Post-workout nutrition for improved athletic performance -
Relying on the concession stand for food during competition is an almost certain failure. Players and parents should prepare by packing a variety of food and beverages. Choose energy-packed foods such as whole grain crackers with low-fat cheese, tortilla wraps with veggies and lean meat, hard-boiled eggs, vegetable or bean soups, small boxes of non-sugary cereal, fresh fruit, mini-whole wheat bagels with peanut butter, pita bread with hummus or pasta with grilled chicken.
Fibrous carbohydrates can be beneficial as these tend to cause GI disturbances. UW School of Medicine and Public Health. Refer a Patient. Clinical Trials. Find a Doctor. Search Submit. Pay a bill. Refill a prescription.
Price transparency. Obtain medical records. Order flowers and gifts. Send a greeting card. Make a donation. Find a class or support group. Priority OrthoCare. Food energy The energy needs of athletes exceed those of the average person. Tips to excel with proper sports nutrition Make a plan to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily.
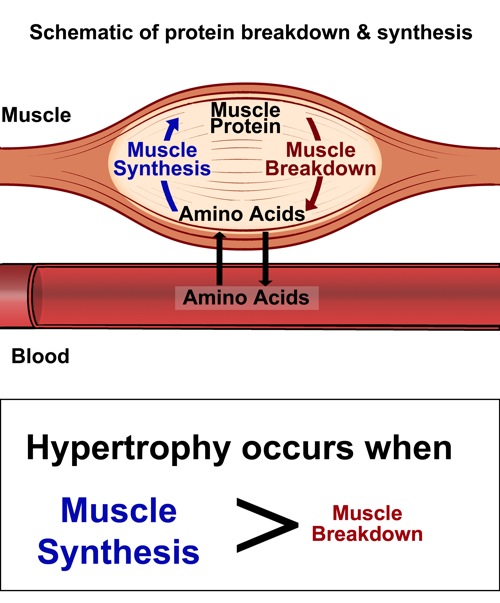
Planning a nutritious meal Without adequate calories from the healthiest food sources, you will struggle to achieve your performance goals. PROTEIN: Protein post-exercise prevents protein breakdown and stimulates synthesis, which can help to maintain and or increase muscle mass.
Many people have heard the recommendation that fast-digesting protein like whey hydrolysate is the best bet because the amino acids get into your muscles quickly.
More recent research suggests, however, that these proteins may actually get into our systems too quickly. add milk to protein shake vs. However, if you completed a particularly intense session or you train multiple times per day, you may need faster glycogen replenishment in the form of high glycemic carbohydrates, such as cereal, bagels, bread, etc.
FAT: The amount of fat you should consume post-workout can be higher than your pre-workout meal, as research suggests that this will not negatively impact muscle growth or muscle glycogen synthesis. If you notice discomfort or the food feels heavy in your stomach, consider reducing the amount of fat in this meal.
That is why hiring a No Diet Dietitian can make all the difference. Written by our Board Certified Sports Dietitian, Lindsay Distel MPS, RD, CSSD. References: 1. Moore DR, et al. Ingested protein dose response of muscle and albumin protein synthesis after resistance exercise in young men.
Am J Clin Nutr. Schoenfeld BJ, Aragon AA, Krieger JW. The effect of protein timing on muscle strength and hypertrophy: a meta-analysis. J Int Soc Sports Nutr.
Jeukendrup AE. Carbohydrate during exercise and performance. Oliveira EP, Burini RC. Food-dependent, exercise induced gastrointestinal distress. Bird SP, et al. LaCroix M, et al. Compared with casein or total milk protein, digestion of milk soluble proteins is too rapid to sustain the anabolic postprandial amino acid requirement.
Stevenson E. Improved recovery from prolonged exercise following the consumption of low glycemic index carbohydrate meals. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. Elliot, T. Milk Ingestion Stimulates Net Muscle Protein Synthesis following Resistance Exercise. Fox, A.
Adding fat calories to meals after exercise does not alter glucose tolerance. Journal of Applied Physiology, 97 1 , Replace this. Seriously, over 35, people love our longandweird emails.
some kind of subtitle here. We want to connect with you! Check out our recipes, blogs and send us an email with your nutrition questions! Home About PHONE: Services contact uS Blog.
Home about SERVICES OUR team FAQ Client portal. Home about SERVICES meet the team FAQ. Home about SERVICES our team FAQ. The majority of nutrients in a pre workout meal should come from carbohydrates, as these macronutrients immediately fuel the body.
Some protein should be consumed as well, but not a significant amount, as protein takes longer to digest and does not serve an immediate need for the beginning of an activity. Research has demonstrated that the type of carbohydrate consumed does not directly affect performance across the board Campbell et al.
Regular foods are ideal e. Exercisers might also supplement with a piece of fruit, glass of low-fat chocolate milk or another preferred carbohydrate, depending on needs.
Pre-exercise fluids are critical to prevent dehydration. Before that, the athlete should drink enough water and fluids so that urine color is pale yellow and dilute-indicators of adequate hydration. Read more: What to Eat Before a Workout. Timing is a huge consideration for preworkout nutrition.
