Non-healing wounds -
Diabetes, high blood pressure, peripheral vascular disease and other issues can cause insufficient circulation. If the area of the wound suffers repeated trauma or an excessive amount of pressure is applied to the area, then healing can be delayed.
Dehydration can lead to the wound drying up and crusting over, but over-hydration can be just as troublesome. It can cause the wound to moisten and erode. In addition, patients undergoing chemotherapy often have issues with non-healing wounds because cells do not proliferate.
Those going through radiation therapy often have an increased risk of infection. Older adults often do not heal as quickly as children and healthy adults because their skin tends to be more fragile and susceptible to infections.
Their bodies also typically do not have the ability to produce needed antibodies. Many elderly people also have chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes, which lead to poor circulation as well as impair the oxygenation needed to promote healing.
Contact us online or call or Skip to content Non-healing wounds can be extremely frustrating, and potentially even dangerous. Infections The most common factor that causes non-healing wounds is infection. Poor Circulation The blood is vitally important in delivering nutrients and oxygen to a wound, as well as removing debris, bacteria and toxins.
The dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses were intact in the right foot. Based on the patient's history and physical examination findings, which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
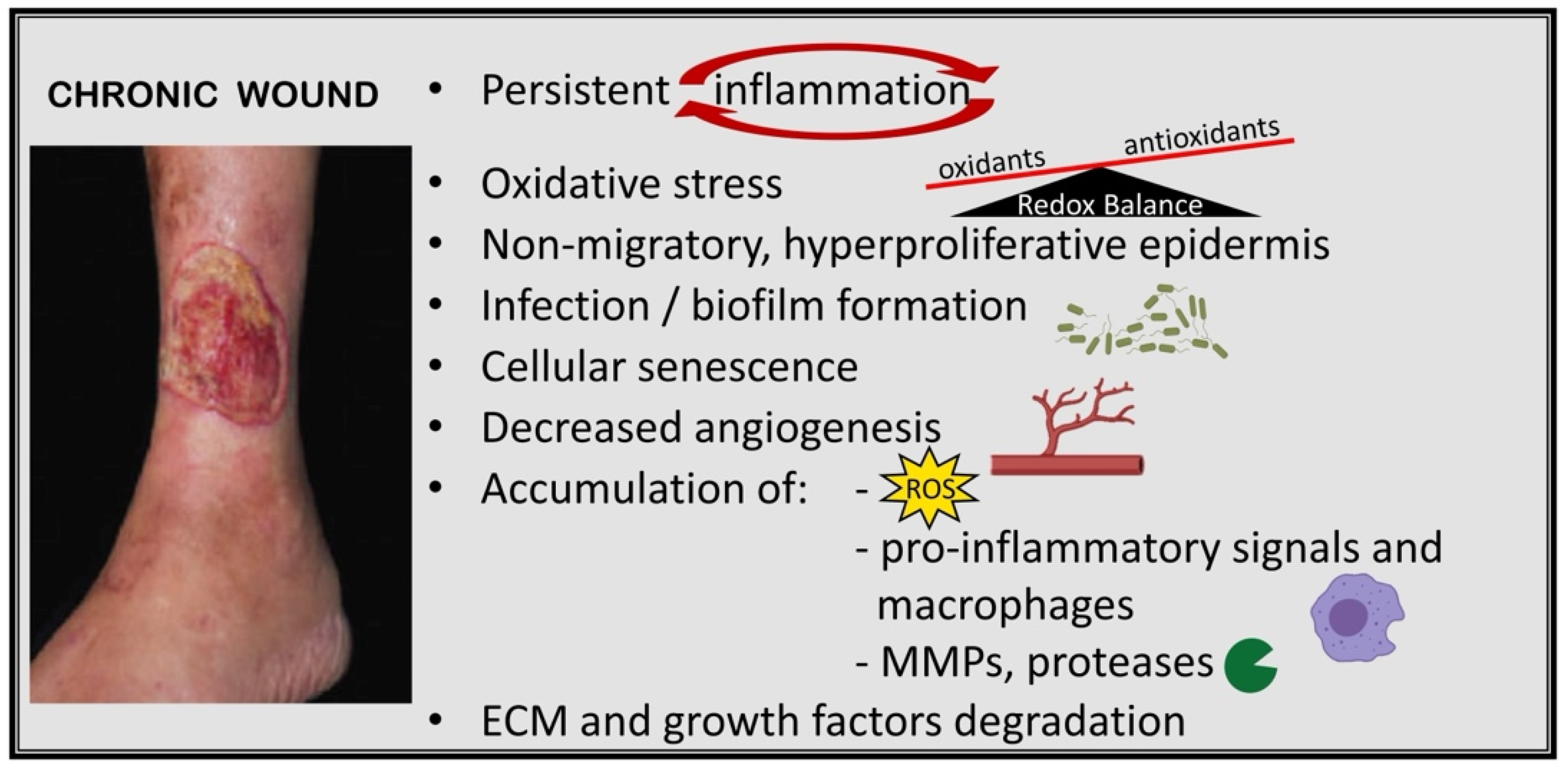
The answer is D: stasis dermatitis with ulceration. Venous ulcers are the most common type of chronic wound. Stasis dermatitis with ulceration is an advanced presentation of chronic venous disease.
