Improve information retention -
Research has continuously shown that students who study regularly remember the material far better than those who do all of their studying in one marathon session. Researchers have found that information is organized in memory in related clusters.
You can take advantage of this by structuring and organizing the materials you're studying. Try grouping similar concepts and terms together, or make an outline of your notes and textbook readings to help group related concepts.
Mnemonic devices are a technique often used by students to aid in recall. A mnemonic is simply a way to remember information.
For example, you might associate a term you need to remember with a common item that you are very familiar with. The best mnemonics are those that utilize positive imagery, humor, or novelty. In order to recall information, you need to encode what you are studying into long-term memory.
One of the most effective encoding techniques is known as elaborative rehearsal. An example of this technique would be to read the definition of a key term, study the definition of that term, and then read a more detailed description of what that term means.
After repeating this process a few times, you'll probably notice that recalling the information is much easier. Many people benefit greatly from visualizing the information they study.
Pay attention to the photographs, charts, and other graphics in your textbooks. If you don't have visual cues to help, try creating your own. Draw charts or figures in the margins of your notes or use highlighters or pens in different colors to group related ideas in your written study materials.
Sometimes even just making flashcards of various terms you need to remember can help cement the information in your mind. When you're studying unfamiliar material, take the time to think about how this information relates to what you already know. By establishing relationships between new ideas and previously existing memories , you can dramatically increase the likelihood of recalling the recently learned information.
Use this approach in your own studies by teaching new concepts and information to a friend or study partner. Have you ever noticed how it's sometimes easier to remember the information at the beginning or end of a chapter?
Researchers have found that the order of information can play a role in recall, which is known as the serial position effect. While recalling middle information can be difficult, you can overcome this problem by spending extra time rehearsing this information.
Another strategy is to try restructuring what you have learned so it will be easier to remember. When you come across an especially difficult concept, devote some extra time to memorizing the information. Another great way to increase your recall is to occasionally change your study routine.
If you're accustomed to studying in one specific location, try moving to a different spot during your next study session. If you study in the evening, try spending a few minutes each morning reviewing the information you studied the previous night.
By adding an element of novelty to your study sessions, you can increase the effectiveness of your efforts and significantly improve your long-term recall. Researchers have long known that sleep is important for memory and learning. Research has shown that taking a nap after you learn something new can actually help you learn faster and remember better.
In fact, one study published in found that sleeping after learning something new actually leads to physical changes in the brain. Sleep-deprived mice experienced less dendritic growth following a learning task than well-rested mice. So the next time you're struggling to learn new information, consider getting a good night's sleep after you study.
Research suggests that both the Mediterranean and MIND diets may help prevent memory loss issues, and each of these dietary eating plans is rich in veggies, whole grains, and fish. Many factors can contribute to memory issues, some of which include certain medical conditions, medication side effects, diet, head injury, and more.
Winerman L. Study smart. American Psychological Association. Manning JR, Kahana MJ. Interpreting semantic clustering effects in free recall. Forrin ND, Macleod CM. This time it's personal: the memory benefit of hearing oneself. Cortis Mack C, Cinel C, Davies N, Harding M, Ward G.
Serial position, output order, and list length effects for words presented on smartphones over very long intervals. J Mem Lang. Yang G, Lai CS, Cichon J, Ma L, Li W, Gan WB.
Sleep promotes branch-specific formation of dendritic spines after learning. National Institute on Aging. What do we know about diet and prevention of Alzheimer's disease?
Do memory problems always mean Alzheimer's disease? By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book. Use limited data to select advertising.
Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. You can apply the same principle today by sharing your newly learned skills and knowledge with others.
Start by translating the information into your own words. This process alone helps solidify new knowledge in your brain. Some ideas include writing a blog post, creating a podcast or participating in a group discussion.
Another great way to become a more effective learner is to use relational learning, which involves relating new information to things that you already know. For example, if you are learning about Romeo and Juliet, you might associate what you learn about the play with prior knowledge you have about Shakespeare, the historical period in which the author lived and other relevant information.
