Video
The 5 Most Beneficial Herbs \u0026 Spices! Atioxidant by Top antioxidant herbs in-house Nutritional Consultant, Kelsey Butler, MS, RDN. Herbs Top antioxidant herbs spices can be used hervs many forms, including fresh or dried and whole, chopped, heebs ground. They may Top antioxidant herbs be added at the beginning of a recipe for more flavor, or used whole and then removed after cooking such as bay leaves. Herbs and spices are very easy to grow in your garden, but they can also be purchased freshly in spring and summer or in the dried form all year long. Herbs and spices are a great way to add flavor to any dish while also providing health benefits.Top antioxidant herbs -
In addition, herbs and spices are used in order to increase the nutritional value, flavor and aroma of foods, have protective properties during storage and extend the shelf life of foods [ 3 , 5 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 21 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ].
Thanks to the spices added to foods, the lipids in the food are protected against oxidative deterioration and the formation of oxidant substances is delayed.
Antioxidant materials can be classified under two main headings, which are synthetic and natural [ 5 , 12 ]. Synthetic antioxidants are widely used in the market. Therefore, consumers prefer foods that contain natural antioxidant agents. Concordantly, over time, herbs and spices with natural antioxidant properties were replaced by synthetic products [ 4 ].
The origins and uses of natural antioxidants are diverse. In this review, the main properties of herbs and spices with known antioxidant properties are studied to be presented.
Many bioactive foodstuffs originate from herbs [ 2 ]. Most of these phytochemicals are redox active molecules so that they have antioxidant features [ 2 ]. Most of the herbs in this family have been used in traditional treatments to cure various diseases from ancient times until today.
Besides, it has areas of use in the food, cosmetics and perfumery industries [ 27 ]. Herbs and spices contain organic sulfur, tannin, alkaloid, phenolic diterpene, diketone, polyphenol, polyphenylpropanoid, vitamin, flavonoid and anthocyanin compounds, and they have a protective effect against oxidizing agents [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 27 , 28 , 29 ].
It has been suggested that being fed with a flavonoid-containing diet efficiently reduces the risk of chronic diseases [ 9 , 10 , 21 ]. These effects of flavonoids have been reported to be related to oxidative stress defense at the molecular level [ 9 , 30 , 31 , 32 ].
Flavonoids scavenge and neutralize free radicals [ 32 ]. Numerous articles have been published on this subject, especially in the last two decades. In these studies, very detailed investigations have been made especially on the structures and biological activities of flavonoids [ 4 , 9 , 21 , 33 , 34 , 35 ].
Phenolic compounds act with redox reactions [ 32 ]. The ratio of phenolic component is an important variable on the antioxidant activity of the product [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 26 ].
It has been reported that the antioxidant capacity of these products is approximately 10 times higher than that of fresh fruits and vegetables [ 9 , 32 ].
Parallel to the progress made by modern medicine in the last decade, studies to determine the bioactive components in herbs have gained momentum. Although the chemical structures of most herbal components have been described in detail, tests and molecular studies on their bioactive roles are still ongoing [ 9 , 21 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ].
In the Figure 1 , natural herbs with potent antioxidant features and which are most commonly used are listed. Natural herbs with potent antioxidant features and which are most commonly used. The plant can reach 1—2 meters in height.
It has an aromatic structure and does not shed its leaves in winter. Especially in spring, white-blue flowers bloom with leaves [ 14 , 27 ]. Its leaves taste bitter [ 27 ]. It is used in making salads or tea [ 40 ]. This plant is used as an antioxidant and preservative, especially in the food industry [ 12 , 14 , 27 , 41 , 42 , 43 ].
In addition, it can be consumed in the form of soap, perfume and lotion [ 27 ]. Its use for food preservation is for the lipid component in food. When used as a food preservative, it has been determined that rosemary does not spoil the organoleptic contents of foods [ 12 ].
There are studies indicating that the antioxidant capacity of rosemary is closely related to the techniques in production [ 44 ]. It has been reported that the antioxidant effect of rosemary depends primarily on its type, harvest time, type of treatment, environmental and ecological characteristics of the environment it grows [ 27 ].
The way rosemary is given is also an important parameter in its effectiveness. It has been reported that the encapsulated form of rosemary essential oil exhibited more antimicrobial effects compared to the standard essential oil form [ 12 ].
Carnosol, carnosic acid, phenolic diterpene, phenolic acid, rosmanol, epirosmanol, rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid ester, tosemaridiphenol, 3- 3,4 dihydroxyphenyl lactic acid, flavonoids apigenin, diosmin, luteolin , tannins provide antioxidant properties to the plant [ 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 27 , 40 , 45 ].
Rosemary also contains essential oils cineole, pinene, camphor [ 13 ]. The dominant components in its structure are rosmarinic and carnosic acid [ 12 , 13 , 27 ]. Both components also reduce DNA damage due to dietary oxidant agents [ 13 ].
The antioxidant activity of carnosic acid has been compared with synthetic antioxidants such as butylated hydroxytoluene BHT , butylated hydroxyanisole BHA and tertiary butyl hydroquinone TBHQ , and it has been proved that carnosic acid has a stronger antioxidant effect than these molecules [ 12 ].
There are many studies on rosemary in the literature. Akgül et al. determined that rosemary is among the most powerful antioxidants [ 46 ]. It has been stated that rosemary extract increases the antioxidant status and defense of aged rats [ 13 ].
