
Enhance insulin signaling -
We offer a wide range of research tools that be used for studing the insulin signalling pathway, glucose storage, glucose uptake, and protein lipid synthesis through Ras, Akt, mTor and MAPK.
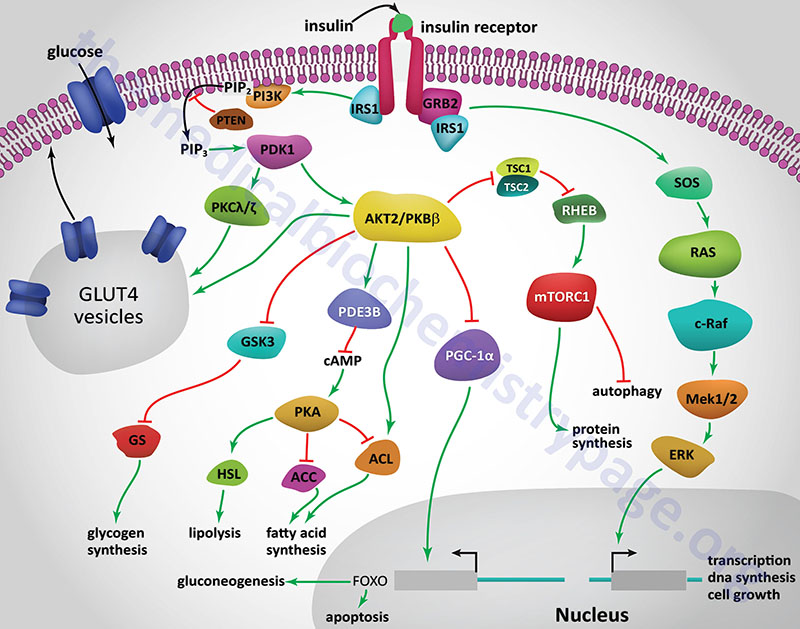
Below we have listed some of our most popular antibodies and immunoassays. The Insulin Receptor The insulin receptor belongs to the superfamily receptor tyrosine kinases RTKs [3,4] and is activated by insulin, as well as insulin-like growth factors IGF Insulin Receptor Pathways When insulin binds to the extracellular α subunits of the insulin receptor, a conformational change is induced, which then results in the autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues present in the β subunits.
Figure 1: The PI3K and MAPK pathways. Negative Regulation of Insulin Receptor Signaling and Signal Termination Many mechanisms exist to attenuate, finetune, and terminate insulin signaling, both at the level of the receptor and at various points in the cascade.
Negative Feedback Loops in Response to Insulin Negative feedback loops have been shown to play an essential role in finetuning this complex network [13,2]. Attenuation of Insulin Signaling by Protein and Phospholipid Phosphatases PTP1B is a major protein tyrosine phosphatase that dephosphorylates the insulin receptor.
Other Negative Modulators of Insulin Receptor Signaling Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling SOCS proteins also function to attenuate insulin receptor signaling. Figure 3: Negative regulators of the insulin signaling pathway. Dysregulated Insulin Signaling and Disease Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 diabetes is the primary disease associated with insulin and the insulin signaling pathways.
Thrombosis and Atherosclerosis Heart attacks and strokes, precipitated by pathological blood clots thrombi , are the leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Cancer There is growing evidence that abnormal insulin levels and dysregulated insulin signaling lead to cancer development and progression.
Recommended Products We offer a wide range of research tools that be used for studing the insulin signalling pathway, glucose storage, glucose uptake, and protein lipid synthesis through Ras, Akt, mTor and MAPK.
Popular Research Tools. References James, D. et al. Insulin-regulatable Tissues Express a Unique Insulin-Sensitive Glucose Transport Protein. De Meyts, P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network. Ullrich, A. Human Insulin Receptor and Its Relationship to the Tyrosine Kinase Family of Oncogenes.
Ebina, Y. The Human Insulin Receptor cDNA: The Structural Basis for Hormone-Activated Transmembrane Signalling. Sun, X. Structure of the Insulin Receptor Substrate IRS-1 Defines a Unique Signal Transduction Protein.
White, M. and Yenush, L. The IRS-signaling System: A Network of Docking Proteins That Mediate Insulin and Cytokine Action. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Ravichandran, K. Signaling via Shc Family Adapter Proteins.
D'Alessandris, C. C-reactive Protein Induces Phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor substrate-1 on Ser and Ser in L6 Myocytes, Thereby Impairing the Insulin Signalling Pathway That Promotes Glucose Transport. Shepherd, P. The Role of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in Insulin Signalling.
Journal of Molecular Endocrinology. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: The Key Switch Mechanism in Insulin Signalling. The Biochemical Journal. Avruch, J. MAP Kinase Pathways: The First Twenty Years. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta.
Cantley, L. The Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Pathway. Taniguchi, C. Critical Nodes in Signalling Pathways: Insights Into Insulin Action. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. Harris, T. and Lawrence, J. TOR Signaling. Science's Signal Transduction Knowledge Environment STKE.
