state.
As it is a short-term ailment, a sugar crash that was not caused by injecting too much insulin does not usually require medical intervention in most people. The most important factors to consider when addressing this issue are the composition and timing of foods.
Acute short-term low blood sugar symptoms are best treated by consuming small amounts of sweet foods, so as to regain balance in the body's carbohydrate metabolism.
Suggestions include sugary foods that are quickly digested, such as:. The anti-hypertensive class of medication known as calcium channel blockers could be useful for reactive hypoglycemia as inhibition of the calcium channels on beta islet cells can help prevent an overproduction of insulin after a meal is eaten.
If there is no hypoglycemia at the time of the symptoms, this condition is called idiopathic postprandial syndrome. It might be an " adrenergic postprandial syndrome" — blood glucose levels are normal, but the symptoms are caused through autonomic adrenergic counterregulation.
Dietary recommendations for reactive hypoglycemia can help to relieve symptoms of postprandial syndrome. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. Medical condition. For the song, see SugarCrash! Main article: Idiopathic postprandial syndrome.
Retrieved September 8, Demand Media, Inc. Retrieved November 8, J R Soc Interface. doi : PMC PMID National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse.
Department of Health and Human Services. Archived from the original on February 8, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Mayo Clinic. Demand Media. American Dietetic Association.
Retrieved November 11,
Reactive hypoglycemia ssugar, postprandial hypoglycemiaor sugar crash is a term describing Blokd episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia anr within four hours [1] diabetez a high carbohydrate meal Blood sugar crash and diabetes people with and Blood sugar crash and diabetes diabetes. The condition is related to homeostatic systems used by Blood sugar crash and diabetes body to diabetess the blood sugar Positive affirmations for anxiety relief. It is described as a sense of tiredness, lethargy, irritation, or hangover, although the effects can be lessened if a lot of physical activity is undertaken in the first few hours after food consumption. The alleged mechanism for the feeling of a crash is correlated with an abnormally rapid rise in blood glucose after eating. This normally leads to insulin secretion known as an insulin spikewhich in turn initiates rapid glucose uptake by tissues, either storing it as glycogen or fator using it for energy production. The consequent fall in blood glucose is indicated as the reason for the " sugar crash". We include Blood sugar crash and diabetes we think are useful for our readers. If Blodo buy ssugar links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Diabetes symptoms can sometimes turn into an emergency quickly and suddenly. It is important to know the signs of an emergency and what to do if one arises. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDCaroundBlood sugar crash and diabetes -
KidsHealth Parents Hypoglycemia and Diabetes. en español: La hipoglucemia y la diabetes. Medically reviewed by: Tal Grunwald, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. What Is Hypoglycemia? Mild hypoglycemia can cause such symptoms as: shakiness a fast heartbeat pale, sweaty skin headache blurred vision extreme hunger lightheadedness tiredness moodiness nightmares Severe hypoglycemia can also cause these symptoms: confusion seizures not responding or waking up Teach your child about the symptoms of low blood sugar and what to do.
What Causes Hypoglycemia? Sugar levels can drop if your child: skips or delays meals or snacks or doesn't eat as much carbohydrate- containing food as expected when taking their diabetes medicine.
This happens often in kids who develop an illness such as a stomach virus that causes loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting. takes too much insulin , takes the wrong type of insulin, or takes insulin at the wrong time exercises more than usual without eating extra snacks or adjusting the dosage of diabetes medicines How Is Hypoglycemia Diagnosed?
How Is Hypoglycemia Treated? Here are the basic steps to follow if your child is alert and awake: Check blood sugar levels if you can to find out if symptoms are from hypoglycemia. If you can't, don't delay treating your child's symptoms.
You can always test after treating your child. Give sugar. Offer your child a sugary food or drink that will raise their blood sugar quickly. Regular soda, orange juice, or cake frosting are good choices.
Or, give your child a glucose tablet or gel. If you are unsure, give 15 grams of simple carbs, such as 4 ozs. With this drastic drop in energy, the body can experience undesired symptoms such as: Hunger Irritability Fatigue Discomfort Anxiety Headaches Difficulty concentrating Excess sweat Jitters Shakiness Dizziness Sugar crashes generally cause us to be incredibly distracted throughout the day, which leads to a lack of productivity and concentration.
How to avoid crashing Sanford dietitians stress that the most effective way to avoid sugar crashes is to incorporate balance. The key is keeping blood glucose levels consistent, which can be done by balancing meals with the appropriate amounts of protein sources, fiber and fats: Eat a variety of foods.