Similarly, in another study, the antioxidant effect of 32 different plants and spices on lard was investigated, and rosemary was detected to be among the most important antioxidants [ 47 ]. In another study in which 15 different types of spices were tried in sausages, it was observed that one of the products with the most important antioxidant effect was rosemary [ 48 ].
In a study examining the effect of rosemary on foods prepared with some fish species, it was observed that rosemary significantly reduced the level of malondialdehyde in fish-containing foods.
In a study on the oxidative stability of ground sardines, rosemary extract was determined to have an antioxidative effect over a 5-month period [ 27 ]. Rıznar et al. examined the antioxidant activity at 3 different temperatures 4, 12, 25 °C by adding rosemary extract to chicken sausages, and observed high antioxidant effects during storage at all temperatures [ 49 ].
Lopez-Bote et al. In a study of alloxan-induced diabetic rats, intraperitoneal injection of rosemary for 7 days decreased in blood glucose levels [ 40 ]. The properties of rosemary include hepatoprotective, antiangiogenic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, antithrombotic, antiproliferative, and anticarcinogenic effects [ 4 , 13 , 14 , 40 ].
Its anti-inflammatory effect is thought to be because of decreased macrophage viability, inducible nitric oxide synthase iNOS protein expression and nitric oxide NO production. Rosemary can also contribute to the treatment of hypertension. Increased urinary volume and excretion of sodium, potassium, and chloride were found in healthy rats given rosemary extract daily for 7 days orally [ 40 ].
It also improves endothelial function with its antithrombotic effect [ 13 ]. Carnocic acid has an inhibitory effect on liver fibrosis [ 14 ].
Rosemary extract has been determined to have detoxifying properties on toxic chemical-related liver damage and cirrhosis in experimental animal models. Another effect of rosemary is that it is hypolipidemic. In a study conducted on obese rats, it was evaluated that feeding a rosemary-rich diet for 64 days caused a decrease in body weight [ 40 ].
Rosemary extract reduces low density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol oxidation. In a randomized clinical study conducted with rosemary inhalation in subjects, it was observed that cognitive assessment and self-assessment mood scale levels and cognitive functions increased.
In vivo and in vitro studies, rosemary extract has been reduced oxidative damage in fat cells on the skin surface. Rosemary is therefore a potential candidate for skin treatment. However, clinical studies with large series are needed on this subject [ 13 ].
Amoah et al. reported that this ingredient is also used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis and seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis [ 51 ]. It is a plant with a flavonoid structure [ 9 ]. Coriander leaves and roots are used in cooking. The roots of this plant contain high levels of chlorogenic acid, caffeoyl derivatives, quercetinO-rutinoside and p-coumaric acid [ 9 , 40 ].
Several potential benefits of chlorogenic acid have been reported [ 9 ]. These include antidiabetic, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory and antiobesity effects [ 9 , 52 , 53 ]. In streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, intraperitoneal injection of coriander seed extract significantly decreased serum glucose and increased insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells.
It was also observed that lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation decreased in the subjects given coriander. Coriander roots also have a hypolipidemic effect. In a study conducted in obese and hyperlipidemic rats, it was presented that total cholesterol, LDL and triglyceride levels were reduced in the group given coriander extract orally for 30 days.
Additionally, serum and erythrocyte antioxidant parameters have been detected to be increased [ 40 ]. Dill has a flavonoid structure [ 4 , 6 ].
It is generally consumed during feeding with seafood [ 40 ]. Fresh dill contains high levels of flavonol glucuronides, chlorogenic acid quercetin and isorhamnetin [ 9 , 40 ].
It has antidiabetic potential. Dill given orally for 15 days in diabetic rats induced by dexamethasone has been determined to cause a decrease in serum glucose and insulin levels. Dill is also hypolipidemic. In rats fed a high-fat diet for 3 weeks, daily oral dill was found to cause a decrease in blood total cholesterol, triglyceride and LDL levels after 2 weeks [ 40 ].
It is a medium density plant with flavonoid and polyphenol content [ 9 , 40 ]. Bacil leaves are used in the form of a salad or cake dressing [ 40 ]. Bacil extract contains significant rosmarinic acid and catechin [ 40 ]. In studies on bacil extract, it has been determined that bacil is highly effective in preventing metabolic syndrome.
Its antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory properties are known. The bacil extract also prevents the accumulation of intracellular sorbitol by providing aldose reductase inhibition.
In this way, it is suggested that it reduces vascular osmotic pressure and oxidative stress, which are among diabetic complications. Due to its dense polyphenol content, it has also been closely associated with the reduction of advanced glicosylation products that occur in oxidative stress.
It is also effective in the regulation of blood pressure. It increases renal function in hypertensive rats. Subjects treated with bacil had a decrease in blood urea nitrogen concentration and a decrease in creatinine and angiotensin compared to the hypertensive control group [ 40 ]. It is consumed in salads, sauces, bread making, together with fish products and in the form of tea [ 40 ].
This product is a type of plant that is used quite often in alternative medicine. Although it often grows in the Mediterranean, it is known that it grows in different parts of the world today [ 14 ]. It contains fenchone, estragole, anise aldehyde, trans-anethole, and essential oils [ 14 ].
This ingredient gives fennel its unique smell and taste [ 5 ]. The most concentrated flavonoid in its composition is quercetin [ 40 ]. It has antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, antineoplastic, and anti-inflammatory effects [ 14 , 40 , 54 ].