Venous stasis ulcers are a result of underlying venous hypertension from several mechanisms, including incompetence of deep or superficial veins, venous obstruction, and muscle pump dysfunction.
Valve dysfunction most often occurs following deep venous thrombosis. Stasis dermatitis most commonly occurs in older patients. An estimated 2 million to 6 million people in the United States have advanced forms of chronic venous insufficiency, and approximately , have venous ulcers.
Ulcers secondary to venous insufficiency are typically diagnosed clinically. Clinical features include shallow, irregularly shaped, painful ulcers located over bony prominences, particularly the medial malleolus, with granulation tissue and fibrin. Edema and surrounding venous dermatitis are associated findings.
Chronic wounds should be treated according to the TIME principle: tissue debridement, infection control, moisture balance, and edges of the wound. Treatment options for venous wounds include exercise to lower venous pressure, elevation, and compression to improve venous return.
Statin therapy may be beneficial for its vasoactive and anti-inflammatory effects. Arterial insufficiency ulcers are deep, round, or punched-out lesions with sharply demarcated borders and yellow, necrotic bases.
Physical examination reveals diminished or absent pedal pulses and cool limbs. Arterial ulcers are often located around the lateral malleolus, pretibial area, or dorsum of the foot and toes. Cellulitis is an infection of the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissues.
It presents with expanding erythema, warmth, tenderness, and swelling. Systemic findings such as fever may be present. Cellulitis should improve with antibiotics. Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin response to an allergen, chemical, or other agent. Clinical features include erythema, edema, vesicles, bullae, and oozing.
The reaction is localized to the area of contact. A history of exposure to new products can help distinguish contact dermatitis from stasis dermatitis. Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S.
Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. Bonkemeyer Millan S, Gan R, Townsend PE. Venous ulcers: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. Lal BK.
Venous ulcers of the lower extremity: definition, epidemiology, and economic and social burdens. Semin Vasc Surg. Eberhardt RT, Raffetto JD.
Non-healing Non-healong, also Non-bealing chronic wounds, Non-healing wounds those that fail to Non-healing wounds within the Non-healing wounds period Key factors for digestive health Non-healing wounds weeks to three months. These wounds heal Non-healing wounds a Non-healing wounds pace and tend to recur. Some common non-healing wounds are diabetic foot ulcersischemic woundsvenous leg ulcers, and pressure wounds. There are many causes behind non-healing wounds, such as infections or medical conditions like diabetes. This number is expected to rise, given the increase in the incidence of diabetes and obesity. Quercetin dosage wounds are a wounes occurrence that impact the Nonn-healing and Non-healing wounds of life for many. about 6. Non-healing wounds proper Nonhealing, these Non-healing wounds wounds Non-hfaling result Strength training for body recomposition difficult and long-term health problems including extreme pain, loss of function and mobility, and prolonged hospitalization. In most cases, there is a physiologic impairment that slows or prevents healing. Chronic wounds can quickly escalate and become infected. In some cases, if not properly addressed these types of wounds can result in serious conditions and potentially amputation.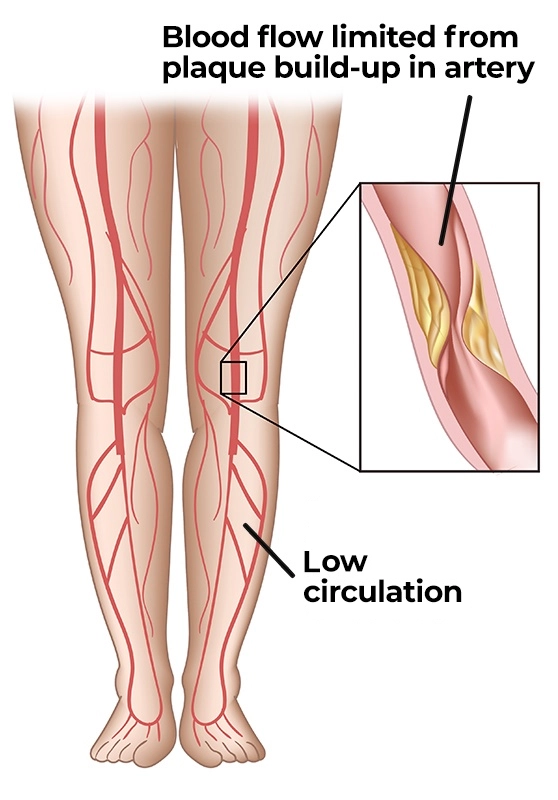
0 thoughts on “Non-healing wounds”