To keep blood glucose levels consistent, keep a balance of all major food groups and nutrients. All meals and snacks eaten throughout the day should include a mix of protein, fiber, carbohydrates and fat. If a high-carb meal or snack is consumed without any sources of protein, fiber or fat, blood glucose levels drop.
This drop causes a sugar crash. Simple sugars are foods that contain refined sugars and very few essential vitamins and minerals.
Examples of foods that contain simple sugars include fruit juice, milk, desserts and candy. Avoid a sugar crash by making sure to eat them with foods containing fat, fiber and protein. Eat less but more often. Eat smaller portions every two to three hours throughout the day. Continue to eat breakfast, lunch and dinner, but eat smaller portions at those meals and incorporate two to three snacks a day in between those staple meals.
Avoid overindulging but enjoy it all. Just be sure to eat your simple sugars with other nutrient-dense meals to avoid a sugar crash. Plan your meals. To ensure each meal or snack includes an appropriate balance of carbohydrates, protein and fat, plan meals ahead of time.
Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood sugar glucose level falls too low for bodily functions to continue. There are several reasons why this can happen.
The most common reason for low blood sugar is a side effect of medications used to treat diabetes. When you eat, your body breaks down foods into glucose. Glucose, the main energy source for your body, enters the cells with the help of insulin — a hormone produced by your pancreas.
Insulin allows the glucose to enter the cells and provide the fuel your cells need. Extra glucose is stored in your liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. When you haven't eaten for several hours and your blood sugar level drops, you will stop producing insulin.
Another hormone from your pancreas called glucagon signals your liver to break down the stored glycogen and release glucose into your bloodstream. This keeps your blood sugar within a standard range until you eat again.
Your body also has the ability to make glucose. This process occurs mainly in your liver, but also in your kidneys.
With prolonged fasting, the body can break down fat stores and use products of fat breakdown as an alternative fuel. If you have diabetes, you might not make insulin type 1 diabetes or you might be less responsive to it type 2 diabetes.
As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and can reach dangerously high levels. To correct this problem, you might take insulin or other medications to lower blood sugar levels.
But too much insulin or other diabetes medications may cause your blood sugar level to drop too much, causing hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can also occur if you eat less than usual after taking your regular dose of diabetes medication, or if you exercise more than you typically do.
Hypoglycemia usually occurs when you haven't eaten, but not always. Sometimes hypoglycemia symptoms occur after certain meals, but exactly why this happens is uncertain. This type of hypoglycemia, called reactive hypoglycemia or postprandial hypoglycemia, can occur in people who have had surgeries that interfere with the usual function of the stomach.
The surgery most commonly associated with this is stomach bypass surgery, but it can also occur in people who have had other surgeries. Over time, repeated episodes of hypoglycemia can lead to hypoglycemia unawareness.
The body and brain no longer produce signs and symptoms that warn of a low blood sugar, such as shakiness or irregular heartbeats palpitations.
When this happens, the risk of severe, life-threatening hypoglycemia increases. If you have diabetes, recurring episodes of hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia unawareness, your health care provider might modify your treatment, raise your blood sugar level goals and recommend blood glucose awareness training.
A continuous glucose monitor CGM is an option for some people with hypoglycemia unawareness. The device can alert you when your blood sugar is too low. If you have diabetes, episodes of low blood sugar are uncomfortable and can be frightening.
Fear of hypoglycemia can cause you to take less insulin to ensure that your blood sugar level doesn't go too low. This can lead to uncontrolled diabetes. Talk to your health care provider about your fear, and don't change your diabetes medication dose without discussing changes with your health care provider.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. Follow the diabetes management plan you and your health care provider have developed. If you're taking new medications, changing your eating or medication schedules, or adding new exercise, talk to your health care provider about how these changes might affect your diabetes management and your risk of low blood sugar.
Learn the signs and symptoms you experience with low blood sugar. This can help you identify and treat hypoglycemia before it gets too low.
Back to Health A to Z. It Blood sugar crash and diabetes to be treated quickly to stop it sugaar worse, cfash you ane usually treat it yourself. You can also have blood sugar that's too high. This is called high blood sugar hyperglycaemia. Low blood sugar usually affects people with diabetes who take insulin or some other diabetes medicines. It's rare in people without diabetes.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1284370009-c309568fadb3446a9487bffa170c28ce.jpg)
0 thoughts on “Blood sugar crash and diabetes”