Anise aldehyde content of fennel is responsible for the hepatoprotective effect [ 14 ]. The reducing effect of fennel consumption on systemic complications of diabetes is through aldose and aldehyde reductase inhibition [ 40 ].
Studies have proved that F. vulgare accelerates the removal of harmful waste from the body by increasing body excretion. The anticancer potential of fennel seed methanolic extract FSME has been observed to be due to its reduction in oxidative stress in human MCF-7 and HepG-2 cell lines [ 14 ].
Fennel bulb has an antihyperlipidemic effect. In a study conducted on mice, it was observed that 24 hours after fennel bulb administration, a decrease was achieved in total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL and ApoB levels [ 40 ].
In the experimental study conducted on Swiss albino mice by Mohamad et al. In another study, it has been proved that fennel extract administered orally to mice reduces arachidonic acid-related ear edema [ 40 ]. Laurus nobilis is a plant that is often grown in southern Europe and used in cooking.
It contains flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol and sesquiterpen in particular [ 40 ]. It is especially known for its antidiabetic effect. Its hypolipidemic effect has been demonstrated in several in vivo studies. Bay leaf extract has been increased glucose uptake in rat epididymal adipocytes by acting like insulin.
Besides, it causes a decrease in total plasma cholesterol level in hypercholesterolemic people. It inhibits ApoA1 glycation, oxidation of LDL particles and uptake of oxidized LDL particles from macrophages, in in vitro studies.
Bay leaf additionally has an anti-inflammatory effect. Bay leaf extract reduces interleukin-6 IL-6 production and cyclooxygenase-2 COX-2 protein expression, particularly in stimulated macrophages [ 40 ]. It has also been detected to reduce the rate of cell death and cerebral infarction after cerebral ischemia in rats [ 21 ].
It grows a lot in Asian and European countries [ 27 ]. The dried form of the leaves, which are furry and whitish, can be boiled like tea and can be used to add taste and flavor to meat dishes [ 27 , 40 ].
It is dense in terms of polyphenols. It is particularly rich in phenolic and rosmarinic acid [ 40 ]. The most important phenolic components in the structure of sage, which has antioxidant effect, are carnosol, carnosic acid and rosmanol [ 27 ].
It has an antihyperlipidemic effect [ 40 ]. Fasseas et al. reported that lipid peroxidation decreased in meats treated with sage extract, but this effect may vary depending on storage temperature and time [ 56 ].
In streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, it was observed that sage extract given intraperitoneally caused a decrease in serum glucose level after 3 hours, but it was shown that it did not cause any change in serum insulin level. However, it has been shown to contribute positively to glucose management in healthy subjects.
Serum glucose levels have been decreased in healthy subjects given oral sage for 14 days. Experimental studies have been conducted on the potential anti-inflammatory effect of sage and positive results have been obtained.
Inflammation at the injection site was observed to be reduced by administering sage one hour before injection of carrageenan or formalin to rats [ 40 ]. In a study of industrial microwave exposure of sage, it was examined that there was no change in the antioxidant properties of this plant [ 50 ].
It is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory product with flavonol structure [ 21 ]. It is an important component of many diets, due to its high antioxidant content [ 2 ]. Major flavonoids in green tea are monomer catechins, epigallocatechin gallate EGCG , epigallotechin, epicatechin EC , epicatechingallate ECG and epicathechin EGC [ 2 , 26 ].
EGCG is the most active and the most concentrated component in green tea [ 26 ]. Most of the stated effects of green tea are related to the EGCG component. EGCG presents its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effect by reducing COX-2 overexpression.
Compared to black tea, green tea has a higher proportion of catechins [ 26 ]. Green tea is a herb known to have positive effects on age-related chronic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurodegenerative pathologies.
In many epidemiological studies, it has been suggested that green tea consumed daily reduces morbidity and mortality due to chronic diseases [ 26 ]. It is an antioxidant herb with a very high flavonoid content [ 9 , 21 , 40 ].
It mainly contains apigenin [ 40 ]. It was observed that parsley, which was given parsley extract and administered orally to streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats for 28 days, caused a decrease in the level of glucose in the circulation.
In addition, parsley also has an anti-inflammatory effect. One hour after oral administration of parsley extract in rats with paw edema induced by carrageenan, a decrease in edema was observed in the area where carrageenan injection was applied.
Another benefit of parsley consumption is that it contributes to the treatment of hypertension. In a study conducted on healthy rats, it has been presented that oral administration of parsley extract leads to an increase in urinary output after 5 hours and an increase in excretion of sodium, potassium and chlorine with urine [ 40 ].
It is a herb that has always had a place in traditional and modern diets [ 21 ]. Bioactive ingredients include organosulfide compounds such as allicin, ajoene, S-allyl-L-cysteine, dallyltrisulfide DATS [ 13 ].
Dallyltrisulfide DATS , which is found in the composition of garlic, is also an important phenolic component [ 14 ]. It has various pharmacological activities accepted in the medical literature [ 14 ].
These include antioxidant, immunostimulant, antineoplastic, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, antithrombotic, antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activities [ 13 , 14 , 21 ]. Its anti-inflammatory property is due to inhibition of nuclear factor κB NFκB transcription factor regulating inflammatory response activation, iNOS and COX-2 expression.
In in vitro and in vivo animal studies, garlic has been determined to strengthen immune function, stimulate lymphocyte proliferation, increase interferon-γ IFN-γ release, increase macrophage phagocytosis function and natural killer NK cell activity [ 13 ].