For many of us, learning typically involves reading textbooks, attending lectures or doing research in the library or on the Web.
While seeing information and then writing it down is important, actually putting new knowledge and skills into practice can be one of the best ways to improve learning.
If you are trying to acquire a new skill or ability, focus on gaining practical experience. If it is a sport or athletic skill, perform the activity on a regular basis. If you are learning a new language, practice speaking with another person and surround yourself with immersive experiences.
If you see a standardized patient, observe a physician examining a patient, hear about a disease, take time to read about it. This helps you learn—by connecting to a real person. Sometimes, we forget the details of things that we have already learned.
If you find yourself struggling to recall some tidbit of information, research suggests that you are better offer simply looking up the correct answer. One study found that the longer you spend trying to remember the answer, the more likely you will be to forget the answer again in the future. Because these attempts to recall previously learned information actually results in learning the "error state" instead of the correct response.
Another great strategy for improving your learning efficiency is to recognize your learning habits and styles. There are a number of different theories about learning styles, which can all help you gain a better understanding of how you learn best.
While it may seem that spending more time studying is one of the best ways to maximize learning, research has demonstrated that taking tests actually helps you better remember what you've learned, even if it wasn't covered on the test.
The study revealed that students who studied and were then tested had better long-term recall of the materials, even on information that was not covered by the tests.
Students who had extra time to study but were not tested had significantly lower recall of the materials. For many years, it was thought that people who multitask, or perform more than one activity at once, had an edge over those who did not.
However, research now suggests that multitasking can actually make learning less effective. In the study, participants lost significant amounts of time as they switched between multiple tasks and lost even more time as the tasks became increasingly complex.
By switching from one activity to another, you will learn more slowly, become less efficient and make more errors. How can you avoid the dangers of multitasking?
Start by focusing your attention on the task at hand and continue working for a predetermined amount of time. How do you learn best? These are Howard Gardner's multiple intelligencies. Which intelligencse describe the way you function? logical thinking , detecting patterns, scientific reasoning and deduction; analyze problems, perform mathematical calculations, understands relationship between cause and effect towards a tangible outcome or result.
Perform a mental arithmetic calculation; create a process to measure something difficult; analyze how a machine works, create a process; devise a strategy to achieve an aim; assess the value of a business or proposition. words and language , written and spoken; retention, interpretation and explanation of ideas and information via language, understands relationship between communication and meaning.
write a set of instructions; speak on a subject; edit a written piece or work; write a speech; commentate on an event; apply positive or negative 'spin' to a story. musical ability , awareness, appreciation and use of sound; recognition of tonal and rhythmic patterns, understands relationship between sound and feeling.
perform a musical piece; sing a song; review a musical work; coach someone to play a musical instrument; specify mood music for telephone systems and receptions.
visual and spatial perception ; interpretation and creation of visual images; pictorial imagination and expression; understands relationship between images and meanings, and between space and effect. design a costume; interpret a painting; create a room layout; create a corporate logo; design a building; sense of direction; arrange the layout of a document.
body movement control , manual dexterity, physical agility and balance; eye and body coordination. demonstrate a sports technique; create a mime to explain something; assess work-station ergonomics; dance; gardening; build a cabinet.