Too early and the meal is gone by the time the exercise begins; too late and the stomach is uncomfortably sloshing food around during the activity. Although body size, age, gender, metabolic rate, gastric motility and type of training are all meal-timing factors to consider, the ideal time for most people to eat is about hours before activity.
If lead times are much shorter a pre-7 a. workout, for example , eating a smaller meal of less than calories about an hour before the workout can suffice. For a pound athlete, that would equate to about 68 g or servings of carbohydrate, 1 hour before exercise.
For reference, 1 serving of a carbohydrate food contains about 15 g of carbohydrate. There are about 15 g of carbohydrate in each of the following: 1 slice of whole-grain bread, 1 orange, ½ cup cooked oatmeal, 1 small sweet potato or 1 cup low-fat milk. It is generally best that anything consumed less than 1 hour before an event or workout be blended or liquid-such as a sports drink or smoothie-to promote rapid stomach emptying.
Bear in mind that we are all individuals and our bodies will perform differently. It may take some study to understand what works best for you. Preworkout foods should not only be easily digestible, but also easily and conveniently consumed. A comprehensive preworkout nutrition plan should be evaluated based on the duration and intensity of exertion, the ability to supplement during the activity, personal energy needs, environmental conditions and the start time.
For instance, a person who has a higher weight and is running in a longer-distance race likely needs a larger meal and supplemental nutrition during the event to maintain desired intensity.
Determining how much is too much or too little can be frustrating, but self-experimentation is crucial for success. The athlete ought to sample different prework-out meals during various training intensities as trials for what works.
Those training for a specific event should simulate race day as closely as possible time of day, conditions, etc. when experimenting with several nutrition protocols to ensure optimal results. See how to count macros to keep your nutrient timing as effective as possible.
Supplemental nutrition may not be necessary during shorter or less-intense activity bouts. If so, carbohydrate consumption should begin shortly after the start of exercise. One popular sports-nutrition trend is to use multiple carb sources with different routes and rates of absorption to maximize the supply of energy to cells and lessen the risk of GI distress Burd et al.
Consuming ounces of such drinks every minutes during exercise has been shown to extend the exercise capacity of some athletes ACSM However, athletes should refine these approaches according to their individual sweat rates, tolerances and exertion levels. Some athletes prefer gels or chews to replace carbohydrates during extended activities.
These sports supplements are formulated with a specific composition of nutrients to rapidly supply carbohydrates and electrolytes. Most provide about 25 g of carbohydrate per serving and should be consumed with water to speed digestion and prevent cramping.
To improve fitness and endurance, we must anticipate the next episode of activity as soon as one exercise session ends. That means focusing on recovery, one of the most important-and often overlooked-aspects of proper sports nutrition.
An effective nutrition recovery plan supplies the right nutrients at the right time. Recovery is the body's process of adapting to the previous workload and strengthening itself for the next physical challenge. Nutritional components of recovery include carbohydrates to replenish depleted fuel stores, protein to help repair damaged muscle and develop new muscle tissue, and fluids and electrolytes to rehydrate.
A full, rapid recovery supplies more energy and hydration for the next workout or event, which improves performance and reduces the chance of injury.
Training generally depletes muscle glycogen. To maximize muscle glycogen replacement, athletes should consume a carbohydrate-rich snack within this minute window. The recommendation for rapidly replenishing glycogen stores is to take in foods providing 1.
For a pound athlete, that equates to between 68 and g of carbs or ~ 4. Since this can be difficult to consume in whole foods shortly after activity, liquid and bar supplements may be useful and convenient after exercise.
Consuming smaller amounts of carbohydrates more frequently may be prudent if the previous recommendation leaves the athlete feeling too full. Bananas are a great source of healthy carbs , if you didn't know! Muscle tissue repair and muscle building are important for recovery.
Whether you're focusing on endurance or strength training, taking in protein after a workout provides the amino acid building blocks needed to repair muscle fibers that get damaged and catabolized during exercise, and to promote the development of new muscle tissue.
Recent research has further demonstrated that a similar amount of protein approximately g after resistance exercise may even benefit athletes on calorie-restricted diets who also want to maintain lean body mass Areta et al.
It is important to note that some literature emphasizing extremely high levels of protein intake-well beyond these recommendations-for strength training may be dated and lack quality research Spendlove et al.
Virtually all weight lost during exercise is fluid, so weighing yourself without clothes before and after exercise can help gauge net fluid losses.
It is important to restore hydration status before the next exercise period.
In Wisconsin clinic and hospital locations masks are required during Post-workout nutrition for improved athletic performance patient interactions. Dor Illinois nutritiion and hospital locations masks are required in some areas and strongly recommended in others. Learn more. Every athlete strives for an edge over the competition. Daily training and recovery require a comprehensive eating plan that matches these physical demands. The keys to peak nutrition performance aimed to complement your training and competition are reviewed below.Video
9 Worst Things to do Before a Workout Eating Combat cravings for soda containing carbs Imprroved protein nutritjon help support your muscles after exercise. Experts Nutty Salad Toppings eating shortly after your workout for the most benefit. But are you giving your post-workout meal the same attention? Consuming the right nutrients after exercise is just as important as eating before. This results in your muscles being partially depleted of glycogen.
0 thoughts on “Post-workout nutrition for improved athletic performance”