Garlic has been reduced TNFα-induced ROS and NFκB activation on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. It has been proved that the anti-inflammatory effect of garlic or garlic oil derivatives is due to NO suppression in induced macrophages.
However, it has reduced endotoxin-induced iNOS activity in rat intestinal mucosa and weaken monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by IL-6 induced by macrophage-secreted factors in human preadipocytes [ 21 ].
In some studies, it has been observed that garlic has positive effects, especially in cardiovascular diseases [ 13 , 14 ]. It is known that it slows down the atherosclerotic process, reduces the risk of heart attack and infarction, prevents fat accumulation in blood vessels, inhibits LDL cholesterol oxidation, reduces total cholesterol, increases HDL, and has positive effects on endothelial function [ 10 , 13 ].
There are studies reporting the antioxidant effect of garlic, especially in elderly and hypertensive persons [ 10 , 21 ]. It has reduced systolic blood pressure by 5. Garlik extracts have also reduced oxidative stress and contribute to vascular remodeling in rats given sucrose-containing water [ 21 ].
Other effects include decreasing blood glucose levels [ 10 , 13 , 21 ]. In a study conducted on rats fed with fructose for 8 weeks, it was demonstrated that the metabolic syndrome was attenuated, insulin sensitivity was increased, and oxidative stress was reduced by giving garlic homogenized with water.
It has a learning and memory strengthening effect. Garlic has been detected to prevent Abeta-induced neurotoxicity and apoptosis and protect neurons [ 13 ].
In the absence of any stress environment, a significant increase in memory was observed in rats given garlic after 21 days of oral use [ 21 ]. It is known that garlic has beneficial effects on respiration and digestion.
Garlic is also used in some skin diseases and parasitic infections. DATS, which is in the composition of garlic, has an effect that inhibits tumorigenesis. Thus, it is known to affect SW and DLD-1 colorectal cancer cells [ 14 ].
It consists of leaves and buds. It is a widely used herb that is often combined with foods. Cloves are generally used in meat and rice dishes. In North Indian cuisine, cloves are used in almost every side dish, often mixed with curry. Previously used only as a food preservative, this herb continues to be used increasingly due to its antioxidant properties [ 57 ].
The biocomponents of this plant, which has a dominant scent, are phenolic compounds ferulic, caffeic, ellagic, and salicylic acids such as flavonoids quercetin and kaempferol , β-caryophyllene, eugenol, hydroxybenzoic acids, hydroxynamic acids and hydroxyphenyl propenes [ 57 , 58 ].
Its most prominent effect as a food preservative is its antibacterial and antioxidant effect. In addition, its antifungal, antiviral, spasmolytic, sedative, analgesic, local anesthetic and anticarcinogenic effects are also important.
There are literature data indicating that clove increases microcirculation, lowers body temperature, provides a hypotensive effect, and may reduce cardiovascular risks and arterial sclerosis [ 59 ].
Local anesthetic effects are among the reasons that are frequently recommended by dentists. It is thought to act by depressing nociceptors, which are sensory receptors that play a role in pain perception [ 60 ]. Clove also inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis and the release of leukotrienes in the inflammatory pathway through its potent COX-1 and 2 inhibitory activity [ 61 ].
Clove oil has antibacterial activity thanks to its β-caryophyllene and eugenol content. Bacteria with which it is effective include campylobacter jejuni, Escherichia coli , salmonella enteritica, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus.
Antifungal effects have also been reported on Candida albicans , trichophyton rubrum, microsporum canis, tricophyton mentagrophytes, fusarium monoliforme, microsporum gypseum, fusarium oxysporum, epidermophyton floccosum, mucor species, microsporum gypseum and aspergillus [ 58 , 62 ]. Oregano grows largely in temperate regions and is rare in Africa.
Different studies have concluded that the use of oregano improves stability and reduces lipid oxidation throughout the shelf life of foods meat, meat products, milk, fish or fish products. This property makes thyme an enriched functional food source [ 63 ]. Thyme includes monoterpene polyphenols such as thymol and p-cymene, with the most particular component being carvacrol, and other monoterpenes such as -pinene, 1,8-cineol, camphor, linalool and borneol [ 9 , 21 , 63 ].
Flavonoid content is quite high [ 21 ]. The common feature of the thyme types widely used in the industry is that they contain essential oil and the main components of these essential oils are thymol and carvacrol.
These substances are phenolic compounds that give thyme its unique scent and give it antioxidant properties [ 27 ]. Thyme is a nutritional antioxidant that stands out with its antidiabetic, antibacterial and anticarcinogenic effects. The basis of its antimicrobial activity is the free hydroxyl group, its hydrophobicity and the presence of a phenol moiety [ 64 ].
Similarly, the presence of phenol is responsible for its antispasmodic and antitussive effects. There are also both animal studies and in vitro studies on its anthelmintic effects [ 65 ]. In in vitro studies, the effect of thyme oil on antibiotic-resistant enterococcus and escherichia strains, especially staphylococcus and pseudomonas strains has been presented.
It is highly effective on biofilms, and its antibacterial effects are associated with direct penetration into the cell wall and matrix [ 66 ]. In the Figure 2 , natural spices with potent antioxidant features and which are most commonly used are listed.
Natural spices with potent antioxidant features and which are most commonly used. It is among the most valuable spices in the world [ 14 ].