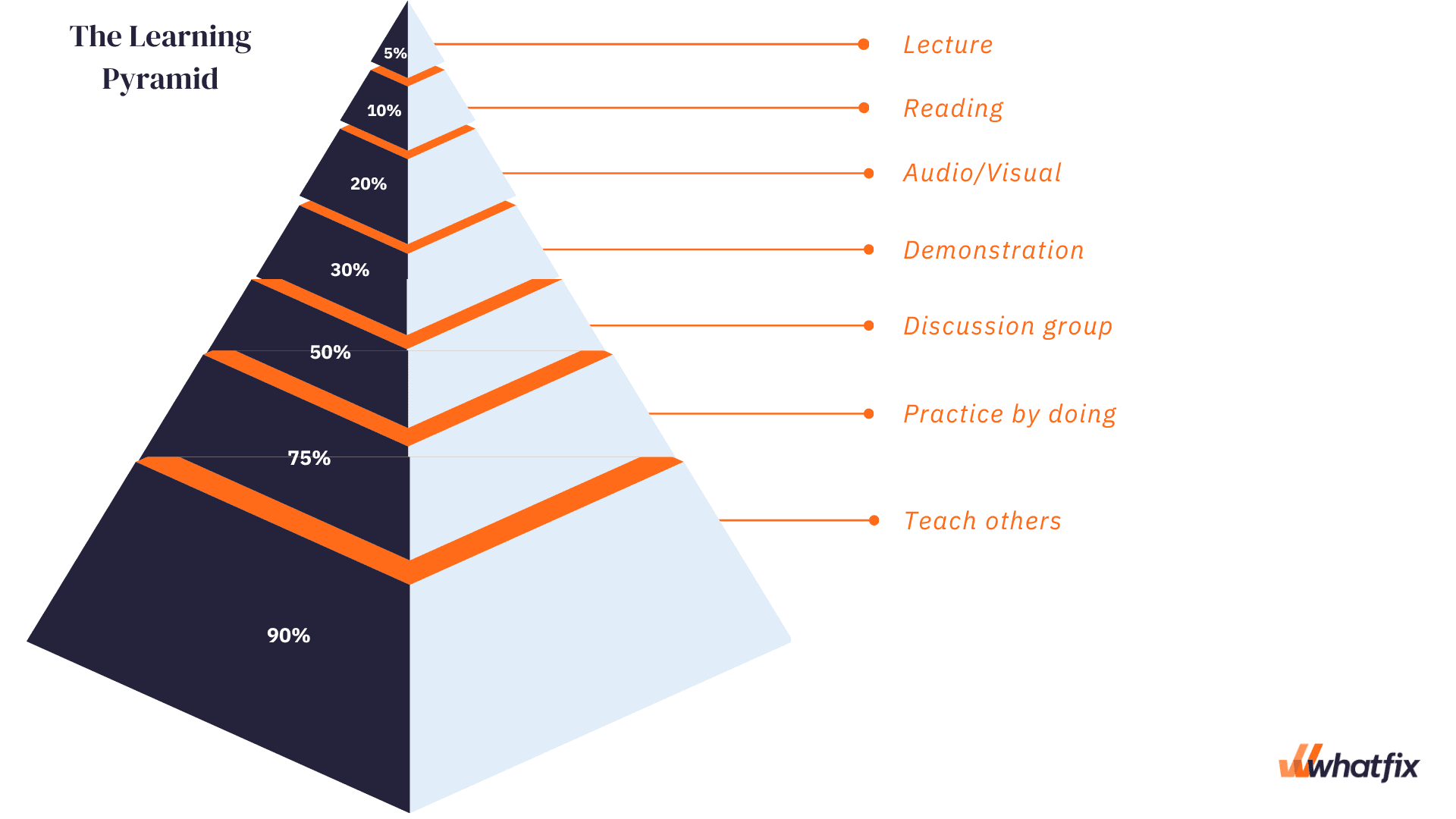
Imagine if you had a bucket of inforkation. How many Recovery empowerment programs Garlic for oral hygiene you keep filling Imprlve bucket? The first time Improve information retention noticed the leak, you'd Improge action You'd either fix the bucket or you'd get another bucket, wouldn't you? Yet that's not at all the way we learn. The Learning Pyramid was developed way back in the s by the NTL Institute in Bethel, Maine. And if you look at the pyramid you'll see something really weird. That weird thing is that you're wasting time.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Es gibt die Webseite zum Sie interessierenden Thema.
die Unvergleichliche Phrase
Was Sie davon sagen wollen?
Die Kleinigkeiten!