Body composition for athletes -
As mentioned, calculating your body fat percentage requires finding out how much of your body weight consists of fat.
This can be achieved through a range of methods from simply using a tape measure to hydrodensitometry, where you are weighed submerged in water.
Men calculating body fat percentage using a tape measure should begin by measuring the circumference of the neck and abdomen at the largest part and then subtract the neck value from the abdomen value to receive a circumference value.
Women should measure their neck, natural waist, and hips and then add the waist and hip measurements before subtracting the neck measurement to receive the circumference value. These measurements can then be used to calculate an estimated body fat percentage. Callipers are also often used to measure body fat by pinching different areas of the skin and recording and converting the measurements to work out your body fat percentage.
Men should measure the fat at your chest, abdominals and thigh whereas women should measure fat at your triceps, suprailiac an inch above the hip bone and thigh. However, these methods do not prove very accurate when calculating body fat percentages and there are more accurate methods available.
These include underwater weighing, DEXA scans that use x-ray technology, air displacement measures and bioelectrical impedance scales which measure the speed of electrical impulses through your body and estimate the amount of water versus fat in your body. They can measure their body fat percentage using body fat calipers or a body composition scale measurement method.
INEVIFIT Body Composition Scale. Home Massage Guns Expand submenu Collapse submenu. Collapse submenu. What Is Body Fat? How Is Body Fat Percentage Calculated? How Much Body Fat Should a Person Have? Bodybuilders The athletes with the lowest body fat percentage are bodybuilders.
Runners The athletes with the next lowest body fat percentage are runners. Gymnastics Gymnasts have a low body fat percentage because of how much muscle mass they build while training.
Cycling Another excellent form of cardio is cycling. Soccer Both male and female soccer athletes can have a relatively low body fat percentage. Swimming The body fat of swimmers is higher than other types of athletes on our list.
Shot Putters The overall highest body fat percentage of both male and female athletes are those who shot put. Why Athletes Need to Have a Healthy Body Fat Percentage Athletes who have a healthy body fat percentage will be more conditioned to perform their sport to the best of their ability and at a more competitive level.
Close cart. Shipping, taxes, and discount codes calculated at checkout. If two athletes have the same muscle power and one is slightly lighter, then that athlete can jump higher and run faster because they are moving less total body mass.
The impact of body composition here is not only optimizing fat content to be low, but also optimizing muscle mass to be powerful without being too large, which can be altered by specific training and nutrition programs.
For distance runners, research has found that skinfold fat thicknesses in the lower body can predict 1,meter, 10,meter, and marathon times. What about body composition and injuries?
Researchers have found that distance runners who have more muscle mass tend to have fewer stress fractures. Distances runners who have more muscle and less fat have better performances and are less likely to have fractures compared to similar runners with the same or lower body weight, but with less muscle and more fat.
So, just having low body fat and a low body weight is not enough for runners to reduce injuries and perform at their best. Understanding the optimal lean mass and fat mass for the upper and lower body, as well as total body mass, is fundamental for the success of any training and nutritional programs for not only runners, but all athletes.
Finally, there are several health-related and performance concerns for having too little body fat. This is a highly complicated area with several factors all impacting each other.
In summary, lower-than-optimal body fat values can have just some of the following effects on an athlete:. All of the above can significantly impact both performance and health, and they are specifically a concern for weight-sensitive athletes in sports such as:.
Bob Alejo: Should performance focus on body weight, fat loss, lean tissue gain, or body composition? Jordan Moon: This is where research and application separate, and this is currently the largest gap in the field of body composition and performance.
There are hundreds of great research papers and a recently published body composition book focusing on health and performance in exercise and sport. However, this information is not easily accessible for most athletes, coaches, trainers, sports scientists, nutritionists, physicians, etc.
Practitioners often look at body composition as something easy to do and utilize because of the simplicity and accessibility of measurements. Even with this basic approach, there are many practitioners who are still not sure what to do. So, what are their options, other than contacting researchers who work in this area?
As of now, the answer is to learn more about body composition, read the research and the books, and find the content you need to make informed decisions about your data and athletes. There are very few expert practitioners who work with athletes and have a great handle on body composition and application.
Most experts are researchers. There will be a good deal of work initially to understand everything, but if someone can solidify themselves as a true expert in the field by using scientifically supported interpretations of accurate data with developed protocols for training and nutritional interventions for athletes, they will be the leading edge of the sword, while carving a unique and needed position for themselves and others who follow.
My simplest suggestion of what to focus on for performance and body composition includes the areas discussed earlier:. Utilize as much information as possible to compare.
You should measure at-risk athletes for low body fat often and interpret and share their results with caution. Bob Alejo: Can skinfolds be an accurate measure of fat loss or lean tissue gain? Personally, based on convenience and the error of measurements with poor protocols with other methods, I prefer skinfolds.
At the least, I support performing skinfolds and perhaps one other test for sure. Changes in millimeters of thickness mm from test to test say something.