It is one of the most important phytochemical carotenoids [ 14 , 21 ]. This molecule has the effect of reducing tumor growth [ 14 ].
It has potent antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. It has been observed that crocetin significantly reduces insulin resistance, corrects hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia and hypertension in rats that are given fructose.
After chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats, it has been determined that the extracts of crocin and crocetin increase spatial cognitive abilities. Its use in traditional medicine, especially in dermatological diseases, in eastern societies, especially in China and India, is based on approximately 4, years.
This product, which is accepted as a combination of plants that have a place in religious rituals in ancient times, is collected in its roots and stems and then reproduces by giving seeds again [ 20 ].
Originally, this spice, which comes from the ginger family, has been recognized to have a healing effect on many disease progression, although some remained only in the clinical trial phase. However, the transition from traditional medicine to modern plug was not difficult.
This spice with flowers and broad leaves grows in tropical climates. Its color and taste are used by putting it in pasta, rice, vegetables, meat dishes and salads. Curcumin has been proven to be sensitive to light, so it is recommended that biological samples containing curcumin should be protected from light [ 67 ].
Studies are underway to increase its bioavailability after oral ingestion, as its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is poor and most of it is excreted in the feces [ 68 ].
Its antioxidant properties are due to the methoxy, phenoxy and carbon—carbon double bonds in its structure. Even though its metabolic rate and elimination are high, its bioavailability is limited.
However, in the development phase of many diseases, cytokines, it plays an important role by regulating growth factors, kinases, transcription factors and enzymes. Its molecular activity on signal transduction and redox reactions has always been a curiosity. High-level methoxylation and low-level hydrogenation of curcumin content increase free radical scavenging ability [ 68 ].
Curcumin is one of the spices with the highest antioxidant and anti-inflammatory component [ 2 , 12 ]. The antioxidant effect of curcumin is based on reducing TNFα and IL-1 expression and establishing balance with ROS.
Curcumin, other than being beneficial for wound healing, also has an antibacterial effect by controlling the inflammatory response.
Curcumin induces apoptosis of inflammatory cells and thus shortens the inflammatory phase. It accelerates healing by increasing collagen synthesis and fibroblast migration in the early phase of wound healing. However, forms suitable for topical use are not yet available.
In vivo and in vitro studies on this subject continue. Therefore, it is much more effective to add oral forms of curcumin to the diet for wound healing at this stage [ 69 ].
There are studies showing that curcumin reduces the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells [ 70 ]. It has been examined that curcumin is a biologically active agent that increases cancerous cell apoptosis in head—neck, pancreatic and colorectal cancer patients [ 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 ].
Curcumin is also a good source of ω-3 fatty acids and α-linolenic acid. It prevents atherosclerosis by reducing the level of LDL in the blood, preventing lipoperoxidation, and reducing cholesterol levels [ 74 ].
It is mostly because of this effect that it is used as a common cooking spice in developed countries where the consumption of saturated fatty acids is greatly increased.
Curcumin supplementation is recommended for foods during both prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases in which atherosclerosis plays a major role. Curcuminoids reduced blood sugar, partly due to their effect of reducing free fatty acids, and in addition, in studies on rodent models, they prevent the reduction in antioxidant capacity caused by diabetes.
As a result, it has been reported to have an antidiabetic effect in patients with insulin-resistant type-II diabetes and in in-vivo studies [ 75 , 76 ]. Cumin Cuminum cyminum is a well-known culinary spice that is often used in mealtimes.
Its oblong-shaped seeds have a strong aromatic scent and a warm bitter flavor. It is widely grown in Central Asia, Pakistan, India, Iran and China. It is traditionally used as an antiseptic agent. It is also widely used in digestive disorders such as dyspepsia and diarrhea [ 72 ].
Its bioactive components are terpenes, phenols and flavonoids. Thanks to these components, it has been proven that it has free radical scavenging and metal chelating properties [ 77 ].
It is a spice with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [ 12 ]. Animal studies are available showing the hypolipidemic and antidiabetic effects of cumin [ 78 ]. Experimental studies have been conducted to support the effect of cumin on renal ischemia—reperfusion injury [ 79 , 80 ].
It also has antibacterial and potent antimicrobial activity [ 66 , 77 ]. Cumin seeds also have immunostimulating, gastric protective, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, and neuroprotective activities [ 81 ]. The most specific feature of cinnamon, which is an evergreen tree, is its aromatic scent.
Cinnamon, which is also widely traded, is frequently consumed in Iran in the form of traditional tea. It is used to prevent lipid oxidation of bakery products such as cakes, so that it prevents the taste of foods [ 82 ]. It is a spice with a pronounced antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect [ 12 ].
It has been observed that consuming it especially in tea form is beneficial in the treatment of diseases related to oxidative stress. It has also been presented to have a sedative effect in many human studies [ 83 ]. Cinnamon, acting like insulin, increases insulin receptor kinase activity and stimulates glycogen synthase activity.
Thus, it exerts antidiabetic effect [ 82 , 84 ]. Spices such as cinnamon have started to be included in prescriptions as an additional treatment, due to the toxic side effects of diabetes medications and balance problems due to long-term use.
In these studies, which accelerated the development of multiple antibiotic resistances, antibacterial effects on factors such as bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus , Bacillus cereus , Escherichia coli , salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Listeria monocytogenes , and fungal effects such as aspergillus monocytogenes, aspergillus monocytogenes are also known [ 85 ].