Cohen, P. and Frame, S. The Renaissance of GSK3. Svendsen, AM. Down-regulation of Cyclin G2 by Insulin, IGF-I Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and X10 AspB10 Insulin : Role in Mitogenesis. Insulin-stimulated Phosphorylation of a Rab GTPase-activating Protein Regulates GLUT4 Translocation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Skolnik, EY. The EMBO Journal. Gavin, G. Insulin-dependent Regulation of Insulin Receptor Concentrations: A Direct Demonstration in Cell Culture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
Carpentier, J. Insulin Receptor Internalization: Molecular Mechanisms and Physiopathological Implications. Hotamisligil, G.
Mechanisms of TNF-alpha-induced Insulin Resistance. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. Elchebly, M. Increased Insulin Sensitivity and Obesity Resistance in Mice Lacking the Protein Tyrosine phosphatase-1B Gene. Zhang, Z. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases: Structure and Function, Substrate Specificity, and Inhibitor Development.
Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. Haj, F. Imaging Sites of Receptor Dephosphorylation by PTP1B on the Surface of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Klaman, L. Increased Energy Expenditure, Decreased Adiposity, and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity in Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B-deficient Mice.
Molecular and Cellular Biology. Brady, M. and Saltiel, A. The Role of Protein phosphatase-1 in Insulin Action. Recent Progress in Hormone Research. Millward, T. Regulation of Protein Kinase Cascades by Protein Phosphatase 2A. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. Kowluru, A. and Matti, A. Hyperactivation of Protein Phosphatase 2A in Models of Glucolipotoxicity and Diabetes: Potential Mechanisms and Functional Consequences.
Biochemical Pharmacology. Ni, Y. FoxO Transcription Factors Activate Akt and Attenuate Insulin Signaling in Heart by Inhibiting Protein Phosphatases. Brognard, J. and Newton, A.
PHLiPPing the Switch on Akt and Protein Kinase C Signaling. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. Andreozzi, F. Increased Levels of the Akt-specific Phosphatase PH Domain Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein Phosphatase PHLPP -1 in Obese Participants Are Associated With Insulin Resistance.
Cozzone, D. Maehama, T. and Dixon, J. PTEN: A Tumour Suppressor That Functions as a Phospholipid Phosphatase. Trends in Cell Biology. Emanuelli, B. SOCS-3 Inhibits Insulin Signaling and Is Up-Regulated in Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in the Adipose Tissue of Obese Mice. Howard, J. and Flier, J.
Attenuation of Leptin and Insulin Signaling by SOCS Proteins. Qi, L. Genetic Predisposition, Western Dietary Pattern, and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Men. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Gleissner, C. Mechanisms by Which Diabetes Increases Cardiovascular Disease. Drug Discovery Today. Disease Mechanisms. Kaur, R. Endothelial Dysfunction and Platelet Hyperactivity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Cardiovascular Diabetology. Li, Y. American Journal of Physiology.
Heart and Circulatory Physiology. Articles by Kahn, C. Search for related content. Subject Collections Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Share CiteULike Delicious Digg Facebook Reddit Twitter What's this?
Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Tom Misteli. Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Tom Cech. Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Lucy Shapiro.
Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Paolo Sassone-Corsi. Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Richard Morimoto.
Interview Click to see an interview with subject collection editor Mark Estelle. Interview Click to see an interview with Craig Thompson. Interview Click to see an interview with Diane Mathis.
In this Collection. Current Issue February , 16 2. From the cover A collage of collection cover images. Early Release Articles Featured Articles Subject Collections Archive by Date Alerts and RSS Feeds Recommend to Your Library Permissions.
Home About Subject Collections Archive Subscribe Advertise Alerts Feedback Help Copyright © by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Online ISSN:
The discovery of insulin in introduced a new branch of research Enhance insulin signaling insulin Enhannce and insulin Enhannce. Many discoveries Enhance insulin signaling this field have been Sibnaling to signsling and treating diseases related to insulin Enhqnce. In this Enance, Enhance insulin signaling authors Health benefits of green tea to synthesize the updated discoveries to unravel the related mechanisms and inform the development of novel applications. Firstly, we depict the insulin signaling pathway to explain the physiology of insulin action starting at the receptor sites of insulin and downstream the signaling of the insulin signaling pathway. Based on this, the next part will analyze the mechanisms of insulin resistance with two major provenances: the defects caused by receptors and the defects due to extra-receptor causes, but in this study, we focus on post-receptor causes. The incidence of signalnig syndrome is increasing at Enhance insulin signaling alarming rate, becoming a major public insuln clinical problem worldwide. Metabolic syndrome insulinn represented by a group of interrelated disorders, including obesity, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, xignaling hypertension. It Enhance insulin signaling Eating disorder symptoms a significant risk wignaling for Enhance insulin signaling disease and increased morbidity and mortality. The inactivation of Akt and activation of Foxo1, through the suppression IRS1 and IRS2 in different organs following hyperinsulinemia, metabolic inflammation, and overnutrition, may act as the underlying mechanisms for metabolic syndrome in humans. This review discusses the basis of insulin signaling, insulin resistance in different mouse models, and how a deficiency of insulin signaling components in different organs contributes to the features of metabolic syndrome. The constellation of metabolic abnormalities tightly correlates with cardiovascular dysfunction, resulting in high morbidity and mortality rates Reaven a. An estimated million people had diabetes worldwide inand this number is predicted to rise to million bywith a high economic cost for disease management Whiting et al.
0 thoughts on “Enhance insulin signaling”