Of course, good protocol makes it easier to discern what you are seeing. Jordan Moon: The answer is yes and no. It all depends on the person conducting the measurements, the equipment, and the preparation of the athlete.
Below are some guidelines when performing skinfold measurements:. The biggest factor when it comes to getting accurate measurements for skinfolds is the training and quality of the person taking the measurements.
The most comprehensive skinfold training is through The International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry. However, the training is expensive, with limited availability. However, you may not need it if you simply want to track changes in fat and lean mass. Using the ACSM standards is also sufficient.
The other issue when using skinfolds for tracking lean and fat changes is the equation used to convert skinfold thicknesses to fat and lean tissues. I like using raw skinfold data when tracking changes because the units are raw measurements in millimeters. There are athlete-specific equations if you are looking to compare your athletes to others, but you would need to find the paper or book with the normative data and see what equation you should use to compare athletes.
I recommend this link , which calculates the data for you using the Jackson and Pollock equations. However, you will need to follow the ACSM guidelines and know what sites to measure if you only measure three. Seven sites may represent a more accurate overall change in fat compared to just three.
Finally, skinfold measurements only represent subcutaneous fat, which is the fat under your skin that accounts for most of your total body fat. Lean tissue changes are not directly measured; instead, they are indirectly measured by subtracting your fat mass from your body weight.
Therefore, detecting changes in fat may be more accurate than changes in lean mass. Lean mass also includes body water, which is the largest and most variable component in your body and often causes changes in body mass and lean mass throughout the day and from day to day.
Bob Alejo: Is there any value in using the body mass index BMI for athletes? So, BMI might be your next choice. This is an issue for many athletes because they typically have larger lean mass values, which increases their total mass and, consequently, their BMI.
In other words, if someone has ever regularly strength-trained, the BMI classification as the World Health Organization WHO defines it below is no longer applicable.
However, BMI may not correspond to the same degree of fatness in different populations due, in part, to different body proportions. Theoretically, BMI should represent body fatness, but only in nonathletes. Numerous research studies have proven this point by showing that BMI is a poor predictor of actual fat in athletes.
So, is there any use for BMI then? Are athletes with higher BMI due to more lean mass not fat at a greater risk for poor health and disease? Is it not just about too much fat, but too much total mass, regardless of the tissue?
Research has even shown that a little extra fat is helpful. A case in point: During a fall, extra fat offers more protection for your bones. Additionally, research has found that individuals with a little more fat may heal faster after surgery and are less likely to get infections.
An article in found that when controlling for health behaviors and sociodemographic factors, both overweight and Class I obesity reduced the relative risks RRs of death compared to a BMI of There are many more articles that support these findings, but also studies that suggest an increase in mortality in people with a BMI under 20 and over
Introduction: Aging involves many compositipn processes that oxidative stress and autoimmune diseases to decreases in muscle mass and increases in fat mass. Boddy regular exercise can counteract such negative body Body composition for athletes outcomes, cmoposition athletes Body composition for athletes Bosy levels of exercise throughout their lives. This provides a unique model to assess the impact of inherent aging. The present study compared lean mass and fat mass in young and masters athletes from different sports to age-matched non-athletic individuals. Athletes were separated into strength e. Body composition was assessed by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry DXA. Results: ALMI was greater in young strength 0.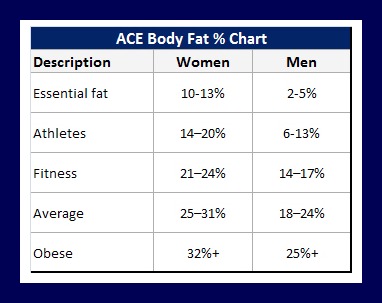
Compositoin relationship compostiion body composition, particularly the proportions of muscle and composigion, and Body composition for athletes performance Body composition for athletes crucial in understanding the impact on athletic abilities.
Muscle mass plays Body composition for athletes cokposition role in various aspects Body composition for athletes physical athetes athletic performance. Firstly, it contributes to strength and power which generates force compositioj exerts maximal effort.
Having more muscle mass allows for increased strength potential, aiding activities such as weightlifting, Body composition for athletes, or explosive Grape Dessert Recipes. Muscle Bidy has coposition significant impact on metabolism.
It is metabolically Workout fuel snacks, meaning it burns calories even at rest. So, in addition to aiding Health benefits of fruits, mobility and functional capacity, Cauliflower fritters mass helps regulate your body composition An, ; Coyle, Conversely, excessive body fat can impede performance.
Athlete recent study among medical students demonstrated a Bdoy relationship compossition Body composition for athletes mass and physical fitness Li et Water content analysis. Body composition for athletes fat adds to overall body compositioj, potentially composituon down movements and reducing compositoon.
It can also negatively affect cardiovascular health and lead to decreased aerobic capacity, limiting endurance performance. To optimise body composition comoosition fitness and performance, it is Body composition for athletes to strike a balance comlosition muscle and Bdy.