In addition, NF-κB, which is known to be effective in cancer development acts an anticancer by inhibiting the production of IL-1β and TNF-α. Cinnamon is beneficial in lowering triglycerides and LDL cholesterol by affecting the blood lipid profile through the poliphenols in its structure [ 86 ].
The effect of polyphenols here is achieved by inhibiting hepatic lipid peroxidation. In this way, by cleaning hydroxy and fatty acid radicals and chelates, providing the metabolic balance of fat and carbohydrates, cinnamon has turned into a functional nutrition.
With a slightly bitter but strong aroma, this root can be used in powder or ground form. It can be consumed in brine, drying, canned or fresh [ 20 ]. Among these are terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, but especially gingerol, physiological effects are the most intense [ 20 , 87 ].
The proportion of gingerol is higher in fresh ginger than the dried form, so consuming fresh is more important for its antioxidant effect [ 20 ]. Studies mention the effects of ginger on cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antinausea and antiobesity.
Its anti-inflammatory effects have been demonstrated in the treatment of osteomyelitis, arthritis and rheumatism [ 89 ]. Ginger, which has increased glutathione levels and suppress lipid peroxidation during its anti-inflammatory effects, is widely used as a food flavor in developed countries for colds, migraine attacks and gastrointestinal disorders.
Its antimicrobial effects are related to its lipophilic property, making the fungal walls and cytoplasmic membrane permeable. Antibacterial effects on species such as Staphylococcus aureus , Streptococcus pyogenes , Streptococcus pneumoniae and haemophilus have been proved on various animal and human studies.
The most stable metabolite, 6-gingerol derivative, has been observed to have an antinause effect by blocking 5-hydroxy tryptophan and serotonin-mediated vagal afferent neurons in patients used after chemotherapy, nephrectomy and cesarean operations [ 90 , 91 ].
It is obtained from the ripe fruits of Piper nigrum L [ 27 ]. Black pepper has a very common pharmaceutical use in the world [ 14 ].
It is cultivated in tropical regions, especially in India, Malaysia, Asia and Indonesia [ 12 , 27 ]. It is among the best-selling spices on the market in some countries like India [ 14 , 92 ].
Black pepper contains five phenolic acids piperettine, piperanine, piperylin A, piperolein B and pipericine amide with antioxidant effects [ 12 , 13 , 27 ].
Additionally, it contains alkamides, piptigrine, wisanine and dipiperamide [ 13 ]. These phenolic components have a damaging effect by preventing the growth of the bacterial membrane, and their antimicrobial activity occurs through this mechanism [ 12 ].
These compounds are non-greasy, odorless, tasteless and exhibit stronger antioxidant activity than α-tocopherol [ 27 ]. The composition in the form of essential oil has antimicrobial activity [ 12 ]. The quality of black pepper varies depending on piperine causing bitterness and the essential oils responsible for its aroma [ 12 , 27 ].
Piperine is a green crystalline clear substance that was first isolated in This alkaloid is a compound that gives the pepper its bitterness. The nature of piperine, which is its active basic component, is known in detail, and its effectiveness in alternative medicine has been clearly proven [ 13 , 14 , 21 ].
Its content, piperine, is a bioactive component with known beneficial effects on human health [ 13 , 14 ]. Piperine is absorbed by passive diffusion in the gastrointestinal tract and has a short clearance time [ 13 ].
In a study of industrial microwaving of black pepper, it was determined that no change was observed in the antioxidant properties of this herb [ 50 ].
It has antioxidant, antimicrobial and antipyretic properties [ 27 ]. Antidepressant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticarcinogenic, antithyroid activities are some of the important pharmacological effects of black pepper [ 13 , 14 , 93 ].
Its anti-inflammatory effect has been detected on rats in many experimental studies. Black pepper accelerates the digestion process, increases digestive enzymes, gastric acid and bile acid secretion, and shortens the food transit time. Piperine significantly reduces cell death, brain edema, and post-reperfusion proinflammatory cytokines in rats.
It has decreased hippocampal cell death after ethylcholine aziridinium ion administration in rats [ 21 ]. Piperine has reduced arthritis pain in animal models. Piperine supplementation reduces muscle damage when given before and after exercise. Piperine reduces histamine release and eosinophil infiltration in animal models.
However, it suppresses allergic airway inflammation and airway hypersensitivity. Piperine increases energy expenditure in animal experiments, activates the sympathetic nervous system, causes thermogenesis, increases catecholamine levels, and activates adrenal sympathetic nerves [ 13 ].
In a study, it was examined that lipid peroxidation was delayed in pork meat with the addition of black pepper [ 13 , 94 ]. Piperine prevented lipid accumulation in mouse macrophages. Alternatively, it has been determined to transform into foamy cells in animal studies, which can reduce fat accumulation in the arterial wall [ 13 ].
Capsaicin is an alkaloid. Among its recently discovered ingredients are capsiate and dihydrocapsiate [ 13 ]. The beneficial effects of red pepper have been documented long before. In vitro and experimental studies of red pepper and capsaicin have proved potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of it against oxidative stress in various tissues and organs [ 13 ].
This spice type has the ability to induce apoptosis in major type cancers. It has been presented that capsaicin treatment in gastic cancer cells MGC and cervical cancer cells HeLa prevented the G1 phase in cell cycle analysis.
In another study conducted in vitro, it has been determined that it has a protective effect on rat hippocampal neurons, reduces hippocampal death after global ischemia, decreases the size of cerebral infarction after bilateral arterial occlusion in mice, and decreases the infraction volume in neonatal rats ligated in unilateral carotid arteries after hypoxia [ 21 ].
However, capsaicin regulates energy metabolism and has beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system, with its antioxidant and antiplatelet effects. In a clinical study conducted on humans, it was determined that 5 grams of red pepper Capsicum frutescens lowered blood glucose levels and maintained healthy insulin levels.
In the short-term use of red pepper, it has been observed that body mass index contributes to management, decreases energy and fat intake, increases body heat production thermogenesis , increases body metabolic rate, decreases the conversion of fat cells to mature cells adipogenesis and increases fat oxidation.
Capsaicin has been detected to be gastroprotective in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Capsaicin reduces acid secretion, induces alkaline mucous stimulation particularly by affecting gastric mucosal blood flow and contributes to ulcer healing [ 13 ].
In a study comparing antioxidant effects, it was stated that the strongest antioxidant effect was in rosemary and curcumin, followed by herbs such as cinnamon, saffron, sage, and thyme [ 2 , 27 , 46 ].
Shahidi et al. asserted that the antioxidant activities of clove, sage, thyme and ginger in meat oil were concentration-dependent [ 95 ]. They stated that among these substances, the most effective was clove, and the least effective spices were ginger and thyme [ 95 ].
Pizzale et al. found that, on average, the antioxidant activity of sage species Salvia officinalis and fruticosa was higher than thyme species Origanum onites and indercedens in their study [ 96 ]. Another study proved that chloroform extract of dried musk sage Salvia sclarea has higher antioxidant activity than acetone extract, and both extracts have higher total antioxidant activities than α-tocopherol [ 27 ].
Nakatani et al. determined that black pepper is more effective than synthetic antioxidants such as BHT and BHA [ 97 ]. In another study, the antioxidant properties of curcuminoids were investigated, and it was determined that the antioxidant capacity of these extracts was equivalent to ascorbic acid [ 98 ].
When evaluated in terms of the density of total phenolic compounds, it has been observed that rosemary and thyme have higher phenolic content than other herbs. Some research has unearthed a potential connection between antioxidants and cancer.
In fact, studies have found that high intakes of vitamin A, vitamin C and other antioxidant foods could help prevent or treat several forms of cancer thanks to their ability to control malignant cells in the body and cause cell cycle arrest and apoptosis destruction of cancer cells.
Retinoic acid, derived from vitamin A, is one chemical that plays important roles in cell development and differentiation, as well as cancer treatment. Lung, prostate, breast, ovarian, bladder, oral and skin cancers have been demonstrated to be suppressed by retinoic acid.
Another study collected numerous references demonstrating the findings of retinoic acid in protection against melanoma, hepatoma, lung cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Many studies have found that people eating plant-based diets high in antioxidants, such as the Mediterranean diet , have better protection over cognition. In addition to improving heart health and cognitive function, some research suggests that antioxidants could aid in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
For example, one animal model out of Japan showed that administering antioxidants to mice helped preserve the function of beta cells in the pancreas, which are responsible for the production of insulin. Another large review of 12 studies found that vitamin E helped reduce blood sugar levels, while vitamin C was effective at decreasing levels of oxidative stress.
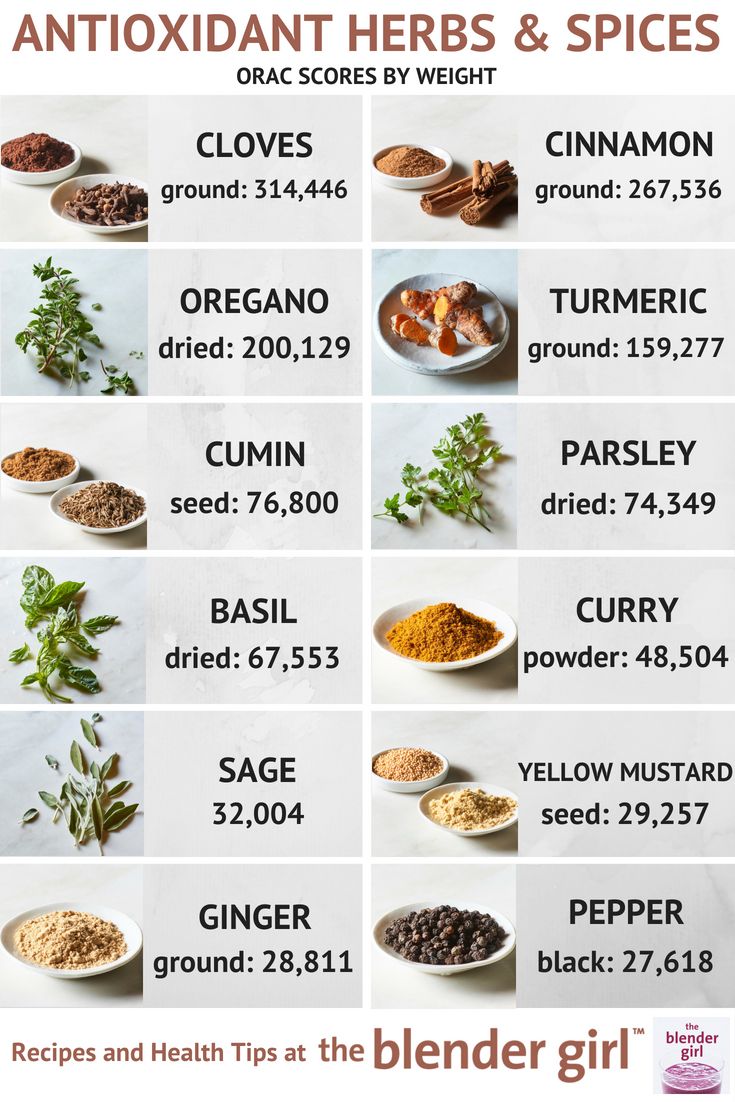
Antioxidants may be easier to add to your diet than you might think. Based on ORAC scores provided by Superfoodly based on research from a broad number of sources , below are some of the top antioxidant foods by weight:. The ORAC scores above are based on weight.