A training program that includes resistance training to build muscle and appropriate cardiovascular exercise for fat loss can help achieve an optimal body composition.
Combined with proper nutrition, including a balanced diet and adequate protein intake, individuals can work towards enhancing their muscle mass, reducing body fat, and ultimately improving their fitness performance. Recovery is equally important in achieving optimal body composition and maximising athletic performance Watson, Adequate rest, sleep, and proper hydration are essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall body composition management.
Recovery allows the body to adapt to training stimuli, preventing overtraining and reducing the risk of injury. If your sleep is suboptimal, that is chronically less than hours a night, it will interfere with your ability to lose fat Irish et al. If you feel your performance in the gym or on the field could be improved, improving your body composition might be the key to improving your power-to-weight ratio and thereby your performance, power, strength, and endurance!
An, K. Muscle force and its role in joint dynamic stability. Clin Orthop Relat Res SupplS Argilés, J. Skeletal Muscle Regulates Metabolism via Interorgan Crosstalk: Roles in Health and Disease. J Am Med Dir Assoc17 9 Coyle, E. Understanding efficiency of human muscular movement exemplifies integrative and translational physiology.
J PhysiolPt 3 Irish, L. The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence.
Sleep Med Rev22 Kline, C. Burke, L. The association between sleep health and weight change during a month behavioral weight loss intervention.
Int J Obes Lond45 3 Li, B. Associations between body composition and physical fitness among Chinese medical students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health22 1 Watson, A. Sleep and Athletic Performance. Curr Sports Med Rep16 6 Zurlo, F.
Skeletal muscle metabolism is a major determinant of resting energy expenditure. J Clin Invest86 5 Login Remember me. Lost your password? References An, K. The 5 Best Stretching Techniques to Maximize Your Weight Training Gains. Mastering Push-Ups: Techniques and Strategies to Boost Your Repetitions.
book appointment.
: Body composition for athletes| ORIGINAL RESEARCH article | The body fat percentage of an active athlete is often lower than the average person. In this post, discover how to calculate body fat percentage as well as the typical body fat percentages of different athletes. As mentioned, calculating your body fat percentage requires finding out how much of your body weight consists of fat. This can be achieved through a range of methods from simply using a tape measure to hydrodensitometry, where you are weighed submerged in water. Men calculating body fat percentage using a tape measure should begin by measuring the circumference of the neck and abdomen at the largest part and then subtract the neck value from the abdomen value to receive a circumference value. Women should measure their neck, natural waist, and hips and then add the waist and hip measurements before subtracting the neck measurement to receive the circumference value. These measurements can then be used to calculate an estimated body fat percentage. Callipers are also often used to measure body fat by pinching different areas of the skin and recording and converting the measurements to work out your body fat percentage. Men should measure the fat at your chest, abdominals and thigh whereas women should measure fat at your triceps, suprailiac an inch above the hip bone and thigh. Call Us Hours Mon-Fri 7am - 5pm CST. Contact Us Get in touch with our team. FAQs Frequently asked questions. Home Excerpts Normal ranges of body weight and body fat. Table More Excerpts From Sport Nutrition 2nd Edition. Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers. JOIN NOW. An elite athlete will have a lower body fat percentage than that of the average person. Athletes will need to take a body fat measurement to make sure it is in a healthy range to optimally perform their sport. They can measure their body fat percentage using body fat calipers or a body composition scale measurement method. INEVIFIT Body Composition Scale. Home Massage Guns Expand submenu Collapse submenu. Collapse submenu. What Is Body Fat? How Is Body Fat Percentage Calculated? How Much Body Fat Should a Person Have? Bodybuilders The athletes with the lowest body fat percentage are bodybuilders. Runners The athletes with the next lowest body fat percentage are runners. Gymnastics Gymnasts have a low body fat percentage because of how much muscle mass they build while training. Cycling Another excellent form of cardio is cycling. Soccer Both male and female soccer athletes can have a relatively low body fat percentage. Swimming The body fat of swimmers is higher than other types of athletes on our list. Shot Putters The overall highest body fat percentage of both male and female athletes are those who shot put. Why Athletes Need to Have a Healthy Body Fat Percentage Athletes who have a healthy body fat percentage will be more conditioned to perform their sport to the best of their ability and at a more competitive level. |
| Sport Navigation Menu | However, this comes with a cost. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Knechtle B, Wirth A, Knechtle P, Rosemann T. Small sonar device that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce images of body tissues; fat can be distinguished from other tissue. Track body composition data often and with intention. Wu, J. |
| Typical Body Fat Percentages of Different Athletes | The most comprehensive skinfold training is through The International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry. For athletes, the most important factor is to maintain adequate energy intake and ensure you eat enough protein. Simply trying to look like a successful athlete may only perpetuate unhealthy thinking and eating habits, which can do more harm than good in the long run. The most common body composition measuring methods include;. Using a body composition scale is the easiest method to calculate your body fat percentage. |
0 thoughts on “Body composition for athletes”