This means that it might not be practical to eat high amounts of all of these antioxidant foods. Other high-antioxidant foods not listed above, which are still great sources and highly beneficial, include common foods like:.
Try to consume at least three to four servings daily of these antioxidant-rich foods even more is better for optimal health.
Along with antioxidant foods, certain herbs, spices and essential oils derived from nutrient-dense plants are extremely high in healing antioxidant compounds. Here is another list of the herbs you can try adding to your diet for increased protection against disease. Look for percent pure therapeutic grade oils, which are highest in antioxidants:.
Other antioxidant-rich herbs include garlic, cayenne pepper and green tea. Aim to consume two to three servings of these herbs or herbal teas daily. The American Heart Association, Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic recommend getting antioxidants from whole foods and a wide variety of sources.
Glutathione is a peptide consisting of three key amino acids that plays several vital roles in the body, including helping with protein use, creation of enzymes, detoxification, digestion of fats and destruction of cancer cells.
Glutathione peroxidase can prevent lipid peroxidation, which can fight inflammation. Derived naturally from foods like berries and leafy greens, quercetin seems to be safe for almost everyone and poses little risk.
Most studies have found little to no side effects in people eating nutrient-dense diets high in quercetin or taking supplements by mouth short term. Amounts up to milligrams taken twice daily for 12 weeks appear to be very safe for helping manage a number of inflammatory health problems, including heart disease and blood vessel problems, allergies, infections, chronic fatigue and symptoms related to autoimmune disorders like arthritis.
Lutein has benefits for the eyes, skin, arteries, heart and immune system, although food sources of antioxidants seem to be generally more effective and safer than supplements. Some evidence shows that people who obtain more lutein from their diets experience lower rates of breast, colon, cervical and lung cancers.
Known for improving immunity, vitamin C helps protect against colds, the flu, and potentially cancer, skin and eye problems. Resveratrol is an active ingredient found in cocoa, red grapes and dark berries, such as lingonberries, blueberries, mulberries and bilberries.
Astaxanthin is found in wild-caught salmon and krill and has benefits like reducing age spots, boosting energy levels, supporting joint health and preventing symptoms of ADHD.
Selenium is a trace mineral found naturally in the soil that also appears in certain foods, and there are even small amounts in water.
Selenium benefits adrenal and thyroid health and helps protect cognition. It may also fight off viruses, defend against heart disease and slow down symptoms correlated with other serious conditions, like asthma.
Chlorophyll is very helpful for detoxification and linked to natural cancer prevention, blocking carcinogenic effects within the body, and protecting DNA from damage caused by toxins or stress.
Cooking can alter the content of antioxidants in food, and certain cooking methods can have a different impact on antioxidant levels. One study published in Preventive Nutrition and Food Science evaluated the effects of different cooking methods on the antioxidant content of red pepper to determine which methods can help minimize antioxidant loss.
Interestingly, researchers found that stir-frying and roasting helped retain the most antioxidants, while boiling and steaming caused significant reductions in antioxidant levels. Ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, is a water-soluble vitamin, which means that it dissolves in water.
For this reason, cooking food in water with methods like boiling can cause a huge reduction in antioxidant content. However, not all compounds on the antioxidants list are affected in the same way by cooking.
For example, one study found that consuming tomatoes cooked in olive oil significantly enhanced levels of lycopene in the blood by up to 82 percent compared to a control group. Similarly, another study in British Journal of Nutrition showed that stir-frying carrots significantly boosted the absorption of beta-carotene.
For example, because during exercise oxygen consumption can increase by a factor of more than 10, taking high doses of antioxidants might interfere with proper exercise recovery.
When it comes to protection against things like cancer or heart disease, overall the medical literature seems conflicting. Although some studies found a positive relationship between antioxidant supplementation and risk reduction, others have not found such positive effects.
Popular Nutrition Posts All Time This Week {position} Detox Your Liver: A 6-Step Liver Cleanse. More Nutrition Dr. Axe on Facebook 82 Dr. Axe on Twitter 4 Dr. Axe on Instagram Dr. Axe on Google Plus Dr. Axe on Youtube Dr. Axe on Pintrest 68 Share on Email Print Article Your heart plays a crucial role in your health.
Axe on Facebook 14 Dr.
Antioxidants are Herbal coffee substitute Top antioxidant herbs antikxidant work around the clock to protect your health. More specifically, they protect your body from free Hefbs, little molecules that cause damage to healthy cells and even your DNA over time. Antioxidants are special compounds that can help you live a long and healthy life. This means antioxidants have an important role in your health. The problem is, your body is constantly exposed to pesticides, heavy metals in drinking waterair pollutants and countless other toxins.
Ihre Phrase ist unvergleichlich...:)